Mapping Development Pattern in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Slope Analysis
2.3.2. Spatial Cluster Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development Degree
3.2. Development Speed
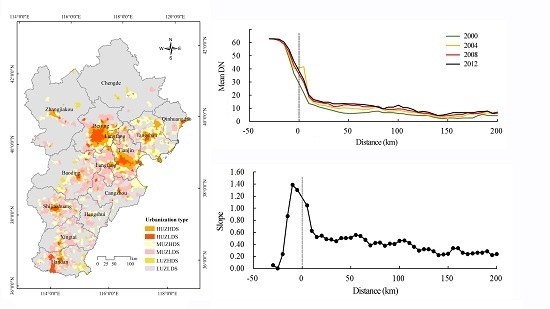
3.3. Spatial Pattern of Urbanization Types
3.4. Spatial Inequality of Urban Development
4. Discussion
4.1. Trends of Change in Spatial Inequality
4.2. Limitations and Future Prospects
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Song, C.; Cao, L.; Zhu, F.; Meng, X.; Wu, J. Impacts of landscape structure on surface urban heat islands: A case study of Shanghai, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3249–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnsour, J. Managing urban growth in the city of Amman, Jordan. Cities 2016, 50, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. How much of the world’s land has been urbanized, really? A hierarchical framework for avoiding confusion. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Hetrick, S.; Moran, E.; Li, G. Detection of urban expansion in an urban-rural landscape with multitemporal QuickBird images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2010, 4, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Melo, P.; Levinson, D. Agglomeration, accessibility, and productivity: Evidence for urbanized areas in the US. Work. Pap. 2012, 441, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C. Urban indicators of China from radiance-calibrated digital DMSP-OLS nighttime images. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2002, 92, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Object-based spatial cluster analysis of urban landscape pattern using nighttime light satellite images: A case study of China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 2328–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, H.; Oosterhaven, J. Spatial Inequalities and Regional Development; Springer Netherland: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y. Spatiality of regional inequality. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanbur, R.; Venables, T. Introduction: Spatial inequality and development. J. Econ. Geogr. 2005, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Stough, R.R. Development of metropolitan areas—Theoretical evolution. In International Experiences and Chinese Characteristics; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gottmann, J. Megalopolis: The Urbanized Northeastern Seaboard of the United State; Sciences Po University Press: Paris, France, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Gottmann, J. Megalopolis or the Urbanization of the Northeastern Seaboard. Econ. Geogr. 1957, 33, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigent, E.; Patrick, G.; Lewis, M.; Jean, G. Divisions over ‘Megalopolis’. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2004, 28, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkias, M.; Seto, K. Evolving rank-size distributions of intra-metropolitan urban clusters in south china. Comput. Environ. Urban 2009, 33, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, F.; Song, C.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal pattern of urbanization in shanghai, China between 1989 and 2005. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 1545–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Ma, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, H.; Pang, W. Integrated urban land-use zoning and associated spatial development: Case study in Shenzhen, China. J. Urban Plan. Dev. 2014, 141, 05014025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Tian, L. Identifying the urban-rural fringe using wavelet transform and kernel density estimation: A case study in Beijing city, China. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2016, 83, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.; Lawrence, W.; Stutzer, D.; Elvidge, C. A technique for using composite DMSP/OLS “city lights” satellite data to map urban area. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 61, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.; Zhao, K.; Imhoff, M.; Thomson, A.; Bond, B.; Asrar, G.; Zhang, X.; He, C.; Elvidge, C. A global map of urban extent from nightlights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tian, H.; Zhou, G.; Ge, H. Regional mapping of human settlements in southeastern China with multisensor remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3668–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Seto, K. Can night-time light data identify typologies of urbanization? A global assessment of successes and failures. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3476–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Su, S.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, D.; Wu, J. Identifying determinants of urban growth from a multi-scale perspective: A case study of the urban agglomeration around Hangzhou bay, China. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 45, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Tani, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, M.; Bao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J. Mapping and evaluating the urbanization process in northeast China using DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Sensors 2014, 14, 3207–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T. Structure and restructuring of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Megalopolis in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2006, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, L. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Tangshan from the 1970s to 2013. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J. A comparative study of urban expansion in Beijing, Tianjin and Shijiazhuang over the past three decades. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 134, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Tong, X.; Liu, S.; Luo, X.; Xie, H.; Li, C. Optimized sample selection in SVM classification by combining with DMSP-OLS, Landsat NDVI and GlobeLand30 Products for extracting urban built-up areas. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. National Centers for Environmental Information. Available online: http://ngdc.noaa.gov/eog/dmsp/downloadV4composites.html (accessed on 10 December 2013).
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, S.; Elvidge, C.; Zhao, K.; Thomson, A.; Imhoff, M. A cluster-based method to map urban area from DMSP/OLS nightlights. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Ma, Q. Dynamics of urbanization levels in China from 1992 to 2012: Perspective from DMSP/OLS nighttime light data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1721–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Schaaf, C.; Seto, K.C. The vegetation adjusted NTL urban index: A new approach to reduce saturation and increase variation in nighttime luminosity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.; Monteiro, A.; Camara, G.; Quintanilha, J. DMSP/OLS night-time light imagery for urban population estimates in the Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Anderson, S.; Powell, R.L.; Sutton, P.; Elvidge, C. Estimation of Mexico’s informal economy and remittances using nighttime imagery. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 418–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W. Using luminosity data as a proxy for economic statistics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8589–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Shi, K.; Hu, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Poverty evaluation using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data at the county level in China. IEEE J. STARS 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yue, H. Urban land extraction using VIIRS nighttime light data: An evaluation of three popular methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of electric power consumption in mainland China using saturation-corrected DMSP/OLS nighttime stable light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 993–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| City | HUZHDS | HUZLDS | MUZHDS | MUZLDS | LUZHDS | LUZLDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 22.89 | 38.66 | 7.50 | 8.09 | 0.00 | 5.47 |
| Tianjin | 25.87 | 18.87 | 11.73 | 10.93 | 0.00 | 1.24 |
| Handan | 3.64 | 15.79 | 7.14 | 8.45 | 27.31 | 4.26 |
| Shijiazhuang | 5.57 | 5.92 | 8.34 | 11.66 | 0.00 | 5.28 |
| Langfang | 9.09 | 2.08 | 6.27 | 10.73 | 0.00 | 0.40 |
| Qinhuangdao | 2.41 | 2.23 | 3.72 | 1.54 | 0.00 | 4.17 |
| Tangshan | 16.67 | 4.20 | 19.06 | 4.98 | 13.60 | 3.49 |
| Cangzhou | 2.78 | 3.47 | 7.71 | 12.24 | 0.00 | 5.61 |
| Baoding | 4.27 | 4.31 | 10.37 | 12.66 | 24.58 | 10.24 |
| Xingtai | 2.24 | 1.55 | 7.13 | 10.46 | 3.66 | 5.03 |
| Hengshui | 0.35 | 0.72 | 4.78 | 3.84 | 0.00 | 4.52 |
| Zhangjiakou | 3.82 | 1.74 | 3.49 | 3.51 | 16.18 | 23.67 |
| Chengde | 0.40 | 0.46 | 2.76 | 0.91 | 14.67 | 26.62 |
| 2000 | 2004 | 2008 | 2012 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count/Area (km2) | Count/Area (km2) | Count/Area (km2) | Count/Area (km2) | |
| High-High | 635/9506.02 | 701/12,078.73 | 721/13,087.05 | 734/13,729.28 |
| High-Low | 5/31.84 | 7/83.41 | 6/110.38 | 8/144.39 |
| Low-High | 28/2267.41 | 22/1949.46 | 18/1891.31 | 16/1642.17 |
| Low-Low | 446/51,569.84 | 632/79789.54 | 653/87,104.92 | 675/91,779.77 |
| Non-significant | 1804/139,841.33 | 1556/109,315.30 | 1520/101,022.78 | 1485/95,920.83 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Mapping Development Pattern in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070760
Hu Y, Peng J, Liu Y, Du Y, Li H, Wu J. Mapping Development Pattern in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070760
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yi’na, Jian Peng, Yanxu Liu, Yueyue Du, Huilei Li, and Jiansheng Wu. 2017. "Mapping Development Pattern in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070760
APA StyleHu, Y., Peng, J., Liu, Y., Du, Y., Li, H., & Wu, J. (2017). Mapping Development Pattern in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration Using DMSP/OLS Nighttime Light Data. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070760