Erosion Associated with Seismically-Induced Landslides in the Middle Longmen Shan Region, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Tectonic Setting
3. Data and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Landslide Volume
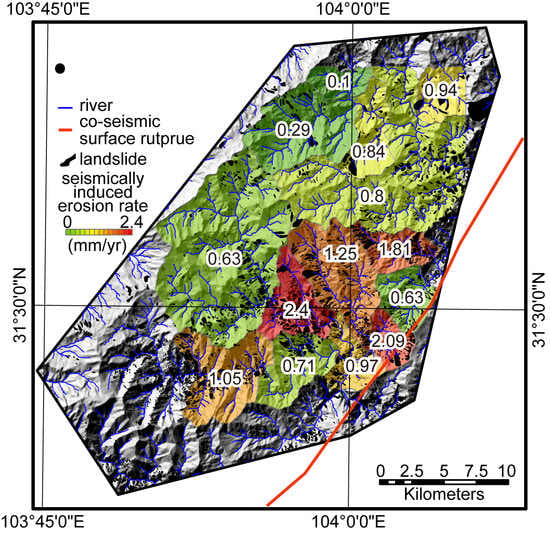
4.2. Erosion Rate
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avouac, J.P. Dynamic processes in extensional and compressional settings-mountain building. In Treatise on Geophysics; Watts, A.B., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 6, pp. 377–439. [Google Scholar]
- Burbank, D.W.; Anderson, R.S. Tectonic Geomorphology; Blackwell Science: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; p. 454. [Google Scholar]
- Hovius, N.; Meunier, P.; Lin, C.-W.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.-G.; Dadson, S.; Horng, M.-J.; Lines, M. Prolonged seismically induced erosion and the mass balance of a large earthquake. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 304, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.N.; Densmore, A.L.; Rosser, N.J.; de Michele, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, R.; Whadcoat, S.; Petley, D.N. Mass wasting triggered by the 2008 wenchuan earthquake is greater than orogenic growth. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korup, O.; Densmore, A.L.; Schlunegger, F. The role of landslides in mountain range evolution. Geomorphology 2010, 120, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, S.J.; Hovius, N.; Chen, H.; Dade, W.B.; Lin, J.-C.; Hsu, M.-L.; Lin, C.-W.; Horng, M.-J.; Chen, T.-C.; Milliman, J.; et al. Earthquake-triggered increase in sediment delivery from an active mountain belt. Geology 2004, 32, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, D.K. The importance of earthquake-induced landslides to long-term slope erosion and slope-failure hazards in seismically active regions. Geomorphology 1994, 10, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamud, B.D.; Turcotte, D.L.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P. Landslides, earthquakes, and erosion. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 229, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, P.; Hovius, N.; Haines, A.J. Regional patterns of earthquake-triggered landslides and their relation to ground motion. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, I.J.; Montgomery, D.R.; Korup, O. Landslide erosion controlled by hillslope material. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; West, A.J.; Densmore, A.L.; Jin, Z.; Parker, R.N.; Hilton, R.G. Seismic mountain building: Landslides associated with the 2008 wenchuan earthquake in the context of a generalized model for earthquake volume balance. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Gorum, T.; van Westen, C.J.; Fan, X. Did the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake lead to a net volume loss? In Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment: Volume 3: Targeted Landslides; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Yin, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xu, X.; Shen, L.; Yao, Q.; Tan, X.; Kang, W.; Ma, S.; Wu, X.; Cai, J.; Gao, M.; et al. Optimized volume models of earthquake-triggered landslides. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, G.; Liu, L. Quantification of mass wasting volume associated with the giant landslide daguangbao induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake from persistent scatterer insar. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Han, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Zhang, X. Modeling accumulated volume of landslides using remote sensing and dtm data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1514–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Ren, Z.; Jia, D.; Wu, X. Co-seismic thrusting rupture and slip distribution produced by the 2008 mw 7.9 wenchuan earthquake, china. Tectonophysics 2009, 471, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Zeng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, L.; Tapponnier, P.; Sun, J.; Xing, X.; Hu, G.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, L.; Ding, L.; et al. Co-seismic ruptures of the 12 may 2008, ms 8.0 wenchuan earthquake, sichuan: East–west crustal shortening on oblique, parallel thrusts along the eastern edge of tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 286, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wen, X.; Yu, G.; Chen, G.; Klinger, Y.; Hubbard, J.; Shaw, J. Coseismic reverse- and oblique-slip surface faulting generated by the 2008 Mw 7.9 wenchuan earthquake, China. Geology 2009, 37, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbank, D.W.; Blythe, A.E.; Putkonen, J.; Pratt-Sitaula, B.; Gabet, E.; Oskin, M.; Barros, A.; Ojha, T.P. Decoupling of erosion and precipitation in the Himalayas. Nature 2003, 426, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godard, V.; Cattin, R.; Lavé, J. Erosional control on the dynamics of low-convergence rate continental plateau margins. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 179, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R.; Brandon, M.T. Topographic controls on erosion rates in tectonically active mountain ranges. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2002, 201, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, V.; Lavé, J.; Carcaillet, J.; Cattin, R.; Bourlès, D.; Zhu, J. Spatial distribution of denudation in Eastern Tibet and regressive erosion of plateau margins. Tectonophysics 2010, 491, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.; Ouimet, W. Tectonic geomorphology along the eastern margin of Tibet: Insights into the pattern and processes of active deformation adjacent to the Sichuan basin. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2011, 353, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Zeng, J.; Wen, L.; Oskin, M.; Zeng, L. Focused modern denudation of the Longmen Shan margin, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Lin, A. Co-seismic landslides induced by the 2008 Wenchuan magnitude 8.0 earthquake, as revealed by alos prism and avnir2 imagery data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3479–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, F.; Yin, J.; Zhang, H. Topographic changes due to the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake as revealed by the differential dem method. Geomorphology 2014, 217, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Dai, F.; Zhang, H. Morphogenic uncertainties of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake: Generating or reducing? J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.; Reiners, P.W.; Krol, M.A.; Whipple, K.X.; Hodges, K.V.; Farley, K.A.; Tang, W.; Chen, Z. Late cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Inferences from 40ar/39ar and (u-th)/he thermochronology. Tectonics 2002, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, W.B. Landslides associated with the May 12, 2008 Wenchuan earthquake: Implications for the erosion and tectonic evolution of the Longmen Shan. Tectonophysics 2010, 491, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, W.B.; Whipple, K.X.; Granger, D.E. Beyond threshold hillslopes: Channel adjustment to base-level fall in tectonically active mountain ranges. Geology 2009, 37, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, Z.; Hilton, R.G.; Zhang, F.; Densmore, A.L.; Li, G.; West, A.J. Controls on fluvial evacuation of sediment from earthquake-triggered landslides. Geology 2015, 43, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, A.J.; Hetzel, R.; Li, G.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hilton, R.G.; Densmore, A.L. Dilution of 10Be in detrital quartz by earthquake-induced landslides: Implications for determining denudation rates and potential to provide insights into landslide sediment dynamics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 396, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burchfiel, B.C.; Zhiliang, C.; Yupinc, L.; Royden, L.H. Tectonics of the Longmen Shan and adjacent regions, central China. Int. Geol. Rev. 1995, 37, 661–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Wilson, C.J.L. Emplacement of the Longmen Shan thrust—Nappe belt along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Struct. Geol. 1996, 18, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.D.; Chen, S.F.; Zhao, X.L. Tectonics, seismicity and dynamics of Longmenshan Mountains and its adjacent regions. Seismol. Geol. 1994, 16, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Densmore, A.L.; Ellis, M.A.; Li, Y.; Zhou, R.; Hancock, G.S.; Richardson, N. Active tectonics of the Beichuan and Pengguan faults at the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics 2007, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, D.; Wei, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, G. Longmen Shan fold-thrust belt and its relation to the western Sichuan Basin in central China: New insights from hydrocarbon exploration. AAPG Bull. 2006, 90, 1425–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, E.; Whipple, K.; Harkins, N. Topography reveals seismic hazard. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Tu, X.B.; Xu, C.; Gong, Q.M.; Yao, X. Rock avalanches triggered by oblique-thrusting during the 12 May 2008 Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China. Geomorphology 2011, 132, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Xu, C.; Yao, X.; Xu, L.; Tu, X.B.; Gong, Q.M. Spatial distribution of landslides triggered by the 2008 Ms 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2011, 40, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowgill, E.; Bernardin, T.S.; Oskin, M.E.; Bowles, C.; Yıkılmaz, M.B.; Kreylos, O.; Elliott, A.J.; Bishop, S.; Gold, R.D.; Morelan, A.; et al. Interactive terrain visualization enables virtual field work during rapid scientific response to the 2010 Haiti earthquake. Geosphere 2012, 8, 787–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, G.; Zech, G. Introduction to Statistics and Data Analysis for Physicists; Deutsches Elekstrone-Synchrotron: Hamburg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, C.V.; Hu, Y. A comprehensive study of the rational function model for photogrammetric processing. Anglais 2001, 67, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Chen, A.; Chen, M.; Wang, X. Test and analysis for precision of gps precise point positioning. J. Chin. Inert. Technol. 2006, 14, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Y.-K.; Chen, W.-S.; Xu, X.-W.; Chen, L.-C.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.-C.; Dong, S.-P. Paleoseismic events and recurrence interval along the Beichuan–Yingxiu fault of longmenshan fault zone, Yingxiu, Sichuan, China. Tectonophysics 2014, 584, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.-K.; Sun, J.; Zhang, P.; Wan, Y.; Wang, M.; Burgmann, R.; Zeng, Y.; Gan, W.; Liao, H.; Wang, Q. Slip maxima at fault junctions and rupturing of barriers during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wen, X.; Shen, Z.; Chen, J. Oblique, high-angle, listric-reverse faulting and associated development of strain: The Wenchuan earthquake of May 12, 2008, Sichuan, China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 353–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipple, K.X.; Kirby, E.; Brocklehurst, S.H. Geomorphic limits to climate-induced increases in topographic relief. Nature 1999, 401, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| No. | Path | Row | Date | Resolution (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 659 | 250 | 20080603 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 659 | 251 | 20080603 | |
| 3 | 659 | 252 | 20080603 | |
| 4 | 659 | 253 | 20080603 | |
| 5 | 659 | 254 | 20080603 |
| Catchment Area (1 × 106 m2) | Sum Volume (1 × 106 m3) | Average Erosion (m) | EMax (mm/year) | EMin (mm/year) | Eave (mm/year) | Eerror (mm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.06 | 2.51 ± 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.02 |
| 15.03 | 33.97 ± 1.82 | 2.26 | 1.13 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 0.19 |
| 41.97 | 29.50 ± 2.84 | 0.71 | 0.35 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.06 |
| 19.62 | 39.21 ± 2.58 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.17 |
| 94.66 | 182.12 ± 1.17 | 1.92 | 0.96 | 0.64 | 0.8 | 0.16 |
| 15.98 | 69.31 ± 5.41 | 4.34 | 2.17 | 1.45 | 1.81 | 0.36 |
| 16.61 | 24.82 ± 2.30 | 1.49 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 0.13 |
| 23.12 | 133.00 ± 7.55 | 5.75 | 2.88 | 1.92 | 2.4 | 0.48 |
| 39.73 | 119.08 ± 7.76 | 3.00 | 1.50 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 0.25 |
| 109.11 | 163.27 ± 0.35 | 1.50 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.63 | 0.13 |
| 11.27 | 56.14 ± 3.07 | 4.98 | 2.50 | 1.67 | 2.09 | 0.42 |
| 15.15 | 35.08 ± 3.29 | 2.32 | 1.16 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 0.20 |
| 23.73 | 40.34 ± 3.33 | 1.70 | 0.85 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.14 |
| 37.46 | 94.62 ± 8.28 | 2.53 | 1.26 | 0.84 | 1.05 | 0.21 |
| Catchment Area (1 × 106 m2) | Sum Volume (1 × 106 m3) | Average Erosion (m) | EMax (mm/year) | EMin (mm/year) | Eave (mm/year) | Eerror (mm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 124.19 | 3.96 | 3.19 | 1.60 | 1.06 | 1.33 | 0.27 |
| 131.45 | 1.29 | 0.98 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.08 |
| 310.04 | 2.00 | 0.64 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.05 |
| 685.05 | 3.58 | 0.52 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.22 | 0.04 |
| 144.67 | 0.73 | 0.50 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.04 |
| 134.13 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.04 |
| 282.31 | 1.19 | 0.42 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.04 |
| 124.54 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| 130.21 | 0.54 | 0.41 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| 128.79 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.20 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.03 |
| 88.53 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.03 |
| 245.31 | 0.71 | 0.29 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.02 |
| 197.02 | 0.46 | 0.23 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.02 |
| 129.22 | 0.28 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.02 |
| 244.69 | 0.42 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.01 |
| 272.35 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| 459.91 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| 30.16 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| 251.97 | 0.29 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| 249.58 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| 327.19 | 0.26 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| 52.69 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 445.14 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 808.06 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 514.30 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 220.88 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 65.27 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 187.41 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 |
| 1063.00 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 613.53 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 346.56 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 332.62 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 394.67 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 18.42 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 129.69 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 394.32 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 692.51 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| 212.18 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J. Erosion Associated with Seismically-Induced Landslides in the Middle Longmen Shan Region, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080864
Ren Z, Zhang Z, Yin J. Erosion Associated with Seismically-Induced Landslides in the Middle Longmen Shan Region, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080864
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Zhikun, Zhuqi Zhang, and Jinhui Yin. 2017. "Erosion Associated with Seismically-Induced Landslides in the Middle Longmen Shan Region, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080864
APA StyleRen, Z., Zhang, Z., & Yin, J. (2017). Erosion Associated with Seismically-Induced Landslides in the Middle Longmen Shan Region, Eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sensing, 9(8), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080864