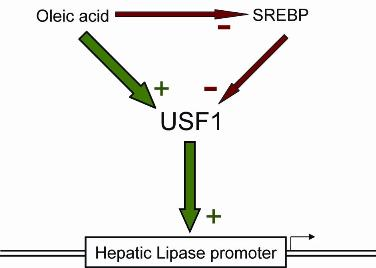
Activation of Hepatic Lipase Expression by Oleic Acid: Possible Involvement of USF1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Oleate Increases HL Expression and Down-Regulates SREBP Activity

2.2. HL Promoter Activity Is Down-Regulated by SREBP-2 but not by SREBP-1



2.3. Down-Regulation of the HL Promoter by SREBP2 Requires an Intact DNA Binding Domain
2.4. nSREBP2 Exerts Its Effect Predominantly via the -307/-312 Region of the HL Promoter


2.5. Nuclear USF1 Is Increased by Oleate and Reduced by nSREBP2 Overexpression
2.6. Discussion

3. Experimental
3.1. Cell Culture
3.2. Plasmids
3.3. Promoter-Reporter Assays
3.4. Protein Expression
3.5. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Jump, D.B. Dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and regulation of gene transcription. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2002, 13, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Bordoni, A.; Di Nunzio, M.; Danesi, F.; Biagi, P.L. Polyunsaturated fatty acids: from diet to binding to PPARs and other nuclear receptors. Genes Nutr. 2006, 1, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda, J.; Pei, L.; Evans, R.M. Nuclear receptors: decoding metabolic disease. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, J.D.; Shimomura, I. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins: activators of cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1999, 10, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ikonen, E. Cellular cholesterol trafficking and compartmentalization. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Worgall, T.S.; Sturley, S.L.; Seo, T.; Osborne, T.F.; Deckelbaum, R.J. Polyunsaturated fatty acids decrease expression of promoters with sterol regulatory elements by decreasing levels of mature sterol regulatory element-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 25537–25540. [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson, L.M.; de Groot, P.J.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Koppen, A.; Kalkhoven, E.; Müller, M.; Kersten, S. Effect of synthetic dietary triglycerides: a novel research paradigm for nutrigenomics. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1681. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Cho, H.; O'Malley, S.; Park, J.H.; Clarke, S.D. Dietary polyunsaturated fats regulate rat liver sterol regulatory element binding proteins-1 and -2 in three distinct stages and by different mechanisms. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya, M.; Yahagi, N.; Matsuzaka, T.; Najima, Y.; Nakakuki, M.; Nagai, R.; Ishibashi, S.; Osuga, J.; Yamada, N.; Shimano, H. Polyunsaturated fatty acids ameliorate hepatic steatosis in obese mice by SREBP-1 suppression. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Le Jossic-Corcos, C.; Gonthier, C.; Zaghini, I.; Logette, E.; Shechter, I.; Bournot, P. Hepatic farnesyl diphosphate synthase expression is suppressed by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochem. J. 2005, 385, 787–794. [Google Scholar]
- Botolin, D.; Wang, Y.; Christian, B.; Jump, D.B. Docosahexaneoic acid (22:6,n-3) regulates rat hepatocyte SREBP-1 nuclear abundance by Erk- and 26S proteasome-dependent pathways. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nunzio, M.; van Deursen, D.; Verhoeven, A.J.M.; Bordoni, A. n-3 and n-6 PUFAs suppress SREBP activity and increase flow of free cholesterol in HepG2 cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2009, (in press). [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, H.; Verhoeven, A.J.M.; Sijbrands, E.J.G. Hepatic lipase: a pro- or anti-atherogenic protein? J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perret, B.; Mabile, L.; Martinez, L.; Tercé, F.; Barbaras, R.; Collet, X. Hepatic lipase: structure/function relationship, synthesis, and regulation. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santamarina-Fojo, S.; González-Navarro, H.; Freeman, L.; Wagner, E.; Nong, Z. Hepatic lipase, lipoprotein metabolism, and atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1750–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berk-Planken, I.I.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; Stolk, R.P.; Bootsma, A.H.; Jansen, H. DALI Study Group. Atorvastatin dose-dependently decreases hepatic lipase activity in type 2 diabetes: effect of sex and the LIPC promoter variant. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 427–432. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, H.; Verhoeven, A.J.; Weeks, L.; Kastelein, J.J.; Halley, D.J.; van den Ouweland, A.; Jukema, J.W.; Seidell, J.C.; Birkenhäger, J.C. Common C-to-T substitution at position -480 of the hepatic lipase promoter associated with a lowered lipase activity in coronary artery disease patients. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17, 2837–2842. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, M.C.; Hokanson, J.E.; Deeb, S.S.; Purnell, J.Q.; Mitchell, E.S.; Brunzell, J.D. A hepatic lipase gene promoter polymorphism attenuates the increase in hepatic lipase activity with increasing intra-abdominal fat in women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 2701–2707. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, M.C.; Hokanson, J.E.; Zambon, A.; Deeb, S.S.; Barrett, P.H.; Purnell, J.Q.; Brunzell, J.D. The contribution of intraabdominal fat to gender differences in hepatic lipase activity and low/high density lipoprotein heterogeneity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar]
- Summerfield, J.A.; Applebaum-Bowden, D.; Hazzard, W.R. Effects of diet and age on lipoprotein lipase and hepatic triglyceride lipase activities in the rat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1984, 175, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Benhizia, F.; Hainault, I.; Serougne, C.; Lagrange, D.; Hajduch, E.; Guichard, C.; Malewiak, M.I.; Quignard-Boulange, A.; Lavau, M.; Griglio, S. Effects of a fish oil-lard diet on rat plasma lipoproteins, liver FAS, and lipolytic enzymes. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, E975–E982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nimmo, L.; McColl, A.J.; Rosankiewicz, J.Z.; Richmond, W.; Elkeles, R.S. Regulation of hepatic lipase expression in HepG2 cells. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1997, 25, S689. [Google Scholar]
- Botma, G.J.; van Deursen, D.; Vieira, D.; van Hoek, M.; Jansen, H.; Verhoeven, A.J. Sterol-regulatory-element binding protein inhibits upstream stimulatory factor-stimulated hepatic lipase gene expression. Atherosclerosis 2005, 179, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, F.; Harvengt, C. Effects of clofibrate, bezafibrate, fenofibrate and probucol on plasma lipolytic enzymes in normolipaemic subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1983, 25, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desager, J.P.; Horsmans, Y.; Vandenplas, C.; Harvengt, C. Pharmacodynamic activity of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase, and pharmacokinetic parameters measured in normolipidaemic subjects receiving ciprofibrate (100 or 200 mg/day) or micronised fenofibrate (200 mg/day) therapy for 23 days. Atherosclerosis 1996, 124, S65–S73. [Google Scholar]
- Staels, B.; Peinado-Onsurbe, J.; Auwerx, J. Down-regulation of hepatic lipase gene expression and activity by fenofibrate. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1123, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogerbrugge, N.; Jansen, H. Atorvastatin increases low-density lipoprotein size and enhances high-density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration in male, but not in female patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 1999, 146, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Benhizia, F.; Lagrange, D.; Malewiak, M.I.; Griglio, S. In vivo regulation of hepatic lipase activity and mRNA levels by diets which modify cholesterol influx to the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1211, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corre, S.; Galibert, M.D. Upstream stimulating factors: highly versatile stress-responsive transcription factors. Pigment Cell Res. 2005, 18, 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Lusis, A.J.; Pajukanta, P. Familial combined hyperlipidemia: upstream transcription factor 1 and beyond. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2006, 17, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- van Deursen, D.; van Leeuwen, M.; Vaulont, S.; Jansen, H.; Verhoeven, A.J. Upstream Stimulatory Factors 1 and 2 activate the human hepatic lipase promoter via E-box dependent and independent mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1791, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- van Deursen, D.; Jansen, H.; Verhoeven, A.J. Glucose increases hepatic lipase expression in HepG2 liver cells through upregulation of upstream stimulatory factors 1 and 2. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Part of this paper has been presented at the FoodOmics meeting in Cesena, Italy, May 2009.
- Horton, J.D.; Shah, N.A.; Warrington, J.A.; Anderson, N.N.; Park, S.W.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Combined analysis of oligonucleotide microarray data from transgenic and knockout mice identifies direct SREBP target genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12027–12032. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, C.; Wang, X.; Briggs, M.R.; Admon, A.; Wu, J.; Hua, X.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. SREBP-1, a basic-helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene. Cell 1993, 75, 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Evans, M.J.; Ho, Y.K.; Goldstein, J.L.; Brown, M.S. Assignment of the membrane attachment, DNA binding, and transcriptional activation domains of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1). J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 17267–17273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nowak, M.; Helleboid-Chapman, A.; Jakel, H.; Martin, G.; Duran-Sandoval, D.; Staels, B.; Rubin, E.M.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Taskinen, M.R.; Fruchart-Najib, J.; Fruchart, J.C. Insulin-mediated down-regulation of apolipoprotein A5 gene expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway: role of upstream stimulatory factor. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, R.H.; Chang, I.; Hudak, C.S.; Hyun, S.; Kwan, H.Y.; Sul, H.S. A role of DNA-PK for the metabolic gene regulation in response to insulin. Cell 2009, 136, 1056–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Handel, M.V.; Schartner, J.M.; Hagar, A.; Allen, G.; Curet, M.; Badie, B. Regulation of IL-10 expression by upstream stimulating factor (USF-1) in glioma-associated microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 184, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, P.; Wood, M.A.; Walker, W.H. FSH transiently blocks FSH receptor transcription by increasing ID2 and decreasing Upstream Stimulatory Factor (USF) expression in rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar]
- van Deursen, D.; di Nunzio, M. Unpublished observations.
- Athanikar, J.N.; Osborne, T.F. Specificity in cholesterol regulation of gene expression by coevolution of sterol regulatory DNA element and its binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4935–4940. [Google Scholar]
- Leichman, J.G.; Aguilar, D.; King, T.M.; Vlada, A.; Reyes, M.; Taegtmeyer, H. Association of plasma free fatty acids and left ventricular diastolic function in patients with clinically severe obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 84, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, A.J.; Neve, B.P.; Jansen, H. Secretion and apparent activation of human hepatic lipase requires proper oligosaccharide processing in the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochem. J. 1999, 337, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi, R.; Krummel, B.; Saiki, R. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucl. Acids Res. 1988, 16, 7351–7367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Miyamoto, W.; Inoue, J.; Terada, T.; Imanaka, T.; Maeda, M. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein negatively regulates microsomal triglyceride transfer protein gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 24714–24720. [Google Scholar]
- Yabe, D.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Insig-2, a second endoplasmic reticulum protein that binds SCAP and blocks export of sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12753–12758. [Google Scholar]
- Samples Availability: Plasmids are available from the authors.
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Deursen, D.; Van Leeuwen, M.; Akdogan, D.; Adams, H.; Jansen, H.; Verhoeven, A.J.M. Activation of Hepatic Lipase Expression by Oleic Acid: Possible Involvement of USF1. Nutrients 2009, 1, 133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020133
Van Deursen D, Van Leeuwen M, Akdogan D, Adams H, Jansen H, Verhoeven AJM. Activation of Hepatic Lipase Expression by Oleic Acid: Possible Involvement of USF1. Nutrients. 2009; 1(2):133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020133
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Deursen, Diederik, Marije Van Leeuwen, Deniz Akdogan, Hadie Adams, Hans Jansen, and Adrie J. M. Verhoeven. 2009. "Activation of Hepatic Lipase Expression by Oleic Acid: Possible Involvement of USF1" Nutrients 1, no. 2: 133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020133
APA StyleVan Deursen, D., Van Leeuwen, M., Akdogan, D., Adams, H., Jansen, H., & Verhoeven, A. J. M. (2009). Activation of Hepatic Lipase Expression by Oleic Acid: Possible Involvement of USF1. Nutrients, 1(2), 133-147. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu1020133