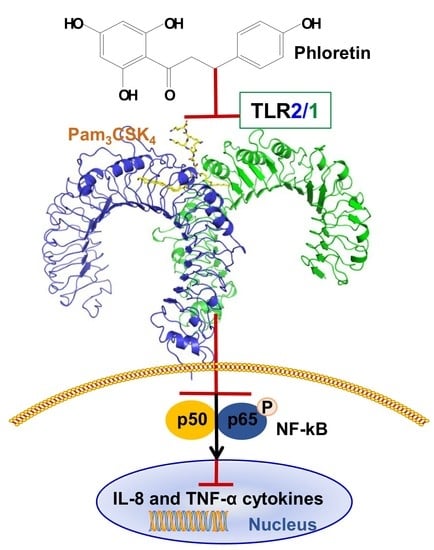
Phloretin as a Potent Natural TLR2/1 Inhibitor Suppresses TLR2-Induced Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of Raw264.7 Cells and HEK293-hTLR2 Cells
2.2. Specificity of Phloretin Against Various TLRs
2.3. Measurement of Inflammatory Cytokines in Pam3CSK4- and Pam2CSK4-Stimulated HEK293-hTLR2 Cells
2.4. Cytotoxicity of Phloretin Against Mouse Raw264.7 and Human HEK293-hTLR2 Cells
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Binding Assay of TLR1, TLR2, and Phloretin
2.7. Molecular Docking Study
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phloretin Effectively Reduced the TNF-α Production through TLR2/1 Signaling in Raw264.7 Cells
3.2. Effects of Phloretin and CU-CPT22 on Proinflammatory Cytokines in Pam3CSK4-Stimulated HEK293-hTLR2 Cells
3.3. Toxicity Against Raw264.7 Cells and HEK293-hTLR2 Cells
3.4. Effect of Phloretin and CU-CPT22 on Protein Expression in Pam3CSK4-Stimulated Raw 264.7 Cells
3.5. Determination of Binding Affinity of Phloretin to TLR1 and TLR2 Using BLI
3.6. Docking Analysis of Phloretin with TLR2/1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.Y.; Nan, X.; Jin, M.S.; Youn, S.J.; Ryu, Y.H.; Mah, S.; Han, S.H.; Lee, H.; Paik, S.G.; Lee, J.O. Recognition of lipopeptide patterns by Toll-like receptor 2-Toll-like receptor 6 heterodimer. Immunity 2009, 31, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Massari, P.; Wetzler, L.M. The Role of TLR2 in Infection and Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.K.; Ha, S.; Son, J.A.; Song, J.H.; Houh, Y.; Cho, E.; Chun, J.H.; Yoon, S.R.; Yang, Y.; Bang, S.I.; et al. Polyphenon-60 displays a therapeutic effect on acne by suppression of TLR2 and IL-8 expression via down-regulating the ERK1/2 pathway. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2012, 304, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botos, I.; Segal, D.M.; Davies, D.R. The structural biology of Toll-like receptors. Structure 2011, 19, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.Y.; Lee, J.O. Structural biology of the Toll-like receptor family. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 917–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, N.J.; Symmons, M.F.; Gangloff, M.; Bryant, C.E. Assembly and localization of Toll-like receptor signalling complexes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Dissecting negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, A.E. Toll-like receptor polymorphisms, inflammatory and infectious diseases, allergies, and cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013, 33, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A. Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for inflammatory and infectious diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, P.; Schieber, A.; Yildirim, C.; Arnold, G.; Klaiber, I.; Conrad, J.; Beifuss, U.; Carle, R. Detection of phloridzin in strawberries (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) by HPLC-PDA-MS/MS and NMR spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2896–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, B.M.; Haenen, G.R.; van der Vijgh, W.J.; Bast, A. The antioxidant activity of phloretin: The disclosure of a new antioxidant pharmacophore in flavonoids. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 295, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oresajo, C.; Stephens, T.; Hino, P.D.; Law, R.M.; Yatskayer, M.; Foltis, P.; Pillai, S.; Pinnell, S.R. Protective effects of a topical antioxidant mixture containing vitamin C, ferulic acid, and phloretin against ultraviolet-induced photodamage in human skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.S.; Landau, J.M.; Huang, M.T.; Newmark, H.L. Inhibition of carcinogenesis by dietary polyphenolic compounds. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2001, 21, 381–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, D.; Jeong, M.C.; Jacob, B.; Bang, J.K.; Kim, E.H.; Cheong, C.; Jung, I.D.; Park, Y.; Kim, Y. Investigation of cationicity and structure of pseudin-2 analogues for enhanced bacterial selectivity and anti-inflammatory activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, K.W.; Shin, S.; Lee, J.U.; Kim, Y. Antimicrobial natural products as beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5408–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangl, V.; Lorenz, M.; Ludwig, A.; Grimbo, N.; Guether, C.; Sanad, W.; Ziemer, S.; Martus, P.; Baumann, G.; Stangl, K. The flavonoid phloretin suppresses stimulated expression of endothelial adhesion molecules and reduces activation of human platelets. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fordham, J.B.; Raza Naqvi, A.; Nares, S. Leukocyte production of inflammatory mediators is inhibited by the antioxidants phloretin, silymarin, hesperetin, and resveratrol. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 938712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.Q.; Pope, R.M. The role of toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2009, 11, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahashi, M.; Yamamura, M.; Aita, T.; Okamoto, A.; Ueno, A.; Ogawa, N.; Akashi, S.; Miyake, K.; Godowski, P.J.; Makino, H. Expression of Toll-like receptor 2 on CD16+ blood monocytes and synovial tissue macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.P.; Lin, S.C.; Li, S.; Chao, Y.H.; Hwang, G.Y.; Lin, C.C. Potent Antiarthritic Properties of Phloretin in Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 9831263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozinsky, A.; Underhill, D.M.; Fontenot, J.D.; Hajjar, A.M.; Smith, K.D.; Wilson, C.B.; Schroeder, L.; Aderem, A. The repertoire for pattern recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system is defined by cooperation between toll-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13766–13771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buwitt-Beckmann, U.; Heine, H.; Wiesmuller, K.H.; Jung, G.; Brock, R.; Akira, S.; Ulmer, A.J. Toll-like receptor 6-independent signaling by diacylated lipopeptides. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jnawali, H.N.; Lee, E.; Jeong, K.W.; Shin, A.; Heo, Y.S.; Kim, Y. Anti-inflammatory activity of rhamnetin and a model of its binding to c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 and p38 MAPK. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jnawali, H.N.; Jeon, D.; Jeong, M.C.; Lee, E.; Jin, B.; Ryoo, S.; Yoo, J.; Jung, I.D.; Lee, S.J.; Park, Y.M.; et al. Antituberculosis Activity of a Naturally Occurring Flavonoid, Isorhamnetin. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, E.; Shin, S.; Jeong, K.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Bae, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, D.G.; et al. Structure and function of papiliocin with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities isolated from the swallowtail butterfly, Papilio xuthus. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41296–41311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, M.S.; Kim, S.E.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, M.E.; Kim, H.M.; Paik, S.G.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. Crystal structure of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 2007, 130, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yin, H. Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of the TLR1/TLR2 complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 12246–12249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durai, P.; Shin, H.J.; Achek, A.; Kwon, H.K.; Govindaraj, R.G.; Panneerselvam, S.; Yesudhas, D.; Choi, J.; No, K.T.; Choi, S. Toll-like receptor 2 antagonists identified through virtual screening and experimental validation. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 2264–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgueitio, M.S.; Henneke, P.; Glossmann, H.; Santos-Sierra, S.; Wolber, G. Prospective virtual screening in a sparse data scenario: Design of small-molecule TLR2 antagonists. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Liu, L.J.; Dong, Z.Q.; Lu, L.; Wang, M.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L.; Wang, Y. Structure-based discovery of an immunomodulatory inhibitor of TLR1-TLR2 heterodimerization from a natural product-like database. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11178–11181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Durai, P.; Jeon, D.; Jung, I.D.; Lee, S.J.; Park, Y.-M.; Kim, Y. Phloretin as a Potent Natural TLR2/1 Inhibitor Suppresses TLR2-Induced Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070868
Kim J, Durai P, Jeon D, Jung ID, Lee SJ, Park Y-M, Kim Y. Phloretin as a Potent Natural TLR2/1 Inhibitor Suppresses TLR2-Induced Inflammation. Nutrients. 2018; 10(7):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070868
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jieun, Prasannavenkatesh Durai, Dasom Jeon, In Duk Jung, Seung Jun Lee, Yeong-Min Park, and Yangmee Kim. 2018. "Phloretin as a Potent Natural TLR2/1 Inhibitor Suppresses TLR2-Induced Inflammation" Nutrients 10, no. 7: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070868
APA StyleKim, J., Durai, P., Jeon, D., Jung, I. D., Lee, S. J., Park, Y. -M., & Kim, Y. (2018). Phloretin as a Potent Natural TLR2/1 Inhibitor Suppresses TLR2-Induced Inflammation. Nutrients, 10(7), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070868