Limited Effects of Low-to-Moderate Aerobic Exercise on the Gut Microbiota of Mice Subjected to a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design and Exercise Training
2.3. Fecal DNA Extraction and 16S rDNA Gene Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of 16S rDNA Sequences
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Accession Number
3. Results
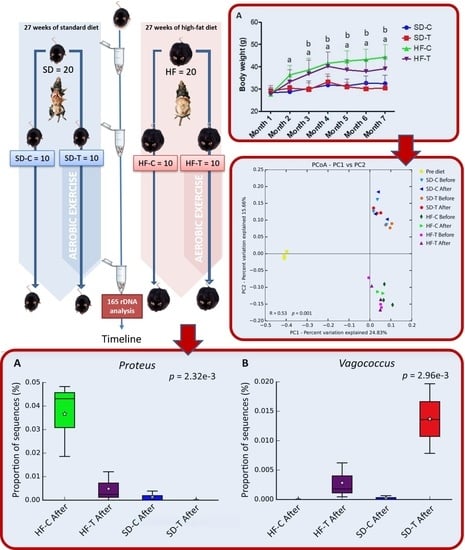
3.1. Effect of High-Fat Diet and Low-to-Moderate Exercise on Body Weight, Adiposity, Food Intake and Calorie Consumption
3.2. Effect of Low-to-Moderate Aerobic Exercise on Aerobic Power (Vmax2)
3.3. Characterization of the Bacterial Community by Gut Microbiota Profiling
3.4. Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA)
3.5. Effects of Low-to-Moderate Exercise on Bacterial Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parikh, N.I.; Pencina, M.J.; Wang, T.J.; Lanier, K.J.; Fox, C.S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Vasan, R.S. Increasing trends in incidence of overweight and obesity over 5 decades. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight—Fact Sheet; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lehnert, T.; Sonntag, D.; Konnopka, A.; Riedel-Heller, S.; Konig, H.H. Economic costs of overweight and obesity. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration; Di Angelantonio, E.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Wormser, D.; Gao, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Cairns, B.J.; Huxley, R.; Jackson, C.L.; et al. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: Individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet 2016, 388, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M.; Riffenburg, K.M. Perspectives on the global obesity epidemic. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, P.G.; Santacruz, A.; Trejo, F.M.; Sanz, Y. Bifidobacterium CECT 7765 improves metabolic and immunological alterations associated with obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Obesity 2013, 21, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Riaz Rajoka, M.S.; Shao, D.; Jiang, C.; Jin, M.; Huang, Q.; Yang, H.; Shi, J. Strategies to increase the efficacy of using gut microbiota for the modulation of obesity. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2017, 18, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, S.A.; Karelis, A.D.; Bergeron, K.F.; Mounier, C. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Health: The Potential Beneficial Effects of a Medium Chain Triglyceride Diet in Obese Individuals. Nutrients 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermon, S.; Petriz, B.; Kajeniene, A.; Prestes, J.; Castell, L.; Franco, O.L. The microbiota: An exercise immunology perspective. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 21, 70–79. [Google Scholar]
- Org, E.; Mehrabian, M.; Lusis, A.J. Unraveling the environmental and genetic interactions in atherosclerosis: Central role of the gut microbiota. Atherosclerosis 2015, 241, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Nunez, G. Gut microbiota: Role in pathogen colonization, immune responses, and inflammatory disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Modulation of gut microbiota by berberine and metformin during the treatment of high-fat diet-induced obesity in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Houghton, D.; Stewart, C.J.; Day, C.P.; Trenell, M. Gut Microbiota and Lifestyle Interventions in NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.H.; Paul, H.A.; Hart, D.A.; Reimer, R.A.; Smith, I.C.; Rios, J.L.; Seerattan, R.A.; Herzog, W. A High-Fat High-Sucrose Diet Rapidly Alters Muscle Integrity, Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Male Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malikowski, T.; Khanna, S.; Pardi, D.S. Fecal microbiota transplantation for gastrointestinal disorders. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 33, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petriz, B.A.; Castro, A.P.; Almeida, J.A.; Gomes, C.P.; Fernandes, G.R.; Kruger, R.H.; Pereira, R.W.; Franco, O.L. Exercise induction of gut microbiota modifications in obese, non-obese and hypertensive rats. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressa, C.; Bailen-Andrino, M.; Perez-Santiago, J.; Gonzalez-Soltero, R.; Perez, M.; Montalvo-Lominchar, M.G.; Mate-Munoz, J.L.; Dominguez, R.; Moreno, D.; Larrosa, M. Differences in gut microbiota profile between women with active lifestyle and sedentary women. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wiklund, P.; Tan, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, X.; Tikkanen, O.; Zhang, C.; Munukka, E.; Cheng, S. The Association between Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Gut Microbiota Composition in Premenopausal Women. Nutrients 2017, 9, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denou, E.; Marcinko, K.; Surette, M.G.; Steinberg, G.R.; Schertzer, J.D. High-intensity exercise training increases the diversity and metabolic capacity of the mouse distal gut microbiota during diet-induced obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E982–E993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhan, Q.; Lai, W.; Zeng, Q.; Ren, H.; Xu, D. Moderate-Intensity Exercise Affects Gut Microbiome Composition and Influences Cardiac Function in Myocardial Infarction Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, E.V.; Grandy, S.A.; Langille, M.G.I. Moderate Exercise Has Limited but Distinguishable Effects on the Mouse Microbiome. MSystems 2017, 2, e00006-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.M.; Berg Miller, M.E.; Pence, B.D.; Whitlock, K.; Nehra, V.; Gaskins, H.R.; White, B.A.; Fryer, J.D.; Woods, J.A. Voluntary and forced exercise differentially alters the gut microbiome in C57BL/6J mice. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 118, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monda, V.; Villano, I.; Messina, A.; Valenzano, A.; Esposito, T.; Moscatelli, F.; Viggiano, A.; Cibelli, G.; Chieffi, S.; Monda, M.; et al. Exercise Modifies the Gut Microbiota with Positive Health Effects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3831972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.J.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, J.S.; Chen, Y.M.; Ho, S.T.; Huang, C.C.; Tung, Y.T. Kefir Supplementation Modifies Gut Microbiota Composition, Reduces Physical Fatigue, and Improves Exercise Performance in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welly, R.J.; Liu, T.W.; Zidon, T.M.; Rowles, J.L., 3rd; Park, Y.M.; Smith, T.N.; Swanson, K.S.; Padilla, J.; Vieira-Potter, V.J. Comparison of Diet versus Exercise on Metabolic Function and Gut Microbiota in Obese Rats. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Evans, C.C.; LePard, K.J.; Kwak, J.W.; Stancukas, M.C.; Laskowski, S.; Dougherty, J.; Moulton, L.; Glawe, A.; Wang, Y.; Leone, V.; et al. Exercise prevents weight gain and alters the gut microbiota in a mouse model of high fat diet-induced obesity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, F.; Nguyen, T.L.; Brinkman, B.; Yunta, R.G.; Cauwe, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Liston, A.; Raes, J. Inflammation-associated enterotypes, host genotype, cage and inter-individual effects drive gut microbiota variation in common laboratory mice. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramdhave, A.S.; Ojha, S.; Nandave, M. Energy intake correlates with the levels of fatty acid synthase and insulin-like growth factor-1 in male and female C57BL/6 mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 830–844. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, B.A.; Phillips, S.J. Detection of obesity QTLs on mouse chromosomes 1 and 7 by selective DNA pooling. Genomics 1996, 34, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.A.; Petriz Bde, A.; da Costa Gomes, C.P.; Pereira, R.W.; Franco, O.L. Assessment of maximal lactate steady state during treadmill exercise in SHR. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.A.; Petriz, B.A.; Gomes, C.P.; Rocha, L.A.; Pereira, R.W.; Franco, O.L. Determination of the maximal lactate steady state in obese Zucker rats. Int. J. Sports Med. 2013, 34, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daniel, H.; Gholami, A.M.; Berry, D.; Desmarchelier, C.; Hahne, H.; Loh, G.; Mondot, S.; Lepage, P.; Rothballer, M.; Walker, A.; et al. High-fat diet alters gut microbiota physiology in mice. ISME J. 2014, 8, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Li, J.; Tang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, H.; Wood, R.J.; Liu, Z. High Fat Diet Alters Gut Microbiota and the Expression of Paneth Cell-Antimicrobial Peptides Preceding Changes of Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9474896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.E. Diet, exercise or diet with exercise: Comparing the effectiveness of treatment options for weight-loss and changes in fitness for adults (18–65 years old) who are overfat, or obese; systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2015, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzidis, A.; Hicks, J.A.; Gelineau, R.R.; Arruda, N.L.; Monteiro De Pina, I.; O’Connell, K.E.; Seggio, J.A. Removal of a high-fat diet, but not voluntary exercise, reverses obesity and diabetic-like symptoms in male C57BL/6J mice. Hormones 2017, 16, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.A.; Petriz, B.A.; Gomes, C.P.; Araujo, R.C.; Pereira, R.W.; Franco, O.L. Exercise training at MLSS decreases weight gain and increases aerobic capacity in obese Zucker rats. Int J. Sports Med. 2014, 35, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentish, S.J.; Wittert, G.A.; Blackshaw, L.A.; Page, A.J. A chronic high fat diet alters the homologous and heterologous control of appetite regulating peptide receptor expression. Peptides 2013, 46, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covasa, M.; Ritter, R.C. Rats maintained on high-fat diets exhibit reduced satiety in response to CCK and bombesin. Peptides 1998, 19, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abete, I.; Astrup, A.; Martinez, J.A.; Thorsdottir, I.; Zulet, M.A. Obesity and the metabolic syndrome: Role of different dietary macronutrient distribution patterns and specific nutritional components on weight loss and maintenance. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.N.; Liao, Y.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Li, Z.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, G.J.; Lin, C.H.; Wong, A.M. Diet-induced obesity accelerates blood lactate accumulation of rats in response to incremental exercise to maximum. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 313, R601–R607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, S.; Kinugawa, S.; Matsushima, S.; Takemoto, D.; Furihata, T.; Mizushima, W.; Fukushima, A.; Yokota, T.; Ono, Y.; Shibata, H.; et al. Sesamin prevents decline in exercise capacity and impairment of skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in mice with high-fat diet-induced diabetes. Exp. Physiol. 2015, 100, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, L.; Lei, T.; Chen, L.; Shen, Q.; Qin, L.; Wan, Z. Effects of treadmill running and rutin on lipolytic signaling pathways and TRPV4 protein expression in the adipose tissue of diet-induced obese mice. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 71, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardare, C.; Kruger, K.; Liebisch, G.; Seimetz, M.; Couturier, A.; Ringseis, R.; Wilhelm, J.; Weissmann, N.; Eder, K.; Mooren, F.C. Endurance and Resistance Training Affect High Fat Diet-Induced Increase of Ceramides, Inflammasome Expression, and Systemic Inflammation in Mice. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 4536470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Borer, K.; Lin, P.J. Low-Carbohydrate-High-Fat Diet: Can it Help Exercise Performance? J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 56, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindseth, I. Methodological issues question the validity of observed performance impairment of a low carbohydrate, high fat diet. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estaki, M.; Pither, J.; Baumeister, P.; Little, J.P.; Gill, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Ahmadi-Vand, Z.; Marsden, K.R.; Gibson, D.L. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a predictor of intestinal microbial diversity and distinct metagenomic functions. Microbiome 2016, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.J.; Chiu, C.C.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, W.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, C.C.; Chuang, H.L. Effect of intestinal microbiota on exercise performance in mice. J. Strength Cond. Res. Natl. Strength Cond. Assoc. 2015, 29, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cui, Y.S.; Kwon, C.S.; Lee, S.T.; Lee, J.S.; Im, W.T. Vagococcus acidifermentans sp. nov., isolated from an acidogenic fermentation bioreactor. Int. J. Syst Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juturu, V.; Wu, J.C. Microbial production of lactic acid: The latest development. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonejima, Y.; Ushida, K.; Mori, Y. Effect of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Lipid Metabolism and Fat Synthesis in Mice Fed a High-fat Diet. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2013, 32, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Usman; Hosono, A. Bile tolerance, taurocholate deconjugation, and binding of cholesterol by Lactobacillus gasseri strains. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadooka, Y.; Sato, M.; Imaizumi, K.; Ogawa, A.; Ikuyama, K.; Akai, Y.; Okano, M.; Kagoshima, M.; Tsuchida, T. Regulation of abdominal adiposity by probiotics (Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055) in adults with obese tendencies in a randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfalzer, A.C.; Nesbeth, P.D.; Parnell, L.D.; Iyer, L.K.; Liu, Z.; Kane, A.V.; Chen, C.Y.; Tai, A.K.; Bowman, T.A.; Obin, M.S.; et al. Diet- and Genetically-Induced Obesity Differentially Affect the Fecal Microbiome and Metabolome in Apc1638N Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.M.; Davy, B.M.; Hulver, M.W.; Neilson, A.P.; Bennett, B.J.; Davy, K.P. Does Exercise Alter Gut Microbial Composition? A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, F.M.; Ribeiro, C.F.A.; Garcia, A.C.M.; Castro, A.P.; Almeida, J.A.; Franco, O.L.; Petriz, B.A. Limited Effects of Low-to-Moderate Aerobic Exercise on the Gut Microbiota of Mice Subjected to a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010149
Ribeiro FM, Ribeiro CFA, Garcia ACM, Castro AP, Almeida JA, Franco OL, Petriz BA. Limited Effects of Low-to-Moderate Aerobic Exercise on the Gut Microbiota of Mice Subjected to a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2019; 11(1):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010149
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Filipe M., Camila F. A. Ribeiro, Ana C. M. Garcia, Alinne P. Castro, Jeeser A. Almeida, Octavio L. Franco, and Bernardo A. Petriz. 2019. "Limited Effects of Low-to-Moderate Aerobic Exercise on the Gut Microbiota of Mice Subjected to a High-Fat Diet" Nutrients 11, no. 1: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010149
APA StyleRibeiro, F. M., Ribeiro, C. F. A., Garcia, A. C. M., Castro, A. P., Almeida, J. A., Franco, O. L., & Petriz, B. A. (2019). Limited Effects of Low-to-Moderate Aerobic Exercise on the Gut Microbiota of Mice Subjected to a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients, 11(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010149