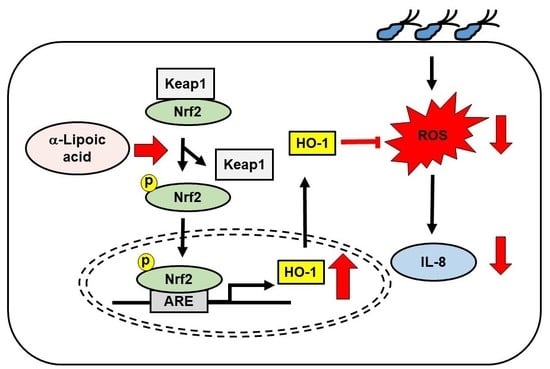
α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits IL-8 Expression by Activating Nrf2 Signaling in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.3. Cell Culture with H. pylori Infection
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Levels
2.6. Real-time PCR Analysis
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Preparation of Whole-Cell Extracts and Nuclear Extracts
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Immunoprecipitation of the Nrf2-KEAP 1 Complex
2.11. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. α-LA Increases Expression, Phosphorylation, and Nuclear Translocation of Nrf2, and Expression of HO-1 in AGS Cells
3.2. α-LA Decreases Interaction between KEAP1 and Nrf2 in AGS Cells
3.3. α-LA Decreases IL-8 Expression and ROS Levels, but Increases HO-1 Expression in H. pylori-infected AGS Cells
3.4. Nrf2 Inhibitor Trigonelline Abolishes the Effect of α-LA on IL-8, HO-1 and ROS Levels in H. pylori-infected AGS Cells
3.5. HO-1 Inhibitor ZnPP Inhibits the Effect of α-LA on ROS Levels and Expression of IL-8 in H. pylori-infected AGS Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durrani, A.I.; Schwartz, H.; Nagl, M.; Sontag, G. Determination of free α-lipoic acid in foodstuffs by HPLC coupled with CEAD and ESI-MS. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, A.; Wlodek, L. Lipoic acid-the drug of the future. Pharmacol. Rep. 2005, 57, 570–577. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, S.; Ruus, P.; Hermann, R.; Tritschler, H.J.; Maerker, E.; Renn, W.; Augustin, H.J.; Dietze, G.J.; Rett, K. Oral administration of RAC-alpha-lipoic acid modulates insulin sensitivity in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus: a placebo-controlled pilot trial. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenova, P. Improvement of insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after oral administration of alpha-lipoic acid. Hormones 2006, 5, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Pirritano, D.; Plastino, M.; Cristiano, D.; Puccio, G.; Colica, C.; Ermio, C.; De Bartolo, M.; Mauro, G.; Bosco, D. The Effect of Lipoic Acid Therapy on Cognitive Functioning in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 454253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, K.; Kenklies, M.; McAfoose, J.; Engel, J.; Münch, G. Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease--a 48 months follow-up analysis. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2007, 72, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.H.; Cho, S.O.; Kim, H. α-Lipoic acid inhibits expression of IL-8 by suppressing activation of MAPK, Jak/Stat, and NF-κB in H. pylori-infected gastric epithelial AGS cells. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, E.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, H. α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Helicobacter pylori-Induced Oncogene Expression and Hyperproliferation by Suppressing the Activation of NADPH Oxidase in Gastric Epithelial Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 380830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.; Hayes, J.D.; Brown, K.; Wolf, C.R.; Whitelaw, C.B.A. Peroxiredoxin Gene Expression Signatures in Liver Reflect Toxic Insult. ASSAY Drug Dev. Technol. 2010, 8, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, A.; Kang, M.I.; Okawa, H.; Ohtsuji, M.; Zenke, Y.; Chiba, T.; Igarashi, K.; Yamamoto, M. Oxidative Stress Sensor Keap1 Functions as an Adaptor for Cul3-Based E3 Ligase To Regulate Proteasomal Degradation of Nrf2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayes, J.D.; McMahon, M.; Chowdhry, S.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T. Cancer Chemoprevention Mechanisms Mediated Through the Keap1–Nrf2 Pathway. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010, 13, 1713–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, P.J.; Pickett, C.B.; Nguyen, T. Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 233–260. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lim, M.-J.; Kim, M.-H.; Yu, C.-H.; Yun, Y.-S.; Ahn, J.; Song, J.-Y. An effective strategy for increasing the radiosensitivity of Human lung Cancer cells by blocking Nrf2-dependent antioxidant responses. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Naito, Y.; Okada, H.; Ishii, T.; Mizushima, K.; Akagiri, S.; Adachi, S.; Handa, O.; Kokura, S.; Ichikawa, H.; et al. Lansoprazole, a Proton Pump Inhibitor, Mediates Anti-Inflammatory Effect in Gastric Mucosal Cells through the Induction of Heme Oxygenase-1 via Activation of NF-E2-Related Factor 2 and Oxidation of Kelch-Like ECH-Associating Protein 1. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 331, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R.; Bassi, R.; Green, C.J. Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogborne, R.M.; Rushworth, S.A.; O’Connell, M.A. α-Lipoic Acid–Induced Heme Oxygenase-1 Expression Is Mediated by Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 and p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Human Monocytic Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koriyama, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Matsugo, S.; Kato, S. Protective effect of lipoic acid against oxidative stress is mediated by KEAP1/Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 induction in the RGC-5 cell line. Brain Res. 2013, 1499, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Saracco, G.M.; Mégraud, F. A 2016 panorama of Helicobacter pylori infection: key messages for clinicians. Panminerva Med. 2016, 58, 304–317. [Google Scholar]
- Buzás, G.M. Benign and malignant gastroduodenal diseases associated with Helicobacter pylori: a narrative review and personal remarks in 2018. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2018, 64, 280–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicano, R.; Oliaro, E.; Fagoonee, S.; Astegiano, M.; Berrutti, M.; Saracco, G.; Smedile, A.; Repici, A.; Leone, N.; Castelli, A.; et al. Clinical and biochemical parameters related to cardiovascular disease after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Int. Angiol. 2009, 28, 469–473. [Google Scholar]
- Negrini, R.; Savio, A.; Poiesi, C.; Appelmelk, B.; Buffoli, F.; Paterlini, A.; Cesari, P.; Graffeo, M.; Vaira, D.; Franzin, G. Antigenic mimicry between Helicobacter pylori and gastric mucosa in the pathogenesis of body atrophic gastritis. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kita, M.; Kodama, T.; Sawai, N.; Tanahashi, T.; Kashima, K.; Imanishi, J. Chemokines in the gastric mucosa in Helicobacter pylori infection. Gut 1998, 42, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remick, D.G. Interleukin-8. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, S466–S467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.M.; Territo, M.C.; Karnes, W.E.; Walsh, J.H. Helicobacter pylori secretes a chemotactic factor for monocytes and neutrophils. Gut 1992, 33, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Miura, S.; Imaeda, H.; Suzuki, M.; Han, J.Y.; Mori, M.; Fukumura, D.; Tsuchiya, M.; Ishii, H. Enhanced levels of chemiluminescence and platelet activating factor in urease-positive gastric ulcers. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1996, 20, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T. Molecular and cellular mechanisms involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002, 33, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. Astaxanthin inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction and interleukin-8 expression in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, J.E.; Covacci, A.; Farmery, S.M.; Xiang, Z.; Tompkins, D.S.; Perry, S.; Lindley, I.J.; Rappuoli, R. Helicobacter pylori induced interleukin-8 expression in gastric epithelial cells is associated with CagA positive phenotype. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 48, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, D.T.; Elliott, T.B.; Verspaget, H.W.; Jones, D.; Allen, C.R.; Vernon, K.G.; Bremner, T.; Kidd, L.C.R.; Kim, K.S.; Groupman, J.D.; et al. Influence of Helicobacter pylori on reactive oxygen-induced gastric epithelial cell injury. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 2091–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.H. Transcriptional regulation by thiol compounds in Helicobacter pylori induced IL-8 production in human gastric epithelial cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 973, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Zhai, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Fu, C.; Zhu, M. Alpha lipoic acid inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by modulating of Nrf2 signalling pathway after traumatic brain injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4088–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.; Choi, H.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, B.G.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J. Protective effects of α-lipoic acid on cultured human nasal fibroblasts exposed to urban particulate matter. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, C.M.; Cipriano, M.A.; Botelho, M.F.; Seiça, R.M. Lipoic Acid Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Goto Kakizaki Rats by Reducing Oxidative Stress Through Nrf2 Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhuang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, G.; Cai, W. Alpha-lipoic acid prevents oxidative stress and peripheral neuropathy in nab-paclitaxel-treated rats through the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 3142732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Paonessa, J.D.; Zhang, Y. Mechanism of Chemical Activation of Nrf2. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.P.; Verriere, T.; Asim, M.; Barry, D.P.; Piazuelo, M.B.; De Sablet, T.; Delgado, A.G.; Bravo, L.E.; Correa, P.; Peek, R.M.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 dysregulates macrophage polarization and the immune response to Helicobacter pylori. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3013–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Rho, D.J.; Jeon, J.I.; Kim, Y.-J.; Woo, H.A.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.M. Crude Preparations of Helicobacter pylori Outer Membrane Vesicles Induce Upregulation of Heme Oxygenase-1 via Activating Akt-Nrf2 and mTOR-IκB Kinase-NF-κB Pathways in Dendritic Cells. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 2162–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.Y.; Lee, H.G.; Piao, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Na, H.K.; Surh, Y.J. Helicobacter pylori infection promotes autophagy through Nrf2-mediated heme oxygenase upregulation in human gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 162, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, A.P.; Verriere, T.; Sablet, T.; Peek, R.M.; Chaturvedi, R.; Wilson, K.T. Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits phosphorylation of the Helicobacter pylori oncoprotein CagA in gastric epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buommino, E.; Donnarumma, G.; Manente, L.; De Filippis, A.; Silvestri, F.; Iaquinto, S.; Tufano, M.A.; De Luca, A. TheHelicobacter PyloriProtein HspB Interferes with Nrf2/Keap1 Pathway Altering The Antioxidant Response of Ags Cells. Helicobacter 2012, 17, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, R.A.; Cordwell, S.J.; Coombs, G.W.; Walsh, B.J.; Forbes, G.M. Proteome analysis of Helicobacter pylori: major proteins of type strain NCTC 11637. Pathology 2001, 33, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuhu, A.A. Bioactive Micronutrients in Coffee: Recent Analytical Approaches for Characterization and Quantification. ISRN Nutr. 2014, 2014, 384230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.C.; Lee, K.T.; You, B.J.; Lee, C.L.; Chang, W.T.; Wu, Y.C.; Lee, H.-Z. Raf/ERK/Nrf2 signaling pathway and MMP-7 expression involvement in the trigonelline-mediated inhibition of hepatocarcinoma cell migration. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 59, 29884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sova, M.; Saso, L. Design and development of Nrf2 modulators for cancer chemoprevention and therapy: a review. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3181–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, R.F.; Vreman, H.J.; Stevenson, D.K. Zinc protoporphyrin: A metabolite with a mission. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 2060–2072. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, K.; Sasahira, T.; Ohmori, H.; Fujii, K.; Kuniyasu, H. Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 by zinc protoporphyrin IX reduces tumor growth of LL/2 lung cancer in C57BL mice. Intl. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Greish, K.; Qin, H.; Liao, L.; Nakamura, H.; Takeya, M.; Maeda, H. HSP32 (HO-1) inhibitor, copoly(styrene-maleic acid)-zinc protoporphyrin IX, a water-soluble micelle as anticancer agent: In vitro and in vivo anticancer effect. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyants, N.S.; Jiang, Q.; Taylor, D.E.; Berg, D.E. Corrected Identity of Isolates ofHelicobacter PyloriReference Strain NCTC11637. Helicobacter 1997, 2, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, M.; Feller, S.M.; Romer, G.; Wessler, S. Phosphorylation of Helicobacter pylori CagA by c-Abl leads to cell motility. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.A.; Tummuru, M.K.; Miller, G.G.; Blaser, M.J. Interleukin-8 response of gastric epithelial cell lines to Helicobacter pylori stimulation in vitro. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 1681–1687. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ikuta, N.; Okamoto, H.; Furune, T.; Uekaji, Y.; Terao, K.; Uchida, R.; Iwamoto, K.; Miyajima, A.; Hirota, T.; Sakamoto, N. Bioavailability of an R-α-Lipoic Acid/γ-Cyclodextrin Complex in Healthy Volunteers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kyung, S.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits IL-8 Expression by Activating Nrf2 Signaling in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102524
Kyung S, Lim JW, Kim H. α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits IL-8 Expression by Activating Nrf2 Signaling in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients. 2019; 11(10):2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102524
Chicago/Turabian StyleKyung, Seoyeon, Joo Weon Lim, and Hyeyoung Kim. 2019. "α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits IL-8 Expression by Activating Nrf2 Signaling in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells" Nutrients 11, no. 10: 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102524
APA StyleKyung, S., Lim, J. W., & Kim, H. (2019). α-Lipoic Acid Inhibits IL-8 Expression by Activating Nrf2 Signaling in Helicobacter pylori-infected Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients, 11(10), 2524. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102524