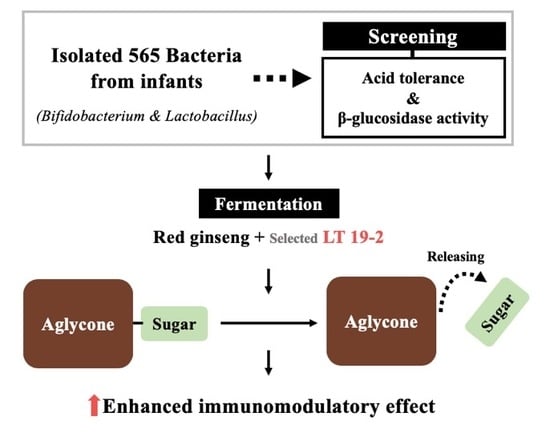
Enhancing Immunomodulatory Function of Red Ginseng Through Fermentation Using Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis LT 19-2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Probiotic Strains from Infant Feces
2.2. DNA Extraction and 16S Ribosomal RNA (16S rRNA) Gene Sequencing
2.3. Acid Tolerance Tests
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Tests
2.5. β-Glucosidase Activity Assay
2.6. Fermentation of FRG
2.7. Cell Culture and Macrophage Stimulatory Activity
2.8. Immunoblot Analysis
2.9. Splenocyte Proliferation Assay
2.10. Isolation of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Screening of 565 Strains for Discovery of Novel Probiotics
3.2. Fermented Red Ginseng Using LT 19-2 Shows Enhanced Immunomodulatory Function and Activation of MAPKs and NF-κB Signaling Pathways
3.3. FRG Displays Immune-Stimulatory Effects in Primary Immune Cells
3.4. Analysis of the Ginsenoside Content in FRG Showed an Increase in Aglycone Metabolites
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.M.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.L.; Chen, S.L.; Xu, H.X. Holistic quality evaluation of commercial white and red ginseng using a UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 62, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeon, J.N.; Wang, C.; Min, J.W.; Noh, H.Y.; Yang, D.C. Effect of white, red and black ginseng on physicochemical properties and ginsenosides. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr 2015, 70, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.S.; Hyun, S.H.; Han, C.K. Red ginseng monograph. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Ok, H.M.; Kwon, O. Protective Effects of Korean Red Ginseng against Alcohol-Induced Fatty Liver in Rats. Molecules 2015, 20, 11604–11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.S.; Auyeung, K.K.; Yip, K.M.; Ye, R.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Mao, Q.; Xu, J.; Chen, H.B.; Li, S.L. Stronger anti-obesity effect of white ginseng over red ginseng and the potential mechanisms involving chemically structural/compositional specificity to gut microbiota. Phytomedicine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.H.; Park, H.M.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, H.; Kim, N.; Do, J.H.; Kang, C.; Cho, Y.; Kim, S.Y. Effects of red ginseng extract on UVB irradiation-induced skin aging in hairless mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Song, M.S.; Seo, H.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, J.C.; Jo, S.K.; Jang, J.S.; Kim, S.H. Photoprotective effect of red ginseng against ultraviolet radiation-induced chronic skin damage in the hairless mouse. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Anderson, S.; Du, W.; He, T.C.; Yuan, C.S. Red ginseng and cancer treatment. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 7–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, M.; Kwon, B.S.; Suh, D.H.; Song, Y.S. Effect of Red Ginseng on Genotoxicity and Health-Related Quality of Life after Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: A Randomized, Double Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2017, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; Roh, Y.S.; Uyangaa, E.; Park, S.; Kim, J.W.; Lim, K.H.; Kwon, J.; Eo, S.K.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, B. Protective effects of red ginseng extract against vaginal herpes simplex virus infection. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Ahn, H.; Han, B.C.; Lee, S.H.; Cho, Y.W.; Kim, C.H.; Hong, E.J.; An, B.S.; Jeung, E.B.; Lee, G.S. Korean red ginseng extracts inhibit NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Immunol. Lett. 2014, 158, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.U.; Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J.; Kim, N.J.; Kim, D.H. Hepatoprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Zhou, X.W.; Zhou, W.; Li, X.W.; Feng, M.Q.; Zhou, P. Purification and properties of a novel beta-glucosidase, hydrolyzing ginsenoside Rb1 to CK, from Paecilomyces Bainier. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, A.; Sun, H.; Ye, Y.; Fang, W. Ginsenoside Rd elicits Th1 and Th2 immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vaccine 2007, 25, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Qiu, L.; Ding, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Song, F.; Hu, J. Ginsenoside Rb1 and paeoniflorin inhibit transient receptor potential vanilloid-1-activated IL-8 and PGE(2) production in a human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Sun, J.; Zhu, X.; Nian, S.; Liu, J. Compound K increases type I procollagen level and decreases matrix metalloproteinase-1 activity and level in ultraviolet-A-irradiated fibroblasts. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, S.; Chin, M.Y.; Adomat, H.; Guns, E.S. Ginsenoside-mediated blockade of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inactivation in human liver and intestine in vitro. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 141, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, C.K.; Kwok, H.H.; Poon, P.Y.; Lau, C.C.; Jiang, Z.H.; Tai, W.C.; Hsiao, W.W.; Mak, N.K.; Yue, P.Y.; Wong, R.N. Ginsenoside compound K induces apoptosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via activation of apoptosis-inducing factor. Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.O.; Seo, C.H.; Cho, H.H.; Oh, S.; Hong, S.P.; Yoo, H.S.; Hong, J.T.; Oh, K.W.; Lee, Y.M. Ginsenoside compound K inhibits angiogenesis via regulation of sphingosine kinase-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kang, K.S.; Yamabe, N.; Nagai, R.; Yokozawa, T. Protective effect of heat-processed American ginseng against diabetic renal damage in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8491–8497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Song, J.H.; Choi, P.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Shin, K.S.; Ham, J.; Kang, K.S. Stimulation of Innate Immune Function by Panax ginseng after Heat Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4652–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, E.; Lim, T.G.; Byun, S. The ginsenoside metabolite compound K inhibits hormone-independent breast cancer through downregulation of cyclin D1. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 46, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Yoo, Y.C.; Matsuzawa, K.; Sato, K.; Saiki, I.; Tono-oka, S.; Samukawa, K.; Azuma, I. Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside-Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside-Rg3, of red ginseng. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Z.; Du, G.J.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, X.D.; Calway, T.; Zhen, Z.; Musch, M.W.; Bissonnette, M.; Chang, E.B.; Yuan, C.S. Ginsenoside compound K, not Rb1, possesses potential chemopreventive activities in human colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.L.; Lv, G.Y.; He, B.C.; Zhang, B.Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.Z.; Du, W.; Yuan, C.S.; He, T.C. Ginseng saponin metabolite 20(S)-protopanaxadiol inhibits tumor growth by targeting multiple cancer signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chi, H.; Kim, D.H.; Ji, G.E. Transformation of ginsenosides Rb2 and Rc from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.H.; Piao, J.Y.; Min, J.W.; Yang, D.U.; Lee, H.N.; Yang, D.C. Bioconversion of ginsenoside rb1 into compound k by Leuconostoc citreum LH1 isolated from kimchi. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, L.H.; Wang, C.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.R.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Isolation and characterization of novel ginsenoside-hydrolyzing glycosidase from Microbacterium esteraromaticum that transforms ginsenoside Rb2 to rare ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2013, 104, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, K.H.; Son, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, D.K. Ginsenoside compound K production from ginseng root extract by a thermostable beta-glycosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.I.; Jeong, C.S.; Chung, D.K.; Choi, H.S. Purification and some properties of a beta-glucosidase from Trichoderma harzianum type C-4. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 2028–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.; Bik, E.M.; DiGiulio, D.B.; Relman, D.A.; Brown, P.O. Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Heilig, H.G.; Molenaar, D.; Kajander, K.; Surakka, A.; Smidt, H.; de Vos, W.M. Development and application of the human intestinal tract chip, a phylogenetic microarray: Analysis of universally conserved phylotypes in the abundant microbiota of young and elderly adults. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, R.; Ross, R.P.; Ryan, C.A.; Hussey, S.; Murphy, B.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. Role of gut microbiota in early infant development. Clin. Med. Pediatr. 2009, 3, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartosch, S.; Fite, A.; Macfarlane, G.T.; McMurdo, M.E. Characterization of bacterial communities in feces from healthy elderly volunteers and hospitalized elderly patients by using real-time PCR and effects of antibiotic treatment on the fecal microbiota. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3575–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringel-Kulka, T.; Cheng, J.; Ringel, Y.; Salojarvi, J.; Carroll, I.; Palva, A.; de Vos, W.M.; Satokari, R. Intestinal microbiota in healthy U.S. young children and adults--a high throughput microarray analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowarah, R.; Verma, A.K.; Agarwal, N.; Singh, P.; Singh, B.R. Selection and characterization of probiotic lactic acid bacteria and its impact on growth, nutrient digestibility, health and antioxidant status in weaned piglets. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masco, L.; Van Hoorde, K.; De Brandt, E.; Swings, J.; Huys, G. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Bifidobacterium strains from humans, animals and probiotic products. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Youn, S.Y.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Identification of the beta-glucosidase gene from Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis and its expression in B. bifidum BGN4. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriantsoanirina, V.; Allano, S.; Butel, M.J.; Aires, J. Tolerance of Bifidobacterium human isolates to bile, acid and oxygen. Anaerobe 2013, 21, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasapathy, K.; Chin, J. Survival and therapeutic potential of probiotic organisms with reference to Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2000, 78, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musende, A.G.; Eberding, A.; Jia, W.; Ramsay, E.; Bally, M.B.; Guns, E.T. Rh2 or its aglycone aPPD in combination with docetaxel for treatment of prostate cancer. Prostate 2010, 70, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Yamabe, N.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Cheon, G.J.; Ham, J.; Kang, K.S. Stereospecific anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 epimers isolated from heat-processed American ginseng on human gastric cancer cell. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Whole-Cell Biocatalysis for Producing Ginsenoside Rd from Rb1 Using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, F.L.; Ma, R.; Jiang, M.; Dong, W.W.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Li, D.; Quan, L.H. Cloning and Characterization of Ginsenoside-Hydrolyzing beta-Glucosidase from Lactobacillus brevis That Transforms Ginsenosides Rb1 and F2 into Ginsenoside Rd and Compound K. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, D.L. Macrophages and inflammatory mediators in chemical toxicity: A battle of forces. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Chawla, A.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature 2013, 496, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S. Phagocytosis: An Immunobiologic Process. Immunity 2016, 44, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Henkel, T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloberas, J.; Valverde-Estrella, L.; Tur, J.; Vico, T.; Celada, A. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and Mitogen Kinase Phosphatase 1: A Critical Interplay in Macrophage Biology. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, E.K.; Shin, Y.W.; Lee, H.U.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, D.H. Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K on NO and prostaglandin E2 biosyntheses of RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, E.H.; Lee, I.A.; Jung, I.H.; Kim, D.H. Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1 activation—The key step of inflammation. Biochem. Pharm. 2011, 82, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, Y.J.; Na, H.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Keum, Y.S. Molecular mechanisms underlying anti-tumor promoting activities of heat-processed Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, S38–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Strains | Survival Rate (%) at pH 2 1 |
|---|---|
| 2.0 | |
| KT13-5 | 100.00 |
| KT9-7 | 100.00 |
| KT11-6 | 100.00 |
| KT11-9 | 99.97 |
| KT11-1 | 99.80 |
| KT13-3 | 99.79 |
| KT9-6 | 99.74 |
| KT11-5 | 99.65 |
| LT19-2 | 99.41 |
| KT11-7 | 98.35 |
| Strains | Shape | Color | Morphology | Catalase | Gram | 16S rRNA Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KT9-7 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT11-1 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT9-6 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT11-5 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT11-6 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT11-7 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT11-9 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT13-3 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| KT13-5 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
| LT19-2 | Round | White | Short rod | - | + | Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Doo, E.-H.; Jeong, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.W.; Huh, C.S.; et al. Enhancing Immunomodulatory Function of Red Ginseng Through Fermentation Using Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis LT 19-2. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071481
Kim JH, Doo E-H, Jeong M, Kim S, Lee Y-Y, Yang J, Lee JS, Kim JH, Lee KW, Huh CS, et al. Enhancing Immunomodulatory Function of Red Ginseng Through Fermentation Using Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis LT 19-2. Nutrients. 2019; 11(7):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071481
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jae Hwan, Eun-Hee Doo, Minju Jeong, Seungil Kim, Yun-Yeol Lee, Jaesik Yang, Ji Su Lee, Jong Hun Kim, Ki Won Lee, Chul Sung Huh, and et al. 2019. "Enhancing Immunomodulatory Function of Red Ginseng Through Fermentation Using Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis LT 19-2" Nutrients 11, no. 7: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071481
APA StyleKim, J. H., Doo, E. -H., Jeong, M., Kim, S., Lee, Y. -Y., Yang, J., Lee, J. S., Kim, J. H., Lee, K. W., Huh, C. S., & Byun, S. (2019). Enhancing Immunomodulatory Function of Red Ginseng Through Fermentation Using Bifidobacterium animalis Subsp. lactis LT 19-2. Nutrients, 11(7), 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11071481