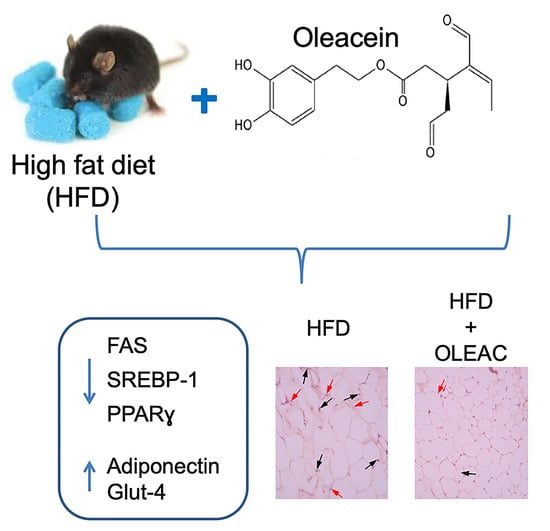
Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Care and Experimental Protocol
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture, Differentiation and Oil Red O Staining
2.4. Protein Extraction, Western Blot Analysis and RT-PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Oleacein on Adipose Tissue In Vivo
3.2. Oleacein Regulates Markers of Adipogenesis In Vivo
3.3. Effects of Oleacein on Glut-4 Expression In Vivo
3.4. Effects of Oleacein in 3T3-L1 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gluvic, Z.; Zaric, B.; Resanovic, I.; Obradovic, M.; Mitrovic, A.; Radak, D.; Isenovic, E.R. Link between Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foti, D.; Chiefari, E.; Fedele, M.; Iuliano, R.; Brunetti, L.; Paonessa, F.; Manfioletti, G.; Barbetti, F.; Brunetti, A.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Lack of the architectural factor HMGA1 causes insulin resistance and diabetes in humans and mice. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, A.; Brunetti, L.; Foti, D.; Accili, D.; Goldfine, I.D. Human diabetes associated with defects in nuclear regulatory proteins for the insulin receptor gene. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahyoun, N.R.; Sankavaram, K. Historical origins of the Mediterranean Diet, Regional Dietary Profiles, and the Development of the Dietary Guidelines. In Mediterranean Diet; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bulotta, S.; Celano, M.; Lepore, S.M.; Montalcini, T.; Pujia, A.; Russo, D. Beneficial effects of the olive oil phenolic components oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol: Focus on protection against cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, L.; Cicerale, S. The Health Benefiting Mechanisms of Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds. Molecules 2016, 21, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorzynik-Debicka, M.; Przychodzen, P.; Cappello, F.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Knap, N.; Wozniak, M.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerale, S.; Lucas, L.; Keast, R. Biological activities of phenolic compounds present in virgin olive oil. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Covas, M.I.; Fitó, M.; Kušar, A.; Pravst, I. Health effects of olive oil polyphenols: Recent advances and possibilities for the use of health claims. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celano, M.; Maggisano, V.; Lepore, S.M.; Russo, D.; Bulotta, S. Secoiridoids of olive and derivatives as potential coadjuvant drugs in cancer: A critical analysis of experimental studies. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 142, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montedoro, G.; Servili, M.; Baldioli, M.; Selvaggini, R.; Miniati, E.; Macchioni, A. Simple and hydrolyzable compounds in virgin olive oil. 3. Spectroscopic characterizations of the secoiridoid derivatives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 2228–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, M.; Kiss, A.K.; Naruszewicz, M. A comparison of antioxidant activities of oleuropein and its dialdehydic derivative from olive oil, oleacein. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindona, G.; Caruso, A.; Cozza, A.; Fiorentini, S.; Lorusso, B.; Marini, E.; Nardi, M.; Procopio, A.; Zicari, S. Anti-inflammatory effect of 3,4-DHPEA-EDA[2-(3,4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl(3S,4E)-4-formyl-3-(2-oxoethyl) hex-4-enoate] on primary human vascular endothelial cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 4006–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipek, A.; Czerwińska, M.E.; Kiss, A.K.; Wrzosek, M.; Naruszewicz, M. Oleacein enhances anti-inflammatory activity of human macrophages by increasing CD163 receptor expression. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Lepore, S.M.; Morittu, V.M.; Arcidiacono, B.; Colica, C.; Procopio, A.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Costa, N.; Mignogna, C.; et al. Effects of Oleacein on High-Fat Diet-Dependent Steatosis, Weight Gain, and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collins, T.J. Image J for microscopy. Biotechniques 2007, 43, S25–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacono, B.; Chiefari, E.; Laria, A.E.; Messineo, S.; Bilotta, F.L.; Britti, D.; Foti, D.P.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Kintscher, U.; Brunetti, A. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-11 is inceased under conditions of insulin resistance. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, A.; Foti, D.; Goldfine, I.D. Identification of unique nuclear regulatory proteins for the insulin receptor gene, which appear during myocyte and adipocyte differentiation. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laria, A.E.; Messineo, S.; Arcidiacono, B.; Varano, M.; Chiefari, E.; Semple, R.K.; Rocha, N.; Russo, D.; Cuda, G.; Gaspari, M.; et al. Secretome Analysis of Hypoxia-Induced 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Uncovers Novel Proteins Potentially Involved in Obesity. Proteomics 2018, 18, e1700260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lombardo, G.E.; Arcidiacono, B.; De Rose, R.F.; Lepore, S.M.; Costa, N.; Montalcini, T.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; De Sarro, G.; Celano, M. Normocaloric Diet Restores Weight Gain and Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Mice. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiritano, S.; Chiefari, E.; Ventura, V.; Arcidiacono, B.; Possidente, K.; Nocera, A.; Nevolo, M.T.; Fedele, M.; Greco, A.; Greco, M.; et al. The HMGA1-IGF-I/IGFBP system: A novel pathway for modulating glucose uptake. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiefari, E.; Nevolo, M.T.; Arcidiacono, B.; Maurizio, E.; Nocera, A.; Iiritano, S.; Sgarra, R.; Possidente, K.; Palmieri, C.; Paonessa, P.; et al. HMGA1 is a novel downstream nuclear target of the insulin receptor signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffin, M.J.; Sul, H.S. Insulin regulation of fatty acid synthase gene transcription: Roles of USF and SREBP-1c. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.; Foti, D.; Paonessa, F.; Chiefari, E.; Palaia, L.; Brunetti, G.; Gulletta, E.; Fusco, A.; Brunetti, A. The insulin receptor: A new anticancer target for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) and thiazolidinedione-PPARγ agonists. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepore, S.M.; Morittu, V.M.; Celano, M.; Trimboli, F.; Oliverio, M.; Procopio, A.; Di Loreto, C.; Damante, G.; Britti, D.; Bulotta, S.; et al. Oral Administration of Oleuropein and Its Semisynthetic Peracetylated Derivative Prevents Hepatic Steatosis, Hyperinsulinemia, and Weight Gain in Mice Fed with High Fat Cafeteria Diet. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 431453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Choi, Y.; Um, S.J.; Yoon, S.K.; Park, T. Oleuropein attenuates hepatic steatosis induced by high-fat diet in mice. J. Hepathol. 2011, 54, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Soong, S.J.; Keum, N.; Park, T. Olive leaf extract attenuates obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice by modulating the expression of molecules involved in adipogenesis and thermogenesis. Evid. Based Complement Alter. Med. 2014, 2014, 971890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Stelt, I.; Hoek-van den Hil, E.F.; Swarts, H.J.; Vervoort, J.J.; Hoving, L.; Skaltsounis, L.; Lemonakis, N.; Andreadou, I.; van Schothorst, E.M.; Keijer, J. Nutraceutical oleuropein supplementation prevents high fat diet-induced adiposity in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.; Park, T. Hepatoprotective effect of oleuropein in mice: Mechanisms uncovered by gene expression profiling. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 950–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, P.; Bonacci, S.; Cariati, L.; Nardi, M.; Oliverio, M.; Procopio, A. Simple and efficient sustainable semi-synthesis of oleacein [2-(3,4-hydroxyphenyl) ethyl (3S,4E)-4-formyl-3-(2-oxoethyl)hex-4-enoate] as potential additive for edible oils. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svobodova, M.; Andreadou, I.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Kopecky, J.; Flachs, P. Oleuropein as an inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Genes Nutr. 2014, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuem, N.; Song, S.J.; Yu, R.; Yun, J.W.; Park, T. Oleuropein attenuates visceral adiposity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice through the modulation of WNT10b- and galanin-mediated signalings. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Reviewof the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiefari, E.; Paonessa, F.; Iiritano, S.; Le Pera, I.; Palmieri, D.; Brunetti, G.; Lupo, A.; Colantuoni, V.; Foti, D.; Gulletta, E.; et al. The cAMP-HMGA1-RBP4 system: A novel biochemical pathway for modulating glucose homeostasis. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lepore, S.M.; Maggisano, V.; Bulotta, S.; Mignogna, C.; Arcidiacono, B.; Procopio, A.; Brunetti, A.; Russo, D.; Celano, M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829
Lepore SM, Maggisano V, Bulotta S, Mignogna C, Arcidiacono B, Procopio A, Brunetti A, Russo D, Celano M. Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829
Chicago/Turabian StyleLepore, Saverio Massimo, Valentina Maggisano, Stefania Bulotta, Chiara Mignogna, Biagio Arcidiacono, Antonio Procopio, Antonio Brunetti, Diego Russo, and Marilena Celano. 2019. "Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829
APA StyleLepore, S. M., Maggisano, V., Bulotta, S., Mignogna, C., Arcidiacono, B., Procopio, A., Brunetti, A., Russo, D., & Celano, M. (2019). Oleacein Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Adiposity and Ameliorates Some Biochemical Parameters of Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Nutrients, 11(8), 1829. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081829