Antitumor, Inhibition of Metastasis and Radiosensitizing Effects of Total Nutrition Formula on Lewis Tumor-Bearing Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Cell Culture
2.2. Mice and Tumor Model
- (1)
- C group: control receiving normal saline;
- (2)
- T group: LLC-inoculated mice received normal saline;
- (3)
- T + TNuF group: LLC-inoculated mice treated with 1 g TNuF administration orally once daily;
- (4)
- T + R group: LLC-inoculated mice treated with a conventional fractionated dose of 3.3 Gy, one fraction per day, three days per week group;
- (5)
- T + R + TNuF group: LLC-inoculated mice treated with the combination of TNuF and radiotherapy.
2.3. Components of the TNuF
2.4. Delivery of Radiation
2.5. Assessment of Tumor Volume and Metastasis
2.6. Blood Sample Preparation and Analyses
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assay
2.8. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
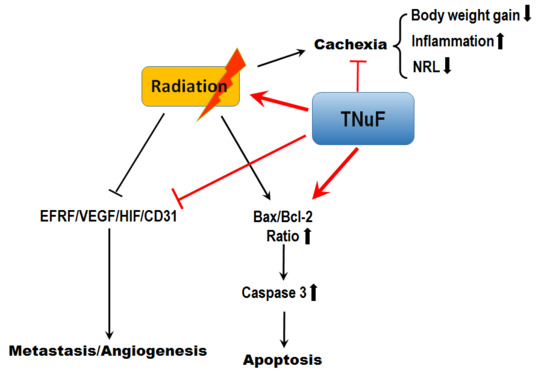
3.1. Effects of TNuF in Combination with Radiotherapy on Spontaneous Apoptosis and Tumor Growth
3.2. Cachectic Symptoms and Hematology Parameters
3.3. Inhibition of Growth and Angiogenesis of C57BL/6JNarl Mice by TNuF
3.4. Inhibition of Lung Metastatic Colonization of LLC Cells in C57BL/6JNarl Mice by TNuF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global epidemiology of lung cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Heymach, J.V.; Lippman, S.M. Lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detillon, D.D.E.M.A.; Veen, E.J. Postoperative outcome after pulmonary surgery for non-small cell lung cancer in elderly patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2018, 105, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, S.G.; Silvestri, G.A. One hundred years of lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, K.R.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Taylor, S.H.; Wei, W.; Raber, M.N.; Lenzi, R.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Metastatic patterns in adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2006, 106, 1624–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, P.K.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Blackhall, F.H.; De Ruysscher, D. Targeted agents in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Clinical developments and rationale for the combination with thoracic radiotherapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Heigener, D.F.; Mok, T.; Soria, J.C.; Rabe, K.F. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent developments. Lancet 2013, 382, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Komaki, R.; Allen, P.; Schea, R.A.; Milas, L. Effectiveness of accelerated radiotherapy for patients with inoperable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and borderline prognostic factors without distant metastasis: A retrospective review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 44, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Rodemann, H.P. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling as a key mediator of tumor cell responsiveness to radiation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waselenko, J.K.; MacVittie, T.J.; Blakely, W.F.; Pesik, N.; Wiley, A.L.; Dickerson, W.E.; Tsu, H.; Confer, D.L.; Coleman, C.N.; Seed, T.; et al. Medical management of the acute radiation syndrome: Recommendations of the strategic national stockpile radiation working group. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, N.; Baumann, M.; Flentjie, M.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.; Senan, S.; Zamboglou, N.; Kosmidis, P. Predictive factors in radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Present status. Lung Cancer 2001, 31, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.; McGibney, C. The impact of three-dimensional radiation on the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2000, 56, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.M.; Hayman, J.A.; Griffith, K.A.; Kalemkerian, G.P.; Arenberg, D.; Lyons, S.; Turrisi, A.; Lichter, A.; Fraass, B.; Eisbruch, A.; et al. Final toxicity results of a radiation-dose escalation study in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Predictors for radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yorke, E.D.; Jackson, A.; Rosenzweig, K.E.; Braban, L.; Leibel, S.A.; Ling, C.C. Correlation of dosimetric factors and radiation pneumonitis for non-small-cell lung cancer patients in a recently completed dose escalation study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 63, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, M.T.; Constine, L.S.; Okunieff, P. Normal tissue tolerance dose metrics for radiation therapy of major organs. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 17, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anscher, M.S. Targeting the TGF-beta1 pathway to prevent normal tissue injury after cancer therapy. Oncologist 2010, 15, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Q. Intracellular calcium promotes radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells through activating Akt signaling. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317695970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, J.; Yahyanejad, S.; Habets, R.; Span, P.; Dubois, L.; Paesmans, K.; Kattenbeld, B.; Cleutjens, J.; Groot, A.J.; Schuurbiers, O.C.J.; et al. High NOTCH activity induces radiation resistance in non small cell lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, F.; Sorg, O.; Granci, V.; Lecumberri, E.; Miralbell, R.; Dupertuis, Y.M.; Pichard, C. Interaction of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with radiation therapy in two different colorectal cancer cell lines. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh-Gupta, V.; Joiner, M.C.; Runyan, L.; Yunker, C.K.; Sarkar, F.H.; Miller, S.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Konski, A.A.; Hillman, G.G. Soy isoflavones augment radiation effect by inhibiting APE1/Ref-1 DNA repair activity in non small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 4, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh-Gupta, V.; Zhang, H.; Banerjee, S.; Kong, D.; Raffoul, J.J.; Sarkar, F.H.; Hillman, G.G. Radiation-induced HIF-1alpha cell survival pathway is inhibited by soy isoflavones in prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Qiu, J.; Wang, D.; Tao, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.U.; Yang, Z.; et al. Traditional chinese medicine curcumin sensitizes human colon cancer to radiation by altering the expression of DNA repair-related genes. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van der Meij, B.S.; Phernambucq, E.C.; Fieten, G.M.; Smit, E.F.; Paul, M.A.; van Leeuwen, P.A.; Oosterhuis, J.W. Nutrition during trimodality treatment in stage III non-small cell lung cancer: Not only important for underweight patients. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravasco, P.; Monteiro-Grillo, I.; Marques Vidal, P.; Camilo, M.E. Impact of nutrition on outcome: A prospective randomized controlled trial in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing radiotherapy. Head Neck 2005, 27, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.S.; Hua, Y.J.; Su, L.; Zhang, H.R.; Lv, W.L.; Chen, X.Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, W.J. Modified-nutrition index is a significant prognostic factor for the overall survival of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients who undergo intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, G.; Maccio, A.; Madeddu, C.; Serpe, R.; Massa, E.; Gramignano, G.; Lusso, M.R.; Curreli, N.; Rinaldi, A. Selenium is effective in inducing lymphocyte progression through cell cycle in cancer patients: Potential mechanisms for its activity. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2004, 4, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rusciani, L.; Proietti, I.; Rusciani, A.; Paradisi, A.; Sbordoni, G.; Alfano, C.; Panunzi, S.; De Gaetano, A.; Lippa, S. Low plasma coenzyme Q10 levels as an independent prognostic factor for melanoma progression. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, D.; Mateo, J.; Templeton, A.J.; Zafeiriou, Z.; Bianchini, D.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Bahl, A.; Shen, L.; Su, Z.; Sartor, O.; et al. Baseline neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with survival and response to treatment with second-line chemotherapy for advanced prostate cancer independent of baseline steroid use. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, W.; Charles, K.A.; Baracos, V.E.; Clarke, S.J. Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio predicts chemotherapy outcomes in patients with advancedcolorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, A.C.; Stewart, F.A.; Vens, C. Strategies to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Oh, E.S.; Park, S.; Han, I.O. Ionising radiation induces changes associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation and increased cell motility of A549 lung epithelial cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, M.; Dubrovska, A.; Linge, A.; Baumann, M. Cancer stem cells: Radioresistance, prediction of radiotherapy outcome and specific targets for combined treatments. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 109, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.F.; Wu, C.T.; Chen, Y.J.; Keng, P.C.; Chen, W.C. Cell killing and radiosensitization by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in lung cancer cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2004, 45, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.F.; Kuo, C.D.; Yang, Y.C.; Lin, C.P.; Tai, H.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.J. Resveratrol enhances radiosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H838 cells accompanied by inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B activation. J. Radiat. Res. 2005, 46, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.C.; Jun, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, I.G. Enhancement of radiation response with combined ganoderma lucidum and duchesneachrysantha extracts in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 21, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.C.; Tseng, S.H. Effects of tetrandrine plus radiation on neuroblastoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3163–3171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.M.; Liu, Y.K.; Wang, L.W.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, P.I.; Tsai, T.H.; Chen, Y.J. The medicinal fungus Antrodia cinnamomea regulates DNA repair and enhances the radiosensitivity of human esophageal cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 6651–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisdale, M.J. Mechanisms of cancer cachexia. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Masoni, M.C.; Fini, M.; Pagani, S.; Giampietro, O.; Carpi, A. Malnutrition, anorexia and cachexia in cancer patients: A mini-review on pathogenesis and treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2013, 67, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, M.; Dijk, F.J.; Hartog, A.; van Norren, K.; Verlaan, S.; van Helvoort, A.; Jaspers, R.T.; Luiking, Y. Reduced dietary intake of micronutrients with antioxidant properties negatively impacts muscle health in aged mice. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeidat, N.; Awidi, A.; Ababneh, N.; Shomaf, M.; Al-Adaily, T.; Jaber, M.; Al-Khateeb, M.; Abbasi, S. Frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in Jordanian lung adenocarcinoma patients at diagnosis. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yuan, Q. Current mechanism of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors and updated therapy strategies in human nonsmall cell lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, C131–C137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wouters, A.; Boeckx, C.; Vermorken, J.B.; Van den Weyngaert, D.; Peeters, M.; Lardon, F. The intriguing interplay between therapies targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor, the hypoxic microenvironment and hypoxia-inducible factors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, T.T.; Sutherland, R.M. Differences in EGF related radiosensitisation of human squamous carcinoma cells with high and low numbers of EGF receptors. Br. J. Cancer 1991, 64, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.Z.; Sun, X.D.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.Z.; Gu, T.; Shao, S.S. Relationship between serum VEGF level and radiosensitivity of patients with nonsmall cell lungcancer among Asians: A meta-analysis. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Pan, S.L.; Wang, J.C.; Kuo, S.H.; Cheng, J.C.; Teng, C.M. Radiation-induced VEGF-C expression and endothelial cell proliferation in lung cancer. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2014, 190, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, G.L.; Zhu, X.H.; Lin, C.Z.; Wang, L.J.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Y.W.; Wang, F.F. 125I seed irradiation induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis by decreasing HIF-1α and VEGF expression in lung carcinoma xenografts. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3075–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Graef, G.L.; Yee, J.A.; Yan, L. Dietary supplementation with high-selenium soy protein reduces pulmonary metastasis of melanoma cells in mice. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Yan, L. Dietary Supplementation with methylseleninic acid inhibits mammary tumorigenesis and metastasis in male MMTV-PyMT mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Lai, H.; Huang, Y.; He, L.; Zheng, W.; Chen, T. RGD peptide-conjugated selenium nanoparticles: Antiangiogenesis by suppressing VEGF-VEGFR2-ERK/AKT pathway. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| NutraWell Powder | Serving Size: 5 Scoops (75 g) |
|---|---|
| Components (units) | Amount Per Serving |
| Total Calories (Kcal) | 298 |
| Total Fat (g) | 8.7 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 0 |
| Sodium (mg) | 350 |
| Total Carbohydrate (g) | 38 |
| Protein (g) | 17 |
| Vitamin A | |
| Retinyl Acetate (IU) | 1167 |
| β-carotene (IU) | 1000 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 100 |
| Vitamin D (IU) | 150 |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 10 |
| Vitamin K (mcg) | 30 |
| Vitamin B1 (mg) | 1.2 |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 1.2 |
| Niacin (mg) | 12 |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 1.3 |
| Folate (mcg) | 100 |
| Vitamin B12 (mcg) | 1.5 |
| Biotin (mcg) | 50 |
| Pantothenic Acid (mg) | 3 |
| Choline (mg) | 250 |
| Calcium (mg) | 350 |
| Iron (mg) | 4 |
| Phosphorous (mg) | 200 |
| Iodine (mcg) | 40 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 100 |
| Zinc (mg) | 6 |
| Selenium (mcg) | 65 |
| Copper (mcg) | 250 |
| Manganese (mg) | 1.5 |
| Chromium (mcg) | 90 |
| Molybdenum (mcg) | 56.3 |
| Potassium (mg) | 550 |
| Coenzyme Q10 (mg) | 20 |
| Treatment | Cachectic Parameters | Hematology Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin (g/dL) | TNF-α (pg/mL) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | RBC (1012/L) | WBC (103/mm3) | Lym (%) | NLR | |
| Con | 2.88 ± 0.07 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 7.39 ± 1.63 | 9.20 ± 0.32 | 82.10 ± 0.99 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| T | 2.57 ± 0.06 a | 2.50 ± 1.31 a | 20.05 ± 8.13 a | 7.52 ± 1.27 | 3.64 ± 1.27 a | 63.24 ± 1.67 a | 1.17 ± 0.05 a |
| T + TNuF | 3.18 ± 0.05 | 0.63 ± 0.49 b | 15.87 ± 9.09 b | 7.18 ± 1.28 | 5.11 ± 0.60 | 73.26 ± 0.85 b | 0.93 ± 0.00 b |
| T + R | 2.75 ± 0.06 b | 1.42 ± 0.73 b | 6.16 ± 1.23 b | 7.20 ± 1.02 | 4.42 ± 0.76 | 67.72 ± 0.61 b | 0.95 ± 0.02 b |
| T + R + TNuF | 2.85 ± 0.06 | 0.40 ± 0.17 b | 10.87 ± 4.17 b | 8.19 ± 0.66 | 5.87 ± 0.64 | 75.21 ± 0.11 b | 0.99 ± 0.01 b |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-M.; Chan, Y.-L.; Wu, T.-H.; Li, T.-L.; Hsia, S.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-J. Antitumor, Inhibition of Metastasis and Radiosensitizing Effects of Total Nutrition Formula on Lewis Tumor-Bearing Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081944
Liu Y-M, Chan Y-L, Wu T-H, Li T-L, Hsia S, Chiu Y-H, Wu C-J. Antitumor, Inhibition of Metastasis and Radiosensitizing Effects of Total Nutrition Formula on Lewis Tumor-Bearing Mice. Nutrients. 2019; 11(8):1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081944
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu-Ming, Yi-Lin Chan, Tsung-Han Wu, Tsung-Lin Li, Simon Hsia, Yi-Han Chiu, and Chang-Jer Wu. 2019. "Antitumor, Inhibition of Metastasis and Radiosensitizing Effects of Total Nutrition Formula on Lewis Tumor-Bearing Mice" Nutrients 11, no. 8: 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081944
APA StyleLiu, Y. -M., Chan, Y. -L., Wu, T. -H., Li, T. -L., Hsia, S., Chiu, Y. -H., & Wu, C. -J. (2019). Antitumor, Inhibition of Metastasis and Radiosensitizing Effects of Total Nutrition Formula on Lewis Tumor-Bearing Mice. Nutrients, 11(8), 1944. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081944