The Antiviral Properties of Human Milk: A Multitude of Defence Tools from Mother Nature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Specific Antiviral Properties
3. Aspecific Antiviral Properties: The Bioactive Compounds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarke, N.; May, J. Effect of antimicrobial factors in human milk on rhinoviruses and milk-borne cytomegalovirus in vitro. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Labbok, M.H.; Clark, D.; Goldman, A.S. Breastfeeding: Maintaining an irreplaceable immunological resource. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grulee, C.G.; Sanford, H.N.; Schwartz, H. Breast and artificially fed infants. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1935, 104, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, G.; Marzollo, R.; Cortinovis, S.; Fonte, C.; Gasparoni, A. Antiinfective Properties of Human Milk. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 1801S–1806S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ip, S.; Chung, M.; Raman, G.; Chew, P.; Magula, N.; Devine, D.; Trikalinos, T.; Lau, J. Breastfeeding and maternal and infant health outcomes in developed countries. Évid. Rep. Assess. 2007, 153, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Verduci, E.; Giannì, M.; Vizzari, G.; Vizzuso, S.; Cerasani, J.; Mosca, F.; Zuccotti, G. The Triad Mother-Breast Milk-Infant as Predictor of Future Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binns, C.; Lee, M.; Low, W.Y. The Long-Term Public Health Benefits of Breastfeeding. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2016, 28, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oddy, W.H. Breastfeeding protects against illness and infection in infants and children: A review of the evidence. Breastfeed. Rev. 2001, 9, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Morozov, V.; Hansman, G.; Hanisch, F.G.; Schroten, H.; Kunz, C. Human Milk Oligosaccharides as Promising Antivirals. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1700679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Newburg, D.S. Human Milk Glycoproteins Protect Infants Against Human Pathogens. Breastfeed. Med. 2013, 8, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adkins, B.; Leclerc, C.; Marshall-Clarke, S. Neonatal adaptive immunity comes of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorbach, C.; Capecchi, M.R.; Penninger, J.M. Evolution of the mammary gland from the innate immune system? BioEssays 2006, 28, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrick, B.M.; Yao, X.-D.; Nasser, L.; Roozrogousheh, A.; Rosenthal, K.L. Breastfeeding Behaviors and the Innate Immune System of Human Milk: Working Together to Protect Infants against Inflammation, HIV-1, and Other Infections. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliff, P.J.; Piwoz, E.G.; Tavengwa, N.V.; Zunguza, C.D.; Marinda, E.T.; Nathoo, K.J.; Moulton, L.H.; Ward, B.J.; Humphrey, J.H. Early exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of postnatal HIV-1 transmission and increases HIV-free survival. AIDS 2005, 19, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donalisio, M.; Rittà, M.; Tonetto, P.; Civra, A.; Coscia, A.; Giribaldi, M.; Cavallarin, L.; Moro, G.E.; Bertino, E.; Lembo, D. Anti-Cytomegalovirus Activity in Human Milk and Colostrum From Mothers of Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, S.; Pannaraj, P.S. Beyond the Bacterial Microbiome: Virome of Human Milk and Effects on the Developing Infant. Milk Mucosal Immun. Microbiome Impact Neonate 2020, 94, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G.; Bauer, I.K.; Droit, L.; Ndao, I.M.; Warner, B.B.; Tarr, P.I.; Wang, D.; Holtz, L.R. Early life dynamics of the human gut virome and bacterial microbiome in infants. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Mattei, L.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Bittinger, K.; Kessler, L.R.; Wu, G.D.; Baldassano, R.N.; DeRusso, P.; et al. The stepwise assembly of the neonatal virome is modulated by breastfeeding. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 581, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, S.; Lugli, G.A.; Mancabelli, L.; Armanini, F.; Turroni, F.; James, K.; Ferretti, P.; Gorfer, V.; Ferrario, C.; Milani, C.; et al. Maternal inheritance of bifidobacterial communities and bifidophages in infants through vertical transmission. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francese, R.; Civra, A.; Donalisio, M.; Volpi, N.; Capitani, F.; Sottemano, S.; Tonetto, P.; Coscia, A.; Maiocco, G.; Moro, G.E.; et al. Anti-Zika virus and anti-Usutu virus activity of human milk and its components. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favara, D.M.; Ceron-Gutierrez, M.L.; Carnell, G.W.; Heeney, J.L.; Corrie, P.; Doffinger, R. Detection of breastmilk antibodies targeting SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid, spike and receptor-binding-domain antigens. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2728–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouar, A. Maternal Leukocytes and Infant Immune Programming during Breastfeeding. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labayo, H.K.M.; Pajuelo, M.J.; Tohma, K.; Ford-Siltz, L.A.; Gilman, R.H.; Cabrera, L.; Mayta, H.; Sanchez, G.J.; Cornejo, A.T.; Bern, C.; et al. Norovirus-specific immunoglobulin A in breast milk for protection against norovirus-associated diarrhea among infants. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 27, 100561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne-Castagna, V.P.; Mills, D.A.; Lönnerdal, B. Effects of Milk Secretory Immunoglobulin A on the Commensal Microbiota. Milk Mucosal Immun. Microbiome Impact Neonate 2020, 94, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishna, K.P.; Macadangdang, B.R.; Rogers, M.B.; Tometich, J.T.; Firek, B.A.; Baker, R.; Ji, J.; Burr, A.H.P.; Ma, C.; Good, M.; et al. Maternal IgA protects against the development of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donalisio, M.; Cirrincione, S.; Rittà, M.; Lamberti, C.; Civra, A.; Francese, R.; Tonetto, P.; Sottemano, S.; Manfredi, M.; Lorenzato, A.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Human Preterm Colostrum Inhibit Infection by Human Cytomegalovirus In Vitro. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gila-Diaz, A.; Arribas, S.M.; Algara, A.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; López de Pablo, Á.L.; De Pipaón, M.S.; Ramiro-Cortijo, D. A Review of Bioactive Factors in Human Breastmilk: A Focus on Prematurity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaacs, C.E.; Kashyap, S.; Heird, W.C.; Thormar, H. Antiviral and antibacterial lipids in human milk and infant formula feeds. Arch. Dis. Child. 1990, 65, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gardner, A.S.; Rahman, I.A.; Lai, C.T.; Hepworth, A.; Trengove, N.; Hartmann, P.E.; Geddes, D.T. Changes in Fatty Acid Composition of Human Milk in Response to Cold-Like Symptoms in the Lactating Mother and Infant. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Arachidonic acid and other unsaturated fatty acids and some of their metabolites function as endogenous antimicrobial molecules: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Can Bioactive Lipids Inactivate Coronavirus (COVID-19)? Arch. Med Res. 2020, 51, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, B.; Piët, M.P.; Prince, A.M.; Edwards, C.A.; Lippin, A.; Walakovits, L.A. Inactivation of Lipid-Enveloped Viruses in Labile Blood Derivatives by Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Vox Sang. 1988, 54, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civra, A.; Leoni, V.; Caccia, C.; Sottemano, S.; Tonetto, P.; Coscia, A.; Peila, C.; Moro, G.E.; Gaglioti, P.; Bertino, E.; et al. Antiviral oxysterols are present in human milk at diverse stages of lactation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 193, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Wan, L.; Jiang, M.; Chu, Y. Lactoferrin for the treatment of COVID-19 (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Ng, T.B.; Sun, W.-Z. Lactoferrin as potential preventative and adjunct treatment for COVID-19. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campione, E.; Cosio, T.; Rosa, L.; Lanna, C.; Di Girolamo, S.; Gaziano, R.; Valenti, P.; Bianchi, L. Lactoferrin as Protective Natural Barrier of Respiratory and Intestinal Mucosa against Coronavirus Infection and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, H.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Zaim, A.; Ibrahim, W.H. The role of iron in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 and possible treatment with lactoferrin and other iron chelators. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kell, D.B.; Heyden, E.L.; Pretorius, E. The Biology of Lactoferrin, an Iron-Binding Protein That Can Help Defend Against Viruses and Bacteria. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, R.J.; Stamper, L.; Ohashi, T.; Eudailey, J.A.; Go, E.P.; Jaeger, F.H.; Itell, H.L.; Watts, B.E.; Fouda, G.G.; Erickson, H.P.; et al. Determinants of Tenascin-C and HIV-1 envelope binding and neutralization. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, G.G.; Jaeger, F.H.; Amos, J.D.; Ho, C.; Kunz, E.L.; Anasti, K.; Stamper, L.W.; Liebl, B.E.; Barbas, K.H.; Ohashi, T.; et al. Tenascin-C is an innate broad-spectrum, HIV-1-neutralizing protein in breast milk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18220–18225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mall, A.S.; Habte, H.; Mthembu, Y.; Peacocke, J.; De Beer, C. Mucus and Mucins: Do they have a role in the inhibition of the human immunodeficiency virus? Virol. J. 2017, 14, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morniroli, D.; Giannì, M.L.; Consales, A.; Pietrasanta, C.; Mosca, F. Human Sialome and Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic: An Understated Correlation? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Quental, O.B.; França, E.L.; Honório-França, A.C.; Morais, T.C.; Daboin, B.E.G.; Bezerra, I.M.P.; Komninakis, S.V.; De Abreu, L.C. Zika Virus Alters the Viscosity and Cytokines Profile in Human Colostrum. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 9020519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Bie, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zou, L.; Lin, S.-H.; Zhou, X. Omics study reveals abnormal alterations of breastmilk proteins and metabolites in puerperant women with COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, C.; Krogstad, P.; Bertrand, K.; Contreras, D.; Tobin, N.H.; Bode, L.; Aldrovandi, G. Evaluation for SARS-CoV-2 in Breast Milk From 18 Infected Women. JAMA 2020, 324, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogra, P.L.; Walker, W.A.; Lönnerdal, B. Milk, Mucosal Immunity and the Microbiome: Impact on the Neonate. Nestlé Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2020, 94, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.-S.; Wang, Y.; Shane, A.L.; Nguyen, T.; Ray, P.; Dennehy, P.; Baek, L.J.; Parashar, U.; Glass, R.I.; Jiang, B. Inhibitory Effect of Breast Milk on Infectivity of Live Oral Rotavirus Vaccines. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2010, 29, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramani, S.; Stewart, C.J.; Laucirica, D.R.; Ajami, N.J.; Robertson, B.; Autran, C.A.; Shinge, D.; Rani, S.; Anandan, S.; Hu, L.; et al. Human milk oligosaccharides, milk microbiome and infant gut microbiome modulate neonatal rotavirus infection. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
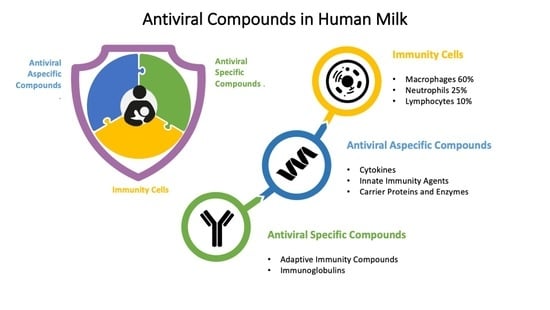
| Immunity Cells | Macrophages 60%, Neutrophils 25%, Lymphocytes 10% |
| Antiviral Specific Compounds | |
| Adaptive Immunity Compounds | Immunoglobulins sIgA, IgA, IgG, IgM, IgE, IgD |
| Antiviral Nonspecific Compounds | |
| Cytokines | IL-1b, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-13, IL-16, IL-18, IL-10, IFNg, TNFa, G-CSF, M-CSF, GM-CSF, TGFb1 and -2, sCD14 |
| Innate Immunity Agents | Complement, Chemotactic Factors, Interferon, α-Fetoprotein, Mannose Binding Lectin, β-Defensin-1 Antiadherence substances: Oligosaccharides, Mucins, Lactadherin, Glycolipids and Glycosaminoglycans, K-Casein Milk Fat Globule Antiviral Factors: Fatty acids and Monoglycerides |
| Carrier Proteins and Enzymes | Lactoferrin, Transferrin, Vitamin B-12 binding protein, Steroid binding protein, Leukocyte enzymes, Antiproteases, Platelet-Activating-Factor, Nucleotides, Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morniroli, D.; Consales, A.; Crippa, B.L.; Vizzari, G.; Ceroni, F.; Cerasani, J.; Colombo, L.; Mosca, F.; Giannì, M.L. The Antiviral Properties of Human Milk: A Multitude of Defence Tools from Mother Nature. Nutrients 2021, 13, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020694
Morniroli D, Consales A, Crippa BL, Vizzari G, Ceroni F, Cerasani J, Colombo L, Mosca F, Giannì ML. The Antiviral Properties of Human Milk: A Multitude of Defence Tools from Mother Nature. Nutrients. 2021; 13(2):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020694
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorniroli, Daniela, Alessandra Consales, Beatrice Letizia Crippa, Giulia Vizzari, Federica Ceroni, Jacopo Cerasani, Lorenzo Colombo, Fabio Mosca, and Maria Lorella Giannì. 2021. "The Antiviral Properties of Human Milk: A Multitude of Defence Tools from Mother Nature" Nutrients 13, no. 2: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020694
APA StyleMorniroli, D., Consales, A., Crippa, B. L., Vizzari, G., Ceroni, F., Cerasani, J., Colombo, L., Mosca, F., & Giannì, M. L. (2021). The Antiviral Properties of Human Milk: A Multitude of Defence Tools from Mother Nature. Nutrients, 13(2), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020694