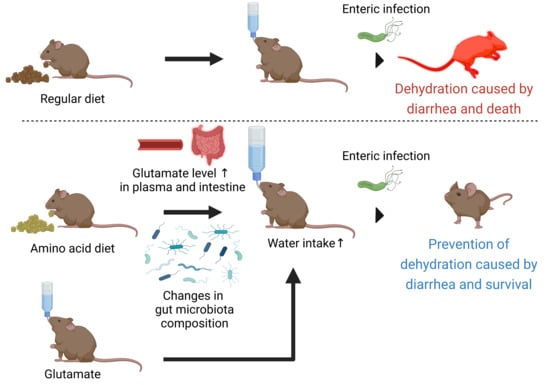
Amino Acid-Based Diet Prevents Lethal Infectious Diarrhea by Maintaining Body Water Balance in a Murine Citrobacter rodentium Infection Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. C. rodentium Infection
2.3. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining of the Colonic Tissue
2.4. Glutamate Administration
2.5. Amino Acid Concentration
2.6. Fecal Lipocalin-2
2.7. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
2.8. Colonic Epithelial Barrier Permeability
2.9. Plasma IgA ELISA
2.10. Fecal Pellet DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. AD Protects the Mice from Lethal C. rodentium Infection
3.2. AD neither Promotes Pathogen Clearance nor Suppresses Intestinal Damage
3.3. AD Promotes Water Intake, Thereby Protecting from Lethal Infectious Diarrhea
3.4. AD Changes Plasma and Fecal Amino Acid Levels
3.5. Oral Glutamate Treatment Protects Mice from Lethal Diarrheal C. rodentium Infection
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotloff, K.L.; Nataro, J.P.; Blackwelder, W.C.; Nasrin, D.; Farag, T.H.; Panchalingam, S.; Wu, Y.; Sow, S.O.; Sur, D.; Breiman, R.F.; et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet 2013, 382, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kabir, F.; Manneh, J.; Lertsethtakarn, P.; Begum, S.; Gratz, J.; Becker, S.M.; Operario, D.J.; Taniuchi, M.; Janaki, L.; et al. Development and assessment of molecular diagnostic tests for 15 enteropathogens causing childhood diarrhoea: A multicentre study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Babji, S.; Bodhidatta, L.; Gratz, J.; Haque, R.; Havt, A.; McCormick, B.J.; McGrath, M.; Olortegui, M.P.; Samie, A.; et al. Pathogen-specific burdens of community diarrhoea in developing countries: A multisite birth cohort study (MAL-ED). Lancet Glob. Health 2015, 3, e564–e575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugboko, H.U.; Nwinyi, O.C.; Oranusi, S.U.; Oyewale, J.O. Childhood diarrhoeal diseases in developing countries. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Linscott, A.J. Practical guidance for clinical microbiology laboratories: Diagnosis of bacterial gastroenteritis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 3–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarr, G.A.M.; Chui, L.; Lee, B.E.; Pang, X.L.; Ali, S.; Nettel-Aguirre, A.; Vanderkooi, O.G.; Berenger, B.M.; Dickinson, J.; Tarr, P.I.; et al. Performance of stool-testing recommendations for acute gastroenteritis when used to identify children with 9 potential bacterial enteropathogens. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxen, M.A.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartland, E.L.; Leong, J.M. Enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic E. coli: Ecology, pathogenesis, and evolution. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 142–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaytan, M.O.; Martinez-Santos, V.I.; Soto, E.; Gonzalez-Pedrajo, B. Type three secretion system in attaching and effacing pathogens. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, J.W.; Keeney, K.M.; Crepin, V.F.; Rathinam, V.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Finlay, B.B.; Frankel, G. Citrobacter rodentium: Infection, inflammation and the microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullineaux-Sanders, C.; Sanchez-Garrido, J.; Hopkins, E.G.D.; Shenoy, A.R.; Barry, R.; Frankel, G. Citrobacter rodentium-host-microbiota interactions: Immunity, bioenergetics and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthold, S.W.; Coleman, G.L.; Jacoby, R.O.; Livestone, E.M.; Jonas, A.M. Transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Vet. Pathol. 1978, 15, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mundy, R.; MacDonald, T.T.; Dougan, G.; Frankel, G.; Wiles, S. Citrobacter rodentium of mice and man. Cell Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthold, S.W.; Osbaldiston, G.W.; Jonas, A.M. Dietary, bacterial, and host genetic interactions in the pathogenesis of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1977, 27, 938–945. [Google Scholar]
- Borenshtein, D.; Fry, R.C.; Groff, E.B.; Nambiar, P.R.; Carey, V.J.; Fox, J.G.; Schauer, D.B. Diarrhea as a cause of mortality in a mouse model of infectious colitis. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borenshtein, D.; Nambiar, P.R.; Groff, E.B.; Fox, J.G.; Schauer, D.B. Development of fatal colitis in FVB mice infected with Citrobacter rodentium. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 3271–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.H. Diarrhea and malnutrition. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 328S–332S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petri, W.A., Jr.; Miller, M.; Binder, H.J.; Levine, M.M.; Dillingham, R.; Guerrant, R.L. Enteric infections, diarrhea, and their impact on function and development. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, Z.A.; Hendricks, K.M. Nutritional management of persistent diarrhea in childhood: A perspective from the developing world. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1996, 22, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mattos, A.P.; Ribeiro, T.C.; Mendes, P.S.; Valois, S.S.; Mendes, C.M.; Ribeiro, H.C., Jr. Comparison of yogurt, soybean, casein, and amino acid-based diets in children with persistent diarrhea. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Functions and signaling pathways of amino acids in intestinal inflammation. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9171905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, C.A. Therapeutic potential of amino acids in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Xiong, X.; Tan, B.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Fang, J. Dietary chitosan supplementation increases microbial diversity and attenuates the severity of citrobacter rodentium infection in mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9236196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, R.; Piao, M.; Song, Y. Dietary quercetin increases colonic microbial diversity and attenuates colitis severity in citrobacter rodentium-infected mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, A.G.; Ellermann, M.; Abbott, W.; Sperandio, V. Diet-derived galacturonic acid regulates virulence and intestinal colonization in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli and Citrobacter rodentium. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, T.; Kennelly, J.P.; Jacobs, R.L.; Willing, B.P. Insufficient dietary choline aggravates disease severity in a mouse model of Citrobacter rodentium-induced colitis. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maattanen, P.; Lurz, E.; Botts, S.R.; Wu, R.Y.; Yeung, C.W.; Li, B.; Abiff, S.; Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Lepp, D.; Power, K.A.; et al. Ground flaxseed reverses protection of a reduced-fat diet against Citrobacter rodentium-induced colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G788–G798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.G.; Sakamoto, K.; Seo, S.U.; Pickard, J.M.; Gillilland, M.G., 3rd; Pudlo, N.A.; Hoostal, M.; Li, X.; Wang, T.D.; Feehley, T.; et al. Neonatal acquisition of clostridia species protects against colonization by bacterial pathogens. Science 2017, 356, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armenta, J.M.; Cortes, D.F.; Pisciotta, J.M.; Shuman, J.L.; Blakeslee, K.; Rasoloson, D.; Ogunbiyi, O.; Sullivan, D.J., Jr.; Shulaev, V. Sensitive and rapid method for amino acid quantitation in malaria biological samples using AccQ.Tag ultra performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-MS/MS with multiple reaction monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chassaing, B.; Srinivasan, G.; Delgado, M.A.; Young, A.N.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Fecal lipocalin 2, a sensitive and broadly dynamic non-invasive biomarker for intestinal inflammation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pruesse, E.; Quast, C.; Knittel, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Ludwig, W.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. SILVA: A comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7188–7196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Peddada, S.; Amir, A.; Bittinger, K.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozupone, C.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Birmingham, A.; et al. Normalization and microbial differential abundance strategies depend upon data characteristics. Microbiome 2017, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papapietro, O.; Teatero, S.; Thanabalasuriar, A.; Yuki, K.E.; Diez, E.; Zhu, L.; Kang, E.; Dhillon, S.; Muise, A.M.; Durocher, Y.; et al. R-spondin 2 signalling mediates susceptibility to fatal infectious diarrhoea. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schweinfest, C.W.; Spyropoulos, D.D.; Henderson, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; Chapman, J.M.; Barone, S.; Worrell, R.T.; Wang, Z.; Soleimani, M. Slc26a3 (dra)-deficient mice display chloride-losing diarrhea, enhanced colonic proliferation, and distinct up-regulation of ion transporters in the colon. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37962–37971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerutti, A.; Rescigno, M. The biology of intestinal immunoglobulin A responses. Immunity 2008, 28, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilmore, J.R.; Gaudette, B.T.; Atria, D.G.; Hashemi, T.; Jones, D.D.; Gardner, C.A.; Cole, S.D.; Misic, A.M.; Beiting, D.P.; Allman, D. Commensal microbes induce serum IgA responses that protect against polymicrobial sepsis. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitkanen, H.T.; Oja, S.S.; Kemppainen, K.; Seppa, J.M.; Mero, A.A. Serum amino acid concentrations in aging men and women. Amino Acids 2003, 24, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Corsetti, G.; Flati, V.; Pasini, E.; Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Marzetti, E.; Dioguardi, F.S. Influence of Diets with varying essential/nonessential amino acid ratios on mouse lifespan. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neis, E.P.; Dejong, C.H.; Rensen, S.S. The role of microbial amino acid metabolism in host metabolism. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2930–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Brown, M.A.; Qiao, S. Dietary protein and gut microbiota composition and function. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Miranda, V.; Soto-Montenegro, M.L.; Uranga-Ocio, J.A.; Vera, G.; Herradon, E.; Gonzalez, C.; Blas, C.; Martinez-Villaluenga, M.; Lopez-Perez, A.E.; Desco, M.; et al. Effects of chronic dietary exposure to monosodium glutamate on feeding behavior, adiposity, gastrointestinal motility, and cardiovascular function in healthy adult rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2015, 27, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, J.M.; Keku, E.O.; Quinn, J.; Woosely, J.; Lecce, J.G. l-glutamine stimulates jejunal sodium and chloride absorption in pig rotavirus enteritis. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordoff, M.G.; Bachmanov, A.A.; Reed, D.R. Forty mouse strain survey of water and sodium intake. Physiol. Behav. 2007, 91, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Germano, C.M.; Migliorini, R.H. Dietetic supplementation with branched chain amino acids attenuates the severity of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Acta Diabetol. Lat. 1988, 25, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukano, K.; Inoue, H.; Suzuki, K. Increase in branched-chain amino acids due to acidemia in neonatal calves with diarrhoea. Vet. Rec. Open 2017, 4, e000234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawase, T.; Nagasawa, M.; Ikeda, H.; Yasuo, S.; Koga, Y.; Furuse, M. Gut microbiota of mice putatively modifies amino acid metabolism in the host brain. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitt, D.D.; Demoss, R.D. Effect of microflora on the free amino acid distribution in various regions of the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 30, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, C.; Macfarlane, G.T. Influence of pH, nutrient availability, and growth rate on amine production by Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium perfringens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 2894–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.L.; Wu, G.; Zhu, W.Y. Amino acid metabolism in intestinal bacteria: Links between gut ecology and host health. Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 1768–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davila, A.M.; Blachier, F.; Gotteland, M.; Andriamihaja, M.; Benetti, P.H.; Sanz, Y.; Tome, D. Re-print of “Intestinal luminal nitrogen metabolism: Role of the gut microbiota and consequences for the host”. Pharmacol. Res. 2013, 69, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, F.; Davids, M.; Schwarz, J.; Muller, M.; Tome, D.; Schaap, P.; Hooiveld, G.; Smidt, H.; Kleerebezem, M. Metatranscriptome analysis of the microbial fermentation of dietary milk proteins in the murine gut. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Diet | PD | AD | FD | RD * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g% | g% | g% | g% | |
| Protein | 20 | 18 | 26.2 | 24.8 ** |
| Carbohydrate | 64 | 66 | 26.3 | 54.55 *** |
| Fat | 7 | 7 | 34.9 | 4.6 **** |
| (kcal/gm) | 4 | 4 | 5.2 | 3.4 |
| Ingredient | g | g | g | g |
| Casein | 200 | 0 | 258.4 | - |
| L-Cystine | 3 | 4.3 | 3.9 | - |
| L-Arginine | - | 6.1 | - | - |
| L-Histidine-HCl-H2O | - | 4.7 | - | - |
| L-Isoleucine | - | 7.7 | - | - |
| L-Leucine | - | 16.0 | - | - |
| L-Lysine-HCl | - | 13.4 | - | - |
| L-Methionine | - | 5.2 | - | - |
| L-Phenylalanine | - | 8.5 | - | - |
| L-Threonine | - | 7.3 | - | - |
| L-Tryptophan | - | 2.1 | - | - |
| L-Valine | - | 9.4 | - | - |
| L-Alanine | - | 5.2 | - | - |
| L-Asparagine-H2O | - | 6.8 | - | - |
| L-Aspartate | - | 5.5 | - | - |
| L-Glutamic Acid | - | 22.0 | - | - |
| L-Glutamine | - | 16.7 | - | - |
| Glycine | - | 3 | - | - |
| L-Proline | - | 18.1 | - | - |
| L-Serine | - | 10.1 | - | - |
| L-Tyrosine | - | 9.3 | - | - |
| Corn Starch | 397.5 | 403.4 | 0 | - |
| Maltodextrin | 132 | 134 | 162 | - |
| Sucrose | 100 | 108.7 | 88.9 | - |
| Cellulose, BW200 | 50 | 51 | 65 | - |
| Corn Oil | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Soybean Oil | 70 | 71 | 32 | - |
| Lard | 0 | 0 | 317 | - |
| t-butylhydroquinone | 0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Vitamins | mg | mg | mg | mg |
| Vitamin A | 6.6 | 6.7 | 8.5 | 8.1 |
| Vitamin B1 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 6.8 | 18 |
| Vitamin B2 | 6 | 6.1 | 7.8 | 14 |
| Vitamin B6 | 5.8 | 5.9 | 7.5 | 13 |
| Vitamin B12 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0 |
| Vitamin D3 | 10 | 10.1 | 12.9 | 0.1 |
| Vitamin E | 131.7 | 133.7 | 113.5 | 71 |
| Pantothenic acid | 13.5 | 13.7 | 17.4 | 30 |
| Biotin | 20 | 2 | 2.6 | 0.5 |
| Folic Acid | 2 | 6.7 | 8.5 | 8.1 |
| Total (g) | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 |
| Genes | Primer Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| Ctnnb1 | Forward | ATG GAG CCG GAC AGA AAA GC |
| Reverse | TGG GAG GTG TCA ACA TCT TCT T | |
| Mmp7 | Forward | GCA TTT CCT TGA GGT TGT CC |
| Reverse | CAC ATC AGT GGG AAC AGG C | |
| Il1b | Forward | GAA ATG CCA CCT TTT GAC AGT G |
| Reverse | TGG ATG CTC TCA TCA GGA CAG | |
| Il6 | Forward | TGA TGC ACT TGC AGA AAA CA |
| Reverse | ACC AGA GGA AAT TTT CAA TAG GC | |
| Il17a | Forward | TCAGCGTGTCCAAACACTGAG |
| Reverse | CGCCAAGGGAGTTAAAGACTT | |
| Il22 | Forward | GTG CTC AAC TTC ACC CTG GA |
| Reverse | TGG ATG TTC TGG TCG TCA CC | |
| Slc26a3 | Forward | AACATCCCTCCAGCCTACG |
| Reverse | TGGACCCACAGATATGTGTCT | |
| Rpl19 | Forward | TAC CGG GAA TCC AAG AAG ATT GA |
| Reverse | AGG ATG CGC TTG TTT TTG AAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimizuka, T.; Seki, N.; Yamaguchi, G.; Akiyama, M.; Higashi, S.; Hase, K.; Kim, Y.-G. Amino Acid-Based Diet Prevents Lethal Infectious Diarrhea by Maintaining Body Water Balance in a Murine Citrobacter rodentium Infection Model. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061896
Kimizuka T, Seki N, Yamaguchi G, Akiyama M, Higashi S, Hase K, Kim Y-G. Amino Acid-Based Diet Prevents Lethal Infectious Diarrhea by Maintaining Body Water Balance in a Murine Citrobacter rodentium Infection Model. Nutrients. 2021; 13(6):1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061896
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimizuka, Tatsuki, Natsumi Seki, Genki Yamaguchi, Masahiro Akiyama, Seiichiro Higashi, Koji Hase, and Yun-Gi Kim. 2021. "Amino Acid-Based Diet Prevents Lethal Infectious Diarrhea by Maintaining Body Water Balance in a Murine Citrobacter rodentium Infection Model" Nutrients 13, no. 6: 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061896
APA StyleKimizuka, T., Seki, N., Yamaguchi, G., Akiyama, M., Higashi, S., Hase, K., & Kim, Y. -G. (2021). Amino Acid-Based Diet Prevents Lethal Infectious Diarrhea by Maintaining Body Water Balance in a Murine Citrobacter rodentium Infection Model. Nutrients, 13(6), 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061896