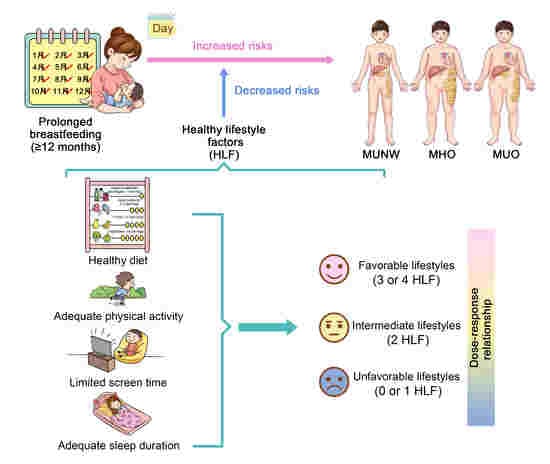
Associations between Breastfeeding Duration and Obesity Phenotypes and the Offsetting Effect of a Healthy Lifestyle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection and Questionnaire Survey
2.2.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2.2. Blood Sample Collection and Detection
2.2.3. Questionnaire Survey
2.3. Definition and Categorization of Indicators
2.3.1. Obesity Phenotypes
2.3.2. Breastfeeding Duration
2.3.3. Healthy Lifestyle
2.3.4. Confounding Variables
2.4. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Associations between Breastfeeding Duration and Obesity Phenotypes
3.3. The Offsetting Effect of Healthy Lifestyle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mokdad, A.H.; Ford, E.S.; Bowman, B.A.; Dietz, W.H.; Vinicor, F.; Bales, V.S.; Marks, J.S. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003, 289, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoy, D.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Wareham, N.; Luben, R.; Welch, A.; Bingham, S.; Buchan, I.; Day, N.; Khaw, K. Body fat distribution and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women in the European Prospective Investigation Into Cancer and Nutrition in Norfolk cohort: A population-based prospective study. Circulation 2007, 116, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bijlsma, J.W.; Berenbaum, F.; Lafeber, F.P. Osteoarthritis: An update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet 2011, 377, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sorić, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.-P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, C.K.; Zinman, B.; Retnakaran, R. Are metabolically healthy overweight and obesity benign conditions? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekharzadeh, A.; Asghari, G.; Serahati, S.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Azizi, A.; Barzin, M.; Mirmiran, P.; Azizi, F. Predictors of incident obesity phenotype in nonobese healthy adults. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 47, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, B.; Abdi, H.; Serahati, S.; Barzin, M.; Niroomand, M.; Azizi, F.; Hosseinpanah, F. Cardiovascular risk in different obesity phenotypes over a decade follow-up: Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study. Atherosclerosis 2017, 258, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, E.-J.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, J.D.; Jeon, W.S.; Bae, J.C.; Park, S.E.; Park, C.-Y.; Oh, K.-W.; Park, S.-W.; Lee, W.-Y. Metabolic health is a more important determinant for diabetes development than simple obesity: A 4-year retrospective longitudinal study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marseglia, L.; Manti, S.; D’Angelo, G.; Cuppari, C.; Salpietro, V.; Filippelli, M.; Trovato, A.; Gitto, E.; Salpietro, C.; Arrigo, T. Obesity and breastfeeding: The strength of association. Women Birth 2015, 28, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, M.B.; Allison, D.B. Critical review of the World Health Organization’s (WHO) 2007 report on ‘evidence of the long-term effects of breastfeeding: Systematic reviews and meta-analysis’ with respect to obesity. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, F.; Giannì, M.L. Human milk: Composition and health benefits. Pediatr. Med. Chir. 2017, 39, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pietrobelli, A.; Agosti, M. Nutrition in the First 1000 Days: Ten Practices to Minimize Obesity Emerging from Published Science. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horta, B.L.; Loret de Mola, C.; Victora, C.G. Long-term consequences of breastfeeding on cholesterol, obesity, systolic blood pressure and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, C.G.; Bahl, R.; Barros, A.J.D.; Franca, G.V.A.; Horton, S.; Krasevec, J.; Murch, S.; Sankar, M.J.; Walker, N.; Rollins, N.C.; et al. Breastfeeding in the 21st century: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect. Lancet 2016, 387, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arenz, S.; Rückerl, R.; Koletzko, B.; von Kries, R. Breast-feeding and childhood obesity—A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harder, T.; Bergmann, R.; Kallischnigg, G.; Plagemann, A. Duration of breastfeeding and risk of overweight: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spatz, D.L. Preventing obesity starts with breastfeeding. J. Périnat. Neonatal Nutr. 2014, 28, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, S.S.; Baum, C.F.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Oken, E.; Taveras, E.M. Examining Associations between Perinatal and Postnatal Risk Factors for Childhood Obesity Using Sibling Comparisons. Child. Obes. 2019, 15, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colen, C.G.; Ramey, D.M. Is breast truly best? Estimating the effects of breastfeeding on long-term child health and wellbeing in the United States using sibling comparisons. Soc. Sci. Med. 2014, 109, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metzger, M.W.; McDade, T.W. Breastfeeding as obesity prevention in the United States: A sibling difference model. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2010, 22, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contarato, A.A.; Rocha, E.D.; Czarnobay, S.A.; Mastroeni, S.S.; Veugelers, P.J.; Mastroeni, M.F. Independent effect of type of breastfeeding on overweight and obesity in children aged 12–24 months. Cad. Saude Publ. 2016, 32, e00119015. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.S.; Matush, L.; Vanilovich, I.; Platt, R.W.; Bogdanovich, N.; Sevkovskaya, Z.; Dzikovich, I.; Shishko, G.; Collet, J.; Martin, R.M.; et al. Effects of prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding on child height, weight, adiposity, and blood pressure at age 6.5 y: Evidence from a large randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1717–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.M.; Patel, R.; Kramer, M.S.; Guthrie, L.; Vilchuck, K.; Bogdanovich, N.; Sergeichick, N.; Gusina, N.; Foo, Y.; Palmer, T.; et al. Effects of promoting longer-term and exclusive breastfeeding on adiposity and insulin-like growth factor-I at age 11.5 years: A randomized trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.M.; Patel, R.; Kramer, M.S.; Vilchuck, K.; Bogdanovich, N.; Sergeichick, N.; Gusina, N.; Foo, Y.; Palmer, T.; Thompson, J.; et al. Effects of promoting longer-term and exclusive breastfeeding on cardiometabolic risk factors at age 11.5 years: A cluster-randomized, controlled trial. Circulation 2014, 129, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sata, M.; Yamagishi, K.; Sairenchi, T.; Irie, F.; Sunou, K.; Watanabe, H.; Iso, H.; Ota, H. Breastfeeding in Infancy in Relation to Subsequent Physical Size: A 20-year Follow-up of the Ibaraki Children’s Cohort Study (IBACHIL). J. Epidemiol. 2021; advance online publication. [Google Scholar]
- Wallby, T.; Lagerberg, D.; Magnusson, M. Relationship Between Breastfeeding and Early Childhood Obesity: Results of a Prospective Longitudinal Study from Birth to 4 Years. Breastfeed Med. 2017, 12, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, C.H.; Borja, J.B.; Osmond, C.; Richter, L.; Bhargava, S.K.; Martorell, R.; Stein, A.D.; Barros, F.C.; Victora, C.G.; the COHORTS Group. Infant-feeding patterns and cardiovascular risk factors in young adulthood: Data from five cohorts in low- and middle-income countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taveras, E.M.; Gillman, M.W.; Kleinman, K.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L. Racial/ethnic differences in early-life risk factors for childhood obesity. Pediatrics 2010, 125, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, Y.J.; Watt, R.G.; Nazroo, J.Y. Racial/ethnic differences in breastfeeding initiation and continuation in the United Kingdom and comparison with findings in the United States. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e1428–e1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Qiao, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, W.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Chaput, J.; Fogelholm, M.; Kuriyan, R.; Lambert, E.; Maher, C.; et al. Breastfeeding and childhood obesity: A 12-country study. Matern. Child Nutr. 2020, 16, e12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamulka, J.; Zielinska, M.A.; Jeruszka-Bielak, M.; Górnicka, M.; Głąbska, D.; Guzek, D.; Hoffmann, M.; Gutkowska, K. Analysis of Association between Breastfeeding and Vegetable or Fruit Intake in Later Childhood in a Population-Based Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrine, C.G.; Galuska, D.A.; Thompson, F.E.; Scanlon, K.S. Breastfeeding duration is associated with child diet at 6 years. Pediatrics 2014, 134 (Suppl. 1), S50–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, P.C.D.A.; Ribeiro, S.A.V.; Andreoli, C.S.; de Carvalho, C.A.; Pessoa, M.C.; de Novaes, J.F.; Priore, S.E.; Franceschini, S.D.C.C. Association of exclusive breastfeeding duration with consumption of ultra-processed foods, fruit and vegetables in Brazilian children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Yoo, J.E.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Park, S.M. Associations between birth weight, obesity, fat mass and lean mass in Korean adolescents: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasylyeva, T.L.; Barche, A.; Chennasamudram, S.P.; Sheehan, C.; Singh, R.; Okogbo, M.E. Obesity in prematurely born children and adolescents: Follow up in pediatric clinic. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zou, Z.Y.; Dong, Y.H.; Xu, R.B.; Yang, Y.D.; Ma, J. A Healthy Lifestyle Offsets the Increased Risk of Childhood Obesity Caused by High Birth Weight: Results from a Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 736900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.H.; Zou, Z.Y.; Yang, Z.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Jing, J.; Luo, J.Y.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.P.; et al. Association between high birth weight and hypertension in children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study in China. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2017, 31, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Pan, D.; et al. A national school-based health lifestyles interventions among Chinese children and adolescents against obesity: Rationale, design and methodology of a randomized controlled trial in China. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehm, C.D.; Peñalvo, J.L.; Afshin, A.; Mozaffarian, D. Dietary Intake Among US Adults, 1999–2012. JAMA 2016, 315, 2542–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association for Maternal Child Health Study; Expert Committee on Obesity Controlling for Women Children; Expert Committee on Definition of Metabolically Healthy Obesity; Screening Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity in Chinese Children. The expert consensus on definition of metabolically healthy obesity and screening metabolically healthy obesity in Chinese children. Matern. Child Health China 2019, 30, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Screening for Overweight and Obesity among School-Age Children and Adolescents; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Liberali, R.; Kupek, E.; Assis, M.A.A. Dietary Patterns and Childhood Obesity Risk: A Systematic Review. Child Obes. 2020, 16, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, D.; Ranjit, N.; Nielsen, A.; Akhavan, N.; van den Berg, A. Characterizing Micro-scale Disparities in Childhood Obesity: Examining the Influence of Multilevel Factors on 4-Year Changes in BMI, Healthy Eating, and Physical Activity, Among a Cohort of Children Residing in Disadvantaged Urban Enclaves. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essman, M.; Popkin, B.M.; Corvalán, C.; Reyes, M.; Taillie, L.S. Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Intake among Chilean Preschoolers and Adolescents in 2016: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, S.; Dehghan, M.; Lear, S.A.; Swaminathan, S.; Ibrahim, Q.; Rangarajan, S.; Punthakee, Z. Relationship between diet and acculturation among South Asian children living in Canada. Appetite 2020, 147, 104524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary Guidelines for School-Age Children; People ’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Lyu, J.; He, P. Chinese guidelines for data processing and analysis concerning the International Physical Activity Questionnaire. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2014, 35, 961–964. [Google Scholar]
- Hirshkowitz, M.; Whiton, K.; Albert, S.M.; Alessi, C.; Bruni, O.; DonCarlos, L.; Hazen, N.; Herman, J.; Adams Hillard, P.J.; Katz, E.S.; et al. National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: Final report. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.M.; Kramer, M.S.; Patel, R.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Thompson, J.; Yang, S.; Vilchuck, K.; Bogdanovich, N.; Hameza, M.; Tilling, K.; et al. Effects of Promoting Long-term, Exclusive Breastfeeding on Adolescent Adiposity, Blood Pressure, and Growth Trajectories: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Pediatrics 2017, 171, e170698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Tierney, P.F.; Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Kajantie, E.; Eriksson, J.G. Duration of breast-feeding and adiposity in adult life. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 422S–425S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.I.; Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C. Infant feeding, fetal growth and adult thyroid function. Acta Endocrinol. 1993, 129, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimberg, M.; Olubadewo, J.O.; Wilcox, H.G. Plasma lipoproteins and regulation of hepatic metabolism of fatty acids in altered thyroid states. Endocr. Rev. 1985, 6, 590–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, C.H.; Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Winter, P.D.; Clark, P.M.; Hales, C.N. Relation of infant feeding to adult serum cholesterol concentration and death from ischaemic heart disease. BMJ 1992, 304, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agostoni, C.; Decsi, T.; Fewtrell, M.; Goulet, O.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Michaelsen, K.F.; van Goudoever, J. Complementary feeding: A commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2008, 46, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Gao, D.; Chen, L.; Ma, T.; Ma, Y.; Chen, M.; Dong, B.; Dong, Y.; Ma, J.; Arnold, L. The Association between Breastfeeding Duration and Lipid Profile among Children and Adolescents. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, J.; The European Childhood Obesity Trial Study Group; Luque, V.; Ferré, N.; Mendez-Riera, G.; Koletzko, B.; Grote, V.; Demmelmair, H.; Bluck, L.; Wright, A.; et al. Effect of protein intake and weight gain velocity on body fat mass at 6 months of age: The EU Childhood Obesity Programme. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearce, J.; Taylor, M.A.; Langley-Evans, S.C. Timing of the introduction of complementary feeding and risk of childhood obesity: A systematic review. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobti, J.; Mathur, G.P.; Gupta, A. WHO’s proposed global strategy for infant and young child feeding: A viewpoint. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 2002, 100, 502–504. [Google Scholar]
- Forsyth, J.S. Policy and pragmatism in breast feeding. Arch. Dis. Child. 2011, 96, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, M.; Wilson, D.C.; Booth, I.; Lucas, A. Six months of exclusive breast feeding: How good is the evidence? BMJ 2010, 342, c5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieuwoudt, S.; Daniels, L.; Sayed, N. Food and Nutrition Security of Infants and Young Children: Breastfeeding and Complementary Feeding; Children’s Institute, University of Cape Town: Cape Town, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- OECD Directorate for Employment LaSASPD. OECD Family Database. CO1.5 Breastfeeding Rates. 2009. Available online: www.oecd.org/dataoecd/30/56/43136964.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2022).
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e827–e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition; Agostoni, C.; Braegger, C.; Decsi, T.; Kolacek, S.; Koletzko, B.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mihatsch, W.; Moreno, L.A.; Puntis, J.; et al. Breast-feeding: A commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 49, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grummer-Strawn, L.M.; Rollins, N. Summarising the health effects of breastfeeding. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardo, H.; Cesar, V.; World Health Organization. Long-Term Effects of Breastfeeding: A Systematic Review; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]



| Breastfeeding Duration (Months) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0–5 (n = 2373) | 6–11 (n = 3184) | ≥12 (n = 2651) | ||
| Characteristics of children and adolescents | |||||
| Age * | 11.2 (4.0) | 11.1 (6.0) | 11.2 (6.0) | 11.3 (4.0) | 0.016 |
| Sex | 0.013 | ||||
| Boys | 3914 (47.7) | 1180 (49.7) # | 1458 (45.8) | 1276 (48.1) | |
| Girls | 4294 (52.3) | 1193 (50.3) # | 1726 (54.2) | 1375 (51.9) | |
| Residence | <0.001 | ||||
| Urban | 4623 (56.3) | 1533 (64.6) # | 1844 (57.9) | 1246 (47.0) # | |
| Rural | 3585 (43.7) | 840 (35.4) # | 1340 (42.1) | 1405 (53.0) # | |
| Obesity phenotypes | |||||
| Normal weight | <0.001 | ||||
| MHNW | 4776 (68.1) | 1472 (72.8) # | 1927 (69.5) | 1377 (62.0) # | |
| MUNW | 2242 (31.9) | 551 (27.2) # | 847 (30.5) | 844 (38.0) # | |
| Obesity | 0.002 | ||||
| MHO | 488 (41.0) | 171 (48.9) # | 153 (37.3) | 164 (38.1) | |
| MUO | 702 (59.0) | 179 (51.1) # | 257 (62.7) | 266 (61.9) | |
| Healthy lifestyle category | 0.001 | ||||
| Favorable | 1213 (14.8) | 367 (15.5) | 487 (15.3) | 359 (13.5) # | |
| Intermediate | 2838 (34.6) | 825 (34.8) | 1150 (36.1) | 863 (32.6) # | |
| Unfavorable | 4157 (50.6) | 1181 (49.8) | 1547 (48.6) | 1429 (53.9) | |
| Single-child status | <0.001 | ||||
| Single children | 5493 (66.9) | 1733 (73.0) # | 2188 (68.7) | 1572 (59.3) # | |
| Non-single children | 2715 (33.1) | 640 (27.0) # | 996 (31.3) | 1079 (40.7) # | |
| Delivery time | <0.001 | ||||
| Normal | 3802 (46.3) | 1083 (45.6) # | 1340 (42.1) | 1379 (52.0) # | |
| Premature delivery | 2435 (29.7) | 803 (33.8) | 993 (31.2) | 639 (24.1) # | |
| Delayed delivery | 1971 (24.0) | 487 (20.5) # | 851 (26.7) | 633 (23.9) # | |
| Delivery model | <0.001 | ||||
| Caesarean | 3428 (41.8) | 1192 (50.2) # | 1288 (40.5) | 948 (35.8) # | |
| Eutocia | 4780 (58.2) | 1181 (49.8) # | 1896 (59.5) | 1703 (64.2) # | |
| Birth weight | <0.001 | ||||
| NBW | 6881 (83.8) | 1954 (82.3) | 2665 (83.7) | 2262 (85.3) | |
| LBW | 569 (6.9) | 213 (9.0) | 233 (7.3) | 123 (4.6) # | |
| HBW | 758 (9.2) | 206 (8.7) | 286 (9.0) | 266 (10.0) | |
| Family history of diseases $ | 0.022 | ||||
| Yes | 1254 (15.3) | 403 (17.0) # | 459 (14.4) | 392 (14.8) | |
| No | 6954 (84.7) | 1970 (83.0) # | 2725 (85.6) | 2259 (85.2) | |
| Parental characteristics | |||||
| Paternal education level | <0.001 | ||||
| Primary or below | 581 (7.1) | 133 (5.6) | 169 (5.3) | 279 (10.5) # | |
| Secondary or equivalent | 5338 (65.0) | 1381 (58.2) # | 2010 (63.1) | 1947 (73.4) # | |
| Junior college or above | 2289 (27.9) | 859 (36.2) # | 1005 (31.6) | 425 (16.0) # | |
| Maternal education level | <0.001 | ||||
| Primary or below | 769 (9.4) | 159 (6.7) # | 273 (8.6) | 337 (12.7) # | |
| Secondary or equivalent | 5221 (63.6) | 1351 (56.9) # | 1956 (61.4) | 1914 (72.2) # | |
| Junior college or above | 2218 (27.0) | 863 (36.4) # | 955 (30.0) | 400 (15.1) # | |
| Paternal tobacco consumption | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 4327 (52.7) | 1220 (51.4) | 1612 (50.6) | 1495 (56.4) # | |
| No | 3881 (47.3) | 1153 (48.6) | 1572 (49.4) | 1156 (43.6) # | |
| Maternal tobacco consumption | 0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 97 (1.2) | 38 (1.6) # | 20 (0.6) | 39 (1.5) # | |
| No | 8111 (98.8) | 2335 (98.4) # | 3164 (99.4) | 2612 (98.5) # | |
| Paternal alcohol consumption | 0.120 | ||||
| Yes | 2560 (31.2) | 732 (30.8) | 962 (30.2) | 866 (32.7) | |
| No | 5648 (68.8) | 1641 (69.2) | 2222 (69.8) | 1785 (67.3) | |
| Maternal alcohol consumption | 0.453 | ||||
| Yes | 152 (1.9) | 48 (2.0) | 62 (1.9) | 42 (1.6) | |
| No | 8056 (98.1) | 2325 (98.0) | 3122 (98.1) | 2609 (98.4) | |
| Maternal age at delivery * | 26.4 (4.8) | 27.0 (4.8) # | 26.1 (4.7) | 26.1 (4.8) | <0.001 |
| Monthly household income | 0.835 | ||||
| <5000 CNY | 6803 (82.9) | 1958 (82.5) | 2641 (82.9) | 2204 (83.1) | |
| ≥5000 CNY | 1405 (17.1) | 415 (17.5) | 543 (17.1) | 447 (16.9) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dang, J.; Chen, T.; Ma, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, P.; Shi, D.; Dong, Y.; Zou, Z.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; et al. Associations between Breastfeeding Duration and Obesity Phenotypes and the Offsetting Effect of a Healthy Lifestyle. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14101999
Dang J, Chen T, Ma N, Liu Y, Zhong P, Shi D, Dong Y, Zou Z, Ma Y, Song Y, et al. Associations between Breastfeeding Duration and Obesity Phenotypes and the Offsetting Effect of a Healthy Lifestyle. Nutrients. 2022; 14(10):1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14101999
Chicago/Turabian StyleDang, Jiajia, Ting Chen, Ning Ma, Yunfei Liu, Panliang Zhong, Di Shi, Yanhui Dong, Zhiyong Zou, Yinghua Ma, Yi Song, and et al. 2022. "Associations between Breastfeeding Duration and Obesity Phenotypes and the Offsetting Effect of a Healthy Lifestyle" Nutrients 14, no. 10: 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14101999
APA StyleDang, J., Chen, T., Ma, N., Liu, Y., Zhong, P., Shi, D., Dong, Y., Zou, Z., Ma, Y., Song, Y., & Ma, J. (2022). Associations between Breastfeeding Duration and Obesity Phenotypes and the Offsetting Effect of a Healthy Lifestyle. Nutrients, 14(10), 1999. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14101999