Effects of Classic Ketogenic Diet in Children with Refractory Epilepsy: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Kingdom of Bahrain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Patients and Data Collection Protocol
2.3. Ketogenic Diet Protocol
2.4. Statistical Analysis
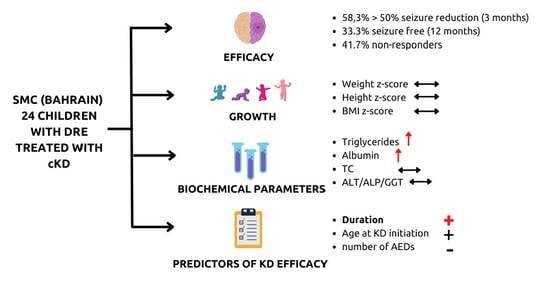
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Data
3.2. Efficacy on Seizure Reduction at 3 and 12 Months Follow up
3.3. General Characteristics of the Sample
3.4. Effect on Biochemical Markers
3.5. Effects on Growth
3.6. Predictive Factors for cKD Efficacy
3.7. Reasons for cKD Discontinuation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, H.J.; Elger, C.E.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; et al. ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Epilepsy. Key Facts. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 23 January 2022).
- Kossoff, E.H.; Zupec-Kania, B.A.; Auvin, S.; Ballaban-Gil, K.R.; Christina Bergqvist, A.G.; Blackford, R.; Buchhalter, J.R.; Caraballo, R.H.; Cross, J.H.; Dahlin, M.G.; et al. Optimal clinical management of children receiving dietary therapies for epilepsy: Updated recommendations of the International Ketogenic Diet Study Group. Epilepsia Open 2018, 3, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirrell, E.C.; Grossardt, B.; Wong-Kisiel, L.C.; Nickels, K.C. Incidence and classification of new-onset epilepsy and epilepsy syndromes in children in Olmsted County, Minnesota from 1980 to 2004: A population-based study. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 95, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Kinderen, R.J.A.; Lambrechts, D.A.J.E.; Wijnen, B.F.M.; Postulart, D.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Majoie, M.H.J.M.; Evers, S.M.A.A. An economic evaluation of the ketogenic diet versus care as usual in children and adolescents with intractable epilepsy: An interim analysis. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalic, L.; Cook, M.J. Managing drug-resistant epilepsy: Challenges and solutions. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2016, 12, 2605–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwan, P.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Berg, A.T.; Brodie, M.J.; Allen Hauser, W.; Mathern, G.; Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Wiebe, S.; French, J. Definition of drug resistant epilepsy: Consensus proposal by the ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Commission on Therapeutic Strategies. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.M.; Kossoff, E.H.; Hartman, A.L. The Ketogenic Diet: One Decade Later. Pediatricts 2007, 119, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, J.; Swaminathan, A.; Paseka, J.; Hanson, C. Efficacy and Safety of a Ketogenic Diet in Children and Adolescents with Refractory Epilepsy—A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, E.G.; Chaffe, H.; Schwartz, R.H.; Lawson, M.S.; Edwards, N.; Fitzsimmons, G.; Whitney, A.; Cross, J.H. A randomized trial of classical and medium-chain triglyceride ketogenic diets in the treatment of childhood epilepsy. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bough, K.J.; Rho, J.M. Anticonvulsant Mechanisms of the Ketogenic Diet. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Luo, R.; Gan, J.; Li, S.-P.; Mu, D.Z.; Wan, C.-M. Safety and tolerability of the ketogenic diet used for the treatment of refractory childhood epilepsy: A systematic review of published prospective studies. World J. Pediatr. 2017, 13, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-McGill, K.J.; Bresnahan, R.; Levy, R.G.; Cooper, P.N. Ketogenic diets for drug-resistant epilepsy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehmeijer, F.O.L.; Van Der Louw, E.J.T.M.; Arts, W.F.M.; Catsman-Berrevoets, C.E.; Neuteboom, R.F. Can we predict efficacy of the ketogenic diet in children with refractory epilepsy? Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrechts, D.A.J.E.; de Kinderen, R.J.A.; Vles, H.S.H.; de Louw, A.J.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Majoie, M.J.M. The MCT-ketogenic diet as a treatment option in refractory childhood epilepsy: A prospective study with 2-year follow-up. Epilepsy Behav. 2015, 51, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnowska, I.M. Therapeutic Use of the Ketogenic Diet in Refractory Epilepsy: What We Know and What Still Needs to Be Learned. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Pasca, L.; De Giorgis, V.; Ferraro, O.E.; Brambilla, I.; Leone, A.; De Amicis, R.; Bertoli, S.; Veggiotti, P.; et al. Impact of the Ketogenic Diet on Linear Growth in Children: A Single-Center Retrospective Analysis of 34 Cases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoli, S.; Masnada, S.; De Amicis, R.; Sangiorgio, A.; Leone, A.; Gambino, M.; Lessa, C.; Tagliabue, A.; Ferraris, C.; De Giorgis, V.; et al. Glucose transporter 1 deficiency syndrome: Nutritional and growth pattern phenotypes at diagnosis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julious, S.A. Sample size of 12 per group rule of thumb for a pilot study. Pharm. Stat. 2005, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency Guideline on Missing Data in Confirmatory Clinical Trials. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-missing-data-confirmatory-clinical-trials_en.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Yan, J.; Fine, J. Estimating equations for association structures. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locascio, J.J.; Atri, A. An Overview of Longitudinal Data Analysis Methods for Neurological Research. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 2011, 1, 330–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kossoff, E.H. Long-Term Follow-Up of Children Treated with the Modified Atkins Diet. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, A.M.; Turner, Z.; Hamdy, R.F.; Kossoff, E.H. Infantile spasms treated with the ketogenic diet: Prospective single-center experience in 104 consecutive infants. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, R.; Vaccarezza, M.; Cersósimo, R.; Rios, V.; Soraru, A.; Arroyo, H.; Agosta, G.; Escobal, N.; Demartini, M.; Maxit, C.; et al. Long-term follow-up of the ketogenic diet for refractory epilepsy: Multicenter Argentinean experience in 216 pediatric patients. Seizure 2011, 20, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Numis, A.L.; Yellen, M.B.; Chu-Shore, C.J.; Pfeifer, H.H.; Thiele, E.A. The relationship of ketosis and growth to the efficacy of the ketogenic diet in infantile spasms. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 96, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayyali, H.R.; Luniova, A.; Abdelmoity, A. Ketogenic Diet Decreases Emergency Room Visits and Hospitalizations Related to Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. Treat. 2016, 2016, 5873208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groleau, V.; Schall, J.I.; Stallings, V.A.; Bergqvist, C.A. Long-term impact of the ketogenic diet on growth and resting energy expenditure in children with intractable epilepsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2014, 56, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirrell, E.; Eckert, S.; Wong-Kisiel, L.; Payne, E.; Nickels, K. Ketogenic Diet Therapy in Infants: Efficacy and Tolerability. Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 82, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armeno, M.; Verini, A.; Del Pino, M.; Araujo, M.B.; Mestre, G.; Reyes, G.; Caraballo, R.H. A Prospective Study on Changes in Nutritional Status and Growth Following Two Years of Ketogenic Diet (KD) Therapy in Children with Refractory Epilepsy. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dressler, A.; Stöcklin, B.; Reithofer, E.; Benninger, F.; Freilinger, M.; Hauser, E.; Reiter-Fink, E.; Seidl, R.; Trimmel-Schwahofer, P.; Feucht, M. Long-term outcome and tolerability of the ketogenic diet in drug-resistant childhood epilepsy—The Austrian experience. Seizure 2010, 19, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, M.E.; Ilea, A.; Bourel, E.; Bellavoine, V.; Merdariu, D.; Berquin, P.; Auvin, S. Ketogenic diet for infantile spasms refractory to first-line treatments: An open prospective study. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 105, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, D.A.J.E.; de Kinderen, R.J.A.; Vles, J.S.H.; de Louw, A.J.A.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; Majoie, H.J.M. A randomized controlled trial of the ketogenic diet in refractory childhood epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2016, 135, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nizamuddin, J.; Turner, Z.; Rubenstein, J.E.; Pyzik, P.L.; Kossoff, E.H. Management and Risk Factors for Dyslipidemia with the Ketogenic Diet. J. Child Neurol. 2008, 23, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, G.R.; Mohammadi, M.; Ashrafi, M.R.; Karimi, P.; Mahmoudi, M.; Badv, R.S.; Tavasoli, A.R.; Malamiri, R.A. The effects of classic ketogenic diet on serum lipid profile in children with refractory seizures. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2016, 116, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-M.C.; Lowe, H.; Zak, M.M.; Kobayashi, J.; Chan, V.W.; Donner, E.J. Can Children with Hyperlipidemia Receive Ketogenic Diet for Medication-Resistant Epilepsy? J. Child Neurol. 2013, 28, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumas, R.; Lopes Cardoso, A.; Marques-Dias, J.; Vieira, A. Ketogenic diet in epileptic children: Clinical and laboratory assessment. Nutr. Hosp. 2010, 25, 317–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibisono, C.; Rowe, N.; Beavis, E.; Kepreotes, H.; Mackie, F.E.; Lawson, J.A.; Cardamone, M. Ten-Year Single-Center Experience of the Ketogenic Diet: Factors Influencing Efficacy, Tolerability, and Compliance. J. Pediatr. 2015, 166, 1030–1036.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, N.; Guzel, O.; Kose, E.; Yılmaz, U.; Kuyum, P.; Aksoy, B.; Çalık, T. Is ketogenic diet treatment hepatotoxic for children with intractable epilepsy? Seizure 2016, 43, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballaban-Gil, K.; Callahan, C.; O’Dell, C.; Pappo, M.; Moshé, S.; Shinnar, S. Complications of the Ketogenic Diet. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 744–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.D.; Terra, V.C.; Nicoletti, C.F.; Chiarello, P.G.; Marchini, J.S.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Nonino-Borges, C.B. Effect of the classic ketogenic diet on the treatment of refractory epileptic seizures. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 25, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tagliabue, A.; Bertoli, S.; Trentani, C.; Borrelli, P.; Veggiotti, P. Effects of the ketogenic diet on nutritional status, resting energy expenditure, and substrate oxidation in patients with medically refractory epilepsy: A 6-month prospective observational study. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, C.; Liao, J.; Lu, X.; Fang, K.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Cao, D.; Huang, T.; Li, B.; Li, C. Efficacy and safety of the ketogenic diet in Chinese children. Seizure 2013, 22, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppola, G.; Verrotti, A.; Ammendola, E.; Operto, F.F.; della Corte, R.; Signoriello, G.; Pascotto, A. Ketogenic diet for the treatment of catastrophic epileptic encephalopathies in childhood. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2010, 14, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, R.H.; Fortini, S.; Fresler, S.; Armeno, M.; Ariela, A.; Cresta, A.; Mestre, G.; Escobal, N. Ketogenic diet in patients with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Seizure 2014, 23, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baby, N.; Vinayan, K.P.; Pavithran, N.; Roy, A.G. A pragmatic study on efficacy, tolerability and long term acceptance of ketogenic diet therapy in 74 South Indian children with pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Seizure 2018, 58, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karimzadeh, P.; Moosavian, T.; Moosavian, H.R. Effects of a Formula-Based Ketogenic Diet on Refractory Epilepsy in 1 to 3 Year-Old Patients under Classic Ketogenic Diet. Iran. J. Child Neurol. 2019, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Gender | 11 Females (45.83) |
| 13 Males (54.17) | |
| Seizure etiology | Genetic, 8 (33.33) |
| Structural, 2 (8.33) | |
| Infectious, 1 (4.17) | |
| Unknown, 13 (54.17) | |
| Epilepsy syndrome | Epileptic spasm, 5 (20.83) |
| Infantile spasm, 5 (12.5) | |
| Ohtahara syndrome, 3 (12.5) | |
| Myoclonic epilepsy, 2 (8.33) | |
| Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, 1 (4.17) | |
| Multifocal seizure syndrome, 1 (4.17) | |
| Complex partial seizure, 1 (4.17) | |
| Myoclonic encephalopathy, 1 (4.17) | |
| Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, 1 (4.17) | |
| Aicardi syndrome, 1 (4.17) | |
| Unknown, 3 (12.5) | |
| Median; IQR; age at epilepsy onset | 7 months (36 months) |
| Median; IQR; age at cKD initiation | 24 months (28.5 months) |
| Median, IQR; cKD duration | 21 months (72 months) |
| Mode IQR number of AEDs | 2 drugs (1–5 drugs) |
| Type of cKD (n, %) | cKD 3:1, 15 (62.5) |
| cKD 4:1, 9 (37.5) | |
| Administration route | Oral, 19 (79.17) |
| Enteral, 5 (20.83) | |
| Overall drop-out rate at 6 months | 14 (58.33%) |
| Variable | Baseline (Median ± IQR) | 6 Months (Median ± IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 3.45 ± 1.30 | 3.50 ± 2.60 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.80 ± 0.05 | 1.76 ± 1.77 |
| ALP levels (U/L) | 214.50 ± 119.75 | 173.00 ± 118.00 |
| ALT levels (U/L) | 15.50 ± 10.50 | 18.00 ± 5.00 |
| GGT levels (U/L) | 21.00 ± 8.25 | 13.00 ± 12.75 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 42.00 ± 9.00 | 44.00 ± 3.00 |
| Pre–Post | Time × cKD Type Interaction Modeling | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modeling | ||||
| Variable | MDtime | MDtime | MDtype | MDtimextype |
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | |
| 95% CI | 95% CI | 95% CI | 95% CI | |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 0.210 | 0.143 | −0.290 | 0.224 |
| 0.75 | 0.86 | 0.5657 | 0.8767 | |
| [−1.09; 1.51] | [−1.40; 1.690] | [−1.28; 0.701] | [−2.60; 3.051] | |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.4661 | 1.4571 | 0.1571 | 0.0429 |
| 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.096 | 0.940 | |
| [0.507; 2.425] | [0.342; 2.573] | [−0.028; 0.342] | [−1.073; 1.158] | |
| ALP levels (U/L) | −26.4 | −1.2 | 20.3 | −93.0 |
| 0.43 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 0.13 | |
| [−92.4; 39.6] | [−82.2; 79.8] | [−87.1; 127.7] | [−213.3; 27.2] | |
| ALT levels (U/L) | 6.29 | 8.10 | 2.55 | −6.35 |
| 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.53 | 0.35 | |
| [−2.34; 14.9] | [−3.60; 19.80] | [−5.39; 10.49] | [−19.71; 7.01] | |
| GGT levels (U/L) | −2.06 | −8.2 | −20.4 | 21.4 |
| 0.895 | 0.701 | 0.198 | 0.398 | |
| [−32.8; 28.7] | [−50.2; 33.8] | [−51.6; 10.7] | [−28.2; 70.9] | |
| Albumin (g/L) | 4.30 | 2.50 | −6.90 | 5.30 |
| 0.034 | 0.187 | 0.096 | 0.234 | |
| [0.32; 8.28] | [−1.21; 6.21] | [−15.04; 1.24] | [−3.43; 14.03] | |
| Variable | Baseline (Median ± IQR) | 12 Months (Median ± IQR) |
|---|---|---|
| Weight z-score | −0.05 ± 2.00 | −0.48 ± 1.76 |
| Height z-score | −0.46 ± 3.29 | −0.76 ± 1.92 |
| BMI or (weight-for-length) z-score | 0.22 ± 1.98 | 0.43 ± 1.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perna, S.; Ferraris, C.; Guglielmetti, M.; Alalwan, T.A.; Mahdi, A.M.; Guido, D.; Tagliabue, A. Effects of Classic Ketogenic Diet in Children with Refractory Epilepsy: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Kingdom of Bahrain. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091744
Perna S, Ferraris C, Guglielmetti M, Alalwan TA, Mahdi AM, Guido D, Tagliabue A. Effects of Classic Ketogenic Diet in Children with Refractory Epilepsy: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Kingdom of Bahrain. Nutrients. 2022; 14(9):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091744
Chicago/Turabian StylePerna, Simone, Cinzia Ferraris, Monica Guglielmetti, Tariq A. Alalwan, Alaa M. Mahdi, Davide Guido, and Anna Tagliabue. 2022. "Effects of Classic Ketogenic Diet in Children with Refractory Epilepsy: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Kingdom of Bahrain" Nutrients 14, no. 9: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091744
APA StylePerna, S., Ferraris, C., Guglielmetti, M., Alalwan, T. A., Mahdi, A. M., Guido, D., & Tagliabue, A. (2022). Effects of Classic Ketogenic Diet in Children with Refractory Epilepsy: A Retrospective Cohort Study in Kingdom of Bahrain. Nutrients, 14(9), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14091744