Revealing Edible Bird Nest as Novel Functional Foods in Combating Metabolic Syndrome: Comprehensive In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
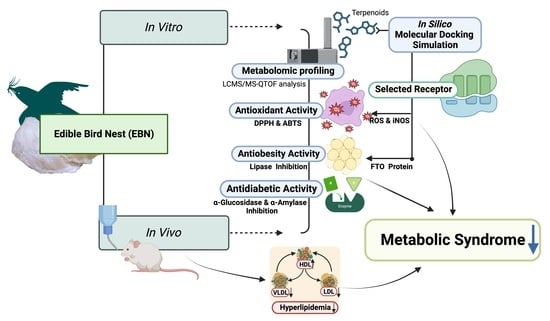
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Edible Bird Nest
2.2. Metabolites Screening by LCMS/MS-QTOF Analysis
2.3. In Silico Molecular Docking Analysis
2.4. Antioxidant Activity by ABTS and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity Assays
2.5. In Vitro Antidiabetic Assay via α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibition
2.6. In Vitro Antiobesity Evaluation via Lipase Inhibition Assay
2.7. In Vivo Study Design on Rats Fed on Cholesterol- and Fat-Enriched Diet
2.7.1. Animal Handling and Ethical Approval
2.7.2. Study Design of Treatments
2.7.3. Feed or Pellet Composition and CFED Production
2.7.4. Biomedical Analysis of Collected Blood Samples
2.8. Data Analysis and Management
3. Results
3.1. Terpenoids Observed in EBN
3.2. In Silico Molecular Docking Simulation in Selected Receptors
3.3. In Vitro Study Reveals the Antioxidants, Antidiabetic, and Antiobesity Potential of EBN
3.4. In Vivo Study Reveals Attenuation Metabolic Syndrome by EBN Supplementation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grundy, S.M. Metabolic Syndrome Update. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 26, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrowolski, P.; Prejbisz, A.; Kuryłowicz, A.; Baska, A.; Burchardt, P.; Chlebus, K.; Dzida, G.; Jankowski, P.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Jaworski, P.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome—A New Definition and Management Guidelines. Arch. Med. Sci. 2022, 18, 1133–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, S.M. The Metabolic Syndrome: Inflammation, Diabetes Mellitus, and Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 97, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World Obesity Day 2022—Accelerating Action to Stop Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/04-03-2022-world-obesity-day-2022-accelerating-action-to-stop-obesity (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuneš, J.; Vaněčková, I.; Mikulášková, B.; Behuliak, M.; Maletínská, L.; Zicha, J. Epigenetics and a New Look on Metabolic Syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Poudyal, H.; Panchal, S.K. Functional Foods as Potential Therapeutic Options for Metabolic Syndrome. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 914–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, L. A Comprehensive Review of Edible Bird’s Nest. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Wani, W.A.; Lee, C.H.; Cheng, K.K.; Shreaz, S.; Wong, S.; Hamdan, N.; Azmi, N.A. Edible Bird’s Nest: The Functional Values of the Prized Animal-Based Bioproduct from Southeast Asia—A Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 626233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun Lee, T.; Hau Lee, C.; Alia Azmi, N.; Kavita, S.; Wong, S.; Znati, M.; Ben Jannet, H. Characterization of Polar and Non-Polar Compounds of House Edible Bird’s Nest (EBN) from Johor, Malaysia. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, M.C.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Law, C.L.; Tan, S.W. Characterization of Edible Bird’s Nest of Different Production, Species and Geographical Origins Using Nutritional Composition, Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activities. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.J.W.; Chang, L.S.; Babji, A.S.; Latip, J.; Koketsu, M.; Lim, S.J. Review of Sialic Acid’s Biochemistry, Sources, Extraction and Functions with Special Reference to Edible Bird’s Nest. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Liu, D. Sketch of the Edible Bird’s Nest and Its Important Bioactivities. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yida, Z.; Imam, M.U.; Ismail, M.; Ooi, D.-J.; Sarega, N.; Azmi, N.H.; Ismail, N.; Chan, K.W.; Hou, Z.; Yusuf, N.B. Edible Bird’s Nest Prevents High Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance in Rats. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 760535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akmal, M.N.; Intan-Shameha, A.R.; Ajat, M.; Mansor, R.; Zuki, A.B.Z.; Ideris, A. Edible Bird’s Nest (EBN) Supplementation Ameliorates the Progression of Hepatic Changes and Atherosclerosis in Hypercholesterolaemic-Induced Rats. Malays. J. Microsc. 2018, 14, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, K.W.; Zain, Z.M.; Murugan, D.D.; Giribabu, N.; Zamakshshari, N.H.; Lim, Y.M.; Mustafa, M.R. Effect of Hydrolyzed Bird’s Nest on β-Cell Function and Insulin Signaling in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 632169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Hardinsyah, H.; Taslim, N.A.; Sabrina, N.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Visnu, J.; Kumalawati, D.A.; Febriana, S.A.; Sudargo, T.; et al. Metabolomic Assay, Computational Screening, and Pharmacological Evaluation of Caulerpa Racemosa as an Anti-Obesity with Anti-Aging by Altering Lipid Profile and Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Coactivator 1-α Levels. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 939073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Lewis, R.; Hooper, A.; Morphet, J.; Tan, X.; Yu, K. Using Natural Products Application Solution with UNIFI for the Identification of Chemical Ingredients of Green Tea Extract; Report No. APNT134775221; Waters Corporation: Milford, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hardinsyah, H.; Gunawan, W.B.; Nurkolis, F.; Alisaputra, D.; Kurniawan, R.; Mayulu, N.; Taslim, N.A.; Tallei, T.E. Antiobesity Potential of Major Metabolites from Clitoria ternatea Kombucha: Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling and Molecular Docking Simulations. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabrina, N.; Rizal, M.; Nurkolis, F.; Hardinsyah, H.; Tanner, M.J.; Gunawan, W.B.; Handoko, M.N.; Mayulu, N.; Taslim, N.A.; Puspaningtyas, D.S.; et al. Bioactive Peptides Identification and Nutritional Status Ameliorating Properties on Malnourished Rats of Combined Eel and Soy-Based Tempe Flour. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 963065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Nurkolis, F.; Gunawan, W.B.; Yusuf, V.M.; Yusuf, M.; Kusuma, R.J.; Sabrina, N.; Muharram, F.R.; Taslim, N.A.; Mayulu, N.; et al. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Markers of Metabolic Syndrome in Mice on Cholesterol and Fat Enriched Diet by Butterfly Pea Flower Kombucha. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Kang, S.; Moon, M.; Choi, J.; Choi, M.; Park, M.N.; Mayulu, N.; Kim, B. Ulvophyte Green Algae Caulerpa lentillifera: Metabolites Profile and Antioxidant, Anticancer, Anti-Obesity, and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkolis, F.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Kurniawan, R.; Hardinsyah, H.; Gunawan, W.B.; Kusuma, R.J.; Yusuf, V.M.; Pramono, A.; Kang, S.; et al. Dietary Supplementation of Caulerpa racemosa Ameliorates Cardiometabolic Syndrome via Regulation of PRMT-1/DDAH/ADMA Pathway and Gut Microbiome in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Yu, G.; Liang, Y.; Song, T.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Oda, T. Inhibitory Effects of a Sulfated Polysaccharide Isolated from Edible Red Alga Bangia Fusco-Purpurea on α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permatasari, H.K.; Firani, N.K.; Prijadi, B.; Irnandi, F.D.; Riawan, W.; Yusuf, M.; Amar, N.; Chandra, L.A.; Yusuf, V.; Subali, A.D. Kombucha Drink Enriched with Sea Grapes (Caulerpa racemosa) as Potential Functional Beverage to Contrast Obesity: An In Vivo and In Vitro Approach. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuswari, M.; Nurkolis, F.; Mayulu, N.; Ibrahim, F.M.; Taslim, N.A.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sabrina, N.; Arifin, G.R.; Mantik, K.E.K.; Bahar, M.R.; et al. Sea Grapes Extract Improves Blood Glucose, Total Cholesterol, and PGC-1α in Rats Fed on Cholesterol- and Fat-Enriched Diet. F1000Research 2021, 10, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piché, M.-E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdy, N.E.; Abdel-Baki, P.M.; El-Rashedy, A.A.; Ibrahim, R.M. Modulatory Effect of Pyrus Pyrifolia Fruit and Its Phenolics on Key Enzymes against Metabolic Syndrome: Bioassay-Guided Approach, HPLC Analysis, and In Silico Study. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khella, M.S.; Hamdy, N.M.; Amin, A.I.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. The (FTO) Gene Polymorphism Is Associated with Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Egyptian Females: A Case-Control Study. BMC Med. Genet. 2017, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkolis, F.; Purnomo, A.F.; Alisaputra, D.; Gunawan, W.B.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Park, W.; Moon, M.; Taslim, N.A.; Park, M.N.; Kim, B. In Silico and in Vitro Studies Reveal a Synergistic Potential Source of Novel Anti-Ageing from Two Indonesian Green Algae. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 104, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.; Wu, X.; Ji, T.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Sun, M.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Hu, W.; Deng, C.; et al. Bakuchiol: A Newly Discovered Warrior against Organ Damage. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 141, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Kwon, E.B.; Li, W. Linderolide U, a New Sesquiterpene from Lindera aggregata Root. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1914–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhong, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, J. Saponins as Modulators of Nuclear Receptors. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui Yan, T.; Babji, A.S.; Lim, S.J.; Sarbini, S.R. A Systematic Review of Edible Swiftlet’s Nest (ESN): Nutritional Bioactive Compounds, Health Benefits as Functional Food, and Recent Development as Bioactive ESN Glycopeptide Hydrolysate. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Nasir, N.N.; Mohamad Ibrahim, R.; Abu Bakar, M.Z.; Mahmud, R.; Ab Razak, N.A. Characterization and Extraction Influence Protein Profiling of Edible Bird’s Nest. Foods 2021, 10, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; El-Tawil, O.S.; Bungau, S.G.; Atanasov, A.G. Applications of Antioxidants in Metabolic Disorders and Degenerative Diseases: Mechanistic Approach. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4179676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liao, B.; Wang, C.; Zhong, O.; Lei, X.; Yang, Y. Effects of Antioxidant Supplementation on Metabolic Disorders in Obese Patients from Randomized Clinical Controls: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 7255413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-T.; Liu, X.-T.; Chen, Q.-X.; Shi, Y. Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Teng, C.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G.; Richel, A. Anti-Obesity Effects of α-Amylase Inhibitor Enriched-Extract from White Common Beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Associated with the Modulation of Gut Microbiota Composition in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, D.D.; Md Zain, Z.; Choy, K.W.; Zamakshshari, N.H.; Choong, M.J.; Lim, Y.M.; Mustafa, M.R. Edible Bird’s Nest Protects against Hyperglycemia-Induced Oxidative Stress and Endothelial Dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius-Pérez, S.; Torres-Cuevas, I.; Millán, I.; Ortega, Á.L.; Pérez, S.; Sandhu, M.A. PGC-1 α, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress: An Integrative View in Metabolism. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1452696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.F.; Ku, H.C.; Lin, H. Pgc-1α as a Pivotal Factor in Lipid and Metabolic Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.H. Functional Implications of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition on Glucose Metabolism. Korean Circ. J. 2018, 48, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Bao, L.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, J.; Liao, M.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Structural Modification of Natural Product Ganomycin I Leading to Discovery of a α-Glucosidase and HMG-CoA Reductase Dual Inhibitor Improving Obesity and Metabolic Dysfunction in Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3609–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.D.; Buscemi, J.; Milsom, V.; Malcolm, R.; O’Neil, P.M. Effects on Cardiovascular Risk Factors of Weight Losses Limited to 5–10%. Transl. Behav. Med. 2016, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Quetglas-Llabrés, M.; Capó, X.; Bouzas, C.; Mateos, D.; Pons, A.; Tur, J.A.; Sureda, A. Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with Oxidative Stress and Proinflammatory State. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Component Name | Formula | Observed RT (min) | Mass Error (ppm) | Total Fragments Found | Isotope Match Mz RMS PPM | Isotope Match Intensity y RMS Percent | Response | Adducts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bakuchiol | C18H24O | 16.82 | 0.7 | 2 | 0.90 | 2.93 | 817 | +H |
| Curculigosaponin A | C36H60O9 | 17.19 | −3.9 | 19 | 4.47 | 2.13 | 26866 | +H |
| Dehydrolindestrenolide | C15H16O2 | 16.67 | −1.4 | 17 | 3.32 | 3.19 | 1272 | +H |
| 1-Methyl-3-(1-methyl-ethyl)-benzene | C11H16 | 16.72 | −1.4 | 12 | 1.58 | 2.41 | 1493 | +H |
| No. | Drug Target | PDBID | Docking Site (x;y;z) | Docking Area (x;y;z) | RMSD (Å) | ΔG (kcal/mol) | Numb in Cluster (/100) | Judgment (<2 Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | iNOS | 3E7G | 55.022, 21.817, 78.677, | 40 × 40 × 40 | 1.789 | −6.67 | 98 | Valid |
| 2 | ROS1 kinase | 3ZBF | 42.521, 19.649, 3.987, | 40 × 40 × 40 | 1.216 | −7.83 | 90 | Valid |
| 3 | Human pancreatic lipase | 1LPB | −0.423, 16.723, 26.546, | 42 × 40 × 40 | 1.499 | −4.13 | 26 | Valid |
| 4 | Fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) protein | 3LFM | 29.043, −6.644, −29.329, | 42 × 42 × 42 | 0.715 | −6.29 | 90 | Valid |
| No. | Substance | Number in Cluster (/100) | ΔG (kcal/mol) | Ki | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3E7G | 3ZBF | 1LPB | 3LFM | 3E7G | 3ZBF | 1LPB | 3LFM | 3E7G | 3ZBF | 1LPB | 3LFM | ||
| Control | |||||||||||||
| 1 | S-ibuprofen | 33 | −4.73 | 128.28 μM | |||||||||
| 2 | Trolox | 100 | −5.36 | 85.58 uM | |||||||||
| 3 | Orlistat | 6 | 5 | −2.38 | −3.71 | 5.22 mM | 212.83 uM | ||||||
| 1 | Bakuchiol | 74 | 66 | 68 | 89 | −5.85 | −6.12 | −5.94 | −6.80 | 19.90 uM | 9.04 uM | 11.59 uM | 6.14 uM |
| 2 | Curculigosaponin A | 52 | 20 | 23 | 34 | −5.53 | −4.70 | −6.51 | −5.36 | 15.85 uM | 26.89 uM | 386.01 nM | 10.51 uM |
| 3 | Dehydrolindestrenolide | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | −7.34 | −6.95 | −6.74 | −7.04 | 4.14 uM | 7.85 uM | 11.38 uM | 6.85 uM |
| 4 | 1-methyl-3-(1-methyl-ethyl)-benzene | 100 | 100 | 96 | 77 | −4.47 | −4.74 | −4.47 | −4.75 | 515.43 uM | 329.80 uM | 525.40 uM | 268.68 uM |
| Group | Normal | CFED | CFED + Low Dose EBN | CFED + High Dose EBN | p ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial BW (g) | 203.62 ± 2.99 | 203.11 ± 2.80 | 204.19 ± 4.32 | 205.20 ± 4.53 | 0.2805 |
| Final BW (g) | 244.63 ± 3.19 | 277.09 ± 6.70 | 235.48 ± 3.23 | 230.10 ± 2.01 | <0.0001 |
| p * | <0.000001 | <0.000001 | <0.000001 | <0.000001 | |
| Weight gain (g/day) | 0.89 ± 0.08 | 1.61 ± 0.17 | 0.68 ± 0.08 | 0.55 ± 0.10 | 0.8004 |
| Food intake (g) | 4.79 ± 0.47 | 4.89 ± 0.50 | 4.94 ± 0.69 | 5.05 ± 0.87 | 0.9960 |
| Water intake (mL) | 5.44 ± 0.63 | 5.37 ± 0.83 | 5.26 ± 0.79 | 5.01 ± 0.61 | 0.9822 |
| FER (%) | 18.74 ± 2.09 | 33.01 ± 3.15 | 13.96 ± 2.22 | 11.39 ± 3.84 | 0.0004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Permatasari, H.K.; Permatasari, Q.I.; Taslim, N.A.; Subali, D.; Kurniawan, R.; Surya, R.; Qhabibi, F.R.; Tanner, M.J.; Batubara, S.C.; Mayulu, N.; et al. Revealing Edible Bird Nest as Novel Functional Foods in Combating Metabolic Syndrome: Comprehensive In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183886
Permatasari HK, Permatasari QI, Taslim NA, Subali D, Kurniawan R, Surya R, Qhabibi FR, Tanner MJ, Batubara SC, Mayulu N, et al. Revealing Edible Bird Nest as Novel Functional Foods in Combating Metabolic Syndrome: Comprehensive In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183886
Chicago/Turabian StylePermatasari, Happy Kurnia, Queen Intan Permatasari, Nurpudji Astuti Taslim, Dionysius Subali, Rudy Kurniawan, Reggie Surya, Faqrizal Ria Qhabibi, Melvin Junior Tanner, Siti Chairiyah Batubara, Nelly Mayulu, and et al. 2023. "Revealing Edible Bird Nest as Novel Functional Foods in Combating Metabolic Syndrome: Comprehensive In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183886
APA StylePermatasari, H. K., Permatasari, Q. I., Taslim, N. A., Subali, D., Kurniawan, R., Surya, R., Qhabibi, F. R., Tanner, M. J., Batubara, S. C., Mayulu, N., Gunawan, W. B., Syauki, A. Y., Salindeho, N., Park, M. N., Lele, J. A. J. M. N., Tjandrawinata, R. R., Kim, B., & Nurkolis, F. (2023). Revealing Edible Bird Nest as Novel Functional Foods in Combating Metabolic Syndrome: Comprehensive In Silico, In Vitro, and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients, 15(18), 3886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15183886