Beneficial Effects of Citrus Bergamia Polyphenolic Fraction on Saline Load-Induced Injury in Primary Cerebral Endothelial Cells from the Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model
Abstract
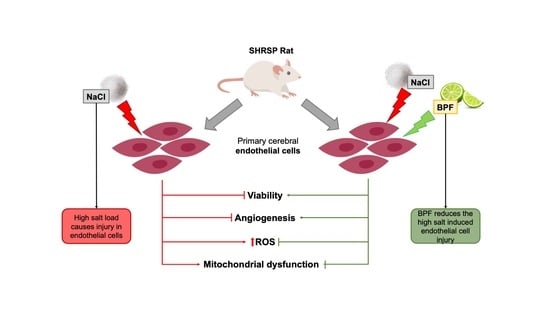
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF)
2.2. Cell Isolation and Culture
2.3. Immunostaining of Primary Cerebral ECs for CD31
2.4. Cell Treatments
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Measurement
2.7. Angiogenesis Assay
2.8. Wound-Healing Assay
wound (t0) × 100.
2.9. Assessment of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Using JC-1 Staining
2.10. Assessment of Mitochondrial Function
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubattu, S.; Stanzione, R.; Volpe, M. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Contributes to Hypertensive Target Organ Damage: Lessons from an Animal Model of Human Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1067801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volpe, M.; Camargo, M.J.; Mueller, F.B.; Campbell, W.G., Jr.; Sealey, J.E.; Pecker, M.S.; Sosa, R.E.; Laragh, J.H. Relation of plasma renin to end organ damage and to protection of K+ feeding in stroke-prone hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1990, 15, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubattu, S.; Volpe, M.; Kreutz, R.; Ganten, U.; Ganten, D.; Lindpaintner, K. Chromosomal mapping of quantitative trait loci contributing to stroke in a rat model of complex human disease. Nat. Genet. 1996, 13, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubattu, S.; Hubner, N.; Ganten, U.; Evangelista, A.; Stanzione, R.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Plehm, R.; Langanki, R.; Gianazza, E.; Sironi, L.; et al. Reciprocal congenic lines for a major stroke QTL on rat chromosome 1. Physiol. Genom. 2006, 27, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubattu, S.; Di Castro, S.; Schulz, H.; Geurts, A.M.; Cotugno, M.; Bianchi, F.; Maatz, H.; Hummel, O.; Falak, S.; Stanzione, R.; et al. Ndufc2 Gene Inhibition Is Associated With Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Increased Stroke Susceptibility in an Animal Model of Complex Human Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffa, S.; Scrofani, C.; Valente, S.; Micaloni, A.; Forte, M.; Bianchi, F.; Coluccia, R.; Geurts, A.M.; Sciarretta, S.; Volpe, M.; et al. In vitro characterization of mitochondrial function and structure in rat and human cells with a deficiency of the NADH: Ubiquinone oxidoreductase Ndufc2 subunit. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 4541–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raffa, S.; Chin, X.L.D.; Stanzione, R.; Forte, M.; Bianchi, F.; Cotugno, M.; Marchitti, S.; Micaloni, A.; Gallo, G.; Schirone, L.; et al. The reduction of NDUFC2 expression is associated with mitochondrial impairment in circulating mononuclear cells of patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 286, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, G.; Migliarino, S.; Cotugno, M.; Stanzione, R.; Burocchi, S.; Bianchi, F.; Marchitti, S.; Autore, C.; Volpe, M.; Rubattu, S. Impact of a NDUFC2 Variant on the Occurrence of Acute Coronary Syndromes. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 921244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, M.; Bianchi, F.; Cotugno, M.; Marchitti, S.; De Falco, E.; Raffa, S.; Stanzione, R.; Di Nonno, F.; Chimenti, I.; Palmerio, S.; et al. Pharmacological restoration of autophagy reduces hypertension-related stroke occurrence. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1468–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, C.; Bernardini, C.; Marchi, S.; Forte, M.; Tallarida, M.A.; Bianchi, F.; La Mantia, D.; Algieri, V.; Stanzione, R.; Cotugno, M.; et al. 1,5-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles counteract mitochondrial dysfunction acting on F(1)F(O)-ATPase in models of cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 187, 106561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliaro, B.; Santolamazza, C.; Simonelli, F.; Rubattu, S. Phytochemical Compounds and Protection from Cardiovascular Diseases: A State of the Art. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 918069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubattu, S.; Di Castro, S.; Cotugno, M.; Bianchi, F.; Mattioli, R.; Baima, S.; Stanzione, R.; Madonna, M.; Bozzao, C.; Marchitti, S.; et al. Protective effects of Brassica oleracea sprouts extract toward renal damage in high-salt-fed SHRSP: Role of AMPK/PPARalpha/UCP2 axis. J. Hypertens. 2015, 33, 1465–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubattu, S.; Stanzione, R.; Bianchi, F.; Cotugno, M.; Forte, M.; Della Ragione, F.; Fioriniello, S.; D’Esposito, M.; Marchitti, S.; Madonna, M.; et al. Reduced brain UCP2 expression mediated by microRNA-503 contributes to increased stroke susceptibility in the high-salt fed stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollace, V.; Sacco, I.; Janda, E.; Malara, C.; Ventrice, D.; Colica, C.; Visalli, V.; Muscoli, S.; Ragusa, S.; Muscoli, C.; et al. Hypolipemic and hypoglycaemic activity of bergamot polyphenols: From animal models to human studies. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, V.; Gliozzi, M.; Nucera, S.; Carresi, C.; Maiuolo, J.; Mollace, R.; Paone, S.; Bosco, F.; Scarano, F.; Scicchitano, M.; et al. The effect of bergamot polyphenolic fraction on lipid transfer protein system and vascular oxidative stress in a rat model of hyperlipemia. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maiuolo, J.; Carresi, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Scarano, F.; Coppoletta, A.R.; Guarnieri, L.; Nucera, S.; Scicchitano, M.; Bosco, F.; et al. Effects of Bergamot Polyphenols on Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizzo, A.; Izzo, C.; Forte, M.; Sommella, E.; Di Pietro, P.; Venturini, E.; Ciccarelli, M.; Galasso, G.; Rubattu, S.; Campiglia, P.; et al. A Novel Promising Frontier for Human Health: The Beneficial Effects of Nutraceuticals in Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrella, E.; Gussago, C.; Porrini, V.; Benarese, M.; Pizzi, M. From Preclinical Stroke Models to Humans: Polyphenols in the Prevention and Treatment of Stroke. Nutrients 2020, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliozzi, M.; Walker, R.; Muscoli, S.; Vitale, C.; Gratteri, S.; Carresi, C.; Musolino, V.; Russo, V.; Janda, E.; Ragusa, S.; et al. Bergamot polyphenolic fraction enhances rosuvastatin-induced effect on LDL-cholesterol, LOX-1 expression and protein kinase B phosphorylation in patients with hyperlipidemia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 170, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carresi, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Scicchitano, M.; Scarano, F.; Bosco, F.; Nucera, S.; Maiuolo, J.; Macri, R.; Ruga, S.; et al. The Effect of Natural Antioxidants in the Development of Metabolic Syndrome: Focus on Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirarchi, A.; Mare, R.; Musolino, V.; Nucera, S.; Mollace, V.; Pujia, A.; Montalcini, T.; Romeo, S.; Maurotti, S. Bergamot Polyphenol Extract Reduces Hepatocyte Neutral Fat by Increasing Beta-Oxidation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Di Paola, R.; Ahmad, A.; Campolo, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E.; Navarra, M. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of bergamot juice extract (BJe) in an experimental model of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlazzo, N.; Cirmi, S.; Calapai, G.; Ventura-Spagnolo, E.; Gangemi, S.; Navarra, M. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Citrus bergamia Derivatives: Where Do We Stand? Molecules 2016, 21, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Algieri, C.; Bernardini, C.; Oppedisano, F.; La Mantia, D.; Trombetti, F.; Palma, E.; Forni, M.; Mollace, V.; Romeo, G.; Nesci, S. Mitochondria Bioenergetic Functions and Cell Metabolism Are Modulated by the Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction. Cells 2022, 11, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, E.; Salerno, R.; Martino, C.; Lascala, A.; La Russa, D.; Oliverio, M. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the proautophagic activity of Citrus flavonoids from Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction. Data Brief 2018, 19, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carresi, C.; Musolino, V.; Gliozzi, M.; Maiuolo, J.; Mollace, R.; Nucera, S.; Maretta, A.; Sergi, D.; Muscoli, S.; Gratteri, S.; et al. Anti-oxidant effect of bergamot polyphenolic fraction counteracts doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy: Role of autophagy and c-kit(pos)CD45(neg)CD31(neg) cardiac stem cell activation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 119, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, B.; Kroemer, G. Biological Functions of Autophagy Genes: A Disease Perspective. Cell 2019, 176, 11–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salerno, R.; Casale, F.; Calandruccio, C.; Procopio, A. Characterization of flavonoids in Citrus bergamia (Bergamot) polyphenolic fraction by liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry (LC/HRMS). Pharmanutrition 2016, 4, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, C.; Bernardini, C.; Oppedisano, F.; La Mantia, D.; Trombetti, F.; Palma, E.; Forni, M.; Mollace, V.; Romeo, G.; Troisio, I.; et al. The Impairment of Cell Metabolism by Cardiovascular Toxicity of Doxorubicin Is Reversed by Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction Treatment in Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, R.; Forte, M.; Cotugno, M.; Bianchi, F.; Marchitti, S.; Rubattu, S. Relevance of stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) in experimental and human stroke. Pflugers Arch. 2022, 474, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, G.; Berndt, S.; Ferratge, S.; Rasband, W.; Cuendet, M.; Uzan, G.; Albanese, P. Angiogenesis Analyzer for ImageJ—A comparative morphometric analysis of “Endothelial Tube Formation Assay” and “Fibrin Bead Assay”. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubattu, S.; Cotugno, M.; Bianchi, F.; Sironi, L.; Gelosa, P.; Stanzione, R.; Forte, M.; De Sanctis, C.; Madonna, M.; Marchitti, S.; et al. A differential expression of uncoupling protein-2 associates with renal damage in stroke-resistant spontaneously hypertensive rat/stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat-derived stroke congenic lines. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 1857–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Rubattu, S.; Savoia, C.; Venturelli, V.; Pagannonne, E.; Volpe, M. Endothelial dysfunction and stroke. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2001, 38 (Suppl. 2), S75–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, M.; Iaccarino, G.; Vecchione, C.; Rizzoni, D.; Russo, R.; Rubattu, S.; Condorelli, G.; Ganten, U.; Ganten, D.; Trimarco, B.; et al. Association and cosegregation of stroke with impaired endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in stroke prone, spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cosentino, F.; Volpe, M. Hypertension, stroke, and endothelium. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2005, 7, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Daidone, M.; Pinto, A. Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Ischemic Stroke Pathogenesis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4209–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollace, V.; Scicchitano, M.; Paone, S.; Casale, F.; Calandruccio, C.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Maiuolo, J.; Nucera, S.; et al. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipemic Effects of a New Lecithin Formulation of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction: A Double Blind, Randomized, Placebo- Controlled Study. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman, M.C.; Johnson, J.J. Clinical application of bergamot (Citrus bergamia) for reducing high cholesterol and cardiovascular disease markers. Integr. Food Nutr. Metab. 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perna, S.; Spadaccini, D.; Botteri, L.; Girometta, C.; Riva, A.; Allegrini, P.; Petrangolini, G.; Infantino, V.; Rondanelli, M. Efficacy of bergamot: From anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms to clinical applications as preventive agent for cardiovascular morbidity, skin diseases, and mood alterations. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forte, M.; Marchitti, S.; Cotugno, M.; Di Nonno, F.; Stanzione, R.; Bianchi, F.; Schirone, L.; Schiavon, S.; Vecchio, D.; Sarto, G.; et al. Trehalose, a natural disaccharide, reduces stroke occurrence in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 173, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, A.; Pandolfo, G.; Crucitti, M.; Cedro, C.; Zoccali, R.A.; Muscatello, M.R.A. Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction Supplementation Improves Cognitive Functioning in Schizophrenia: Data From an 8-Week, Open-Label Pilot Study. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 37, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, A.; Pandolfo, G.; Crucitti, M.; Cacciola, M.; Santoro, V.; Spina, E.; Zoccali, R.A.; Muscatello, M.R.A. Low-Dose of Bergamot-Derived Polyphenolic Fraction (BPF) Did Not Improve Metabolic Parameters in Second Generation Antipsychotics-Treated Patients: Results from a 60-days Open-Label Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bernardi, P.; Rasola, A.; Forte, M.; Lippe, G. The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel Formation by F-ATP Synthase, Integration in Signal Transduction, and Role in Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1111–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tressera-Rimbau, A.; Arranz, S.; Eder, M.; Vallverdu-Queralt, A. Dietary Polyphenols in the Prevention of Stroke. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7467962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scapagnini, G.; Vasto, S.; Abraham, N.G.; Caruso, C.; Zella, D.; Fabio, G. Modulation of Nrf2/ARE pathway by food polyphenols: A nutritional neuroprotective strategy for cognitive and neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 44, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollace, R.; Macri, R.; Tavernese, A.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Carresi, C.; Maiuolo, J.; Fini, M.; Volterrani, M.; Mollace, V. Comparative Effect of Bergamot Polyphenolic Fraction and Red Yeast Rice Extract in Rats Fed a Hyperlipidemic Diet: Role of Antioxidant Properties and PCSK9 Expression. Nutrients 2022, 14, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollace, V.; Ragusa, S.; Sacco, I.; Muscoli, C.; Sculco, F.; Visalli, V.; Palma, E.; Muscoli, S.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, P.; et al. The protective effect of bergamot oil extract on lecitine-like oxyLDL receptor-1 expression in balloon injury-related neointima formation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 13, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, P.P.; Patti, A.M.; Nikolic, D.; Giglio, R.V.; Castellino, G.; Biancucci, T.; Geraci, F.; David, S.; Montalto, G.; Rizvi, A.; et al. Bergamot Reduces Plasma Lipids, Atherogenic Small Dense LDL, and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Subjects with Moderate Hypercholesterolemia: A 6 Months Prospective Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanzione, R.; Forte, M.; Cotugno, M.; Oppedisano, F.; Carresi, C.; Marchitti, S.; Mollace, V.; Volpe, M.; Rubattu, S. Beneficial Effects of Citrus Bergamia Polyphenolic Fraction on Saline Load-Induced Injury in Primary Cerebral Endothelial Cells from the Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061334
Stanzione R, Forte M, Cotugno M, Oppedisano F, Carresi C, Marchitti S, Mollace V, Volpe M, Rubattu S. Beneficial Effects of Citrus Bergamia Polyphenolic Fraction on Saline Load-Induced Injury in Primary Cerebral Endothelial Cells from the Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model. Nutrients. 2023; 15(6):1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061334
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanzione, Rosita, Maurizio Forte, Maria Cotugno, Francesca Oppedisano, Cristina Carresi, Simona Marchitti, Vincenzo Mollace, Massimo Volpe, and Speranza Rubattu. 2023. "Beneficial Effects of Citrus Bergamia Polyphenolic Fraction on Saline Load-Induced Injury in Primary Cerebral Endothelial Cells from the Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model" Nutrients 15, no. 6: 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061334
APA StyleStanzione, R., Forte, M., Cotugno, M., Oppedisano, F., Carresi, C., Marchitti, S., Mollace, V., Volpe, M., & Rubattu, S. (2023). Beneficial Effects of Citrus Bergamia Polyphenolic Fraction on Saline Load-Induced Injury in Primary Cerebral Endothelial Cells from the Stroke-Prone Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat Model. Nutrients, 15(6), 1334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061334