Protective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid on TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of the SphK/S1P Signaling Pathway
Abstract
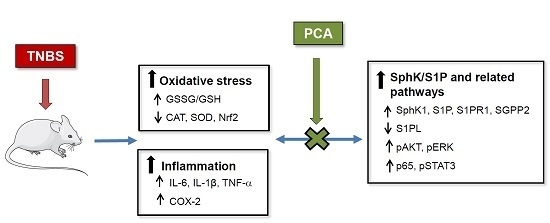
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments and Drug Treatment
2.2. Macroscopic and Microscopic Analysis
2.3. Tissue Myeloperoxidase Activity
2.4. GSH and GSSG Analysis
2.5. Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.8. Assay for S1P Levels
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 3PCA Ameliorates TNBS-Induced Colitis
3.2. PCA Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Increases Antioxidant Enzyme Expression
3.3. PCA Downregulates Expression of Proinflammatory Mediators
3.4. PCA Modulates SphK/S1P and Related Signaling Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAT | catalase |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| GSH | reduced glutathione |
| GSSG | oxidized glutathione |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| IL | interleukin |
| MPO | myeloperoxidase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| PCA | protocatechuic acid |
| S1P | sphingosine-1-phosphate |
| S1PL | S1P lyase |
| SGPP | S1P phosphatase |
| S1PR | S1P receptor |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| SphK | sphingosine kinase |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TNBS | 2,4,6 trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
References
- Loddo, I.; Romano, C. Inflammatory bowel disease: Genetics, epigenetics, and pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.H.; Saba, J.D. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated colon cancer: The fat’s in the fire. Transl. Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Sánchez, D.I.; González-Fernández, B.; Álvarez, M.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Melatonin inhibits the sphingosine kinase 1/sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling pathway in rabbits with fulminant hepatitis of viral origin. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fernández, B.; Sánchez, D.I.; Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Álvarez, M.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. Inhibition of the SphK1/S1P signaling pathway by melatonin in mice with liver fibrosis and human hepatic stellate cells. Biofactors 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degagné, E.; Pandurangan, A.; Bandhuvula, P.; Kumar, A.; Eltanawy, A.; Zhang, M.; Yoshinaga, Y.; Nefedov, M.; de Jong, P.J.; Fong, L.G.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase downregulation promotes colon carcinogenesis through STAT3-activated microRNAs. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5368–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Cabrera, P.J.; Brown, S.; Studer, S.M.; Rosen, H. S1P signaling: New therapies and opportunities. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vezza, T.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Algieri, F.; Utrilla, M.P.; Rodriguez-Cabezas, M.E.; Galvez, J. Flavonoids in inflammatory bowel disease: A review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdin, A.A. Targeting sphingosine kinase 1 (SphK1) and apoptosis by colon-specific delivery formula of resveratrol in treatment of experimental ulcerative colitis in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 718, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.K.; Rashid, R.; Fatima, N.; Mahmood, S.; Mir, S.; Khan, S.; Jabeen, N.; Murtaza, G. Pharmacological activities of protocatechuic acid. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2015, 72, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vari, R.; Archivio, M.D.; Filesi, C.; Carotenuto, S.; Scazzocchio, B.; Santangelo, C.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Protocatechuic acid induces antioxidant/detoxifying enzyme expression through JNK-mediated Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Wang, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, D.; Ling, W. Influence of intestinal microbiota on the catabolism of flavonoids in mice. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, H3026–H3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farombi, E.O.; Adedara, I.A.; Awoyemi, O.V.; Njoku, C.R.; Micah, G.O.; Esogwa, C.U.; Owumi, S.E.; Olopade, J.O. Dietary protocatechuic acid ameliorates dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis and hepatotoxicity in rats. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.P.; Beck, P.L.; Herridge, M.S.; Depew, W.T.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Wallace, J.L. Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the rat colon. Gastroenterology 1989, 96, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzmann, N.A.; Fillmann, H.; Mauriz, J.L.; Marroni, C.A.; Marroni, N.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Effects of glutamine on proinflammatory gene expression and activation of nuclear factor kappa B and signal transducers and activators of transcription in TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuñón, M.J.; San Miguel, B.; Crespo, I.; Jorquera, F.; Santamaría, E.; Álvarez, M.; Prieto, J.; González-Gallego, J. Melatonin attenuates apoptotic liver damage in fulminant hepatic failure induced by the rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 50, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Prause, C.; Marroni, N.; Cuevas, M.J.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Glutamine treatment attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in TNBS-induced colitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De David, C.; Rodrigues, G.; Bona, S.; Meurer, L.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J.; Marroni, N.P. Role of querectin in preventing thioacetamide-induced liver injury in rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 39, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Miguel, B.; Crespo, I.; Kretzmann, N.A.; Mauriz, J.L.; Marroni, N.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. Glutamine prevents fibrosis development in rats with colitis induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, A.J.; Kawamori, T.; Bradshaw, S.G.; Orr, K.A.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. A role for sphingosine kinase 1 in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, I.; Miguel, B.S.; Laliena, A.; Álvarez, M.; Culebras, J.M.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Melatonin prevents the decreased activity of antioxidant enzymes and activates nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 signaling in an animal model of fulminant hepatic failure of viral origin. J. Pineal. Res. 2010, 49, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, S.; Bais, S. A review on protocatechuic acid and its pharmacological potential. ISRN Pharmacol. 2014, 2014, 952943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.H.; Murakami, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ohigashi, H. Dietary rutin, but not its aglycone quercetin, ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice: Attenuation of pro-inflammatory gene expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, A.; Zhang, E.; Ding, L.; Mukherjee, S.; Wei, X.; Chou, G.; Wang, Z.T.; Mani, S. Protective effect of naringenin against experimental colitis via suppression of toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signalling. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, F.; Qian, C.; Guo, W.; Luo, Q.; Xu, Q.; Sun, Y. Inhibition of Th1/Th17 responses via suppression of STAT1 and STAT3 activation contributes to the amelioration of murine experimental colitis by a natural flavonoid glucoside icariin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 798–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, D.I.; González-Fernández, B.; San-Miguel, B.; de Urbina, J.O.; Crespo, I.; González-Gallego, J.; Tuñón, M.J. Melatonin prevents deregulation of the sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling pathway in a mouse model of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, R.; Figliuzzi, M.M.; Monteleone, G. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor: A novel therapeutic target in ulcerative colitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, M.; Ge, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, T.; Fang, L.; Xiao, Q.; Yin, D. Development of hydroxy-based sphingosine kinase inhibitors and anti-inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate induced colitis in mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3218–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Kim, E.Y.; Harikumar, K.B.; Yamada, A.; Huang, W.C.; Hait, N.C.; Allegood, J.C.; Price, M.M.; Avni, D.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate links persistent STAT3 activation, chronic intestinal inflammation, and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahashi, M.; Hait, N.C.; Maceyka, M.; Avni, D.; Takabe, K.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate in chronic intestinal inflammation and cancer. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2014, 54, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; de Haar, C.; Chen, M.; Deuring, J.; Gerrits, M.M.; Smits, R.; Xia, B.; Kuipers, E.J.; van der Woude, C.J. Disease-related expression of the IL6/STAT3/SOCS3 signalling pathway in ulcerative colitis and ulcerative colitis-related carcinogenesis. Gut 2010, 59, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popivanova, B.K.; Kitamura, K.; Wu, Y.; Kondo, T.; Kagaya, T.; Kaneko, S.; Oshima, M.; Fujii, C.; Mukaida, N. Blocking TNF-alpha in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with chronic colitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandurangan, A.K.; Mohebali, N.; Esa, N.M.; Looi, C.Y.; Ismail, S.; Saadatdoust, Z. Gallic acid suppresses inflammation in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice: Possible mechanisms. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandurangan, A.K.; Mohebali, N.; Hasanpourghadi, M.; Looi, C.Y.; Mustafa, M.R.; Mohd Esa, N. Boldine suppresses dextran sulfate sodium-induced mouse experimental colitis: NF-κB and IL-6/STAT3 as potential targets. Biofactors 2016, 42, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H; Banerjee, N.; Barnes, R.C.; Pfent, C.M.; Talcott, S.T.; Dashwood, R.H.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Mango polyphenolics reduce inflammation in intestinal colitis-involvement of the miR-126/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Carcinog.
- Xi, M.; Wang, X.; Ge, J.; Yin, D. N′-[(3-[benzyloxy]benzylidene]-3,4,5-trihydroxybenzohydrazide (1) protects mice against colitis induced by dextran sulfate sodium through inhibiting NFκB/IL-6/STAT3 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maines, L.W.; Fitzpatrick, L.R.; French, K.J.; Zhuang, Y.; Xia, Z.; Keller, S.N.; Upson, J.J.; Smith, C.D. Suppression of ulcerative colitis in mice by orally available inhibitors of sphingosine kinase. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 997–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshioka, K.; Takuwa, N. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in physiology and diseases. Biofactors 2012, 38, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Regmi, S.C.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, E.K.; Chang, J.H.; Ku, S.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.A. Protective effect of 7-O-succinyl macrolactin A against intestinal inflammation is mediated through PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR and NF-κB signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 735, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medicherla, K.; Ketkar, A.; Sahu, B.D.; Sudhakar, G.; Sistal, R. Rosmarinus officinalis extract ameliorates intestinal inflammation through MAP kinases/NF-κB signaling in murine model of acute experimental colitis. Food Funct. 2016, 13, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, Z.; Tan, W.; Wang, L.; Na, D.; Zhang, G.; Yin, A.; Huang, H.; Xia, D.; et al. Expression of the novel adipokine C1qTNF-related protein 4 (CTRP4) suppresses colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Liang, J.; Nagahashi, M.; Avni, D.; Yamada, A.; Maceyka, M.; Wolen, A.R.; Kordula, T.; Milstien, S.; Takabe, K.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphatase 2 promotes disruption of mucosal integrity, and contributes to ulcerative colitis in mice and humans. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2945–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechtcheriakova, D.; Wlachos, A.; Sobanov, J.; Kopp, T.; Reuschel, R.; Bornancin, F.; Cai, R.; Zemann, B.; Urtz, N.; Stingl, G.; et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate phosphatase 2 is induced during inflammatory responses. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crespo, I.; San-Miguel, B.; Mauriz, J.L.; Ortiz de Urbina, J.J.; Almar, M.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. Protective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid on TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of the SphK/S1P Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2017, 9, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030288
Crespo I, San-Miguel B, Mauriz JL, Ortiz de Urbina JJ, Almar M, Tuñón MJ, González-Gallego J. Protective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid on TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of the SphK/S1P Signaling Pathway. Nutrients. 2017; 9(3):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030288
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrespo, Irene, Beatriz San-Miguel, José Luis Mauriz, Juan José Ortiz de Urbina, Mar Almar, María Jesús Tuñón, and Javier González-Gallego. 2017. "Protective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid on TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of the SphK/S1P Signaling Pathway" Nutrients 9, no. 3: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030288
APA StyleCrespo, I., San-Miguel, B., Mauriz, J. L., Ortiz de Urbina, J. J., Almar, M., Tuñón, M. J., & González-Gallego, J. (2017). Protective Effect of Protocatechuic Acid on TNBS-Induced Colitis in Mice Is Associated with Modulation of the SphK/S1P Signaling Pathway. Nutrients, 9(3), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030288