A Complete Survey of Glycoalkaloids Using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a Commercial Variety and a Local Landrace of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and their Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition of Eggplant Extracts
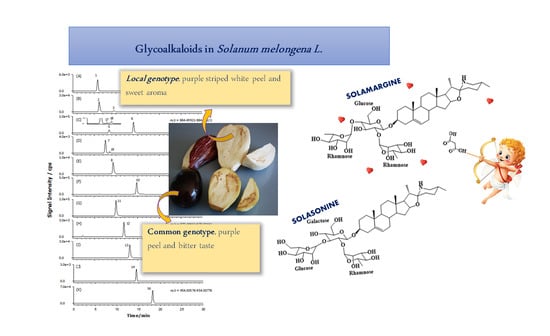
2.2. GAs Profile of S. melongena var. Mirabella Pulp Extracts
2.3. GAs Profile of Melanzana Bianca di Senise Pulp Extracts
2.4. Composition Profile of GAs in Solanum Melongena
2.5. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Activity of Eggplant GAs
2.6. Antioxidant Activity of Eggplant Extracts
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plant Material and Sample Preparation
4.3. Analysis of Glycoalkaloids (GAs)
4.4. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Inhibitory Activity
4.5. Antioxidant Activity
4.5.1. Radical Scavenging Activity
4.5.2. Inhibition of Lipid Peroxidation
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of United Nations (FAO). Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 9 March 2019).
- Marsic, N.K.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Stampar, F. Grafting Influences Phenolic Profile and Carpometric Traits of Fruits of Greenhouse-Grown Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10504–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Hu, Z.L.; Chu, G.H.; Huang, C.; Tian, S.B.; Zhao, Z.P.; Chen, G.P. Anthocyanin Accumulation and Molecular Analysis of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis-Associated Genes in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry and anticarcinogenic mechanisms of glycoalkaloids produced by eggplants, potatoes, and tomatoes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3323–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, S.; Daunay, M.; Pochard, E. Saponosides stéroïdiques de l’aubergine (Solanum melongena L.) I. Intérêt alimentaire, méthodologie d’analyse, localisation dans le fruit. Agronomie 1989, 9, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowański, S.; Adamski, Z.; Marciniak, P.; Rosiński, G.; Büyükgüzel, E.; Büyükgüzel, K.; Falabella, P.; Scrano, L.; Ventrella, E.; Lelario, F. A review of bioinsecticidal activity of Solanaceae alkaloids. Toxins 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Ijaz, S.; Mohammad, I.S.; Muhammad, K.S.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, H.M.S. Aglycone solanidine and solasodine derivatives: A natural approach towards cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, S.E.; Brunton, N.P.; Jones, P.W.; O’Brien, N.M.; Collins, S.G.; Maguire, A.R. Bioactivities of Glycoalkaloids and Their Aglycones from Solanum Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 3454–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Luo, X.; Xu, P.; Chen, L. In Vivo Toxicity of Solasonine and Its Effects on cyp450 Family Gene Expression in the Livers of Male Mice from Four Strains. Toxins 2018, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekry, M.I.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salama, M.M.; Alshehri, O.Y.; Al-Abd, A.M. Bioactive glycoalkaloides isolated from Solanum melongena fruit peels with potential anticancer properties against hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spochacz, M.; Chowański, S.; Szymczak, M.; Lelario, F.; Bufo, S.; Adamski, Z. Sublethal Effects of Solanum nigrum Fruit Extract and Its Pure Glycoalkaloids on the Physiology of Tenebrio molitor (Mealworm). Toxins 2018, 10, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidelis, Q.C.; Faraone, I.; Russo, D.; Aragao Catunda, F.E., Jr.; Vignola, L.; de Carvalho, M.G.; de Tommasi, N.; Milella, L. Chemical and Biological insights of Ouratea hexasperma (A. St.-Hil.) Baill.: A source of bioactive compounds with multifunctional properties. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Malafronte, N.; Frescura, D.; Imbrenda, G.; Faraone, I.; Milella, L.; Fernandez, E.; De Tommasi, N. Antioxidant activities and quali-quantitative analysis of different Smallanthus sonchifolius [(Poepp. and Endl.) H. Robinson] landrace extracts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, W.; Vinke, J.; Scheffer, J. Steroidal glycoalkaloids in tubers and leaves of Solanum species used in potato breeding. Euphytica 1988, 39, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.B.; Meyer, R.S.; Whitaker, B.D.; Litt, A.; Kennelly, E.J. A new liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based strategy to integrate chemistry, morphology, and evolution of eggplant (Solanum) species. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1314, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docimo, T.; Francese, G.; De Palma, M.; Mennella, D.; Toppino, L.; Lo Scalzo, R.; Mennella, G.; Tucci, M. Insights in the fruit flesh browning mechanisms in Solanum melongena genetic lines with opposite postcut behavior. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4675–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, G.; Cahill, M.G.; Vittori, S.; James, K.J. Liquid Chromatography–Hybrid Linear Ion Trap–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LTQ-Orbitrap) Method for the Determination of Glycoalkaloids and Their Aglycons in Potato Samples. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, J.; Laakso, I.; Vaananen, T.; Kuronen, P.; Huopalahti, R.; Pehu, E. Determination of solanidine- and tomatidine-type glycoalkaloid aglycons by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2738–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Mata, M.C.; Yokoyama, W.E.; Hong, Y.J.; Prohens, J. Alpha-solasonine and alpha-solamargine contents of gboma (Solanum macrocarpon L.) and scarlet (Solanum aethiopicum L.) eggplants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5502–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, R.; Navarre, D.A. LC-MS analysis of solanidane glycoalkaloid diversity among tubers of four wild potato species and three cultivars (Solanum tuberosum). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6949–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotelo, A.; Serrano, B. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of the glycoalkaloids alpha-solanine and alpha-chaconine in 12 commercial varieties of Mexican potato. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2472–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, M.; Van den Heuvel, H.; Chen, S.; Derrick, P.J.; Mellon, F.A.; Price, K.R. Comparison of high-and low-energy collision-induced dissociation tandem mass spectrometry in the analysis of glycoalkaloids and their aglycons. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1996, 7, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zywicki, B.; Catchpole, G.; Draper, J.; Fiehn, O. Comparison of rapid liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry methods for determination of glycoalkaloids in transgenic field-grown potatoes. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 336, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agneta, R.; Rivelli, A.R.; Ventrella, E.; Lelario, F.; Sarli, G.; Bufo, S.A. Investigation of glucosinolate profile and qualitative aspects in sprouts and roots of horseradish (Armoracia rusticana) using LC-ESI–hybrid linear ion trap with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry and infrared multiphoton dissociation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7474–7482. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, G.; Lelario, F.; Battista, F.G.; Bufo, S.A.; Cataldi, T.R. Identification of glucosinolates in capers by LC-ESI-hybrid linear ion trap with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-LTQ-FTICR MS) and infrared multiphoton dissociation. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelario, F.; Bianco, G.; Bufo, S.A.; Cataldi, T.R.I. Establishing the occurrence of major and minor glucosinolates in Brassicaceae by LC-ESI-hybrid linear ion-trap and Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 2012, 73, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelario, F.; Labella, C.; Napolitano, G.; Scrano, L.; Bufo, S.A. Fragmentation study of major spirosolane-type glycoalkaloids by collision-induced dissociation linear ion trap and infrared multiphoton dissociation Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 2395–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldi, T.R.; Lelario, F.; Bufo, S.A. Analysis of tomato glycoalkaloids by liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 3103–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agneta, R.; Lelario, F.; De Maria, S.; Möllers, C.; Bufo, S.A.; Rivelli, A.R. Glucosinolate profile and distribution among plant tissues and phenological stages of field-grown horseradish. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.T.; Liang, X.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Peng, X.L.; Guo, X.J.; Zhao, L.S. Rapid separation and identification of 31 major saponins in Shizhu ginseng by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electron spray ionization-MS/MS. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Nakamura, S.; Ozaki, K.; Kumahara, A.; Morikawa, T.; Matsuda, H. Structures of steroidal alkaloid oligoglycosides, robeneosides A and B, and antidiabetogenic constituents from the Brazilian medicinal plant Solanum lycocarpum. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Chen, M.H.; Liu, C.J. Nucleocytoplasmic-localized acyltransferases catalyze the malonylation of 7-O-glycosidic (iso)flavones in Medicago truncatula. Plant J. 2008, 55, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiling, S.; Schuman, M.C.; Schoettner, M.; Mukerjee, P.; Berger, B.; Schneider, B.; Jassbi, A.R.; Baldwin, I.T. Jasmonate and ppHsystemin Regulate Key Malonylation Steps in the Biosynthesis of 17-Hydroxygeranyllinalool Diterpene Glycosides, an Abundant and Effective Direct Defense against Herbivores in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jassbi, A.R.; Zamanizadehnajari, S.; Baldwin, I.T. 17-Hydroxygeranyllinalool glycosides are major resistance traits of Nicotiana obtusifolia against attack from tobacco hornworm larvae. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, G.; Ubukata, T.; Nozue, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; Takahi, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Hayashida, N. Malonylation is a key reaction in the metabolism of xenobiotic phenolic glucosides in Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant J. 2010, 63, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuhara, K.; Shimizu, K.; Kubo, I. Arudonine, an allelopathic steroidal glycoalkaloid from the root bark of Solanum arundo Mattei. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, A.; Santamaria, P. Biodiversity in vegetable crops, a heritage to save: The case of Puglia region. Ital. J. Agron. 2013, 8, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, K.; Laghetti, G. Genetic erosion—Examples from Italy. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2005, 52, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, M.; Vilanova, S.; Plazas, M.; Gramazio, P.; Andujar, I.; Herraiz, F.J.; Castro, A.; Prohens, J. Enhancing conservation and use of local vegetable landraces: The Almagro eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) case study. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2014, 61, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Soukara, S.; Vasilopoulou, E. Traditional foods: A science and society perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roddick, J.G. The acetylcholinesterase-inhibitory activity of steroidal glycoalkaloids and their aglycones. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2631–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucha, L.; Tomsik, P. The Steroidal Glycoalkaloids from Solanaceae: Toxic Effect, Antitumour Activity and Mechanism of Action. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mensinga, T.T.; Sips, A.J.A.M.; Rompelberg, C.J.M.; Van Twillert, K.; Meulenbelt, J.; Van Den Top, H.J.; Van Egmond, H.P. Potato glycoalkaloids and adverse effects in humans: An ascending dose study. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 41, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, L.; Russo, D.; Cetera, P.; Milella, L. Effects of thermo-vacuum treatment on secondary metabolite content and antioxidant activity of poplar (Populus nigra L.) wood extracts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, D.; Bonomo, M.; Salzano, G.; Martelli, G.; Milella, L. Nutraceutical properties of Citrus clementina juices. Pharmacologyonline 2012, 1, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Saltos, M.B.V.; Puente, B.F.N.; Milella, L.; De Tommasi, N.; Dal Piaz, F.; Braca, A. Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Phenolics from Bidens humilis. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Peak Number | Common Name | Molecular Formulae | Monoisotopic Exact Value [M+H]+ (m/z) (Δm) a | Retention Time (Rt, min) | Genotype |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Solanidenetriol chacotriose | C45H71NO16 | 882.48456 (−0.4) | 5.6 | Mir, Sen |
| 2 | Solanidenediol chacotriose | C45H71NO15 | 866.48965 (0.5) | 6.0 | Mir, Sen |
| 3 | Dehydrosolamargine | C45H71NO15 | 866.48965 (−0.2) | 9.2 | Mir, Sen |
| 4 | Solanandaine isomer I | C45H73NO16 | 884.50021 (0.4) | 7.0 | Mir, / |
| 5 | Solanandaine | C45H73NO16 | 884.50021 (−0.4) | 8.2 | Mir, Sen |
| 6 | Solasonine (spirosolenol solatriose) | C45H73NO16 | 884.50021 (−0.2) | 13.6 | Mir, Sen |
| 7 | Robenoside B (solanidenediol chacotriose) | C45H73NO17 | 900.49513 (0.6) | 7.3 | Mir, Sen |
| 8 | Malonyl- solanidenediol chacotriose | C48H73NO18 | 952.49004 (−0.5) | 9.5 | Mir, Sen |
| 9 | Solamargine Isomer (spirosolenol chacotriose) | C45H73NO15 | 868.50530 (1.2) | 7.6 | Mir, / |
| 10 | Solamargine (spirosolenol chacotriose) | C45H73NO15 | 868.50530 (1.3) | 14.3 | Mir, Sen |
| 11 | Solanidatetraenol chacotriose | C45H67NO15 | 862.45835 (0.3) | 9.7 | Mir, Sen |
| 12 | Malonyl-solanandaine | C48H76NO19 | 970.50061 (0.7) | 11.9 | Mir, Sen |
| 13 | Malonyl- solanidatetraenol chacotriose | C48H69NO18 | 948.45874 (−0.9) | 13.4 | Mir, Sen |
| 14 | Arudonine | C50H82NO19 | 1000.54756 (0.2) | 14.1 | Mir, Sen |
| 15 | Malonyl-solamargine isomer | C48H76NO18 | 954.50569 (1.2) 954.50569 (−0.5) | 11.3 | Mir, / |
| 16 | Malonyl-solamargine | C48H76NO18 | 18.5 | Mir, Sen | |
| 17 | Solanandaine Isomer II (spirosolendiol chacotriose) | C45H73NO16 | 884.50021 (−0.9) | 9.5 | Mir, Sen |
| 18 | Solanandaine Isomer III (spirosolendiol chacotriose) | C45H73NO16 | 884.50021 (−0.3) | 10.1 | Mir, Sen |
| 19 | Robenoside B Isomer (solanidenediol chacotriose) | C45H73NO17 | 900.49513 (1.3) | 8.6 | /Sen |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lelario, F.; De Maria, S.; Rivelli, A.R.; Russo, D.; Milella, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L. A Complete Survey of Glycoalkaloids Using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a Commercial Variety and a Local Landrace of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and their Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities. Toxins 2019, 11, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040230
Lelario F, De Maria S, Rivelli AR, Russo D, Milella L, Bufo SA, Scrano L. A Complete Survey of Glycoalkaloids Using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a Commercial Variety and a Local Landrace of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and their Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities. Toxins. 2019; 11(4):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040230
Chicago/Turabian StyleLelario, Filomena, Susanna De Maria, Anna Rita Rivelli, Daniela Russo, Luigi Milella, Sabino Aurelio Bufo, and Laura Scrano. 2019. "A Complete Survey of Glycoalkaloids Using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a Commercial Variety and a Local Landrace of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and their Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities" Toxins 11, no. 4: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040230
APA StyleLelario, F., De Maria, S., Rivelli, A. R., Russo, D., Milella, L., Bufo, S. A., & Scrano, L. (2019). A Complete Survey of Glycoalkaloids Using LC-FTICR-MS and IRMPD in a Commercial Variety and a Local Landrace of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and their Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities. Toxins, 11(4), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11040230