Removal of Positively Buoyant Planktothrix rubescens in Lake Restoration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Floc and Sink Experiment—Ballast Dose
2.2. Floc and Sink Experiment—Cyanobacteria Concentration
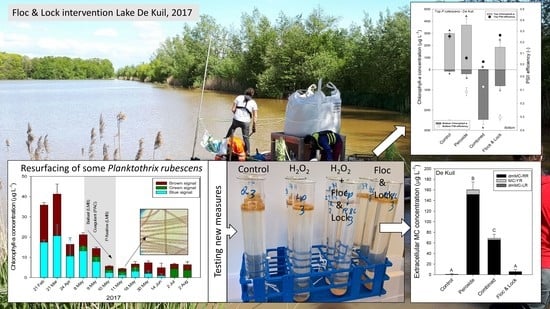
2.3. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on P. rubescens
2.4. Efficacy of a Combined Hydrogen Peroxide and Floc and Sink Treatment on P. rubescens
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Floc and Sink Experiment—Ballast Dose
5.2. Floc and Sink Experiment—Cyanobacteria Concentration
5.3. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on P. rubescens
5.4. Efficacy of a Combined Hydrogen Peroxide and Floc and Sink Treatment on P. rubescens
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B

References
- Downing, J.A. Limnology and oceanography: Two estranged twins reuniting by global change. Inland Waters 2014, 4, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, V.; Tilman, G.; Nekola, J. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Paul, V.J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1349–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.-O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Michalak, A.M.; Balaji, V. Eutrophication will increase during the 21st century as a result of precipitation changes. Science 2017, 357, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Neil, J.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Kronvang, B.; Meerhoff, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Hansen, K.M.; Andersen, H.E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Liboriussen, L.; Beklioglu, M.; Özen, A.; et al. Climate Change Effects on Runoff, Catchment Phosphorus Loading and Lake Ecological State, and Potential Adaptations. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1930–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, J.J.; DelSontro, T.; Downing, J.A. Eutrophication will increase methane emissions from lakes and impoundments during the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OECD. Diffuse Pollution, Degraded Waters; OECD: Paris, France, 2017; ISBN 9789264269057. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, D.P.; Salmaso, N.; Paerl, H.W. Mitigating harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Strategies for control of nitrogen and phosphorus loads. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Joyner, A.R.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Qin, B.; Scott, J.T. Mitigating cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems impacted by climate change and anthropogenic nutrients. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WWAP. United Nations World Water Assessment Programme the United Nations World Water Development Report 2017; Wastewater: Paris, France, 2017.
- OECD. Water Governance in the Netherlands: Fit for the Future? OECD: Paris, France, 2014; ISBN 9789264208940. [Google Scholar]
- Fastner, J.; Abella, S.; Litt, A.; Morabito, G.; Vörös, L.; Pálffy, K.; Straile, D.; Kümmerlin, R.; Matthews, D.; Phillips, M.G.; et al. Combating cyanobacterial proliferation by avoiding or treating inflows with high P load—experiences from eight case studies. Aquat. Ecol. 2015, 50, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cullen, P.; Forsberg, C. Experiences with reducing point sources of phosphorus to lakes. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, D.W.; Ansems, N.; Kukkadapu, R.K.; Jaisi, D.; Orihel, D.M.; Cade-Menun, B.J.; Hu, Y.; Wiklund, J.; Hall, R.I.; Chessell, H.; et al. Changes in Sedimentary Phosphorus Burial Following Artificial Eutrophication of Lake 227, Experimental Lakes Area, Ontario, Canada. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2020, 125, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Mackay, E.; Reitzel, K.; Spears, B.M. Editorial—A critical perspective on geo-engineering for eutrophication management in lakes. Water Res. 2016, 97, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvie, H.P.; Sharpley, A.N.; Spears, B.; Buda, A.R.; May, L.; Kleinman, P.J.A. Water Quality Remediation Faces Unprecedented Challenges from “Legacy Phosphorus”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8997–8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyette, J.-O.; Bennett, E.M.; Maranger, R. Low buffering capacity and slow recovery of anthropogenic phosphorus pollution in watersheds. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Mucci, M. Mitigating eutrophication nuisance: In-lake measures are becoming inevitable in eutrophic waters in the Netherlands. Hydrobiololgia 2020, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Van Oosterhout, F. Controlling eutrophication by combined bloom precipitation and sediment phosphorus inactivation. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6527–6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oosterhout, F.; Waajen, G.; Yasseri, S.; Marinho, M.M.; Noyma, N.P.; Mucci, M.; Douglas, G.; Waajen, M.L.G. Lanthanum in Water, Sediment, Macrophytes and chironomid larvae following application of Lanthanum modified bentonite to lake Rauwbraken (The Netherlands). Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 706, 135–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Kang, L.; Mucci, M.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Noyma, N.P.; Miranda, M.; Huszar, V.L.; Waajen, G.; Marinho, M.M. Coagulation and precipitation of cyanobacterial blooms. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waajen, G.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Douglas, G.; Lürling, M. Management of eutrophication in Lake De Kuil (The Netherlands) using combined flocculant—Lanthanum modified bentonite treatment. Water Res. 2016, 97, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, M.; Waajen, G.; van Oosterhout, F.; Yasseri, S.; Lürling, M. Whole lake application PAC-Phoslock treatment to manage eutrophication and cyanobacterial bloom. Inland Waters. (under review).
- Noyma, N.P.; De Magalhães, L.; Furtado, L.L.; Mucci, M.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Huszar, V.L.; Marinho, M.M.; Lürling, M. Controlling cyanobacterial blooms through effective flocculation and sedimentation with combined use of flocculants and phosphorus adsorbing natural soil and modified clay. Water Res. 2016, 97, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyma, N.P.; De Magalhães, L.; Miranda, M.; Mucci, M.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Marinho, M.M.; Lima, E.R.A.; Lürling, M. Coagulant plus ballast technique provides a rapid mitigation of cyanobacterial nuisance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Noyma, N.; Pacheco, F.S.; De Magalhães, L.; Pinto, E.; Santos, S.; Soares, M.F.A.; Huszar, V.L.; Lürling, M.; Marinho, M.M. The efficiency of combined coagulant and ballast to remove harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a tropical shallow system. Harmful Algae 2017, 65, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lucena-Silva, D.; Molozzi, J.; Severiano, J.D.S.; Becker, V.; Barbosa, J.E.D.L. Removal efficiency of phosphorus, cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins by the “flock & sink” mitigation technique in semi-arid eutrophic waters. Water Res. 2019, 159, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Magalhães, L.; Noyma, N.P.; Furtado, L.L.; Drummond, E.; Leite, V.B.G.; Mucci, M.; Van Oosterhout, F.; Huszar, V.L.D.M.; Lürling, M.; Marinho, M.M. Managing Eutrophication in a Tropical Brackish Water Lagoon: Testing Lanthanum-Modified Clay and Coagulant for Internal Load Reduction and Cyanobacteria Bloom Removal. Estuar. Coast. 2019, 42, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häder, D.P. Photomovement; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 1984; pp. 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Gorczyca, B.; Ganczarczyk, J. Fractal Analysis of Pore Distributions in Alum Coagulation and Activated Sludge Flocs. Water Qual. Res. J. 2001, 36, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromkamp, J.C.; Domin, A.; Dubinsky, Z.; Lehmann, C.; Schanz, F. Changes in photosynthetic properties measured by oxygen evolution and variable chlorophyll fluorescence in a simulated entrainment experiment with the cyanobacterium Planktothrix rubescens. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 63, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhaus, L.; Briand, J.; Leboulanger, C.; Jacquet, S.; Humbert, J.F. Comparative effects of the quality and quantity of light and temperature on the growth of Planktothrix agardhii and P. rubescens. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, R.J.; A Hill, D.R.; Gladman, B. A comparative study of the coagulation behaviour of marine microalgae. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2012, 24, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Qin, H.; Li, Y. An integrated method for removal of harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijs, H.C.; Visser, P.M.; Reeze, B.; Meeuse, J.; Slot, P.C.; Wijn, G.; Talens, R.; Huisman, J. Selective suppression of harmful cyanobacteria in an entire lake with hydrogen peroxide. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1460–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauzá, L.; Aguilera, A.; Echenique, R.; Andrinolo, D.; Giannuzzi, L. Application of Hydrogen Peroxide to the Control of Eutrophic Lake Systems in Laboratory Assays. Toxins 2014, 6, 2657–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziga, D.; Tokodi, N.; Drobac, D.; Kokociński, M.; Antosiak, A.; Puchalski, J.; Strzałka, W.; Madej, M.; Svirčev, Z.; Meriluoto, J.; et al. The Effect of a Combined Hydrogen Peroxide-MlrA Treatment on the Phytoplankton Community and Microcystin Concentrations in a Mesocosm Experiment in Lake Ludoš. Toxins 2019, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lusty, M.W.; Gobler, C.J. The Efficacy of Hydrogen Peroxide in Mitigating Cyanobacterial Blooms and Altering Microbial Communities across Four Lakes in NY, USA. Toxins 2020, 12, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijs, H.C.P.; Jančula, D.; Visser, P.M.; Maršálek, B. Existing and emerging cyanocidal compounds: New perspectives for cyanobacterial bloom mitigation. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dziallas, C.; Grossart, H.-P. Increasing Oxygen Radicals and Water Temperature Select for Toxic Microcystis sp. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drábková, M.; Admiraal, W.; Maršálek, B. Combined Exposure to Hydrogen Peroxide and Light Selective Effects on Cyanobacteria, Green Algae, and Diatoms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drábková, M.; Matthijs, H.C.P.; Admiraal, W.; Marsalek, B. Selective effects of H2O2 on cyanobacterial photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 2007, 45, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piel, T.; Sandrini, G.; White, E.; Xu, T.; Schuurmans, J.M.; Huisman, J.; Visser, P.M. Suppressing Cyanobacteria with Hydrogen Peroxide Is More Effective at High Light Intensities. Toxins 2019, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastien, C.; Cardin, R.; Veilleux, É.; Deblois, C.; Warren, A.; Laurion, I. Performance evaluation of phycocyanin probes for the monitoring of cyanobacteria. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L. Chitosan kills bacteria through cell membrane damage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 95, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Meng, D.; Faassen, E. Effects of Hydrogen Peroxide and Ultrasound on Biomass Reduction and Toxin Release in the Cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins 2014, 6, 3260–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laughinghouse, H.; Lefler, F.W.; Berthold, D.E.; Bishop, W.M. Sorption of dissolved microcystin using lanthanum-modified bentonite clay. J. Aquat. Plant Manag. 2020, 58, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Qian, J.; Hou, J.; Ao, Y.; Wu, B. The performance of chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite during the flocculation and floc storage processes of Microcystis aeruginosa cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11148–11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oosterhout, F.; Yasseri, S.; Noyma, N.; Huszar, V.; Marinho, M.M.; Mucci, M.; Waajen, G.; Lurling, M. Evaluation of a whole lake eutrophication management technique using combined flocculation and in-situ phosphorus immobilization. Inland Waters. (under review).
- Lürling, M.; Faassen, E.J. Dog Poisonings Associated with a Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom in the Netherlands. Toxins 2013, 5, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Zhang, W.; Mei, J. A Data Grid System Oriented Biologic Data. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conferences on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology—Workshops, Silicon Valley, CA, USA, 5–12 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, M.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Meyer, B.; Moldaenke, C.; Lüring, C.; Meyerhöfer, M.; Hansen, U.-P.; Dau, H. A fluorometric method for the differentiation of algal populations in vivo and in situ. Photosynth. Res. 2002, 72, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lürling, M.; Mucci, M.; Waajen, G. Removal of Positively Buoyant Planktothrix rubescens in Lake Restoration. Toxins 2020, 12, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110700
Lürling M, Mucci M, Waajen G. Removal of Positively Buoyant Planktothrix rubescens in Lake Restoration. Toxins. 2020; 12(11):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110700
Chicago/Turabian StyleLürling, Miquel, Maíra Mucci, and Guido Waajen. 2020. "Removal of Positively Buoyant Planktothrix rubescens in Lake Restoration" Toxins 12, no. 11: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110700
APA StyleLürling, M., Mucci, M., & Waajen, G. (2020). Removal of Positively Buoyant Planktothrix rubescens in Lake Restoration. Toxins, 12(11), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110700