Screening Snake Venoms for Toxicity to Tetrahymena Pyriformis Revealed Anti-Protozoan Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
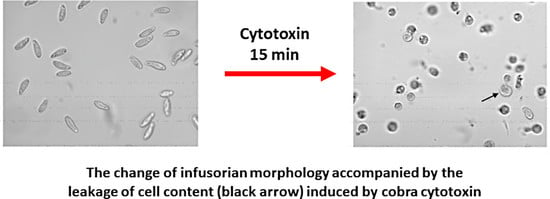
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Snake Venoms
5.2. Anti-Protozoan Activity Measurements
5.3. Venom Fractionation
5.4. Mass Spectrometry and Peptide Mass Fingerprinting
5.5. Microscopy
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Utkin, Y.N. Toxicity of venoms from vipers of Pelias group to crickets Gryllus assimilis and its relation to snake entomophagy. Toxicon 2007, 49, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.P.; Barlow, A.; Wuster, W. Venom lethality and diet: Differential responses of natural prey and model organisms to the venom of the saw-scaled vipers (Echis). Toxicon 2012, 59, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviola, A.J.; Gandara, A.J.; Bryson, R.W., Jr.; Mackessy, S.P. Venom phenotypes of the rock rattlesnake (Crotalus lepidus) and the ridge-nosed rattlesnake (Crotalus willardi) from México and the United States. Toxicon 2017, 138, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal Samy, R.; Pachiappan, A.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Thwin, M.M.; Hian, Y.E.; Chow, V.T.; Bow, H.; Weng, J.T. In vitro antimicrobial activity of natural toxins and animal venoms tested against Burkholderia pseudomallei. BMC Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, B.L.; Santos, D.O.; Dos Santos, A.L.; Rodrigues, C.R.; de Freitas, C.C.; Cabral, L.M.; Castro, H.C. Comparative analysis of Viperidae venoms antibacterial profile: A short communication for proteomics. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2001, 2011, 960267. [Google Scholar]
- Nevalainen, T.J.; Graham, G.G.; Scott, K.F. Antibacterial actions of secreted phospholipases A2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okubo, B.M.; Silva, O.N.; Migliolo, L.; Gomes, D.G.; Porto, W.F.; Batista, C.L.; Ramos, C.S.; Holanda, H.H.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L.; et al. Evaluation of an antimicrobial L-amino acid oxidase and peptide derivatives from Bothropoides mattogrosensis pitviper venom. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Barros, E.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Cardoso, M.H.; Santos, N.C.; Franco, O.L.; Cândido, E.S. Snake venom cathelicidins as natural antimicrobial peptides. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinohara, L.; de Freitas, S.F.; da Silva, R.J.; Guimaraes, S. In vitro effects of Crotalus durissus terrificus and Bothrops jararaca venoms on Giardia duodenalis trophozoites. Parasitol. Res. 2006, 98, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adade, C.M.; Cons, B.L.; Melo, P.A.; Souto-Padron, T. Effect of Crotalus viridis viridis snake venom on the ultrastructure and intracellular survival of Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasitology 2011, 138, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ghosh, P.; De, T.; Gomes, A.; Gomes, A.; Dungdung, S.R. In vivo and in vitro antileishmanial activity of Bungarus caeruleus snake venom through alteration of immunomodulatory activity. Experim. Parasitol. 2013, 135, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, N.; Shahbazzadeh, D.; Maleki, F.; Aghdasi, M.; Tabatabaie, F.; Khanaliha, K. The in vitro study of anti-leishmanial effect of Naja naja oxiana snake venom on Leishmania major. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martos Esteban, A.; Carrington, M.; Laustsen, A.H. Harnessing snake venoms to make T. brucei forever go to sleep. Toxicon 2018, 150, 320–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allane, D.; Oussedik-Oumehdi, H.; Harrat, Z.; Seve, M.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Isolation and characterization of an anti-leishmanial disintegrin from Cerastes cerastes venom. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, H.W.; Dawe, D.L. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Cryptocaryon irritans (phylum Ciliophora). In Fish Diseases and Disorders; Woo, P.T.K., Leatherland, J.F., Eds.; CAB International: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 116–153. [Google Scholar]
- Coyne, R.S.; Hannick, L.; Shanmugam, D.; Hostetler, J.B.; Brami, D.; Joardar, V.S.; Johnson, J.; Radune, D.; Singh, I.; Badger, J.H.; et al. Comparative genomics of the pathogenic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, its free-living relatives and a host species provide insights into adoption of a parasitic lifestyle and prospects for disease control. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharon, G.; Leibowitz, M.P.; Chettri, J.K.; Isakov, N.; Zilberg, D.J. Disease in wildlife or exotic species. Comparative study of infection with Tetrahymena of different ornamental fish species. Comp. Path. 2014, 150, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrofsky, K.M.; Schech, J.M.; Sheppard, B.J.; Obenschain, C.A.; Chin, A.M.; Kacergis, M.C.; Laver, E.R.; Bartholomew, J.L.; Fox, J.G. High mortality due to Tetrahymena sp. infection in laboratory-maintained zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Comp. Med. 2002, 52, 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvant, M.; Pepin, D.; Piccinni, E. Tetrahymena pyriformis: A tool for toxicological studies: A review. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 1631–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilberg, D.; Sinai, T. Optimization and validation of a colorimetric assay for Tetrahymena sp. survival. Res. Microbiol. 2006, 157, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshina, O.N.; Kozlov, L.V.; Cheremnykh, E.G. A universal method for measuring functional activity of complement in humans, laboratory, domestic, and agricultural animals, amphibians, and birds. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 157, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.C.; Figueira, M.M.; Lopes, D.S.; De Souza, D.L.; Izidoro, L.F.; Ferro, E.A.; Souza, M.A.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Yoneyama, K.A. BnSP-7 toxin, a basic phospholipase A2 from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom, interferes with proliferation, ultrastructure and infectivity of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis. Parasitology 2013, 140, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, L.M.; Junior, R.J.; Silva, D.A.; Mineo, J.R.; Vieira, C.U.; Teixeira, D.N.; Homsi-Brandeburgo, M.I.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Hamaguchi, A. Toxoplasma gondii: Effects of neuwiedase, a metalloproteinase from Bothrops neuwiedi snake venom, on the invasion and replication of human fibroblasts in vitro. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 120, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempone, A.G.; Andrade, H.F., Jr.; Spencer, P.J.; Lourenco, C.O.; Rogero, J.R.; Nascimento, N. Bothrops moojeni venom kills Leishmania spp. with hydrogen peroxide generated by its L-amino acid oxidase. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gomez, R.; Zerrouk, H.; Sebti, F.; Loyens, M.; Benslimane, A.; Ouaissi, M.A. Growth inhibition of Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania donovani infantum by different snake venoms: Preliminary identification of proteins from Cerastes cerastes venom which interact with the parasites. Toxicon 1994, 32, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, M.K.; Fung, S.Y.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H. Proteomic characterization of venom of the medically important Southeast Asian Naja sumatrana (Equatorial spitting cobra). Acta Trop. 2014, 133, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, H.P.; Tan, K.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Tan, C.H. Exploring the diversity and novelty of toxin genes in Naja sumatrana, the equatorial spitting cobra from Malaysia through de novo venom-gland transcriptomics. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubovskii, P.V.; Lesovoy, D.M.; Dubinnyi, M.A.; Konshina, A.G.; Utkin, Y.N.; Efremov, R.G.; Arseniev, A.S. Interaction of three-finger toxins with phospholipid membranes: Comparison of S- and P-type cytotoxins. Biochem. J. 2005, 387, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofanov, A.V.; Sharonov, G.V.; Dubinnyi, M.A.; Astapova, M.V.; Kudelina, I.A.; Dubovskii, P.V.; Rodionov, D.I.; Utkin, Y.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Comparative study of structure and activity of cytotoxins from venom of the cobras Naja oxiana, Naja kaouthia, and Naja haje. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2004, 69, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, A.V.; Astapova, M.V.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. The first representative of glycosylated three-fingered toxins. Cytotoxin from the Naja kaouthia cobra venom. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, K.Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Hseu, Y.C.; Vyas, A.A.; Rule, G.S.; Wu, W. Two distinct types of cardiotoxin as revealed by the structure and activity relationship of their interaction with zwitterionic phospholipid dispersions. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14473–14483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gasanov, S.E.; Shrivastava, I.H.; Israilov, F.S.; Kim, A.A.; Rylova, K.A.; Zhang, B.; Dagda, R.K. Naja naja oxiana Cobra Venom Cytotoxins CTI and CTII Disrupt Mitochondrial Membrane Integrity: Implications for Basic Three-Fingered Cytotoxins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Primor, N.; Sabnay, I.; Lave, V.; Zlotkin, E. Toxicity to fish, effect on gill ATPase and gill ultrastructural changes induced by Pardachirus secretion and its derived toxin pardaxin. J. Exptl. Zool. 1980, 211, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feofanov, A.V.; Sharonov, G.V.; Astapova, M.V.; Rodionov, D.I.; Utkin, Y.N.; Arseniev, A.S. Cancer cell injury by cytotoxins from cobra venom is mediated through lysosomal damage. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazanova, A.S.; Zavada, L.L.; Starkov, V.G.; Kovyazina, I.V.; Subbotina, T.F.; Kostyukhina, E.E.; Dementieva, I.N.; Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Utkin, Y.N. Heterodimeric neurotoxic phospholipases A2—The first proteins from venom of recently established species Vipera nikolskii: Implication of venom composition in viper systematics. Toxicon 2008, 51, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.V.; Siniavin, A.E.; Hoang, A.N.; Le, M.T.T.; Pham, C.D.; Phung, T.V.; Nguyen, K.C.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Weng, C.F.; et al. Phospholipase A2 from krait Bungarus fasciatus venom induces human cancer cell death in vitro. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, I.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Cheng, A.C.; Starkov, V.; Osipov, A.; Nikitin, I.; Makarova, Y.; Ziganshin, R.; Utkin, Y. cDNA cloning, structural, and functional analyses of venom phospholipases A2 and a Kunitz-type protease inhibitor from steppe viper Vipera ursinii renardi. Toxicon 2011, 57, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Species | Venom Concentration, mg/mL | Time to Death 50% of Ciliates, min |
|---|---|---|
| N. nigricollis | 0.33 | 1.75 |
| N. sumatrana | 0.33 | 2.5 |
| N. naja | 0.33 | 6.6 |
| N. kaouthia | 0.33 | 14.0 |
| N. oxiana | 1.61 | 2.5 |
| N. nivea | 1.61 | 9.6 |
| N. melanoleuca | 1.61 | 18.0 |
| Toxin | Toxin Type | Time to Death 50% of Ciliates, min |
|---|---|---|
| CX2 N. oxiana | P-type | 1.5 |
| NSIV-11-3 | P-type | 2.0 |
| CX3 N. kaouthia | S-type | 2.3 |
| CX1 N. oxiana | S-type | 5.4 |
| NSIV-10-1 | S-type | 17.5 |
| NSIV-11-1 | n.d. | 8.5 |
| NSIV-11-2 | n.d. | 5.8 |
| Molecular Masses, Da | Position in the Sequence | Amino Acid Sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Determined | Calculated | ||||
| NsIV-10-1 | NsIV-11-1 | Cytotoxin 2C | Cardiotoxin 5A | ||
| 576.15 | 576.13 | 576.28 | 13–18 | TCPAGK | |
| No signal | 598.25 | 598.40 | 32–36 | VPVKR | |
| 605.22 | 605.20 | 605.34 | 1–5 | LKCNK | |
| 640.18 | 640.16 | 640.32 | 19–23 | NLCYK | |
| No signal | 646.26 | 646.41 | 45–50 | SSLLVK | |
| 834.27 | 834.22 | 834.38 | 37–44 | GCIDVCPK | |
| 879.43 | 879.38 | 879.53 | 6–12 | LVPLFYK | |
| No signal | 940.30 | 940.46 | 24–31 | MYMVATPK | |
| 973.25 | 973.23 | 973.39 | 51–58 | YVCCNDTR | |
| 1190.27 | 1190.23 | 1190.44 | 51–60 | YVCCNDTRCN | |
| 1365.57 | No signal | 1365.73 | 24–35 | MFMVSNLTVPVK | |
| 1521.65 | No signal | 1521.83 | 24–36 | MFMVSNLTVPVKR | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuleshina, O.N.; Kruykova, E.V.; Cheremnykh, E.G.; Kozlov, L.V.; Andreeva, T.V.; Starkov, V.G.; Osipov, A.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N. Screening Snake Venoms for Toxicity to Tetrahymena Pyriformis Revealed Anti-Protozoan Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050325
Kuleshina ON, Kruykova EV, Cheremnykh EG, Kozlov LV, Andreeva TV, Starkov VG, Osipov AV, Ziganshin RH, Tsetlin VI, Utkin YN. Screening Snake Venoms for Toxicity to Tetrahymena Pyriformis Revealed Anti-Protozoan Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins. Toxins. 2020; 12(5):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050325
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuleshina, Olga N., Elena V. Kruykova, Elena G. Cheremnykh, Leonid V. Kozlov, Tatyana V. Andreeva, Vladislav G. Starkov, Alexey V. Osipov, Rustam H. Ziganshin, Victor I. Tsetlin, and Yuri N. Utkin. 2020. "Screening Snake Venoms for Toxicity to Tetrahymena Pyriformis Revealed Anti-Protozoan Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins" Toxins 12, no. 5: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050325
APA StyleKuleshina, O. N., Kruykova, E. V., Cheremnykh, E. G., Kozlov, L. V., Andreeva, T. V., Starkov, V. G., Osipov, A. V., Ziganshin, R. H., Tsetlin, V. I., & Utkin, Y. N. (2020). Screening Snake Venoms for Toxicity to Tetrahymena Pyriformis Revealed Anti-Protozoan Activity of Cobra Cytotoxins. Toxins, 12(5), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12050325