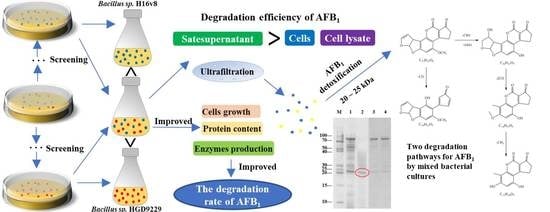
Co-Cultivation of Two Bacillus Strains for Improved Cell Growth and Enzyme Production to Enhance the Degradation of Aflatoxin B1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening of Microbial Strains for AFB1 Degradation
2.2. Degradation of AFB1 by Mixed Bacterial Cultures
2.3. Effect of AFB1 Detoxification with Mixed Bacterial Cultures
2.4. Degradation of AFB1 by Culture Supernatant, Bacterial Cells, and Cell Lysate
2.5. Effects of AFB1 Degradation by the Supernatant with Heat Treatment and Proteinase K
2.6. Effects of AFB1 Degradation by the Supernatant with Different Metal Ions, pH, and Temperature
2.7. Effect of Detoxification Time on AFB1 Degradation Rate
2.8. Determination of the Molecular Weight Range for the Effective Enzymes
2.9. Degradation Pathways of AFB1 by Enzymes from the Mixed Cultures
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Medium
4.2. Isolations of AFB1-Degrading Bacteria
4.2.1. Bacteria Isolations
4.2.2. Molecular Identification of the Isolates
4.3. Tests of AFB1 Degradation
4.4. AFB1 Degradation by Mixed Bacterial Cultures
4.5. AFB1 Degradation by Cells, Culture Supernatant, and Cell Lysate
4.6. The Effects of Heat Treatment, Proteinase K, Metal Ions, Temperature, and pH on AFB1 Degradation by the Supernatant
4.7. Active Fraction of SDS Polyacrylamide Electrophoresis
4.8. Structures of Degradation Products of AFB1 treated by Detoxifying Enzymes Treatment
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caceres, I.; Khoury, A.; Khoury, R.; Lorber, S.; Oswald, I.; Khoury, A.; Atoui, A.; Puel, O.; Bailly, J. Aflatoxin biosynthesis and genetic regulation: A review. Toxins 2020, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emadi, A.; Jayedi, A.; Mirmohammadkhani, M.; Abdolshahi, A. Aflatoxin reduction in nuts by roasting, irradiation and fumigation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lv, A.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Cai, J.; Hu, Y. Insight into the global regulation of laeA in Aspergillus flavus based on proteomic profiling. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 284, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushing, B.; Selim, M. Aflatoxin B1: A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food, occupational exposure, and detoxification methods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, P.; Taehoon, L.; Mok, C. Effect of corona discharge plasma jet treatment on the degradation of aflatoxin B1 on glass slides and in spiked food commodities. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 124, 108333. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Guan, S.; Gao, X.; Ma, Q.; Lei, Y.; Bai, X.; Ji, C. Preparation, purification and characteristics of an aflatoxin degradation enzyme from Myxococcus fulvus ANSM068. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, H.; Das, C.; Mishra, H.; Das, C. A Review on Biological Control and Metabolism of Aflatoxin A Review on Biological Control and Metabolism of Aflatoxin. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 43, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Shen, X.; Jain, R.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, Q. Synthesis of chemicals by metabolic engineering of microbes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3760–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ji, X.; Huang, H. Biotechnological applications of Yarrowia lipolytica: Past, present and future. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1522–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, R.; Kirksey, J. Aflatoxin G1 metabolism by Rhizopus species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1971, 19, 222–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.; Njobeh, P.; Mavumengwana, V. Degradation and detoxification of AFB1 by Staphylocococcus warneri, Sporosarcina sp. and Lysinibacillus fusiformis. Food Control 2016, 68, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; Bosch, F.; Troxell, T.; Bolger, P. Reducing liver cancer-Global control of aflatoxin. Science 1999, 286, 2453–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teniola, O.; Addo, P.; Brost, I.; Färber, P.; Jany, K.; Alberts, J.; Van Zyl, W.; Steyn, P.; Holzapfel, W. Degradation of aflatoxin B1 by cell-free extracts of Rhodococcus erythropolis and Mycobacterium fluoranthenivorans sp. nov. DSM44556T. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, M.; Shi, Z.; Ghassempour, A.; Sedaghat, N.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Mirabolfathy, M.; Javan-Nikkhah, M. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by Bacillus subtilis UTBSP1 isolated from pistachio nuts of Iran. Food Control 2012, 23, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.; Engelbrecht, Y.; Steyn, P.; Holzapfel, W.; van Zyl, W. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by Rhodococcus erythropolis cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.; Sivaramakrishna, A.; Mehta, A. Degradation and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by Pseudomonas putida. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2014, 86, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yao, D.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Song, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, L. Production, purification, and characterization of an intracellular aflatoxin-detoxifizyme from Armillariella tabescens E-20. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2001, 39, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ogata, M.; Hirai, H.; Kawagishi, H. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by manganese peroxidase from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK-624. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2011, 314, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C.; Shen, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, R. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by salt tolerant Tetragenococcus halophilus CGMCC 3792. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mao, H.; Hu, C.; Tron, T.; Lin, J.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Molecular docking studies and in vitro degradation of four aflatoxins AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, and AFG2 by a recombinant laccase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; Jackson, C.; Tattersall, D.; French, N.; Peat, T.; Newman, J.; Briggs, L.; Lapalikar, G.; Campbell, P.; Scott, C.; et al. Identification and characterization of two families of F420H2-dependent reductases from Mycobacteria that catalyse aflatoxin degradation. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yehia, R. Aflatoxin detoxification by manganese peroxidase purified from Pleurotus ostreatus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Lu, F.; Jian, H.; Tan, C.; Yao, D.; Xie, C.; Liu, D. The furofuran-ring selectivity, hydrogen peroxide-production and low Km value are the three elements for highly effective detoxification of aflatoxin oxidase. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, Q. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for microbial synthesis of monolignols. Metab. Eng. 2017, 39, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xing, X.; Liu, M. Production of multienzymes consisting of alkaline amylase and cellulase by mixed alkalophilic culture and their potential use in the saccharification of sweet potato. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 19, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, D.; Lyu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Guo, P.; Cui, Z. Effective degradation of aflatoxin B1 using a novel thermophilic microbial consortium TADC7. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksha Rao, K.; Vipin, A.; Hariprasad, P.; Anu Appaiah, K.; Venkateswaran, G. Biological detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 by Bacillus licheniformis CFR1. Food Control 2017, 71, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.; Njobeh, P.; Sidu, S.; Tlou, M.; Mavumengwana, V. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by liquid cultures and lysates of three bacterial strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 233, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Garba, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, P. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus subtilis strain with aflatoxin B1 biodegradation capability. Food Control 2017, 75, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangare, L.; Zhao, Y.; Folly, Y.M.E.; Chang, J.; Li, J.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Xing, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Aflatoxin B₁ degradation by a Pseudomonas strain. Toxins 2014, 6, 3028–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Ji, C.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Ma, Q.; Niu, T. Aflatoxin B1 degradation by Stenotrophomonas maltophilia and other microbes selected using coumarin medium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Xue, B.; Li, M.; Mu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Shan, A. Screening a strain of Aspergillus niger and optimization of fermentation conditions for degradation of aflatoxin B₁. Toxins 2014, 6, 3157–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ahmed, M.; Sangare, L.; Zhao, Y.; Selvaraj, J.; Xing, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Novel aflatoxin-degrading enzyme from bacillus shackletonii L7. Toxins 2017, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, D.; Brackett, R. The influence of divalent cations and chelators on aflatoxin B1 degradation by Flavobacterium aurantiacum. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, L.; Fang, H. Mixed culture of recombinant Trichoderma reesei and Aspergillus niger for cellulase production to increase the cellulose degrading capability. Biomass Bioenergy. 2018, 112, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyani, D.; Lee, K.; Kim, T.; Li, J.; Dhiman, S.; Kang, Y.; Lee, J. Microbial consortia for saccharification of woody biomass and ethanol fermentation. Fuel 2013, 107, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metreveli, E.; Kachlishvili, E.; Singer, S.; Elisashvili, V. Alteration of white-rot basidiomycetes cellulase and xylanase activities in the submerged co-cultivation and optimization of enzyme production by Irpex lacteus and Schizophyllum commune. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Lan, J.; Duan, C.; Ma, Q.; Feng, J. Predominance of Trichoderma and Penicillium in cellulolytic aerobic filamentous fungi from subtropical and tropical forests in China, and their use in finding highly efficient β-glucosidase. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2014, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Chandra, R. Characterisation of manganese peroxidase and laccase producing bacteria capable for degradation of sucrose glutamic acid-Maillard reaction products at different nutritional and environmental conditions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Huang, H.; Ouyang, P. Microbial 2,3-butanediol production: A state-of-the-art review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Wei, Z. Degradation of bamboo-shoot shell powder by a fungal consortium: Changes in chemical composition and physical structure. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 116, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilova, I.; Krastanov, A. Overproduction of laccase and pectinase by microbial associations in solid substrate fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2008, 149, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; van den Brink, J.; Gruben, B.; Wösten, H.; Gu, J.; de Vries, R. Improved enzyme production by co-cultivation of Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae and with other fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Xie, F.; Xue, X.; Wang, Z.; Fan, B.; Ha, Y. Structure elucidation and toxicity analyses of the radiolytic products of aflatoxin B1 in methanol-water solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iram, W.; Anjum, T.; Iqbal, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas, M. Mass spectrometric identification and toxicity assessment of degraded products of aflatoxin B1 and B2 by Corymbia citriodora aqueous extracts. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Structure elucidation and toxicity analyses of the degradation products of aflatoxin B1 by aqueous ozone. Food Control 2013, 31, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Cooper, B.; Stroshine, R.; Ileleji, K.; Keener, K. Structures of Degradation Products and Degradation Pathways of Aflatoxin B1 by High-Voltage Atmospheric Cold Plasma HVACP Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6222–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanano, A.; Almousally, I.; Shaban, M. Exposure of Aspergillus flavus NRRL 3357 to the Environmental Toxin, 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorinated Dibenzo- p -Dioxin, Results in a Hyper Aflatoxicogenic Phenotype: A Possible Role for Caleosin/Peroxygenase (AfPXG). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amirkhizi, B.; Arefhosseini, S.R.; Ansarin, M.; Nemati, M. Aflatoxin B1 in eggs and chicken livers by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2015, 8, 245–249. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, G.; Joshua, C.; He, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, R.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Q. Furfural tolerance and detoxification mechanism in Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Zhu, K. Polymerization of wheat gluten and the changes of glutenin macropolymer (GMP) during the production of Chinese steamed bread. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L. The relationship between typhoon features and fine particulate matter: Events in Metropolitan Taipei. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 139, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Strain | Degradation (%)/0.1 mg <10 kDa 1 | Degradation (%)/0.1 mg 10–30 kDa 2 | Degradation (%)/0.1 mg >30 kDa 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| H16v8 | 2.9 ± 0.31 | 20.8 ± 0.61 | 2.6 ± 0.21 |
| HGD9229 | 3.2 ± 0.22 | 21.3 ± 0.46 | 2.8 ± 0.32 |
| Mixed cultures | 4.1 ± 0.15 | 24.5 ± 0.52 | 2.7 ± 0.25 |
| Strain | <10 kDa (mg/mL) 1 | 10–30 kDa (mg/mL) 2 | >30 kDa (mg/mL) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| H16v8 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.28 ± 0.02 |
| HGD9229 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.35 ± 0.02 |
| Mixed cultures | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.03 |
| Strain | Protein Concentration (mg/mL) | Degradation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Bacillus sp. H16v8 | 0.7 ± 0.03 | 58.4% ± 0.87 |
| Bacillus sp. HGD9229 | 0.8 ± 0.04 | 60.1% ± 0.83 |
| Mixed bacteria | 1.2 ± 0.02 | 85.2% ± 1.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Sha, Y.; Yin, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, J. Co-Cultivation of Two Bacillus Strains for Improved Cell Growth and Enzyme Production to Enhance the Degradation of Aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2021, 13, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070435
Wang L, Huang W, Sha Y, Yin H, Liang Y, Wang X, Shen Y, Wu X, Wu D, Wang J. Co-Cultivation of Two Bacillus Strains for Improved Cell Growth and Enzyme Production to Enhance the Degradation of Aflatoxin B1. Toxins. 2021; 13(7):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070435
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Le, Wei Huang, Yu Sha, Haicheng Yin, Ying Liang, Xin Wang, Yan Shen, Xingquan Wu, Dapeng Wu, and Jinshui Wang. 2021. "Co-Cultivation of Two Bacillus Strains for Improved Cell Growth and Enzyme Production to Enhance the Degradation of Aflatoxin B1" Toxins 13, no. 7: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070435
APA StyleWang, L., Huang, W., Sha, Y., Yin, H., Liang, Y., Wang, X., Shen, Y., Wu, X., Wu, D., & Wang, J. (2021). Co-Cultivation of Two Bacillus Strains for Improved Cell Growth and Enzyme Production to Enhance the Degradation of Aflatoxin B1. Toxins, 13(7), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13070435