Molecular Basis for Mambalgin-2 Interaction with Heterotrimeric α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channels in Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Modeling of the Mambalgin-2 Complexes with the ASIC1a and α-ENaC/ASIC1/γ-ENaC Channels
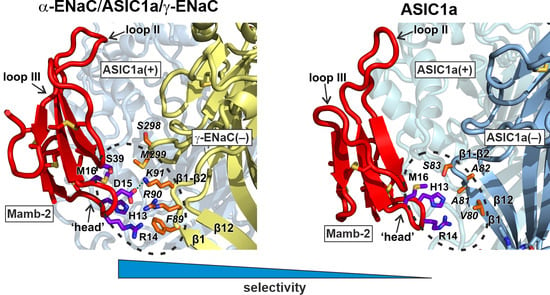
2.2. Mambalgin-2 Interacts More Extensively with the Complementary γ-ENaC(−)-Subunit as Compared with ASIC1(−)
2.3. Interaction with γ-ENaC(−) Determines the High Inhibitory Activity of Mamb-2 at α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Heterotrimers
2.4. Mamb-2 “Head” Mutations Diminish Its Inhibitory Activity at the α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channel but Not at ASIC1a Channel
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Computer Modeling Methods
5.1.1. Molecular Dynamics Calculations
5.1.2. Contacts Analysis
5.2. Recombinant Mambalgin-2 and Its Mutants Production
5.3. Electrophysiological Recordings in X. laevis Oocytes
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Putnam, R.W. 22—Intracellular pH Regulation. In Cell Physiology Source Book, 3rd ed.; Sperelakis, N., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 357–372. ISBN 978-0-12-656976-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dratkiewicz, E.; Simiczyjew, A.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Ziętek, M.; Matkowski, R.; Nowak, D. Hypoxia and Extracellular Acidification as Drivers of Melanoma Progression and Drug Resistance. Cells 2021, 10, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, I.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Acidic Tumor Microenvironment in Human Melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Raghunand, N.; Karczmar, G.S.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. MRI of the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 16, 430–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerweck, L.E.; Seetharaman, K. Cellular pH Gradient in Tumor versus Normal Tissue: Potential Exploitation for the Treatment of Cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland, A.B.; Wu, Q.; Heddleston, J.M.; Choudhary, G.S.; MacSwords, J.; Lathia, J.D.; McLendon, R.; Lindner, D.; Sloan, A.; Rich, J.N. Acidic Stress Promotes a Glioma Stem Cell Phenotype. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Kallinowski, F.; Okunieff, P. Blood Flow, Oxygen and Nutrient Supply, and Metabolic Microenvironment of Human Tumors: A Review. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 6449–6465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Maas, L.; Veith, C.; Van Schooten, F.J.; Godschalk, R.W. Acidic Cellular Microenvironment Modifies Carcinogen-Induced DNA Damage and Repair. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2425–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellenberger, S.; Schild, L. Epithelial Sodium Channel/Degenerin Family of Ion Channels: A Variety of Functions for a Shared Structure. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 735–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellenberger, S.; Schild, L. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCI. Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels and the Epithelial Na+ Channel. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wemmie, J.A.; Taugher, R.J.; Kreple, C.J. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels in Pain and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Lee, W.; Clark, E.; Bartoszewski, R.; McNicholas, C.M.; Latham, C.B.; Bebok, Z.; Parpura, V.; Fuller, C.M.; Palmer, C.A.; et al. Interaction of ASIC1 and ENaC Subunits in Human Glioma Cells and Rat Astrocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C1246–C1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.; Bartoszewski, R.; Qadri, Y.J.; Bebok, Z.; Bubien, J.K.; Fuller, C.M.; Benos, D.J. Knockdown of ASIC1 and Epithelial Sodium Channel Subunits Inhibits Glioblastoma Whole Cell Current and Cell Migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24526–24541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Wu, B.; Leng, T.; Zhu, L.; Xiong, Z. Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1 (ASIC1) Mediates Weak Acid-Induced Migration of Human Malignant Glioma Cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 997–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, C.; Ye, Q.-H.; Yuan, F.-L.; Gu, Y.-L.; Li, J.-P.; Shi, Y.-H.; Shen, X.-M.; Liu, B.; Lin, Z.-H. Involvement of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1α in Hepatic Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Deng, S.-C.; Deng, S.-J.; He, C.; Li, X.; Chen, J.-Y.; Jin, Y.; Hu, Z.-L.; Wang, F.; et al. ASIC1 and ASIC3 Contribute to Acidity-Induced EMT of Pancreatic Cancer through Activating Ca2+/RhoA Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xu, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; Qi, L.; Qian, H.; et al. Involvement of Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a in Gastric Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Ho, T.-T.; Ding, X.; Mo, Y.-Y. ERK-Mediated NF-κB Activation through ASIC1 in Response to Acidosis. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harguindey, S.; Stanciu, D.; Devesa, J.; Alfarouk, K.; Cardone, R.A.; Polo Orozco, J.D.; Devesa, P.; Rauch, C.; Orive, G.; Anitua, E.; et al. Cellular Acidification as a New Approach to Cancer Treatment and to the Understanding and Therapeutics of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 43, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Khasanov, T.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Kozlov, S.A. Animal, Herb, and Microbial Toxins for Structural and Pharmacological Study of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullinan, M.M.; Klipp, R.C.; Bankston, J.R. Regulation of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels by Protein Binding Partners. Channels 2021, 15, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyman, T.R.; Eaton, D.C. Regulating ENaC’s Gate. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C150–C162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanukoglu, I. ASIC and ENaC Type Sodium Channels: Conformational States and the Structures of the Ion Selectivity Filters. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trac, P.T.; Thai, T.L.; Linck, V.; Zou, L.; Greenlee, M.; Yue, Q.; Al-Khalili, O.; Alli, A.A.; Eaton, A.F.; Eaton, D.C. Alveolar Nonselective Channels Are ASIC1a/α-ENaC Channels and Contribute to AFC. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L797–L811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarikova, A.V.; Bychkov, M.L.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Chubinskiy-Nadezhdin, V.I.; Shlepova, O.V.; Shulepko, M.A.; Koshelev, S.G.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Mambalgin-2 Inhibits Lung Adenocarcinoma Growth and Migration by Selective Interaction with ASIC1/α-ENaC/γ-ENaC Heterotrimer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 904742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.C.; Singh, R.; Asters, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pabbidi, M.R.; Watabe, K.; Mo, Y.-Y. Regulation of Breast Tumorigenesis through Acid Sensors. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4102–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, B.; Xiong, Q.-J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Huang, D.-K.; Wu, W.-N. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels Contribute to the Effect of Extracellular Acidosis on Proliferation and Migration of A549 Cells. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, L.-L.; Xu, S.-G.; Ji, H.-L.; Li, X.-M. ENaC/DEG in Tumor Development and Progression. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Ji, H.-L.; Li, X. Potential Roles of Amiloride-Sensitive Sodium Channels in Cancer Development. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2190216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, N.; Gao, J.; Liang, J.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tang, X. ASIC1a Stimulates the Resistance of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Promoting EMT via the AKT/GSK3β/Snail Pathway Driven by TGFβ/Smad Signals. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 2777–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooj, A.K.; McNicholas, C.M.; Bartoszewski, R.; Bebok, Z.; Benos, D.J.; Fuller, C.M. Glioma-Specific Cation Conductance Regulates Migration and Cell Cycle Progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4053–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Salinas, M.; Douguet, D.; Scarzello, S.; Dabert-Gay, A.-S.; Debayle, D.; Friend, V.; Alloui, A.; Lazdunski, M.; et al. Black Mamba Venom Peptides Target Acid-Sensing Ion Channels to Abolish Pain. Nature 2012, 490, 552–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Shulepko, M.A.; Vasileva, V.Y.; Sudarikova, A.V.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. ASIC1a Inhibitor Mambalgin-2 Suppresses the Growth of Leukemia Cells by Cell Cycle Arrest. Acta Naturae 2020, 12, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bychkov, M.; Shulepko, M.; Osmakov, D.; Andreev, Y.; Sudarikova, A.; Vasileva, V.; Pavlyukov, M.S.; Latyshev, Y.A.; Potapov, A.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.; et al. Mambalgin-2 Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Glioma Cells via Interaction with ASIC1a. Cancers 2020, 12, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Kirichenko, A.V.; Shulepko, M.A.; Mikhaylova, I.N.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Mambalgin-2 Inhibits Growth, Migration, and Invasion of Metastatic Melanoma Cells by Targeting the Channels Containing an ASIC1a Subunit Whose Up-Regulation Correlates with Poor Survival Prognosis. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noreng, S.; Bharadwaj, A.; Posert, R.; Yoshioka, C.; Baconguis, I. Structure of the Human Epithelial Sodium Channel by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Elife 2018, 7, e39340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Wen, M.; Shi, P.; Wang, T.; Pan, M.; Chang, S.; et al. Structural Insights into Human Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibition by Snake Toxin Mambalgin1. Elife 2020, 9, e57096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, M.; Kessler, P.; Douguet, D.; Sarraf, D.; Tonali, N.; Thai, R.; Servent, D.; Lingueglia, E. Mambalgin-1 Pain-Relieving Peptide Locks the Hinge between A4 and A5 Helices to Inhibit Rat Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadi, M.; Anyango, S.; Deshpande, M.; Nair, S.; Natassia, C.; Yordanova, G.; Yuan, D.; Stroe, O.; Wood, G.; Laydon, A.; et al. AlphaFold Protein Structure Database: Massively Expanding the Structural Coverage of Protein-Sequence Space with High-Accuracy Models. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D439–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mernea, M.; Ulăreanu, R.Ș.; Cucu, D.; Al-Saedi, J.H.; Pop, C.-E.; Fendrihan, S.; Anghelescu, G.D.C.; Mihăilescu, D.F. Epithelial Sodium Channel Inhibition by Amiloride Addressed with THz Spectroscopy and Molecular Modeling. Molecules 2022, 27, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Patel, D.S.; Ståhle, J.; Park, S.-J.; Kern, N.R.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Valvano, M.A.; Holst, O.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder for Complex Biological Membrane Simulations with Glycolipids and Lipoglycans. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-J.; Lee, J.; Qi, Y.; Kern, N.R.; Lee, H.S.; Jo, S.; Joung, I.; Joo, K.; Lee, J.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI Glycan Modeler for Modeling and Simulation of Carbohydrates and Glycoconjugates. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, A.; Maigret, B.; Hoflack, J.; Gomes, J.N.; Scheraga, H.A. Contribution of Unusual Arginine-Arginine Short-Range Interactions to Stabilization and Recognition in Proteins. J. Protein Chem. 1994, 13, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemmie, J.A.; Price, M.P.; Welsh, M.J. Acid-Sensing Ion Channels: Advances, Questions and Therapeutic Opportunities. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilyeva, N.A.; Loktyushov, E.V.; Bychkov, M.L.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Lyukmanova, E.N. Three-Finger Proteins from the Ly6/uPAR Family: Functional Diversity within One Structural Motif. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 1702–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourier, G.; Salinas, M.; Kessler, P.; Stura, E.A.; Leblanc, M.; Tepshi, L.; Besson, T.; Diochot, S.; Baron, A.; Douguet, D.; et al. Mambalgin-1 Pain-Relieving Peptide, Stepwise Solid-Phase Synthesis, Crystal Structure, and Functional Domain for Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a Inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2616–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Taylor, P.; Marchot, P. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition by Fasciculin: Crystal Structure of the Complex. Cell 1995, 83, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Liu, C.Z.; Joiner, W.J. Structural Analysis and Deletion Mutagenesis Define Regions of QUIVER/SLEEPLESS That Are Responsible for Interactions with Shaker-Type Potassium Channels and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, M.L.; Shulepko, M.A.; Shlepova, O.V.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Chulina, I.A.; Paramonov, A.S.; Baidakova, L.K.; Azev, V.N.; Koshelev, S.G.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; et al. SLURP-1 Controls Growth and Migration of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells, Forming a Complex With A7-nAChR and PDGFR/EGFR Heterodimer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 739391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Schulga, A.A.; Ermolyuk, Y.S.; Mordvintsev, D.Y.; Utkin, Y.N.; Shoulepko, M.A.; Hogg, R.C.; Bertrand, D.; Dolgikh, D.A.; et al. Bacterial Expression, NMR, and Electrophysiology Analysis of Chimeric Short/Long-Chain α-Neurotoxins Acting on Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24784–24791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Chesnokov, Y.M.; Zaigraev, M.M.; Chugunov, A.O.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Kocharovskaya, M.V.; Paramonov, A.S.; Bychkov, M.L.; Shulepko, M.A.; Nolde, D.E.; et al. Membrane-Mediated Interaction of Non-Conventional Snake Three-Finger Toxins with Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesovoy, D.M.; Bocharov, E.V.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Kosinsky, Y.A.; Shulepko, M.A.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Efremov, R.G.; Arseniev, A.S. Specific Membrane Binding of Neurotoxin II Can Facilitate Its Delivery to Acetylcholine Receptor. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, N.; Yoshioka, C.; Gouaux, E. Gating Mechanisms of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels. Nature 2018, 555, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Sheng, S.; Kleyman, T.R. Extracellular Intersubunit Interactions Modulate Epithelial Na+ Channel Gating. J. Biol Chem. 2023, 299, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winarski, K.L.; Sheng, N.; Chen, J.; Kleyman, T.R.; Sheng, S. Extracellular Allosteric Regulatory Subdomain within the Gamma Subunit of the Epithelial Na+ Channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 26088–26096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashlan, O.B.; Kleyman, T.R. ENaC Structure and Function in the Wake of a Resolved Structure of a Family Member. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2011, 301, F684–F696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36m: An Improved Force Field for Folded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.M.; MacKerell, A.D.; Reuter, N. Cation-π Interactions between Methylated Ammonium Groups and Tryptophan in the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernetti, M.; Bussi, G. Pressure Control Using Stochastic Cell Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 114107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical Sampling through Velocity Rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic Transitions in Single Crystals: A New Molecular Dynamics Method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, N.A.; Efremov, R.G. Libxtc: An Efficient Library for Reading XTC-Compressed MD Trajectory Data. BMC Res. Notes 2021, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrkov, T.V.; Chugunov, A.O.; Krylov, N.A.; Nolde, D.E.; Efremov, R.G. PLATINUM: A Web Tool for Analysis of Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Organization of Biomolecular Complexes. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1201–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmakov, D.I.; Koshelev, S.G.; Palikov, V.A.; Palikova, Y.A.; Shaykhutdinova, E.R.; Dyachenko, I.A.; Andreev, Y.A.; Kozlov, S.A. Alkaloid Lindoldhamine Inhibits Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1a and Reveals Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Toxins 2019, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Mambalgin-2 | γ-ENaC(–) | ASIC1a(–) |
|---|---|---|
| H13 | F89 (M) | A81 (M) |
| R90 (M) | ||
| K91 (M) | ||
| R14 | F89 (M) | V80 (M) |
| R90 (M) | A81 (M) | |
| K91 (M) | ||
| D15 | K91 (I, H, M) | |
| M16 | K91 (M) | A81 (M) |
| S298 (M) | A82 (M) | |
| M299 (M) | S83 (M) | |
| S39 | K91 (M) |
| γ-ENaC | IC50, nM | Bottom | nH |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 130 ± 20 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 1.6 ± 0.4 |
| F89A | 150 ± 20 n.s. | 0.14 ± 0.03 n.s. | 2.5 ± 0.7 n.s. |
| R90A | 250 ± 60 **** | 0.18 ± 0.07 n.s. | 1.8 ± 0.6 n.s. |
| K91A | 190 ± 30 ** | 0.26 ± 0.05 n.s. | 2.1 ± 0.6 n.s. |
| Mambalgin-2 Mutation | IC50, nM | Bottom | nH |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 130 ± 20 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | −1.6 ± 0.4 |
| H13A | 350 ± 60 **** | 0.07 ± 0.05 n.s. | −1.4 ± 0.3 n.s. |
| R14A | 200 ± 20 **** | 0.10 ± 0.04 n.s. | −2.2 ± 0.3 * |
| D15A | 230 ± 30 **** | 0.09 ± 0.05 n.s. | −2.0 ± 0.4 n.s. |
| R14A/D15A | 220 ± 40 **** | 0.03 ± 0.08 n.s. | −1.2 ± 0.2 n.s. |
| Mambalgin-2 Mutation | IC50, nM | Bottom | nH |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 310 ± 60 | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 2.9 ± 1.5 |
| H13A | 510 ± 1500 n.s. | 0.28 ± 0.05 ** | 1.5 ± 0.4 * |
| R14A | 250 ± 300 n.s. | 0.44 ± 0.07 n.s. | 1.7 ± 0.9 n.s. |
| D15A | 300 ± 400 n.s. | 0.42 ± 0.06 n.s. | 1.0 ± 0.35 ** |
| R14A/D15A | 470 ± 70 n.s. | 0.13 ± 0.05 **** | 1.9 ± 0.4 n.s. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyukmanova, E.N.; Zaigraev, M.M.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Isaev, A.B.; Kukushkin, I.D.; Bychkov, M.L.; Shulepko, M.A.; Chugunov, A.O.; Kirpichnikov, M.P. Molecular Basis for Mambalgin-2 Interaction with Heterotrimeric α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channels in Cancer Cells. Toxins 2023, 15, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100612
Lyukmanova EN, Zaigraev MM, Kulbatskii DS, Isaev AB, Kukushkin ID, Bychkov ML, Shulepko MA, Chugunov AO, Kirpichnikov MP. Molecular Basis for Mambalgin-2 Interaction with Heterotrimeric α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channels in Cancer Cells. Toxins. 2023; 15(10):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100612
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyukmanova, Ekaterina N., Maxim M. Zaigraev, Dmitrii S. Kulbatskii, Aizek B. Isaev, Ilya D. Kukushkin, Maxim L. Bychkov, Mikhail A. Shulepko, Anton O. Chugunov, and Mikhail P. Kirpichnikov. 2023. "Molecular Basis for Mambalgin-2 Interaction with Heterotrimeric α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channels in Cancer Cells" Toxins 15, no. 10: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100612
APA StyleLyukmanova, E. N., Zaigraev, M. M., Kulbatskii, D. S., Isaev, A. B., Kukushkin, I. D., Bychkov, M. L., Shulepko, M. A., Chugunov, A. O., & Kirpichnikov, M. P. (2023). Molecular Basis for Mambalgin-2 Interaction with Heterotrimeric α-ENaC/ASIC1a/γ-ENaC Channels in Cancer Cells. Toxins, 15(10), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100612