Integrated Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Lipid Metabolic Disorder in NCM460 Cells Caused by Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Alone and in Combination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
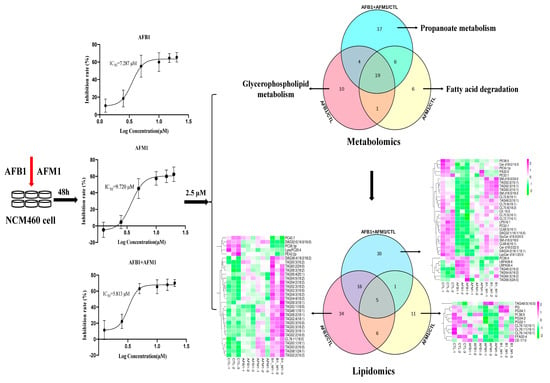
2.1. Effect of AFB1 and AFM1 Treatment on NCM460 Cells Viability
2.2. Multivariate Analysis of NCM460 Cell Metabolic Profiles
2.3. Differential Metabolites in NCM460 Cells Induced by AFB1 and AFM1
2.4. Metabolic Pathway Analysis Affected by AFB1 and AFM1
2.5. Lipid Profiles on NCM460 Induced by AFB1 and AFM1
2.6. Analysis of Differential Lipids in NCM460 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Chemicals and Reagents
5.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
5.3. Cell Viability Assay
5.4. Metabolomics Analysis
5.5. Lipidomic Analysis
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohd-Redzwan, S.; Jamaluddin, R.; Mutalib, A.; Sokhini, M.; Ahmad, Z. A mini review on aflatoxin exposure in Malaysia: Past, present and future. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akinrinmade, F.J.; Akinrinde, A.S.; Amid, A. Changes in serum cytokine levels, hepatic and intestinal morphology in aflatoxin B1-induced injury: Modulatory roles of melatonin and flavonoid-rich fractions from Chromolena odorata. Mycotoxin Res. 2016, 32, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, M.; De Groote, H.; Brouwer, I.D.; De Boevre, M.; Corominas, A.V.; Stoecker, B.J.; Stoecker, B.J.; Feskens, E.J.; Belachew, T.; Karakitsou, A.; et al. Exposure to aflatoxins and fumonisins and linear growth of children in rural Ethiopia: A longitudinal study. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 3662–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.C.; Moore, S.E.; Hall, A.J.; Prentice, A.M.; Wild, C.P. Modification of immune function through exposure to dietary aflatoxin in Gambian children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fouche, T.; Claassens, S.; Maboeta, M. Aflatoxins in the soil ecosystem: An overview of its occurrence, fate, effects and future perspectives. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniwaki, M.H.; Pitt, J.I.; Magan, N. Aspergillus species and mycotoxins: Occurrence and importance in major food commodities. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 23, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Dai, J.; Karrow, N.A.; Sun, L. Occurrence of Aflatoxin B1, deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in feeds in China during 2018–2020. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkerroum, N. Retrospective and Prospective Look at Aflatoxin Research and Development from a Practical Standpoint. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raiola, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Manyes, L.; Meca, G.; Ritieni, A. Risk analysis of main mycotoxins occurring in food for children: An overview. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Ni, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Zhan, H. Aflatoxin B1 impairs leydig cells through inhibiting AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy flux pathway. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, S.; Jarriyawattanachaikul, W.; Girolami, F.; Longobardi, C.; Nebbia, C.; Andretta, E.; Lauritano, C.; Dabbou, S.; Avantaggiato, G.; Schiavone, A.; et al. Curcumin Supplementation Protects Broiler Chickens Against the Renal Oxidative Stress Induced by the Dietary Exposure to Low Levels of Aflatoxin B1. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 822227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens-the IARC Monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushing, B.R.; Selim, M.I. Structure and Oxidation of Pyrrole Adducts Formed between Aflatoxin B(2a) and Biological Amines. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.M.; Ruebner, B.H.; Hsieh, L.S.; Hyde, D.M.; Hsieh, D.P. Carcinogenicity of dietary aflatoxin M1 in male Fischer rats compared to aflatoxin B1. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 1913–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, T.; Fallah, A.A.; Kheiri, S.; Fadaei, A.; Amini, S.A. Aflatoxin M1 in human breast milk in Shahrekord, Iran and association with dietary factors. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveil. 2017, 10, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanda, O.; Oguntubo, A.; Adejumo, O.; Ikeorah, J.; Akpan, I. Aflatoxin M1 contamination of milk and ice cream in Abeokuta and Odeda local governments of Ogun State, Nigeria. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Varzakas, T. Advances in Occurrence, Importance, and Mycotoxin Control Strategies: Prevention and Detoxification in Foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaisheh, S.S.; Rahahleh, R.J.; Algroom, R.M.; Al-Bakheit, A.A.; Al-Khaza’leh, J.M. Al-Dababseh BA: Contamination level and exposure assessment to Aflatoxin M1 in Jordanian infant milk formulas. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2019, 8, 8263. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, D.K.; Kang, J.I.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Sonwal, S.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Xiao, J.; Ali, S.; Huh, Y.S.; et al. Mycotoxins in food and feed: Toxicity, preventive challenges, and advanced detection techniques for associated diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–22, ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, E.; Schatzmayr, G.; Tassis, P.; Tzika, E.; Marin, D.; Taranu, I.; Tabuc, C.; Nicolau, A.; Aprodu, I.; Puel, O. Current situation of mycotoxin contamination and co-occurrence in animal feed--focus on Europe. Toxins 2012, 4, 788–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dlamini, N.Z.; Somboro, A.M.; Amoako, D.G.; Arhin, I.; Khumalo, H.M.; Khan, R.B. Toxicogenicity and mechanistic pathways of aflatoxin B1 induced renal injury. Environ Toxicol. 2021, 36, 1857–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Jia, S.; Xue, D.; Rajput, S.A.; Liu, M.; Qi, D.; Wang, S. Dual effects of zearalenone on aflatoxin B1-induced liver and mammary gland toxicity in pregnant and lactating rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 245, 114115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, L.; Zeng, H.; Fu, W.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, C.; Qiu, Z.; Luo, J.; Lv, C. Low-dose microcystin-LR antagonizes aflatoxin B1 induced hepatocarcinogenesis through decreasing cytochrome P450 1A2 expression and aflatoxin B1-DNA adduct generation. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bao, X.; Meng, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Induce Compromised Intestinal Integrity through Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis. Toxins 2021, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.N.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, H.M.; Zheng, N. Multi-Omics Reveal Additive Cytotoxicity Effects of Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 toward Intestinal NCM460 Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, P.; Qian, C.; Xu, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, A.; Chen, W.; Sun, Z.; Lu, Y. Rhein modulates host purine metabolism in intestine through gut microbiota and ameliorates experimental colitis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10665–10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vecchia, S.; Sebastian, C. Metabolic pathways regulating colorectal cancer initiation and progression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.W.; Qu, J.; Black, D.D.; Tso, P. Regulation of intestinal lipid metabolism: Current concepts and relevance to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.S. Assessment of the adverse impacts of aflatoxin B1 on gut-microbiota dependent metabolism in F344 rats. Chemosphere 2019, 217, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lei, H.; Qin, M.; Chen, G.; Wu, F.; Chen, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wu, M. Characterization of triclosan-induced hepatotoxicity and triclocarban-triggered enterotoxicity in mice by multiple omics screening. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 4, 156570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudan, S.; Zhan, X.; Li, J. A Novel Probiotic Bacillus subtilis Strain Confers Cytoprotection to Host Pig Intestinal Epithelial Cells during Enterotoxic Escherichia coli Infection. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0125721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, M.P.; Manzano, L.A.; Merriman, R.L.; Stauffer, J.S.; Tanzer, L.R. NCM460, a normal human colon mucosal epithelial cell line. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 1996, 32, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Wong, C.C.; Tong, L.; Chu, E.S.H.; Ho Szeto, C.; Go, M.Y.Y.; Coker, O.O.; Chan, A.W.H.; Chan, F.K.L.; Sung, J.J.Y. Peptostreptococcus anaerobius promotes colorectal carcinogenesis and modulates tumour immunity. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warth, B.; Raffeiner, P.; Granados, A.; Huan, T.; Fang, M.; Forsberg, E.M.; Benton, H.P.; Goetz, L.; Johnson, C.H.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics Reveals that Dietary Xenoestrogens Alter Cellular Metabolism Induced by Palbociclib/Letrozole Combination Cancer Therapy. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 291–300.e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Metabolomics analysis underlay mechanisms in the renal impairment of mice caused by combination of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Wang, H. Comprehensive Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Dynamic Metabolic Reprogramming in Hep3B Cells with Aflatoxin B1 Exposure. Toxins 2021, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, S.; Sorice, A.; Ariano, A.; Florio, S.; Budillon, A.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Evaluation of Aflatoxin M1 Effects on the Metabolomic and Cytokinomic Profiling of a Hepatoblastoma Cell Line. Toxins 2018, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, S.M.; Tian, H.; Shui, G. Lipidomics, en route to accurate quantitation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Liu, T.; Feng, F.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Lin, J.M.; Zhang, F. Lipidomics Profiling of HepG2 Cells and Interference by Mycotoxins Based on UPLC-TOF-IMS. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 6719–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiu, J.; Xu, Y.; Liao, G.; Jia, Q.; Pan, Y.; Wang, T.; Qian, Y. Integrated non-targeted lipidomics and metabolomics analyses for fluctuations of neonicotinoids imidacloprid and acetamiprid on Neuro-2a cells. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, X.; Xiang, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, Z. Metabolomics and lipidomics study unveils the impact of polybrominated diphenyl ether-47 on breast cancer mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, C.; De Spiegeleer, M.; Van Meulebroek, L.; De Vos, W.H.; Vanhaecke, L. Validated comprehensive metabolomics and lipidomics analysis of colon tissue and cell lines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1066, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jard, G.; Liboz, T.; Mathieu, F.; Guyonvarc’h, A.; Lebrihi, A. Review of mycotoxin reduction in food and feed: From prevention in the field to detoxification by adsorption or transformation. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 1590–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.L.; Price, W.D. Reduction of aflatoxin hazards using ammoniation. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 171, 139–175. [Google Scholar]
- Giovati, L.; Magliani, W.; Ciociola, T.; Santinoli, C.; Conti, S.; Polonelli, L. AFM1 in Milk: Physical, Biological, and Prophylactic Methods to Mitigate Contamination. Toxins 2015, 7, 4330–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jebali, R.; Abbès, S.; Salah-Abbès, J.B.; Ben Younes, R.; Haous, Z.; Oueslati, R. Ability of Lactobacillus plantarum MON03 to mitigate aflatoxins (B1 and M1) immunotoxicities in mice. J. Immunotoxicol. 2015, 12, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, X.Y.; Li, S.L.; Gao, Y.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Zheng, N. Transcriptome analysis revealed that aflatoxin M1 could cause cell cycle arrest in differentiated Caco-2 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 59, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, T.; Duarte-Hospital, C.; Vignard, J.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Sulyok, M.; Snini, S.P.; Alassane-Kpembi, I.; Lippi, Y.; Puel, S.; Oswald, I.P.; et al. Versicolorin A, a precursor in aflatoxins biosynthesis, is a food contaminant toxic for human intestinal cells. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, D.; Chevallier, O.P.; Woodside, J.V.; Brennan, S.F.; Cantwell, M.M.; Cuskelly, G.; Elliott, C.T. Untargeted metabolomic analysis of human serum samples associated with exposure levels of Persistent organic pollutants indicate important perturbations in Sphingolipids and Glycerophospholipids levels. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Cuenca, S.; Pellegrinelli, V.; Campbell, M.; Oresic, M.; Vidal-Puig, A. Sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids—The “ying and yang” of lipotoxicity in metabolic diseases. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 66, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ji, P.; Hua, Y.; Wei, Y. Mechanism of Huang-lian-Jie-du decoction and its effective fraction in alleviating acute ulcerative colitis in mice: Regulating arachidonic acid metabolism and glycerophospholipid metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Jacobs, M.A.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Choline metabolism in cancer: Implications for diagnosis and therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2006, 6, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.S. Aflatoxin B1 Induces Gut-Inflammation-Associated Fecal Lipidome Changes in F344 Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 183, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.-H.; Do, K.H.; Kim, D.; Moon, Y. Interference with mutagenic aflatoxin B1-induced checkpoints through antagonistic action of ochratoxin A in intestinal cancer cells: A molecular explanation on potential risk of crosstalk between carcinogens. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 39627–39639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Navab, M.; Hough, G.; Grijalva, V.; Mukherjee, P.; Fogelman, H.R.; Hwang, L.H.; Faull, K.F.; Lusis, A.J.; Reddy, S.T.; et al. Tg6F ameliorates the increase in oxidized phospholipids in the jejunum of mice fed unsaturated LysoPC or WD. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Bai, M.; Peng, C.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Intestinal Immunity Mediated by Tryptophan Metabolism. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, T.; Kennelly, J.P.; Jacobs, R.L.; Willing, B.P. Insufficient dietary choline aggravates disease severity in a mouse model of Citrobacter rodentium-induced colitis. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hu, B.; Shao, L.; Tian, Y.; Jin, T.; Jin, Y.; Ji, S.; Fan, X. Integrated analysis of transcriptomics and metabonomics profiles in aflatoxin B1-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J. Membrane breakdown in acute and chronic neurodegeneration: Focus on choline-containing phospholipids. J. Neural Transm. 2000, 107, 1027–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.H.; Yu, H.Z.; Bao, T.R.; Ba, G.N. Anti-obesity and lipid-lowering mechanism of Corydalis Bungeanae Herba: Based on intestinal microflora and metabolomics. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022, 47, 3049–3058. [Google Scholar]
- Connors, J.; Dawe, N.; Van Limbergen, J. The Role of Succinate in the Regulation of Intestinal Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nadjsombati, M.S.; McGinty, J.W.; Lyons-Cohen, M.R.; Jaffe, J.B.; DiPeso, L.; Schneider, C.; Miller, C.N.; Pollack, J.L.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Fontana, M.F.; et al. Detection of Succinate by Intestinal Tuft Cells Triggers a Type 2 Innate Immune Circuit. Immunity 2018, 49, 33–41.e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gondo, Y.; Satsu, H.; Ishimoto, Y.; Iwamotom, T.; Shimizu, M. Effect of taurine on mRNA expression of thioredoxin interacting protein in Caco-2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 426, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Cha, Y.N. Taurine chloramine produced from taurine under inflammation provides anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Guo, Z.; Shen, S.; Shan, W. Effects of taurine on gut microbiota and metabolism in mice. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1601–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Satsu, H.; Fujisawa, M.; Hori, M.; Ishimoto, Y.; Totsuka, M.; Nambu, A.; Kakuta, S.; Ozaki, H.; Shimizu, M. Attenuation by dietary taurine of dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice and of THP-1-induced damage to intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jezkova, A.; Yuan, Z.; Pavlikova, L.; Dohnal, V.; Kuca, K. Biological degradation of aflatoxins. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotimi, O.A.; Rotimi, S.O.; Duru, C.U.; Ebebeinwe, O.J.; Abiodun, A.O.; Oyeniyi, B.O.; Faduyile, F.A. Acute aflatoxin B1—Induced hepatotoxicity alters gene expression and disrupts lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in rats. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Hussain, M.M. Intestinal lipid absorption. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E1183–E1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siloto, E.V.; Oliveira, E.F.; Sartori, J.R.; Fascina, V.B.; Martins, B.A.; Ledoux, D.R.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Sartori, D.R. Lipid metabolism of commercial layers fed diets containing aflatoxin, fumonisin, and a binder. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechynska, K.; Kosek, V.; Fenclova, M.; Muchova, L.; Smid, V.; Suk, J.; Chalupsky, K.; Sticova, E.; Hurkova, K.; Hajslova, J.; et al. The Effect of Mycotoxins and Silymarin on Liver Lipidome of Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzuto, M.; Pelegrin, P. Cardiolipin in Immune Signaling and Cell Death. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Moorthi, S.; Luberto, C. Role and Function of Sphingomyelin Biosynthesis in the Development of Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 140, 61–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennelly, J.P.; van der Veen, J.N.; Nelson, R.C.; Leonard, K.A.; Havinga, R.; Buteau, J.; Kuipers, F.; Jacobs, R.L. Intestinal de novo phosphatidylcholine synthesis is required for dietary lipid absorption and metabolic homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1695–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ugbaja, R.N.; Okedairo, O.M.; Oloyede, A.R.; Ugwor, E.I.; Akinloye, D.I.; Ojo, O.P.; Ademuyiwa, O. Probiotics consortium synergistically ameliorates aflatoxin B1-induced disruptions in lipid metabolism of female albino rats. Toxicon 2020, 186, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coats, S.R.; Hashim, A.; Paramonov, N.A.; To, T.T.; Curtis, M.A.; Darveau, R.P. Cardiolipins Act as a Selective Barrier to Toll-Like Receptor 4 Activation in the Intestine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4264–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, M.E.; Mauch, S.; Rieckmann, M.; Martinez, D.G.; Hause, G.; Noutsias, M.; Hofmann, U.; Lucas, H.; Meister, A.; Ramos, G. Phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylglycerol (PG) nanodispersions as potential anti-inflammatory therapeutics: Comparison of in vitro activity and impact of pegylation. Nanomedicine 2020, 23, 102096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Jiang, M.; Lian, G.; Liu, Q.; Shi, M.; Li, T.Y.; Song, L.; Ye, J.; He, Y.; Yao, L. AIDA Selectively Mediates Downregulation of Fat Synthesis Enzymes by ERAD to Retard Intestinal Fat Absorption and Prevent Obesity. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 843–853.e846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, P.D.; Browse, J. The significance of different diacylgycerol synthesis pathways on plant oil composition and bioengineering. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.A.; Su, W.; Chapman, N.M.; Chi, H. Lipid metabolism in T cell signaling and function. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, T.; Prentice, B.M.; Anderson, K.G.; Raman, A.; Schalck, A.; Codreanu, G.S.; Nava Lauson, C.B.; Tiberti, S.; Raimondi, A.; Jones, M.A.; et al. Accumulation of long-chain fatty acids in the tumor microenvironment drives dysfunction in intrapancreatic CD8+ T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hartman, C.L.; Li, L.; Albert, C.J.; Si, F.; Gao, A.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, W.; Hsueh, E.C.; et al. Reprogramming lipid metabolism prevents effector T cell senescence and enhances tumor immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaaz6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, E.; Richards, J.L.; McLeod, K.H.; Stanley, D.; Yap, Y.A.; Knight, J.; McKenzie, C.; Kranich, J.; Oliveira, A.C.; Rossello, F.J.; et al. Gut microbial metabolites limit the frequency of autoimmune T cells and protect against type 1 diabetes. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Huang, S.; Su, C.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Whole transcriptome-based ceRNA network analysis revealed ochratoxin A-induced compromised intestinal tight junction proteins through WNT/Ca2+ signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.; Chen, L.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Metabolomics and Isotope Tracing. Cell 2018, 173, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.W.; Lam, S.M.; Fan, X.; Cao, W.J.; Wang, S.Y.; Tian, H.; Chua, G.H.; Zhang, C.; Meng, F.P.; Xu, Z. Omics-Driven Systems Interrogation of Metabolic Dysregulation in COVID-19 Pathogenesis. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 188–202.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, S.; Huang, X.; Mo, L.; Li, J.; Lee, B. A multi-omics investigation of the composition and function of extracellular vesicles along the temporal trajectory of COVID-19. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, G.; Cheong, W.F.; Jappar, I.A.; Hoi, A.; Xue, Y.; Fernandis, A.Z.; Tan, B.K.; Wenk, M.R. Derivatization-independent cholesterol analysis in crude lipid extracts by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: Applications to a rabbit model for atherosclerosis. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4357–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Integrated Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Lipid Metabolic Disorder in NCM460 Cells Caused by Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Alone and in Combination. Toxins 2023, 15, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040255
Yang X, Li X, Gao Y, Wang J, Zheng N. Integrated Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Lipid Metabolic Disorder in NCM460 Cells Caused by Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Alone and in Combination. Toxins. 2023; 15(4):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040255
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xue, Xue Li, Yanan Gao, Jiaqi Wang, and Nan Zheng. 2023. "Integrated Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Lipid Metabolic Disorder in NCM460 Cells Caused by Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Alone and in Combination" Toxins 15, no. 4: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040255
APA StyleYang, X., Li, X., Gao, Y., Wang, J., & Zheng, N. (2023). Integrated Metabolomics and Lipidomics Analysis Reveals Lipid Metabolic Disorder in NCM460 Cells Caused by Aflatoxin B1 and Aflatoxin M1 Alone and in Combination. Toxins, 15(4), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040255