Isolation and Characterization of the Zearalenone-Degrading Strain, Bacillus spizizenii B73, Inspired by Esterase Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
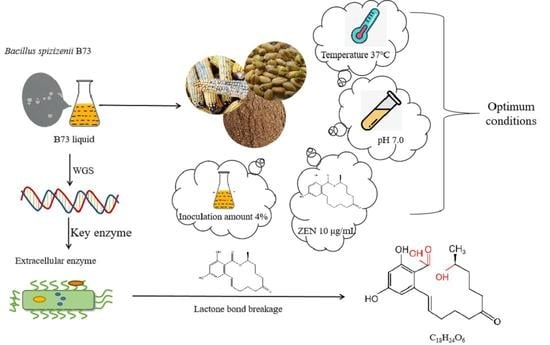
2.1. Isolation, Screening, and Identification of ZEN-Degrading Bacteria
2.2. Degradation of ZEN via B73
2.3. Degradation of ZEN by Different Fractions of the B73 Culture Broth
2.4. Exploration and Analysis of ZEN Degradation Products
2.5. ZEN Degradation by B73 during Semisolid Fermentation of Grain Products
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Culture Media
4.2. Screening and Isolation of Bacillus Strains
4.3. Identification of Bacillus Strains
4.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing
4.5. Effect of Culture Conditions on the Degradation of ZEN
4.6. ZEN Degradation by Different Fractions of the Culture Broth
4.7. Characterization of the Active ZEN-Degrading Component in a Cell-Free Supernatant
4.8. Degradation of ZEN by B73 in Wheat Bran, DDGS and Corn Meal
4.9. Exploration and Analysis of ZEN Degradation Products
4.10. HPLC Analysis of ZEN Degradation
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, H.; Woori, K.; Ju-Hee, P.; Dongho, K.; Choong-Ryeol, K.; Soohyun, C.; Chan, L.J.T. The Occurrence of Zearalenone in South Korean Feedstuffs between 2009 and 2016. Toxins 2017, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinkellner, H.; Binaglia, M.; Dall’Asta, C.; Gutleb, A.C.; Alexander, J.J.F.; Toxicology, C. Combined hazard assessment of mycotoxins and their modified forms applying relative potency factors: Zearalenone and T2/HT2 toxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; Li, P. Analysis of the miRNA Expression Profiles in the Zearalenone-Exposed TM3 Leydig Cell Line. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, A.; Das, M.; Tripathi, A. Occurrence and toxicity of a fusarium mycotoxin, zearalenone. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2710–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.; Freire, F.D.C.O.; Maia, F.; Guedes, M.; Rondina, D.J.F.C. Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health. Food Control 2014, 36, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhauf, S.; Novak, B.; Nagl, V.; Hackl, M.; Hartinger, D.; Rainer, V.; Labudova, S.; Adam, G.; Aleschko, M.; Moll, W.-D.; et al. Biotransformation of the Mycotoxin Zearalenone to its Metabolites Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (HZEN) and Decarboxylated Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (DHZEN) Diminishes its Estrogenicity In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins 2019, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdarta, J.; Meyer, A.S.; Jesionowski, T.; Pinelo, M. A General Overview of Support Materials for Enzyme Immobilization: Characteristics, Properties, Practical Utility. Catalysts 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, N.; Ou, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Huang, H. Recent advances in detoxification strategies for zearalenone contamination in food and feed. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 30, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlayne, G.; Simone, A.; Felicio, J.D. Chemical and biological approaches for mycotoxin control: A review. Recent. Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2009, 1, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhaya, S.D.; Park, M.A.; Ha, J.K. Mycotoxins and Their Biotransformation in the Rumen: A Review. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 23, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Z.; Ji, F.; Yin, X.; Hong, Q.; Shi, J. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ZDS-1: Exploring the degradation of Zearalenone by Bacillus spp. Food Control 2016, 68, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jin, H.; Lan, J.; Zhang, R.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, G. Detoxification of zearalenone by three strains of lactobacillus plantarum from fermented food in vitro. Food Control 2015, 54, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Moltó, J.C.; Mañes, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Pereyra, M.L.; Di Giacomo, A.L.; Lara, A.L.; Martinez, M.P.; Cavaglieri, L. Aflatoxin-degrading Bacillus sp. strains degrade zearalenone and produce proteases, amylases and cellulases of agro-industrial interest. Toxicon 2020, 180, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekiru, E.; Hametner, C.; Mitterbauer, R.; Rechthaler, J.; Adam, G.; Schatzmayr, G.; Krska, R.; Schuhmacher, R. Cleavage of Zearalenone by Trichosporon mycotoxinivorans to a Novel Nonestrogenic Metabolite. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2353–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, J.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, X. Exploration on the Enhancement of Detoxification Ability of Zearalenone and Its Degradation Products of Aspergillus niger FS10 under Directional Stress of Zearalenone. Toxins 2021, 13, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Wang, H.T.; Shih, W.Y.; Ciou, Y.A.; Chang, Y.Y.; Ananda, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Hsu, J.T. Application of Zearalenone (ZEN)-Detoxifying Bacillus in Animal Feed Decontamination through Fermentation. Toxins 2019, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.J.; Kang, J.S.; Cho, W.T.; Lee, C.H.; Ha, J.K.; Bin Song, K. In vitro degradation of zearalenone by Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1921–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Hassan, Z.; Al Thani, R.; Alsafran, M.; Migheli, Q.; Jaoua, S. Selection of Bacillus spp. with decontamination potential on multiple Fusarium mycotoxins. Food Control 2021, 127, 108119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, F.; Ning, H.; Zhang, W.; Niu, D.; Shi, Z.; Chai, S.; Shan, A. Screening of Pig-Derived Zearalenone-Degrading Bacteria through the Zearalenone Challenge Model, and Their Degradation Characteristics. Toxins 2022, 14, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nezami, H.; Polychronaki, N.; Salminen, S.; Mykkanen, H. Binding Rather Than Metabolism May Explain the Interaction of Two Food-Grade Lactobacillus Strains with Zearalenone and Its Derivative ɑ-Zearalenol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Ji, C.; Zhao, L. Enzymatic degradation of deoxynivalenol by a novel bacterium, Pelagibacterium halotolerans ANSP101. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 140, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Quek, W.P.; Li, C.; Gilbert, R.G.; Fox, G.P. Effects of the Starch Molecular Structures in Barley Malts and Rice Adjuncts on Brewing Performance. Fermentation 2018, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepper, C.F.D.; Michiels, P.; Buvé, C.; Loey, A.M.V.; Courtin, C.M. Starch hydrolysis during mashing: A study of the activity and thermal inactivation kinetics of barley malt α-amylase and β-amylase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 255, 117494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wu, Z.; He, R.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous degradation of two mycotoxins enabled by a fusion enzyme in food-grade recombinant Kluyveromyces lactis. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yp, A.; Cl, A.; Jya, B.; Yt, A. Conversion of zearalenone to β-Zearalenol and Zearalenone-14,16-diglucoside by Candida parapsilosis ATCC 7330. Food Control 2021, 131, 108429. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Zhan, B.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Hu, X.-J. The Trp183 is essential in lactonohydrolase ZHD detoxifying zearalenone and zearalenols. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 986–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, M.; Peng, M.; Guo, P.; Cui, Z. Microbial Degradation of Zearalenone by a Novel Microbial Consortium, NZDC-6, and Its Application on Contaminated Corncob by Semisolid Fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Chun, J.; Cha, C.-J. Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the three subspecies of Bacillus subtilis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitru, M.; Ciurescu, G. The beneficial effect of Bacillus spp. As probiotics in poultry nutrition—A review. Sci. Pap.-Ser. D-Anim. Sci. 2022, 65, 75–91. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, M.Y.; Wu, C.H.; Chou, C.C. Fermentation with Bacillus spp. as a bioprocess to enhance anthocyanin content, the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory effect, and the reducing activity of black soybeans. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnaba, T.J.; Gangiredla, J.; Mammel, M.K.; Lacher, D.W.; Tartera, C. Draft Genome Sequences of Nine Bacillus Strains and Two Weizmannia Strains Isolated from Live Dietary Supplements and a Cultured Food Product. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e00908–e00921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Qin, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Pan, L. Strain screening for lowering immune activity of β-conglycinin in defatted whole soybean flour through fermentation. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 94, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggar, R.; Jangra, M.; Dwivedi, A.; Bansal, K.; Patil, P.B.; Bhattacharyya, M.S.; Nandanwar, H.; Sahoo, D.K. Bacteriocin isolated from the natural inhabitant of Allium cepa against Staphylococcus aureus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juodeikiene, G.; Bartkiene, E.; Cernauskas, D.; Cizeikiene, D.; Zadeike, D.; Lele, V.; Bartkevics, V. Antifungal activity of lactic acid bacteria and their application for Fusarium mycotoxin reduction in malting wheat grains. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Cheng, K.-C.; Liu, J.-R. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain with zearalenone removal ability and its probiotic potential. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, T.-C.; Yi, P.-J.; Lee, T.-Y.; Liu, J.-R. Probiotic characteristics and zearalenone-removal ability of a Bacillus licheniformis strain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imade, F.N.; Humza, M.; Dada, O.A.; Ullah, S.; Jahan, I.; Eseigbe, D.; Geng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xing, F.; Liu, Y. Isolation and characterization of novel soil bacterium, Klebsiella pneumoniae strain GS7-1 for the degradation of zearalenone in major cereals. Food Control 2023, 143, 109287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Gao, H.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Characterization and Whole-Genome Analysis of a Zearalenone-Degrading Stappia sp. WLB 29. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, C.; Yu, Y.; Han, J.; Hu, J.; He, D.; Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Mohamed, S.R.; Dawood, D.H.; Wang, G.; et al. Isolation, Characterization, and Application of Clostridium sporogenes F39 to Degrade Zearalenone under Anaerobic Conditions. Foods 2022, 11, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setlow, P. Spores of Bacillus subtilis: Their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat and chemicals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, P.-J.; Pai, C.-K.; Liu, J.-R. Isolation and characterization of a Bacillus licheniformis strain capable of degrading zearalenone. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Borzekowski, A.; Haase, H.; Menzel, R.; Ruess, L.; Koch, M. Toxicity Assay for Citrinin, Zearalenone and Zearalenone-14-Sulfate Using the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as Model Organism. Toxins 2018, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Chelule, P.K.; Gqaleni, N. Reduction of fumonisin B(1) and zearalenone by lactic acid bacteria in fermented maize meal. J. Food Prot. 2005, 68, 2095–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yu, M.; Dong, F.; Shi, J.; Xu, J. Esterase activity inspired selection and characterization of zearalenone degrading bacteria Bacillus pumilus ES-21. Food Control 2017, 77, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, W. Degradation mechanism for Zearalenone ring-cleavage by Zearalenone hydrolase RmZHD: A QM/MM study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 709, 135897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Yang, W.-J.; Zhou, H.-J.; Ming, D.-M.; Sun, K.-L.; Xu, T.-Y.; Hu, X.-J.; Lv, H. The structure of a complex of the lactonohydrolase zearalenone hydrolase with the hydrolysis product of zearalenone at 1.60 angstrom resolution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F-Struct. Biol. Commun. 2017, 73, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, K.R.; Vipin, A.V.; Hariprasad, P.; Appaiah, K.; Venkateswaran, G.J.F.C. Biological detoxification of Aflatoxin B1 by Bacillus licheniformis CFR1. Food Control 2016, 71, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhong, L.; Lu, Z.; Bie, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F. Characterization of Deoxynivalenol Detoxification by Lactobacillus paracasei LHZ-1 Isolated from Yogurt. J. Food Prot. 2019, 82, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.F.; Engelbrecht, Y.; Steyn, P.S.; Holzapfel, W.H.; van Zyl, W.H. Biological degradation of aflatoxin B1 by Rhodococcus erythropolis cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Q.H.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yin, L.F.; Zhang, G.M.; Ma, Y.H. High-level expression of a ZEN-detoxifying gene by codon optimization and biobrick in Pichia pastoris. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wu, N.; Zhang, M.; Xue, F.; Xu, Q. Isolation and Characterization of the Zearalenone-Degrading Strain, Bacillus spizizenii B73, Inspired by Esterase Activity. Toxins 2023, 15, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15080488
Liu X, Wu N, Zhang M, Xue F, Xu Q. Isolation and Characterization of the Zearalenone-Degrading Strain, Bacillus spizizenii B73, Inspired by Esterase Activity. Toxins. 2023; 15(8):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15080488
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xue, Na Wu, Mingyu Zhang, Feng Xue, and Qing Xu. 2023. "Isolation and Characterization of the Zearalenone-Degrading Strain, Bacillus spizizenii B73, Inspired by Esterase Activity" Toxins 15, no. 8: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15080488
APA StyleLiu, X., Wu, N., Zhang, M., Xue, F., & Xu, Q. (2023). Isolation and Characterization of the Zearalenone-Degrading Strain, Bacillus spizizenii B73, Inspired by Esterase Activity. Toxins, 15(8), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15080488