Specificity of Interaction between Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin and Claudin-Family Tight Junction Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CPE Receptors Are Claudin Family Tight Junction proteins

3. Mechanism of Action for CPE Toxicity

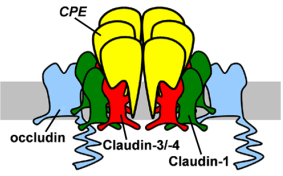
4. Structural Basis and Specificity of CPE-Claudin Interactions


5. CPE as a Tool to Study Epithelial Tight Junctions
6. Targeted Cancer Therapeutics Using CPE
Acknowledgements
References
- Sakurai, J.; Nagahama, M.; Ochi, S. Major Toxins of Clostridium perfringens. Toxin Rev. 1997, 16, 195–214. [Google Scholar]
- McDonel, J.L. Clostridium perfringens toxins (type A, B, C, D, E). Pharmacol. Ther. 1980, 10, 617–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClane, B.A. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin acts by producing small molecule permeability alterations in plasma membranes. Toxicology 1994, 87, 43–67. [Google Scholar]
- Koval, M. Claudins: Key pieces in the tight junction puzzle. Cell Commun. Adhes. 2006, 13, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Angelow, S.; Ahlstrom, R.; Yu, A.S. Biology of claudins. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F867–F876. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Van Itallie, C.M. Physiology and function of the tight junction. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a002584. [Google Scholar]
- Katahira, J.; Sugiyama, H.; Inoue, N.; Horiguchi, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Sugimoto, N. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin utilizes two structurally related membrane proteins as functional receptors in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26652–26658. [Google Scholar]
- Katahira, J.; Inoue, N.; Horiguchi, Y.; Matsuda, M.; Sugimoto, N. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of the receptor for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J. Cell. Biol. 1997, 136, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, K.; Sasaki, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Claudin-11/OSP-based tight junctions of myelin sheaths in brain and Sertoli cells in testis. J. Cell. Biol. 1999, 145, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelmann, R.; Amieva, M.R.; Falkow, S.; Nelson, W.J. Breaking into the epithelial apical-junctional complex—news from pathogen hackers. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, J.R. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, J.A.; Finlay, B.B. Tight junctions as targets of infectious agents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 832–841. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, M. Wikipedia Commons. 2006. Available online: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cellular_tight_junction_en.svg (Accessed on 22 April 2010).
- Daugherty, B.L.; Ward, C.; Smith, T.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; Koval, M. Regulation of heterotypic claudin compatibility. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30005–30013. [Google Scholar]
- Colegio, O.R.; Van Itallie, C.; Rahner, C.; Anderson, J.M. Claudin extracellular domains determine paracellular charge selectivity and resistance but not tight junction fibril architecture. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 284, C1346–C1354. [Google Scholar]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M. Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2006, 68, 403–429. [Google Scholar]
- Umeda, K.; Ikenouchi, J.; Katahira-Tayama, S.; Furuse, K.; Sasaki, H.; Nakayama, M.; Matsui, T.; Tsukita, S.; Furuse, M. ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 2006, 126, 741–754. [Google Scholar]
- Utech, M.; Ivanov, A.I.; Samarin, S.N.; Bruewer, M.; Turner, J.R.; Mrsny, R.J.; Parkos, C.A.; Nusrat, A. Mechanism of ifn-gamma-induced endocytosis of tight junction proteins: myosin II-dependent vacuolarization of the apical plasma membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2005, 16, 5040–5052. [Google Scholar]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Fanning, A.S.; Bridges, A.; Anderson, J.M. ZO-1 stabilizes the tight junction solute barrier through coupling to the perijunctional cytoskeleton. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2009, 20, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.; Goodenough, D.A. Paracellular channels! Science 1999, 285, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, M.D.; Jeansonne, B.G.; Renegar, R.H.; Tatum, R.; Chen, Y.H. The first extracellular domain of claudin-7 affects paracellular Cl- permeability. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 87–91. [Google Scholar]
- Amasheh, S.; Meiri, N.; Gitter, A.H.; Schoneberg, T.; Mankertz, J.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M. Claudin-2 expression induces cation-selective channels in tight junctions of epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Paul, D.L.; Goodenough, D.A. Paracellin-1 and the modulation of ion selectivity of tight junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 5109–5118. [Google Scholar]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Rogan, S.; Yu, A.; Vidal, L.S.; Holmes, J.; Anderson, J.M. Two splice variants of claudin-10 in the kidney create paracellular pores with different ion selectivities. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 291, F1288–F1299. [Google Scholar]
- Piontek, J.; Winkler, L.; Wolburg, H.; Muller, S.L.; Zuleger, N.; Piehl, C.; Wiesner, B.; Krause, G.; Blasig, I.E. Formation of tight junction: determinants of homophilic interaction between classic claudins. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wieckowski, E.U.; Wnek, A.P.; McClane, B.A. Evidence that an approximately 50-kDa mammalian plasma membrane protein with receptor-like properties mediates the amphiphilicity of specifically bound Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10838–10848. [Google Scholar]
- McClane, B.A.; Chakrabarti, G. New insights into the cytotoxic mechanisms of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Anaerobe 2004, 10, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, K.; Katahira, J.; Horiguchi, Y.; Sonoda, N.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin binds to the second extracellular loop of claudin-3, a tight junction integral membrane protein. FEBS Lett. 2000, 476, 258–261. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda, N.; Furuse, M.; Sasaki, H.; Yonemura, S.; Katahira, J.; Horiguchi, Y.; Tsukita, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragment removes specific claudins from tight junction strands: Evidence for direct involvement of claudins in tight junction barrier. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lohrberg, D.; Krause, E.; Schumann, M.; Piontek, J.; Winkler, L.; Blasig, I.E.; Haseloff, R.F. A strategy for enrichment of claudins based on their affinity to Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Mitic, L.L.; Unger, V.M.; Anderson, J.M. Expression, solubilization, and biochemical characterization of the tight junction transmembrane protein claudin-4. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, L.; Gehring, C.; Wenzel, A.; Muller, S.L.; Piehl, C.; Krause, G.; Blasig, I.E.; Piontek, J. Molecular determinants of the interaction between Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragments and claudin-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18863–18872. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, S.L.; Smedley, J.G., III; Singh, U.; Chakrabarti, G.; Van Itallie, C.M.; Anderson, J.M.; McClane, B.A. Compositional and stoichiometric analysis of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin complexes in Caco-2 cells and claudin 4 fibroblast transfectants. Cell Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2734–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, S.P.; Denmead, M.; Parekh, N.; Granum, P.E. Cationic currents induced by Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin in human intestinal CaCO-2 cells. J. Med. Microbiol. 1999, 48, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, G.; McClane, B.A. The importance of calcium influx, calpain and calmodulin for the activation of CaCo-2 cell death pathways by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Cell Microbiol. 2005, 7, 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, G.; Zhou, X.; McClane, B.A. Death pathways activated in CaCo-2 cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 4260–4270. [Google Scholar]
- Smedley, J.G., III; Uzal, F.A.; McClane, B.A. Identification of a prepore large-complex stage in the mechanism of action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geny, B.; Popoff, M.R. Bacterial protein toxins and lipids: pore formation or toxin entry into cells. Biol. Cell 2006, 98, 667–678. [Google Scholar]
- Caserta, J.A.; Hale, M.L.; Popoff, M.R.; Stiles, B.G.; McClane, B.A. Evidence that membrane rafts are not required for the action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5677–5685. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, U.; Van Itallie, C.M.; Mitic, L.L.; Anderson, J.M.; McClane, B.A. CaCo-2 cells treated with Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin form multiple large complex species, one of which contains the tight junction protein occludin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18407–18417. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, A.I.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C.A. Endocytosis of Epithelial Apical Junctional Proteins by a Clathrin-Mediated Pathway into a Unique Storage Compartment. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2004, 15, 176–188. [Google Scholar]
- Daugherty, B.L.; Mateescu, M.; Patel, A.S.; Wade, K.; Kimura, S.; Gonzales, L.W.; Guttentag, S.; Ballard, P.L.; Koval, M. Developmental regulation of claudin localization by fetal alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2004, 287, L1266–L1273. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Turner, J.R. Actin depolymerization disrupts tight junctions via caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 3919–3936. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, J.; Abe, H.; Kamitani, S.; Toshima, H.; Fukui, A.; Miyake, M.; Kamata, Y.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Horiguchi, Y. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin interacts with claudins via electrostatic attraction. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 401–408. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, J.L.; Van Itallie, C.M.; Rasmussen, J.E.; Anderson, J.M. Claudin profiling in the mouse during postnatal intestinal development and along the gastrointestinal tract reveals complex expression patterns. Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, H.; Chiba, H.; Yokozaki, H.; Sakai, N.; Sugimoto, K.; Wada, T.; Kojima, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sawada, N. Differential expression and subcellular localization of claudin-7, -8, -12, -13, and -15 along the mouse intestine. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 933–944. [Google Scholar]
- Van Itallie, C.M.; Betts, L.; Smedley, J.G., III; McClane, B.A.; Anderson, J.M. Structure of the claudin-binding domain of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Addess, K.J.; Chen, J.; Geer, L.Y.; He, J.; He, S.; Lu, S.; Madej, T.; Marchler-Bauer, A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Zhang, N.; Bryant, S.H. MMDB: annotating protein sequences with Entrez's 3D-structure database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D298–D300. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Anderson, J.B.; DeWeese-Scott, C.; Fedorova, N.D.; Geer, L.Y.; He, S.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Liebert, C.A.; Liu, C.; Madej, T.; Marchler-Bauer, A.; Marchler, G.H.; Mazumder, R.; Nikolskaya, A.N.; Rao, B.S.; Panchenko, A.R.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Simonyan, V.; Song, J.S.; Thiessen, P.A.; Vasudevan, S.; Wang, Y.; Yamashita, R.A.; Yin, J.J.; Bryant, S.H. MMDB: Entrez's 3D-structure database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 474–477. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, P.C.; Wnek, A.P.; McClane, B.A. Molecular cloning of the 3' half of the Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin gene and demonstration that this region encodes receptor-binding activity. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 6815–6820. [Google Scholar]
- Granum, P.E.; Richardson, M. Chymotrypsin treatment increases the activity of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Toxicon 1991, 29, 898–900. [Google Scholar]
- Kokai-Kun, J.F.; Benton, K.; Wieckowski, E.U.; McClane, B.A. Identification of a Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin region required for large complex formation and cytotoxicity by random mutagenesis. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 5634–5641. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, P.C.; Mietzner, T.A.; Schoolnik, G.K.; McClane, B.A. Localization of the receptor-binding region of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin utilizing cloned toxin fragments and synthetic peptides. The 30 C-terminal amino acids define a functional binding region. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11037–11043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McClane, B.A. An overview of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Ebihara, C.; Kondoh, M.; Harada, M.; Fujii, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Tsunoda, S.; Horiguchi, Y.; Yagi, K.; Watanabe, Y. Role of Tyr306 in the C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin for modulation of tight junction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 824–830. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, M.; Kondoh, M.; Ebihara, C.; Takahashi, A.; Komiya, E.; Fujii, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Tsunoda, S.; Horiguchi, Y.; Yagi, K.; Watanabe, Y. Role of tyrosine residues in modulation of claudin-4 by the C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, S.L.; Smedley, J.G., III; McClane, B.A. Identification of a claudin-4 residue important for mediating the host cell binding and action of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wray, C.; Mao, Y.; Pan, J.; Chandrasena, A.; Piasta, F.; Frank, J.A. Claudin-4 augments alveolar epithelial barrier function and is induced in acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L219–L227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, M. Tight junctions, but not too tight: fine control of lung permeability by claudins. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2009, 297, L217–L218. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Daugherty, B.; Keise, L.L.; Wei, Z.; Foley, J.P.; Savani, R.C.; Koval, M. Heterogeneity of claudin expression by alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003, 29, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, A.L.; Koval, M.; Fan, X.; Guidot, D.M. Chronic alcohol ingestion alters claudin expression in the alveolar epithelium of rats. Alcohol 2007, 41, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Kominsky, S.L. Claudins: emerging targets for cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2006, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ouban, A.; Ahmed, A.A. Claudins in human cancer: a review. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, K.J.; Agarwal, R.; Morin, P.J. The claudin gene family: expression in normal and neoplastic tissues. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, A.P.; Laughlin, K.V.; Mullin, J.M. Effects of epidermal growth factor versus phorbol ester on kidney epithelial (LLC-PK1) tight junction permeability and cell division. Exp. Cell Res. 1993, 207, 398–406. [Google Scholar]
- Soler, A.P.; Miller, R.D.; Laughlin, K.V.; Carp, N.Z.; Klurfeld, D.M.; Mullin, J.M. Increased tight junctional permeability is associated with the development of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Ikenouchi, J.; Matsuda, M.; Furuse, M.; Tsukita, S. Regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium-mesenchyme transition: direct repression of the gene expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Argani, P.; Korz, D.; Evron, E.; Raman, V.; Garrett, E.; Rein, A.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P.; Sukumar, S. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, F.; White, K.; Kubbies, M.; Swisshelm, K.; Weber, B.H. Genomic organization of claudin-1 and its assessment in hereditary and sporadic breast cancer. Hum. Genet. 2000, 107, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Al Moustafa, A.E.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A.; Batist, G.; Hernandez-Perez, M.; Serruya, C.; Alpert, L.; Black, M.J.; Sladek, R.; Foulkes, W.D. Identification of genes associated with head and neck carcinogenesis by cDNA microarray comparison between matched primary normal epithelial and squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Soini, Y. Expression of claudins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 in various types of tumours. Histopathology 2005, 46, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokes, A.M.; Kulka, J.; Paku, S.; Szik, A.; Paska, C.; Novak, P.K.; Szilak, L.; Kiss, A.; Bogi, K.; Schaff, Z. Claudin-1, -3 and -4 proteins and mRNA expression in benign and malignant breast lesions: a research study. Breast Cancer Res. 2005, 7, R296–R305. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.K.; Moon, J.; Park, S.W.; Song, S.Y.; Chung, J.B.; Kang, J.K. Loss of the tight junction protein claudin 4 correlates with histological growth-pattern and differentiation in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Swisshelm, K.; Machl, A.; Planitzer, S.; Robertson, R.; Kubbies, M.; Hosier, S. SEMP1, a senescence-associated cDNA isolated from human mammary epithelial cells, is a member of an epithelial membrane protein superfamily. Gene 1999, 226, 285–295. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.H.; Frierson, H.F.; Zaika, A.; Powell, S.M.; Roche, J.; Crowe, S.; Moskaluk, C.A.; El-Rifai, W. Expression of tight-junction protein claudin-7 is an early event in gastric tumorigenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Liebner, S.; Fischmann, A.; Rascher, G.; Duffner, F.; Grote, E.H.; Kalbacher, H.; Wolburg, H. Claudin-1 and claudin-5 expression and tight junction morphology are altered in blood vessels of human glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 100, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, M.L.; Goncharuk, V.N.; Diwan, A.H.; Zhang, P.S.; Shen, S.S.; Prieto, V.G. Loss of claudin-1 expression in tumor-associated vessels correlates with acquisition of metastatic phenotype in melanocytic neoplasms. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2005, 32, 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Vali, M.; Korz, D.; Gabig, T.G.; Weitzman, S.A.; Argani, P.; Sukumar, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin elicits rapid and specific cytolysis of breast carcinoma cells mediated through tight junction proteins claudin 3 and 4. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, L.B.; Sherman-Baust, C.A.; Wernyj, R.P.; Schwartz, D.R.; Cho, K.R.; Morin, P.J. Characterization of novel human ovarian cancer-specific transcripts (HOSTs) identified by serial analysis of gene expression. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7225–7232. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.; Crean, C.D.; Lee, W.H.; Cummings, O.W.; Gabig, T.G. Expression of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin receptors claudin-3 and claudin-4 in prostate cancer epithelium. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7878–7881. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, R.; D'Souza, T.; Morin, P.J. Claudin-3 and claudin-4 expression in ovarian epithelial cells enhances invasion and is associated with increased matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7378–7385. [Google Scholar]
- Michl, P.; Barth, C.; Buchholz, M.; Lerch, M.M.; Rolke, M.; Holzmann, K.H.; Menke, A.; Fensterer, H.; Giehl, K.; Lohr, M.; Leder, G.; Iwamura, T.; Adler, G.; Gress, T.M. Claudin-4 expression decreases invasiveness and metastatic potential of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6265–6271. [Google Scholar]
- Morin, P.J. Claudin proteins in human cancer: promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9603–9606. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, E.; Mamelak, A.J.; Gibson, M.; Maitra, A.; Sheikh, S.; Amr, S.S.; Yang, S.; Brock, M.; Forastiere, A.; Zhang, S.; Murphy, K.M.; Berg, K.D. Overexpression of claudin proteins in esophageal adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2006, 14, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, S.C.; Kamangar, F.; Kim, M.P.; Hammoud, S.; Haque, R.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Maitra, A.; Ashfaq, R.; Hustinx, S.; Heitmiller, R.E.; Choti, M.A.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Cameron, J.L.; Yeo, C.J.; Schulick, R.D.; Montgomery, E. Claudin-4, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4, and stratifin are markers of gastric adenocarcinoma precursor lesions. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2006, 15, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Michl, P.; Buchholz, M.; Rolke, M.; Kunsch, S.; Lohr, M.; McClane, B.; Tsukita, S.; Leder, G.; Adler, G.; Gress, T.M. Claudin-4: a new target for pancreatic cancer treatment using Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Gastroenterology 2001, 121, 678–684. [Google Scholar]
- Santin, A.D.; Cane, S.; Bellone, S.; Palmieri, M.; Siegel, E.R.; Thomas, M.; Roman, J.J.; Burnett, A.; Cannon, M.J.; Pecorelli, S. Treatment of chemotherapy-resistant human ovarian cancer xenografts in C.B-17/SCID mice by intraperitoneal administration of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4334–4342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kominsky, S.L.; Tyler, B.; Sosnowski, J.; Brady, K.; Doucet, M.; Nell, D.; Smedley, J.G., III; McClane, B.; Brem, H.; Sukumar, S. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin as a novel-targeted therapeutic for brain metastasis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7977–7982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, C.; Kondoh, M.; Hasuike, N.; Harada, M.; Mizuguchi, H.; Horiguchi, Y.; Fujii, M.; Watanabe, Y. Preparation of a claudin-targeting molecule using a C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X.; Lin, X.; Manorek, G.; Kanatani, I.; Cheung, L.H.; Rosenblum, M.G.; Howell, S.B. Recombinant CPE fused to tumor necrosis factor targets human ovarian cancer cells expressing the claudin-3 and claudin-4 receptors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Litkouhi, B.; Kwong, J.; Lo, C.M.; Smedley, J.G., III; McClane, B.A.; Aponte, M.; Gao, Z.; Sarno, J.L.; Hinners, J.; Welch, W.R.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Mok, S.C.; Garner, E.I. Claudin-4 overexpression in epithelial ovarian cancer is associated with hypomethylation and is a potential target for modulation of tight junction barrier function using a C-terminal fragment of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, R.; Kondoh, M.; Kakutani, H.; Tsunoda, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Hamakubo, T.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Horiguchi, Y.; Yagi, K. A novel tumor-targeted therapy using a claudin-4-targeting molecule. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 918–926. [Google Scholar]
- Ogata, M.; Chaudhary, V.K.; Pastan, I.; FitzGerald, D.J. Processing of Pseudomonas exotoxin by a cellular protease results in the generation of a 37,000-Da toxin fragment that is translocated to the cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 20678–20685. [Google Scholar]
- Saeki, R.; Kondoh, M.; Kakutani, H.; Matsuhisa, K.; Takahashi, A.; Suzuki, H.; Kakamu, Y.; Watari, A.; Yagi, K. A claudin-targeting molecule as an inhibitor of tumor metastasis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kondoh, M.; Masuyama, A.; Takahashi, A.; Asano, N.; Mizuguchi, H.; Koizumi, N.; Fujii, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Horiguchi, Y.; Watanbe, Y. A novel strategy for the enhancement of drug absorption using a claudin modulator. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Sugahara, K.N.; Teesalu, T.; Karmali, P.P.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Agemy, L.; Greenwald, D.R.; Ruoslahti, E. Coadministration of a tumor-penetrating peptide enhances the efficacy of cancer drugs. Science 2010, 328, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, F.M.; Mach, A.S.; Keller, A.M.; Lindsay, J.A. Evidence for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin (CPE) inducing a mitogenic and cytokine response in vitro and a cytokine response in vivo. Curr. Microbiol. 1999, 38, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, K.; Okamura, H.; Kunitoh, D.; Uemura, T. Mitogenic activity of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in human peripheral lymphocytes. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1997, 59, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bowness, P.; Moss, P.A.; Tranter, H.; Bell, J.I.; McMichael, A.J. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin is a superantigen reactive with human T cell receptors V beta 6.9 and V beta 22. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 176, 893–896. [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer, T.; Fleischer, B.; Stevens, D.L.; McClane, B.A.; Stiles, B.G. Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin lacks superantigenic activity but induces an interleukin-6 response from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3485–3488. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitchell, L.A.; Koval, M. Specificity of Interaction between Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin and Claudin-Family Tight Junction Proteins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1595-1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2071595
Mitchell LA, Koval M. Specificity of Interaction between Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin and Claudin-Family Tight Junction Proteins. Toxins. 2010; 2(7):1595-1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2071595
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitchell, Leslie A., and Michael Koval. 2010. "Specificity of Interaction between Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin and Claudin-Family Tight Junction Proteins" Toxins 2, no. 7: 1595-1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2071595
APA StyleMitchell, L. A., & Koval, M. (2010). Specificity of Interaction between Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin and Claudin-Family Tight Junction Proteins. Toxins, 2(7), 1595-1611. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2071595