Recent Advances in Research on Widow Spider Venoms and Toxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physiological and Biochemical Analysis of Venoms
2.1. Physiological Analysis
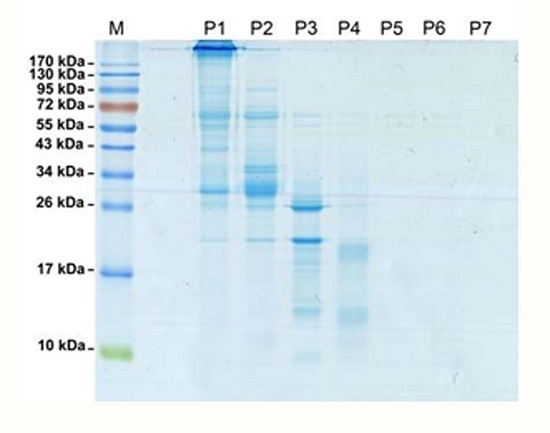
2.2. Whole Venom Proteomics
3. Venom Gland Transcriptome
| Family Name | Number of Member | Function/Activity |
|---|---|---|
| α-LTX-Lt1a family 1 | 12 | main neurotoxins against vertebrates |
| α-LTX-Lt1a family 2 | 7 | main neurotoxins against vertebrates |
| α-LIX-Lt1a family | 2 | main neurotoxins against insects |
| δ-LIX-Lt1a family | 6 | main neurotoxins against insects |
| Ank family | 4 | neurotoxins |
| Theriditoxin family | 62 | assistant toxins |
| SCP family | 3 | ion channel inhibitors |
| Ctenitoxin family | 9 | protease inhibitors |
| Trypsin family | 16 | toxin maturation; hydrolysis of prey tissues |
| Lycotoxin family | 8 | neurotoxins |
| Orphan family | 13 | inhibitors of proteases or ion channels |
| Scorpion toxin like family | 4 | largely unknown |
4. Toxins Purified from Venom
4.1. Main Venom Toxins
| Component | MW(kDa) | Target/Activity | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-LTX | 130 | Vertebrates | [35] |
| α-LCT | 120 | Crustaceans | [37] |
| α-LIT | 120 | Insects | [36] |
| β-LIT | 140 | Insects | [36] |
| γ-LIT | 120 | Insects | [36] |
| δ-LIT | 110 | Insects | [36] |
| ε-LIT | 110 | Insects, C. elegans | [36,38] |
| LMWP | 8 | Increase toxicity of LTXs | [43] |
| LMWP2 | 9.5 | Increase toxicity of LTXs | [43] |
4.2. Diversity of α-LTX
4.3. Action Mechanism and Application of α-LTX
5. Toxins outside Venom Glands
5.1. Egg Toxicity
| Classification | Egg Extract (%) | Venom (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| (i) known typical black widow spider venom proteins | 0 | 10 (8.2) |
| (ii) hydrolases | 12 (7.6) | 13 (10.7) |
| (iii) other enzymes | 51 (32.5) | 20 (16.4) |
| (iv) proteins of unknown function | 14 (8.9) | 25 (20.5) |
| (v) proteins with binding function | 44 (28.0) | 23 (18.9) |
| (vi) other proteins | 36 (22.9) | 31 (25.4) |
| Total | 157 (100) | 122 (100) |
5.2. Toxins Purified from the Eggs
5.3. Spiderling Toxicity
5.4. Implications of the Toxins outside Venom Glands
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Platnick, N.I. Advances in Spider Taxonomy 1992–1995: With Redescriptions 1940–1980; New York Entomological Society: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 1–976. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, H.W. Number of species of black-widow spiders (Theridiidae: Latrodectus). Science 1958, 127, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, R.S.; Isbister, G.K. Medical aspects of spider bites. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garb, J.E.; Hayashi, C.Y. Molecular evolution of α-latrotoxin, the exceptionally potent vertebrate neurotoxin in black widow spider venom. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushkaryov, Y.A.; Volynski, K.E.; Ashton, A.C. The multiple actions of black widow spider toxins and their selective use in neurosecretion studies. Toxicon 2004, 43, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garb, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Gillespie, R.G. The black widow spider genus Latrodectus (Araneae: Theridiidae): Phylogeny, biogeography, and invasion history. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 31, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, G.A. Widow spider envenomation (latrodectism): A worldwide problem. Wilderness Environ. Med. 1997, 8, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, E.V. Black widow spider toxins: The present and the future. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.C.B. Female hunger can explain variation in cannibalistic behaviors despite male sacrifice in redback spiders. Behav. Ecol. 1998, 1, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golcuk, Y.; Velibey, Y.; Gonullu, H.; Sahin, M.; Kocabas, E. Acute toxic fulminant myocarditis after a black widow spider envenomation: Case report and literature review. Clin. Toxicol. (Phila.) 2013, 51, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavusoglu, K.; Bayram, A.; Maras, M.; Krnd, T.; Cavusoglu, K. A morphological study on the venom apparatus of spider Larinioides Cornutus (Araneae, Araneidae). Turk. J. Zool. 2005, 29, 351–356. [Google Scholar]
- White, J. Clinical toxicology of spider bite. In Handbook of Clinical Toxicology of Animal Venoms and Poisons; Meier, J., White, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 259–329. [Google Scholar]
- Camp, N.E. Black widow spider envenomation. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 40, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Lugo, M.; Sanchez, T.; Finol, H.J.; Sánchez, E.E.; Suárez, J.A.; Guerreiro, B.; Rodríguez-Acosta, A. Neurotoxic activity and ultrastructural changes in muscles caused by the brown widow spider Latrodectus geometricus venom. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2009, 51, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, I.H.; Lewin, N.A. Arthropods. In Goldfrank’s Toxicologic Emergencies, 8th ed.; Flomenbaum, N.E., Goldfrank, L., Hoffman, R., Howland, M.A., Lewin, N., Nelson, L., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 1603–1622. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.; Weinstein, S.A. Latrodectism and effectiveness of antivenom. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2015, 65, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbister, G.K.; Page, C.B.; Buckley, N.A.; Fatovich, D.M.; Pascu, O.; MacDonald, S.P.; Calver, L.A.; Brown, S.G. Randomized controlled trial of intravenous antivenom versus placebo for latrodectism: The second Redback Antivenom Evaluation (RAVE-II) study. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2014, 64, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobert, R. Ueber die giftigen spinnen russlads. Sber. Naturf. Ges. Dorpot. 1889, 8, 340–362. [Google Scholar]
- Buffkin, D.C.; Russell, F.E. A poison from the eggs and spiderlings of the black widow spider. Proc. West. Pharmacol. Soc. 1971, 14, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Buffkin, D.C.; Russell, F.E.; Deshmukh, A. Preliminary study on the toxicity of black widow spider eggs. Toxicon 1971, 9, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhunov, A.; Golubenko, Z.; Abdurashidova, N.A.; Mustakimova, E.C.; Ibragimov, F.A.; Mackessy, S. Comparative biochemistry of the physiologically active components of venom, hemolymphy, and eggs of the karakurt spider (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus). Chem. Nat. Compd. 2001, 37, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.S. The toxicology of Latrodectus tredecimguttatus: The mediterranean black widow spider. Homeopathy 2004, 93, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, J.; Navarrete, P.; Marconi, M.; Gutiérrez, R.S.; Martínez-Torres, A.; Mejías, F.R. Tetraethylammonium-sensitive K+ current in the bovine spermatozoa and its blocking by the venom of the Chilean Latrodectus mactans. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2010, 56, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, P.; Martínez-Torres, A.; Gutiérrez, R.S.; Mejía, F.R.; Parodi, J. Venom of the Chilean Latrodectus mactans alters bovine spermatozoa calcium and function by blocking the TEA-sensitive K+ current. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2010, 56, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, B.; Finol, H.J.; Reyes-Lugo, M.; Salazar, A.M.; Sánchez, E.E.; Estrella, A.; Roschman-González, A.; Ibarra, C.; Salvi, I.; Rodríguez-Acosta, A. Activities against hemostatic proteins and adrenal gland ultrastructural changes caused by the brown widow spider Latrodectus geometricus (Araneae: Theridiidae) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 151, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.C.; Duan, Z.G.; Yang, J.; Yan, X.J.; Zhou, H.; He, X.Z.; Liang, S.P. Physiological and biochemical analysis of L. tredecimguttatus venom collected by electrical stimulation. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 63, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Z.; Yan, X.; Cao, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Proteomic analysis of Latrodectus tredecimguttatus venom for uncovering potential latrodectism-related proteins. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2008, 22, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futrell, J.M. Loxoscelism. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1992, 304, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rash, L.D.; Hodgson, W.C. Pharmacology and biochemistry of spider venoms. Toxicon 2002, 40, 225–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawarak, J.; Sinchaikul, S.; Wu, C.Y.; Liau, M.Y.; Phutrakul, S.; Chen, S.T. Proteomics of snake venoms from Elapidae and Viperidae families by multidimensional chromatographic methods. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 2838–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haney, R.A.; Ayoub, N.A.; Clarke, T.H.; Hayashi, C.Y.; Garb, J.E. Dramatic expansion of the black widow toxin arsenal uncovered by multi-tissue transcriptomics and venom proteomics. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Duan, Z.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liang, S. The venom gland transcriptome of Latrodectus tredecimguttatus revealed by deep sequencing and cDNA library analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn-Nentwig, L.; Stöklin, R.; Nentwig, W. Venom composition and strategies in spiders. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2011, 40, 1–86. [Google Scholar]
- Dulubova, I.E.; Krasnoperov, V.G.; Khvotchev, M.V.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Volkova, T.M.; Grishin, E.V.; Vais, H.; Bell, D.R.; Usherwood, P.N. Cloning and structure of delta-latroinsectotoxin, a novel insect-specific member of the latrotoxin family: Functional expression requires C-terminal truncation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7535–7543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grasso, A. Preparation and properties of a neurotoxin purified from the venom of black widow spider (Latrodectus mactans tredecimguttatus). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 439, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnoperov, V.G.; Shamotienko, O.G.; Grishin, E.V. Isolation and properties of insect-specific neurotoxins from venoms of the spider Lactodectus mactans tredecimguttatus. Bioorg. Khim. 1990, 16, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krasnoperov, V.G.; Shamotienko, O.G.; Grishin, E.V. A crustacean-specific neurotoxin from the venom of the black widow spider Latrodectus mactans tredecimguttatus. Bioorg. Khim. 1990, 16, 1567–1569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mee, C.J.; Tomlinson, S.R.; Perestenko, P.V.; de Pomerai, D.; Duce, I.R.; Usherwood, P.N.; Bell, D.R. Latrophilin is required for toxicity of black widow spider venom in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem. J. 2004, 378, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyatkin, N.I.; Dulubova, I.E.; Chekhovskaya, I.A.; Grishin, E.V. Cloning and structure of cDNA encoding α-latrotoxin from black widow spider venom. FEBS Lett. 1990, 270, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyatkin, N.; Dulubova, I.E.; Grishin, E.V. Cloning and structural analysis of α-latroinsectotoxin cDNA: Abundance of ankyrin-like repeats. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 213, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilevich, V.N.; Lukianov, S.A.; Grishin, E.V. Cloning and structure of gene encoded α-latrocrustoxin from the black widow spider venom. Bioorg. Khim. 1999, 25, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orlova, E.V.; Rahman, M.A.; Gowen, B.; Volynski, K.E.; Ashton, A.C.; Manser, C.; van Heel, M.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. Structure of α-latrotoxin oligomers reveals that divalent cation-dependent tetramers form membrane pores. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volkova, T.M.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Woll, P.; Grishin, E.V. Low molecular weight components from black widow spider venom. Toxicon 1995, 33, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, E.V.; Himmelreich, N.H.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Pozdnyakova, N.G.; Storchak, L.G.; Volkova, T.M.; Woll, P.G. Modulation of functional activities of the neurotoxin from black widow spider venom. FEBS Lett. 1993, 336, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyatkin, N.I.; Kulikovskaya, I.M.; Grishin, E.V.; Beadle, D.J.; King, L.A. Functional characterization of black widow spider neurotoxins synthesised in insectcells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 230, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCowan, C.; Garb, J.E. Recruitment and diversification of an ecdysozoan family of neuropeptide hormones for black widow spider venom expression. Gene 2014, 536, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhunov, A.A.; Golubenko, Z.; Sosnina, N. Isolation and characterization of biological properties of inhibitors angiotensin-1-converting enzyme from the spider venom Latrodectus tredecimguttatus. Agents Actions Suppl. 1992, 38, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Akhunov, A.A.; Makevnina, L.G.; Golubenko, Z.; Paskhina, T.S. Kininase of the Latrodectus tredecimguttatus venom: A study of its enzyme substrate specificity. Immunopharmacology 1996, 32, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, B.; Hurlbut, W.P. Ca2+-dependent recycling of synaptic vesicles at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Cell Biol. 1980, 87, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesce, R.; Segal, J.R.; Ceccarelli, B.; Hurlbut, W.P. Effects of black widow spider venom and Ca2+ on quantal secretion at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Gen. Physiol. 1986, 88, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graudins, A.; Little, M.J.; Pineda, S.S.; Hains, P.G.; King, G.F.; Broady, K.W.; Nicholson, G.M. Cloning and activity of a novel α-latrotoxin from red-back spider venom. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graudins, A.; Padula, M.; Broady, K.; Nicholson, G.M. Red-back spider (Latrodectus hasselti) antivenom prevents the toxicity of widow spider venoms. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2001, 37, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, J.; Romero, F. Synaptic effects of low molecular weight components from Chilean black widow spider venom. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhere, K.V.; Haney, R.A.; Ayoub, N.A.; Garb, J.E. Gene structure, regulatory control, and evolution of black widow venom latrotoxins. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3891–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilevich, V.N.; Grishin, E.V. The chromosomal genes for black widow spider neurotoxins do not contain introns. Bioorg. Khim. 2000, 26, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, A.; Rubin, L.L.; Tzeng, M.C. Black widow spider venom: Effect of purified toxin on lipid bilayer membranes. Science 1976, 193, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushkaryov, Y.A.; Rohou, A.; Sugita, S. α-Latrotoxin and its receptors. Hardb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2008, 184, 171–206. [Google Scholar]
- Rohou, A.; Nield, J.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. Insecticidal toxins from black widow spider venom. Toxicon 2007, 49, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.; Suckling, J.; Ushkaryov, Y. Penelope’s web: Using alpha-latrotoxin to untangle the mysteries of exocytosis. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deák, F.; Liu, X.; Khvotchev, M.; Li, G.; Kavalali, E.T.; Sugita, S.; Südhof, T.C. Alpha-latrotoxin stimulates a novel pathway of Ca2+-dependent synaptic exocytosis independent of the classical synaptic fusion machinery. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 8639–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.P.; Ushkaryov, Y.A. The latrophilins, “split-personality” receptors. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 706, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.F.; Muenke, M.; Arcos-Burgos, M. From the black widow spider to human behavior: Latrophilins, a relatively unknown class of G protein-coupled receptors, are implicated in psychiatric disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. B 2011, 156, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, H.; Tadokoro, S.; Nakanishi, M.; Hirashima, N. Latrotoxin-induced exocytosis in mast cells transfected with latrophilin. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesngon, M.; McNutt, P. α-latrotoxin rescues SNAP-25 from BoNT/A-mediated proteolysis in embryonic stem cell-derived neurons. Toxins 2011, 3, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X.; Guo, T.; Wang, J.; Hu, W.; Duan, Z.; Wang, X. Physiological and biochemical characterization of egg extract of black widow spiders to uncover molecular basis of egg toxicity. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Duan, Z.; Cao, R.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Protein compositional analysis of the eggs of black widow spider (L. tredecimguttatus): Implications for the understanding of egg toxicity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, T.; Hu, W.; Duan, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Purification and partial characterization of a novel neurotoxic protein from eggs of black widow spiders (Latrodectus tredecimguttatus). J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2013, 27, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yan, Y.; Yu, H.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Duan, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Isolation and identification of a sodium channel-inhibiting protein from eggs of black widow spiders. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Q.; Yu, H.; Peng, X.; Yan, S.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X. Isolation and preliminary characterization of proteinaceous toxins with insecticidal and antibacterial activities from black widow spider (L. tredecimguttatus) eggs. Toxins 2015, 7, 886–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Lei, Q.; Wang, X.; Liang, S. Physiological and biochemical analysis to reveal the molecular basis for black widow spiderling toxicity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2014, 28, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, F.E.; Maretć, Z. Effects of Latrodectus egg poison on web building. Toxicon 1979, 17, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Wang, X. Recent Advances in Research on Widow Spider Venoms and Toxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 5055-5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124862
Yan S, Wang X. Recent Advances in Research on Widow Spider Venoms and Toxins. Toxins. 2015; 7(12):5055-5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124862
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shuai, and Xianchun Wang. 2015. "Recent Advances in Research on Widow Spider Venoms and Toxins" Toxins 7, no. 12: 5055-5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124862
APA StyleYan, S., & Wang, X. (2015). Recent Advances in Research on Widow Spider Venoms and Toxins. Toxins, 7(12), 5055-5067. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7124862