Binding Studies on Isolated Porcine Small Intestinal Mucosa and in vitro Toxicity Studies Reveal Lack of Effect of C. perfringens Beta-Toxin on the Porcine Intestinal Epithelium
Abstract
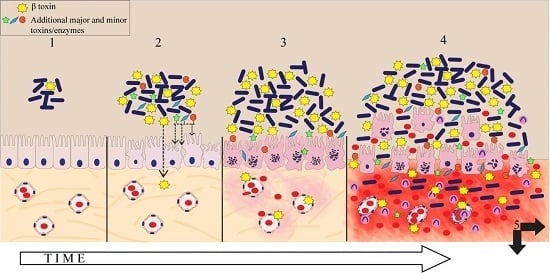
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cellular Binding of CPB in Porcine Jejunal Cryosections

2.2. Cellular Binding of CPB in Porcine Jejunal Explants


2.3. Trans Epithelial Electrical Resistance Measurements (TEER)
2.3.1. Apical Exposure of Polarized Porcine Small Intestinal Cells Layers to C. perfringens Type C Culture Supernatants and rCPB

2.3.2. Basolateral Exposure of Polarized Porcine Small Intestinal Cells Layers to C. perfringens Type C Culture Supernatants and rCPB

2.4. Exposure of Primary Porcine Small Intestinal Epithelial Cells to C. perfringens Type C Culture Supernatants and rCPB

3. Discussion
4. Conclusions

5. Experimental Section
5.1. Production of C. perfringens Culture Supernatants, Recombinant CPB and Aerolysin
5.2. Jejunal Explants, Histology, Immunohistochemistry
5.3. Binding Studies in Intestinal Cryosections
5.4. Antibody Neutralization Experiments
5.5. Cell Cultures
5.6. Transepithelial Resistance Measurements
5.7. Cytotoxicity in Primary Porcine Jejunal Epithelial Cells
5.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Songer, J.G. Clostridial enteric diseases of domestic animals. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 9, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petit, L.; Gibert, M.; Popoff, M.R. Clostridium perfringens: Toxinotype and genotype. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amimoto, K.; Noro, T.; Oishi, E.; Shimizu, M. A novel toxin homologous to large clostridial cytotoxins found in culture supernatant of Clostridium perfringens type C. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoff, M.R.; Bouvet, P. Clostridial toxins. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 1021–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäggi, M.; Wollschlager, N.; Abril, C.; Albini, S.; Brachelente, C.; Wyder, M.; Posthaus, H. Retrospective study on necrotizing enteritis in piglets in switzerland. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2009, 151, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayeed, S.; Uzal, F.A.; Fisher, D.J.; Saputo, J.; Vidal, J.E.; Chen, Y.; Gupta, P.; Rood, J.I.; McClane, B.A. Beta toxin is essential for the intestinal virulence of Clostridium perfringens type C disease isolate cn3685 in a rabbit ileal loop model. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahama, M.; Hayashi, S.; Morimitsu, S.; Sakurai, J. Biological activities and pore formation of Clostridium perfringens beta toxin in hl 60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 36934–36941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahama, M.; Shibutani, M.; Seike, S.; Yonezaki, M.; Takagishi, T.; Oda, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Sakurai, J. The p38 mapk and jnk pathways protect host cells against Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin. Inf. Immun. 2013, 81, 3703–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, F.A.; McClane, B.A. Recent progress in understanding the pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens type C infections. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Los, F.C.; Randis, T.M.; Aroian, R.V.; Ratner, A.J. Role of pore-forming toxins in bacterial infectious diseases. Microbiol .Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, C.; Popescu, F.; Wyder, M.; Sutter, E.; Zeeh, F.; Frey, J.; von Schubert, C.; Posthaus, H. Rapid cytopathic effects of Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin on porcine endothelial cells. Inf. Immun. 2010, 78, 2966–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, F.; Wyder, M.; Gurtner, C.; Frey, J.; Cooke, R.A.; Greenhill, A.R.; Posthaus, H. Susceptibility of primary human endothelial cells to C. perfringens beta-toxin suggesting similar pathogenesis in human and porcine necrotizing enteritis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autheman, D.; Wyder, M.; Popoff, M.; D’Herde, K.; Christen, S.; Posthaus, H. Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin induces necrostatin-inhibitable, calpain-dependent necrosis in primary porcine endothelial cells. PLoS One 2013, 8, e64644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miclard, J.; Jaggi, M.; Sutter, E.; Wyder, M.; Grabscheid, B.; Posthaus, H. Clostridium perfringens β-toxin targets endothelial cells in necrotizing enteritis in piglets. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miclard, J.; van Baarlen, J.; Wyder, M.; Grabscheid, B.; Posthaus, H. Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin binding to vascular endothelial cells in a human case of enteritis necroticans. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 826–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, V.L.; Martel, A.; Pasmans, F.; van Immerseel, F.; Posthaus, H. Endothelial binding of beta toxin to small intestinal mucosal endothelial cells in early stages of experimentally induced Clostridium perfringens type C enteritis in pigs. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierack, P.; Nordhoff, M.; Pollmann, M.; Weyrauch, K.D.; Amasheh, S.; Lodemann, U.; Jores, J.; Tachu, B.; Kleta, S.; Blikslager, A.; et al. Characterization of a porcine intestinal epithelial cell line for in vitro studies of microbial pathogenesis in swine. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 125, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrami, L.; Fivaz, M.; Glauser, P.E.; Sugimoto, N.; Zurzolo, C.; van der Goot, F.G. Sensitivity of polarized epithelial cells to the pore-forming toxin aerolysin. Inf. Immun. 2003, 71, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyen, F.; Pasmans, F.; van Immerseel, F.; Donne, E.; Morgan, E.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F. Porcine in vitro and in vivo models to assess the virulence of salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium for pigs. Lab. Anim. 2009, 43, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosnahan, A.J.; Brown, D.R. Porcine ipec-j2 intestinal epithelial cells in microbiological investigations. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzypek, T.; Valverde Piedra, J.L.; Skrzypek, H.; Kazimierczak, W.; Biernat, M.; Zabielski, R. Gradual disappearance of vacuolated enterocytes in the small intestine of neonatal piglets. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Ellemor, D.M.; Boyd, R.L.; Emmins, J.J.; Rood, J.I. Synergistic effects of alpha-toxin and Perfringolysin O in Clostridium perfringens-mediated gas gangrene. Inf. Immun. 2001, 69, 7904–7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verherstraeten, S.; Goossens, E.; Valgaeren, B.; Pardon, B.; Timbermont, L.; Vermeulen, K.; Schauvliege, S.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Deprez, P.; et al. The synergistic necrohemorrhagic action of Clostridium perfringens perfringolysin and alpha toxin in the bovine intestine and against bovine endothelial cells. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, M.; Gurjar, A.; Theoret, J.R.; Garcia, J.P.; Beingesser, J.; Freedman, J.C.; Fisher, D.J.; McClane, B.A.; Uzal, F.A. Synergistic effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin and beta toxin in rabbit small intestinal loops. Inf. Immun. 2014, 82, 2958–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.E.; McClane, B.A.; Saputo, J.; Parker, J.; Uzal, F.A. Effects of Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin on the rabbit small intestine and colon. Inf. Immun. 2008, 76, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, F.A.; Saputo, J.; Sayeed, S.; Vidal, J.E.; Fisher, D.J.; Poon, R.; Adams, V.; Fernandez-Miyakawa, M.E.; Rood, J.I.; McClane, B.A. Development and application of new mouse models to study the pathogenesis of Clostridium perfringens type C enterotoxemias. Inf. Immun. 2009, 77, 5291–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoff, M.R. Clostridial pore-forming toxins: Powerful virulence factors. Anaerobe 2014, 30, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinthorsdottir, V.; Halldorsson, H.; Andresson, O.S. Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin forms multimeric transmembrane pores in human endothelial cells. Microb. Pathog. 2000, 28, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manich, M.; Knapp, O.; Gibert, M.; Maier, E.; Jolivet-Reynaud, C.; Geny, B.; Benz, R.; Popoff, M.R. Clostridium perfringens delta toxin is sequence related to beta toxin, netb, and staphylococcus pore-forming toxins, but shows functional differences. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatursky, O.; Bayles, R.; Rogers, M.; Jost, B.H.; Songer, J.G.; Tweten, R.K. Clostridium perfringens beta-toxin forms potential-dependent, cation-selective channels in lipid bilayers. Inf. Immun. 2000, 68, 5546–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.E.; Ohtani, K.; Shimizu, T.; McClane, B.A. Contact with enterocyte-like caco-2 cells induces rapid upregulation of toxin production by Clostridium perfringens type C isolates. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1306–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.J.; Fernandez-Miyakawa, M.E.; Sayeed, S.; Poon, R.; Adams, V.; Rood, J.I.; Uzal, F.A.; McClane, B.A. Dissecting the contributions of Clostridium perfringens type C toxins to lethality in the mouse intravenous injection model. Inf. Immun. 2006, 74, 5200–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, D.L.; Mitten, J.; Henry, C. Effects of alpha and theta toxins from Clostridium perfringens on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. Inf. Dis. 1987, 156, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, K.H.; Fivaz, M.; Monod, A.; van der Goot, F.G. Aerolysin induces g-protein activation and Ca2+ release from intracellular stores in human granulocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18122–18129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromter, E.; Diamond, J. Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nat. New Biol. 1972, 235, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roos, S.; Wyder, M.; Candi, A.; Regenscheit, N.; Nathues, C.; Van Immerseel, F.; Posthaus, H. Binding Studies on Isolated Porcine Small Intestinal Mucosa and in vitro Toxicity Studies Reveal Lack of Effect of C. perfringens Beta-Toxin on the Porcine Intestinal Epithelium. Toxins 2015, 7, 1235-1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7041235
Roos S, Wyder M, Candi A, Regenscheit N, Nathues C, Van Immerseel F, Posthaus H. Binding Studies on Isolated Porcine Small Intestinal Mucosa and in vitro Toxicity Studies Reveal Lack of Effect of C. perfringens Beta-Toxin on the Porcine Intestinal Epithelium. Toxins. 2015; 7(4):1235-1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7041235
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoos, Simone, Marianne Wyder, Ahmet Candi, Nadine Regenscheit, Christina Nathues, Filip Van Immerseel, and Horst Posthaus. 2015. "Binding Studies on Isolated Porcine Small Intestinal Mucosa and in vitro Toxicity Studies Reveal Lack of Effect of C. perfringens Beta-Toxin on the Porcine Intestinal Epithelium" Toxins 7, no. 4: 1235-1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7041235
APA StyleRoos, S., Wyder, M., Candi, A., Regenscheit, N., Nathues, C., Van Immerseel, F., & Posthaus, H. (2015). Binding Studies on Isolated Porcine Small Intestinal Mucosa and in vitro Toxicity Studies Reveal Lack of Effect of C. perfringens Beta-Toxin on the Porcine Intestinal Epithelium. Toxins, 7(4), 1235-1252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7041235