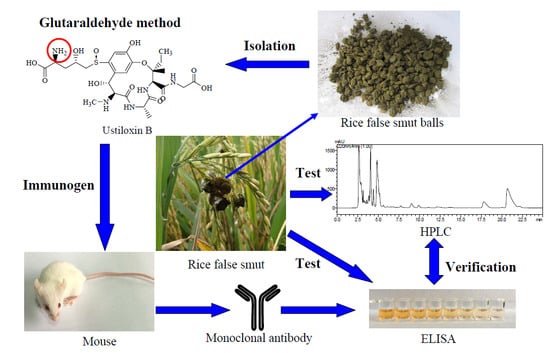
Development of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based icELISA for the Detection of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Balls and Rice Grains
Abstract
:1. Introduction

2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Hapten-Protein Conjugates
2.2. Production and Characterization of mAbs
2.3. Development of icELISA
2.3.1. Optimization of icELISA Conditions
2.3.2. Assay Sensitivity
2.3.3. Antibody Specificity

2.3.4. Recoveries of Ustiloxin B from the Spiked Samples
| Spiked Content of Ustiloxin B (mg/g) | icELISA | HPLC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected Content of Ustiloxin B (mg/g) | Mean Recovery of Ustiloxin B (%) | Detected Content of Ustiloxin B (mg/g) | Mean Recovery of Ustiloxin B (%) | |
| 0.0 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | - | 0.36 ± 0.02 | - |
| 0.2 | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 91.3 ± 10.2 | 0.55 ± 0.003 | 95.2 ± 9.5 |
| 0.4 | 0.76 ± 0.08 | 98.6 ± 13.3 | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 96.4 ± 7.9 |
| 0.8 | 1.21 ± 0.13 | 105.1 ± 21.6 | 1.23 ± 0.04 | 108.3 ± 6.3 |
| 1.6 | 1.86 ± 0.09 | 93.0 ± 2.8 | 2.11 ± 0.16 | 109.2 ± 10.8 |
| 3.2 | 3.46 ± 0.21 | 96.7 ± 7.0 | 3.85 ± 0.15 | 109.1 ± 4.8 |
| Spiked Content of Ustiloxin B (ng/g) | Detected Content of Ustiloxin B (ng/g) | Mean Recovery of Ustiloxin B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | - |
| 100 | 103 ± 3 | 103.5 ± 3.4 |
| 250 | 252 ± 8 | 100.8 ± 3.2 |
| 500 | 506 ± 24 | 101.2 ± 4.8 |
| 1000 | 926 ± 24 | 92.6 ± 2.4 |
| 2000 | 1984 ± 35 | 99.2 ± 1.8 |
| 4000 | 3947 ± 58 | 98.7 ± 1.5 |
| 5000 | 4906 ± 72 | 98.1 ± 1.4 |
2.3.5. Comparison of icELISA and HPLC for Analysis of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Ball Samples and Rice Grain Samples
| Place and Time of Rice False Smut Ball Sample Collection | Ustiloxin B Content (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| icELISA | HPLC | |
| Chengdu, Sichuan, China; September 2014 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.13 ± 0.02 |
| Fengyang, Anhui, China; October 2014 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.01 |
| Hefei, Anhui, China; October 2014 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.28 ± 0.02 |
| Hanshou, Hunan, China; October 2013 | 0.44 ± 0.04 | 0.33 ± 0.005 |
| Linyi, Shandong, China; October 2013 | 0.71 ± 0.05 | 0.51 ± 0.01 |
| Jianyang, Fujian, China; November 2012 | 0.39 ± 0.07 | 0.28 ± 0.03 |
| Qionglai, Sichuan, China; September 2012 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.01 |
| Changsha, Hunan, China; November 2011 | 0.64 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.02 |
| Donggang, Liaoning, China; October 2010 | 0.20 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.02 |
| Donggang, Liaoning, China; December 2011 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.24 ± 0.01 |
| Rice Cultivar (Collection Place and Time) | Ustiloxin B Content (μg/g) | |
|---|---|---|
| icELISA | HPLC | |
| H 329 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 23.89 ± 0.81 a | 28.28 ± 3.19 a |
| H 597 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 44.14 ± 1.62 | 37.04 ± 0.50 |
| Liaojing 212-14 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 1.03 ± 0.07 | nd b |
| Liaokai 79 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 1.84 ± 0.05 | nd |
| Maisui 1 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 8.79 ± 0.04 | nd |
| Shifangliaoyou (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 4.65 ± 0.13 | nd |
| Xiangjing (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 2.28 ± 0.24 | nd |
| Yanfeng 47 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 97.90 ± 2.64 | 93.96 ± 0.57 |
| Yanjing 218 (Donggang, Liaoning, China; November 2014) | 1.96 ± 0.15 | nd |
| Tianyouhuazhan (Hanshou, Hunan, China; October 2013) | 1.71 ± 0.06 | nd |
| Lijiang (Shangzhuang, Beijing, China; October 2011) | nd | nd |
| Zhonghua 17 (Shangzhuang, Beijing, China; October 2013) | nd | nd |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Instruments
3.2. Chemicals and Immunochemicals
3.3. Preparation of UB-Protein Conjugates
3.4. Immunization Protocol, Monoclonal Antibody Production and Purification
3.5. icELISA
3.5.1. Establishment and Optimization of Conventional icELISA
3.5.2. Cross-Reactivity Study
3.5.3. Sample Extraction and Recovery Studies
3.6. icELISA and HPLC Analysis of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Ball Samples and Rice Grain Samples


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix

References
- Tanaka, E.; Ashizawa, T.; Sonoda, R.; Tanaka, C. Villosiclava virens gen. nov., comb. nov., the teleomorph of Ustilaginoidea virens, the causal agent of rice false smut. Mycotaxon 2008, 106, 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Ashizawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Moriwaki, J.; Hirayae, K. Quantification of the rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens from soil in Japan using real–time PCR. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2010, 128, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladhalakshmi, D.; Laha, G.S.; Singh, R.; Karthikeyan, A.; Mangrauthia, S.K.; Sundaram, R.M.; Thukkaiyannan, P.; Viraktamath, B.C. Isolation and characterization of Ustilaginoidea virens and survey of false smut disease of rice in India. Phytoparasitica 2012, 40, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Jin, J.; Hu, D.; Yong, M.; Xu, Y.; He, L. Elucidation of the infection process of Ustilaginoidea virens (teleomorph: Villosiclava virens) in rice spikelets. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.K.; Shier, W.T.; Cartwright, R.D.; Sciumbato, G.L. Ustilaginoidea virens infection of rice in Arkansas: Toxicity of false smut galls, their extracts and the ustiloxin fraction. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Infection processes of Ustilaginoidea virens during artificial inoculation of rice panicles. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2014, 139, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z. Detection of quantitative resistance loci associated with resistance to rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) using introgression lines. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Fang, A.; Han, Y.; Yang, J.; Xue, M.; Bao, J.; Hu, D.; Zhou, B.; Sun, X.; et al. Specific adaptation of Ustilaginoidea virens in occupying host florets revealed by comparative and functional genomics. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koiso, Y.; Li, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Hanaoka, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Fujita, Y.; Yaegashi, H.; Sato, Z. Ustiloxins, antimitotic cyclic peptides from false smut balls on rice panicles caused by Ustilaginoidea virens. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lu, S.; Shan, T.; Wang, P.; Sun, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. Chemistry and biology of mycotoxins from rice false smut pathogen. In Mycotoxins: Properties, Applications and Hazards; Melborn, B.J., Greene, J.C., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 109–130. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Yu, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, W.; et al. Genetic diversity and population structure of rice pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 559–564. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, K.; Izumiyama, N.; Ohtsubo, K.; Koiso, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Sonoda, R.; Fujita, Y.; Yaegashi, H.; Sato, Z. “Lupinosis”-like lesions in mice caused by ustiloxin produced by Ustilaginoidea virens: A morphological study. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luduena, R.F.; Roach, M.C.; Prasad, V.; Banerjee, M.; Koiso, Y.; Li, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Interaction of ustiloxin A with bovine brain tubulin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 47, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Tian, J.; Sun, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, A.; Lai, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L. Bis-naphtho-γ-pyrones from fungi and their bioactivities. Molecules 2014, 19, 7169–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Sun, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Tian, J.; Fu, X.; Dai, J.; Liu, Y.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L. Bioactive bis-naphtho-γ-pyrones from rice false smut pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koiso, Y.; Natori, M.; Iwasaki, S.; Sato, S.; Sonoda, R.; Fujita, Y.; Yaegashi, H.; Sato, Z. Ustiloxin: A phytotoxin and a mycotoxin from false smuth balls on rice panicles. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4157–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koiso, Y.; Morisaki, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Mitsui, Y.; Shirai, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Isolation and structure of an antimitotic cyclic peptide, ustiloxin F: Chemical interrelation with a homologous peptide, ustiloxin B. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Sun, W.; Liu, H.; Gao, S.; Lu, S.; Wang, M.; Sun, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L. Determination and analysis of ustiloxins A and B by LC-ESI-MS and HPLC in false smut balls of rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11275–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Koiso, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Ustiloxins, new antimitotic cyclic peptides: Interaction with porcine brain tubulin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 49, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisaki, N.; Mitsui, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Koiso, Y.; Shirai, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iwasaki, S. Synthesis and anti-tubulin activity of ustiloxin D derivatives. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battilani, P.; Gualla, A.; Dall’Asta, C.; Pellacani, C.; Galaverna, G.; Caglieri, A.; Tagliaferri, S.; Pietri, A.; Dossena, A.; Spadaro, D.; et al. Phomopsins: An overview of phytopathological and chemical aspects, toxicity, analysis and occurrence. World Mycotoxin J. 2011, 4, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Cao, H.; Xu, J.; Yin, X.; Shi, J. Simultaneous quantitative determination of ustiloxin A and ustiloxin D in rice grains by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2012, 26, 246–250. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, A.; Lai, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, L. A monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of ustiloxin A in rice false smut balls and rice samples. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Uchihara, T.; Morimoto, K. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of ustiloxin A in forage rice silage. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2009, 71, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Kang, M.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y. Simultaneous multiresidue determination of mycotoxins in cereal samples by polyvinylidene fluoride membrane based dot immunoassay. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Nolke, G.; Zhang, J.; Niu, L.; Shen, J. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin M1 in food matrices by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Food Anal. Method 2013, 6, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.A.; Wang, S.; Allan, R.D.; Kennedy, I.R. A rapid aflatoxin B1 ELISA: Development and validation with reduced matrix effects for peanuts, corn, pistachio, and soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.Z.; Richard, J.L.; Binder, J. A review of rapid methods for the analysis of mycotoxins. Mycopathologia 2006, 161, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J. An ultra-sensitive monoclonal antibody-based competitive enzyme immunoassay for aflatoxin M1 in milk and infant milk products. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, K.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Li, Q.X.; Liu, S.; Wang, B. Development of a sensitive monoclonal antibody-based indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for analysing chlorantraniliprole residues. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, M.; Butcher, G.; MacMillan, J. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies which recognize different gibberellin epitopes. Planta 1987, 170, 86–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, W.; Nan, T.; Zhai, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.X. Development of a monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the analysis of glycyrrhizic acid. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 386, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Fu, X.; Sun, W.; Zhou, L. Purification of ustiloxins A and B from rice false smut balls by macroporous resins. Molecules 2013, 18, 8181–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cliquet, P.; Cox, E.; van Dorpe, C.; Schacht, E.; Goddeeris, B.M. Generation of class-selective monoclonal antibodies against the penicillin group. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3349–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.J.; Abad, A.; Montoya, A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to the N-methylcarbamate pesticide propoxur. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Ahn, K.C.; Sun, Q.; Hu, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, F. Hapten heterology for a specific and sensitive indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for organophosphorus insecticide fenthion. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 596, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Lin, F.; He, L.; Lai, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, B. Development of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based icELISA for the Detection of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Balls and Rice Grains. Toxins 2015, 7, 3481-3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7093481
Fu X, Wang A, Wang X, Lin F, He L, Lai D, Liu Y, Li QX, Zhou L, Wang B. Development of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based icELISA for the Detection of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Balls and Rice Grains. Toxins. 2015; 7(9):3481-3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7093481
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Xiaoxiang, Ali Wang, Xiaohan Wang, Fengke Lin, Lishan He, Daowan Lai, Yang Liu, Qing X. Li, Ligang Zhou, and Baoming Wang. 2015. "Development of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based icELISA for the Detection of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Balls and Rice Grains" Toxins 7, no. 9: 3481-3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7093481
APA StyleFu, X., Wang, A., Wang, X., Lin, F., He, L., Lai, D., Liu, Y., Li, Q. X., Zhou, L., & Wang, B. (2015). Development of a Monoclonal Antibody-Based icELISA for the Detection of Ustiloxin B in Rice False Smut Balls and Rice Grains. Toxins, 7(9), 3481-3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins7093481