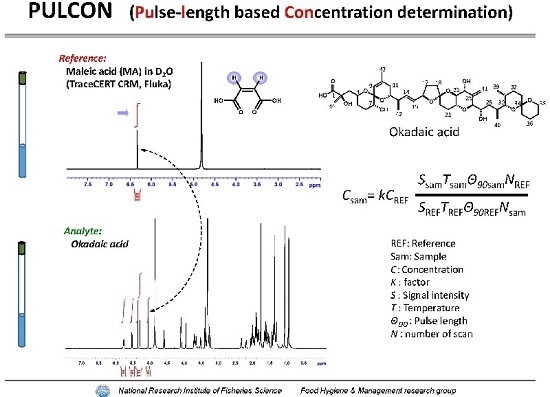
Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Based on PULCON Methodology: Application to Quantification of Invaluable Marine Toxin, Okadaic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Performance Tests of PULCON Method with Different Analytical Conditions
2.2. Relationship of MA Concentrations between Gravimetric and PULCON Method
2.3. Comparison of OA Concentrations between PULCON Method and Internal Standard Method
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. NMR Instrument, Data Acquisition and Data Processing on Performance Tests
4.3. Sample Preparation for Performance Tests of PULCON Method
4.4. Comparison of OA Concentrations between PULCON Method and Internal Standard Method
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tachibana, K.; Scheuer, P.J.; Tsukitani, Y.; Kikuchi, H.; Van Engen, D.; Clardy, J.; Gopichand, Y.; Schmitz, F.J. Okadaic acid, a cytotoxic polyether from two marine sponges of the genus Halichondria. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 2469–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Shimatani, M.; Sugitani, H.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and Structural elucidation of the causative toxin of the diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1982, 48, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, Y.; Murray, S.; Tomaru, A.; Fukuyo, Y. Species Boundaries in the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum Lima (Dinophyceae, Prorocentrales), based on morphological and phylogenetic characters. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Sugawara, W.; Fukuyo, Y.; Oguri, H.; Igarashi, T.; Fujita, N. Identification of Dinophysis fortii as the causative organism of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1980, 46, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yamagichi, M. Occurrence of a new type of shellfish poisoning in the Tohoku district. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1978, 44, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Quilliam, M.A. LC-MS/MS analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins, Okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin analogues, and other lipophilic toxins. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzgrabe, U.; Deubner, R.; Schollmayar, C.; Waibel, B. Quantitative NMR spectroscopy-Application in drug analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 38, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, V.; Pinciroli, V. Quantitative NMR in synthetic and combinatorial chemistry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 38, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, T.; Oshima, Y. Development of quantitative NMR method with internal standard for the standard solutions of paralytic shellfish toxins and characterization of gonyautoxin-5 and gonyautoxin-6. Toxicon 2010, 56, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagnino, D.; Schripsema, S. 1H-NMR quantification in very dilute toxin solutions: Application to anatoxin-a analysis. Toxicon 2005, 46, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larive, C.K.; Jayawickrama, D.; Orfi, L. Quantitative analysis of peptides with NMR spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 1997, 51, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, I.W.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A. Quantitative 1H-NMR with external standards: Use in preparation of calibration solutions for algal toxins and other natural products. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruker. ERETIC2 User’s Guide—Preliminary; Bruker: Billerica, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wider, G.; Dreier, L. Measuring protein concentrations by NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, O.; Kreissl, J.K.; Daschner, A.; Hofmann, T. Accurate determination of reference materials and natural isolates by means of quantitative 1H-NMR spectroscopy. J. Agri. Food chem. 2014, 62, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monakhova, Y.B.; Kohl-Himmelseher, M.; Kuballa, T.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Determination of the purity of pharmaceutical reference materials by 1H-NMR using the standardless PULCON methodology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 100, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohmann, M.; Felbinger, C.; Christoph, N.; Wachter, H.; Wiest, J.; Holzgrabe, U. Quantidication of taurine in energy drinks using 1H NMR. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 93, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.S.; Hwang, K.H.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.E.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, J.T.; Moon, D.C. Survey of ERETIC2 NMR for quantification. J. Kor. Magn. Reson. 2013, 17, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Watanabe, R.; Yoshino, A.; Oikawa, H.; Uchida, H.; Matsushima, R.; Nagai, S.; Kamiyama, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; et al. Preparation of diarrhetic shellfish toxins (DSTs) and paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs) by large algal culture and chemical conversion. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth International conference on Harmful Algae, Wellington, New Zealand, 27–31 October 2014.
- Kato, T.; Saito, M.; Nagae, M.; Fujita, K.; Watai, M.; Igarashi, T.; Yasumoto, T.; Inagaki, M. Absolute quantification of lipophilic shellfish toxins by quantitative nuclear magnetic resonance using removable internal reference substance with SI traceability. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Solvents | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| D2O | 100.3 | 0.0 |
| CD3OD | 100.3 | 0.3 |
| Acetone-d6 | 97.9 | 0.0 |
| DMSO-d6 | 98.1 | 0.2 |
| Acetonitrile-d3 | 97.1 | 0.2 |
| Average | 98.9 | - |
| Stdev | 1.5 | - |
| RSD (%) | 1.5 | - |
| Number of Scans | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 100.7 |
| 8 | 101.4 |
| 16 | 101.4 |
| 32 | 101.4 |
| 64 | 100.7 |
| Average | 101.1 |
| Stdev | 0.4 |
| RSD (%) | 0.4 |
| Samples | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Average | Stdev | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.7 | 100.3 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 99.5 | 100.5 | 99.5 | 99.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 99.7 | 100.0 | 99.2 | 99.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Average | 99.6 | 100.3 | 99.4 | - | - | - |
| Stdev | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | - | - | - |
| RSD (%) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | - | - | - |
| Method | Tube | Signal | Integral Region | Quantitation (µg/g) | Average | Stdev | RSD (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run1 | Run2 | Run3 | |||||||
| Internal standard method | 1 | 1 | 5.85–5.72 | 344.30 | 344.08 | 340.38 | 342.92 | 2.20 | 0.64 |
| 2 | 5.57–5.49 | 346.23 | 345.58 | 344.36 | 345.39 | 0.95 | 0.28 | ||
| 3 | 5.38–5.25 | 345.44 | 349.27 | 354.62 | 349.78 | 4.61 | 1.32 | ||
| 4 | 5.09–5.03 | 367.78 | 332.26 | 345.23 | 348.42 | 17.98 | 5.16 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 5.85–5.72 | 346.39 | 344.29 | 349.36 | 346.68 | 2.55 | 0.74 | |
| 2 | 5.57–5.49 | 362.29 | 360.85 | 357.01 | 360.05 | 2.73 | 0.76 | ||
| 3 | 5.38–5.25 | 365.55 | 361.48 | 355.51 | 360.85 | 5.05 | 1.40 | ||
| 4 | 5.09–5.03 | 361.77 | 355.68 | 355.76 | 357.74 | 3.49 | 0.98 | ||
| PULCON | 1 | 1 | 5.86–5.72 | 344.81 | 333.91 | 340.59 | 339.77 | 5.50 | 1.62 |
| 2 | 5.58–5.48 | 359.29 | 355.49 | 355.08 | 356.62 | 2.32 | 0.65 | ||
| 3 | 5.41–5.24 | 363.20 | 360.73 | 338.95 | 354.29 | 13.34 | 3.77 | ||
| 4 | 5.10–5.01 | 371.00 | 363.92 | 364.74 | 366.55 | 3.87 | 1.06 | ||
| 2 | 1 | 5.86–5.72 | 339.47 | 351.09 | 342.76 | 344.44 | 5.99 | 1.74 | |
| 2 | 5.58–5.48 | 351.92 | 360.04 | 357.88 | 356.61 | 4.21 | 1.18 | ||
| 3 | 5.41–5.24 | 353.67 | 359.63 | 342.35 | 351.88 | 8.78 | 2.49 | ||
| 4 | 5.10–5.01 | 359.73 | 365.08 | 366.31 | 363.71 | 3.50 | 0.96 | ||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, R.; Sugai, C.; Yamazaki, T.; Matsushima, R.; Uchida, H.; Matsumiya, M.; Takatsu, A.; Suzuki, T. Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Based on PULCON Methodology: Application to Quantification of Invaluable Marine Toxin, Okadaic Acid. Toxins 2016, 8, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100294
Watanabe R, Sugai C, Yamazaki T, Matsushima R, Uchida H, Matsumiya M, Takatsu A, Suzuki T. Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Based on PULCON Methodology: Application to Quantification of Invaluable Marine Toxin, Okadaic Acid. Toxins. 2016; 8(10):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100294
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Ryuichi, Chika Sugai, Taichi Yamazaki, Ryoji Matsushima, Hajime Uchida, Masahiro Matsumiya, Akiko Takatsu, and Toshiyuki Suzuki. 2016. "Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Based on PULCON Methodology: Application to Quantification of Invaluable Marine Toxin, Okadaic Acid" Toxins 8, no. 10: 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100294
APA StyleWatanabe, R., Sugai, C., Yamazaki, T., Matsushima, R., Uchida, H., Matsumiya, M., Takatsu, A., & Suzuki, T. (2016). Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Based on PULCON Methodology: Application to Quantification of Invaluable Marine Toxin, Okadaic Acid. Toxins, 8(10), 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8100294