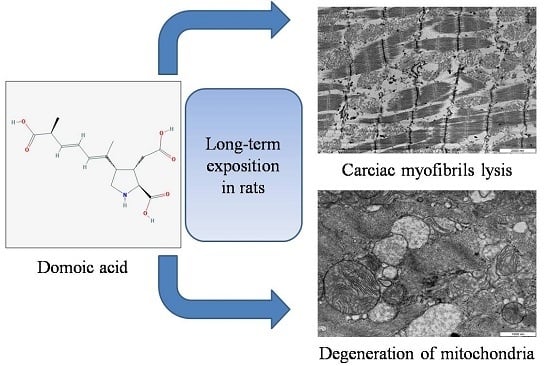
Heart Alterations after Domoic Acid Administration in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Toxin Analysis
5.2. Animals and Toxin Treatment
5.3. Behavioural Analysis
5.4. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
5.5. Preparation of Samples for Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RIADT: | Rede de Infraestruturas de Apoio á Investigación e ao Desenvolvemento Tecnolóxico |
| DA: | Domoic acid |
| ASP: | amnesic shellfish poisoning |
| KA: | kainic acid |
| Glu: | glutamate |
| GluRs: | glutamate receptors |
| AMPA: | alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| Ca2+: | calcium |
| NMDA: | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| ROS: | Reactive Oxide Species |
| CNS: | Central Nervous System |
| i.p.: | intraperitoneal |
| HPLC-UV: | High-performance liquid chromatography-Ultraviolet/Visible |
| H & E: | Haematoxylin and eosin |
| IHC: | immunohistochemistry |
| TEM: | transmission electron microscopy |
| M: | mitochondria |
| IAFLU: | Institute of Agri-Food and Land Use |
| FEDER: | Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional |
| CDTI: | Centro para el Desarrollo Tecnológico e Industrial |
| AGL: | Programa Nacional de Recursos y Tecnologías Agroalimentarias |
| ISIP: | India & Spain Innovating Program |
References
- Hallegraeff, G.M. Harmful algal blooms: A global overview. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae IOC Manuals and Guides No. 33. UNESCO; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.M., Eds.; International Oceanographic Comission, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kotaki, Y.; Koike, K.; Sato, S.; Ogata, T.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Confirmation of domoic acid production of Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries isolated from Ofunato Bay, Japan. Toxicon 1999, 37, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Levin, B.E. Neurobehavioral effects of harmful algal bloom (HAB) toxins: A critical review. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2005, 11, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, E.C. Emerging diseases associated with seafood toxins and other water-borne agents. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 74, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Robertson, A. Domoic acid and human exposure risks: A review. Toxicon 2010, 56, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, T.M.; Bédard, L.; Kosatsky, T.; Hockin, J.C.; Todd, E.C.; Remis, R.S. An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.L.C.; Boyd, R.K.; de Freitas, A.S.W.; Falk, M.; Foxall, R.A.; Jamieson, W.D.; Laylock, M.V.; McCullocj, A.W.; McInnes, A.G.; Odense, P.; et al. Identification of domoic acid, a neuroexcitatory amino acid, in toxic mussels from eastern Prince Edward Island. Can. J. Chem. 1989, 67, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, R.F.; Stewart, J.E. Domoic acid and the eastern Canadian molluscan shellfish industry. Aquaculture 1989, 77, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, P.J.; Pin, J.P. Pharmacology and functions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1997, 37, 205–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traynelis, S.F.; Wollmuth, L.P.; McBain, C.J.; Menniti, F.S.; Vance, K.M.; Ogden, K.K.; Hansen, K.B.; Yuan, H.; Myers, S.J.; Dingledine, R. Glutamate receptor ion channels: Structure, regulation, and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 405–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willard, S.S.; Koochekpour, S. Glutamate signaling in benign and malignant disorders: Current status, future perspectives, and therapeutic implications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, D.E.; Lodge, D.; Collingridge, G.L. Kainate receptors: Pharmacology, function and therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 90–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, B.; Barlow, T.; Moizer, K.; Paul, S.; Boyle, C. Amnesic shellfish poison. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.G.; Giordano, G.; Faustman, E.M. Domoic acid as a developmental neurotoxin. Neurotoxicology 2010, 31, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, F.W.; LePage, K.T.; Murray, T.F. Domoic acid neurotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule neurons is controlled preferentially by the NMDA receptor Ca2+ influx pathway. Brain Res. 2002, 924, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledo, A.; Frade, J.; Barbosa, R.M.; Laranjinha, J. Nitric oxide in brain: Diffusion, targets and concentration dynamics in hippocampal subregions. Mol. Aspects Med. 2004, 25, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, O. Domoic acid toxicologic pathology: A review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 180–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Potvin, J.L. Neural and behavioural effects of domoic acid, an amnesic shellfish toxin, in the rat. Can. J. Psychol. 1992, 46, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.G.; Taylor, T.B.; Finch, R.E.; Switzer, R.C.; Ramsdell, J.S. Neuroexcitatory and neurotoxic actions of the amnesic shellfish poison, domoic acid. Neuroreport 1994, 5, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.F.; Pinsky, C.; Standish, N.M.; Bose, R.; Glavin, G.B. Parenteral domoic acid impairs spatial learning in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1992, 41, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittajallu, R.; Braithwaite, S.P.; Clarke, V.R.; Henley, J.M. Kainate receptors: Subunits, synaptic localization and function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomeli, H.; Wisden, W.; Kohler, M.; Keinanen, K.; Sommer, B.; Seeburg, P.H. High-affinity kainate and domoate receptors in rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1992, 307, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisden, W.; Seeburg, P.H. A complex mosaic of high-affinity kainate receptors in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 3582–3598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Appel, N.M.; Rapoport, S.I.; O’Callaghan, J.P. Sequelae of parenteral domoic acid administration in rats: Comparison of effects on different anatomical markers in brain. Synapse 1997, 25, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiedeken, J.A.; Muha, N.; Ramsdell, J.S. A cupric silver histochemical analysis of domoic acid damage to olfactory pathways following status epilepticus in a rat model for chronic recurrent spontaneous seizures and aggressive behavior. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulland, F.M.D. Domoic acid toxicity in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus) stranded along the central California coast, May–October 1998; Report to the National Marine Fisheries Service Working Group on Unusual Marine Mammal Mortality Events; NOAA Technical Memorandum: Sausalito, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zabka, T.S.; Goldstein, T.; Cross, C.; Mueller, R.W.; Kreuder-Johnson, C.; Gill, S.; Gulland, F.M. Characterization of a degenerative cardiomyopathy associated with domoic acid toxicity in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus). Vet. Pathol. 2009, 46, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuder, C.; Miller, M.A.; Lowenstine, L.J.; Conrad, P.A.; Carpenter, T.E.; Jessup, D.A.; Mazet, J.A. Evaluation of cardiac lesions and risk factors associated with myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy in southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis). Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranyac-Tramoundanas, A.; Harrison, J.C.; Sawant, P.M.; Kerr, D.S.; Sammut, I.A. Ischemic cardiomyopathy following seizure induction by domoic Acid. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Pulido, O.M. Glutamate receptors in peripheral tissues: Current knowledge, future research, and implications for toxicology. Toxicol. Pathol. 2001, 29, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.; Veinot, J.; Kavanagh, M.; Pulido, O. Human heart glutamate receptors—Implications for toxicology, food safety, and drug discovery. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranyac-Tramoundanas, A.; Harrison, J.C.; Clarkson, A.N.; Kapoor, M.; Winburn, I.C.; Kerr, D.S.; Sammut, I.A. Domoic acid impairment of cardiac energetics. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 105, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobotka, T.J.; Brown, R.; Quander, D.Y.; Jackson, R.; Smith, M.; Long, S.A.; Barton, C.N.; Rountree, R.L.; Hall, S.; Eilers, P.; et al. Domoic acid: Neurobehavioral and neurohistological effects of low-dose exposure in adult rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1996, 18, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, J.R.; Nowocin, K.J.; Switzer, R.C.; Trusk, T.C.; Ramsdell, J.S. Mapping and reconstruction of domoic acid-induced neurodegeneration in the mouse brain. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiamulera, C.; Costa, S.; Valerio, E.; Reggiani, A. Domoic acid toxicity in rats and mice after intracerebroventricular administration: Comparison with excitatory amino acid agonists. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1992, 70, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakshinamurti, K.; Sharma, S.K.; Sundaram, M. Domoic acid induced seizure activity in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 127, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuquay, J.M.; Muha, N.; Pennington, P.L.; Ramsdell, J.S. Domoic acid induced status epilepticus promotes aggressive behavior in rats. Physiol. Behav. 2012, 105, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesp, B.R.; Clarkson, A.N.; Sawant, P.M.; Kerr, D.S. Domoic acid preconditioning and seizure induction in young and aged rats. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 76, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iverson, F.; Truelove, J.; Nera, E.; Tryphonas, L.; Campbell, J.; Lok, E. Domoic acid poisoning and mussel-associated intoxication: Preliminary investigations into the response of mice and rats to toxic mussel extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1989, 27, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, P.M.; Holland, P.T.; Mountfort, D.O.; Kerr, D.S. In vivo seizure induction and pharmacological preconditioning by domoic acid and isodomoic acids A, B and C. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallet, A.C.; Kowalke, P.K.; Rountree, R.L.; Thorn, B.T.; Binienda, Z.K. Electroencephalographic, behavioral, and c-fos responses to acute domoic acid exposure. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.; Jandova, K.; Struk, I.; Maresova, D.; Pokorny, J.; Riljak, V. Low dose domoic acid influences spontaneous behavior in adult rats. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tryphonas, L.; Truelove, J.; Nera, E.; Iverson, F. Acute neurotoxicity of domoic acid in the rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 1990, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, E.C.; Peng, Y.G.; Means, L.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Working memory deficits induced by single but not repeated exposures to domoic acid. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1025–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, R.J.; Hoesing, J.M.; Whishaw, I.Q. Domoic acid, an environmental toxin, produces hippocampal damage and severe memory impairment. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 120, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.C.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Bermúdez, R.; Antelo, A.A.; Alemañ, N.; Botana, L.M. Dose-response and histopathological study, with special attention to the hypophysis, of the differential effects of domoic acid on rats and mice. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2015, 78, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.C.; Cifuentes, J.; Botana, L. Histological analysis of heart after domoic acid administration in rats. In Proceedings of the IMMR International Meeting on Marine Research, Peniche, Portugal, 10–11 July 2014.
- Cheville, N.F. Ultrastructural Pathology: The Comparative Cellular Basis of Disease, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ide, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Kinugawa, S.; Utsumi, H.; Kang, D.; Hattori, N.; Uchida, K.; Arimura, K.; Egashira, K.; Takeshita, A. Mitochondrial electron transport complex I is a potential source of oxygen free radicals in the failing myocardium. Circ. Res. 1999, 85, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-García, J.; Goldenthal, M.J.; Moe, G.W. Abnormal cardiac and skeletal muscle mitochondrial function in pacing-induced cardiac failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 52, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, G.; Lee, C.F.; Garcia-Menendez, L.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; Suthammarak, W.; Gong, G.; Sedensky, M.M.; Morgan, P.G.; Wang, W.; Tian, R. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency increases protein acetylation and accelerates heart failure. Cell. MeTable 2013, 18, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayeva, M.; Ardehali, H. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage to sarcomeric proteins. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2010, 12, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maru, E.; Kanda, M.; Ashida, H. Functional and morphological changes in the hippocampal neuronal circuits associated with epileptic seizures. Epilepsia 2002, 43, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bealer, S.L.; Little, J.G. Seizures following hippocampal kindling induce QT interval prolongation and increased susceptibility to arrhythmias in rats. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 105, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, E.C. Domoic acid and amnesic shellfish poisoning—A review. J. Food Prot. 1993, 56, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, C.A.; Hierlihy, S.L. Renal clearance of domoic acid in the rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.; Vilariño, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Rodríguez, P.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Botana, L.M. Multidetection of paralytic, diarrheic, and amnesic shellfish toxins by an inhibition immunoassay using a microsphere-flow cytometry system. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7794–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Time | Hypoactivity | Head Shaking | Convulsions | Scratching | Hematoporphyrin Deposits | Absence of Water Intake (Adipsia) | Absence of Food Intake (Anorexia) | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–24 h | 9/9 | 9/9 | 9/9 | 9/9 | 0/9 | 7/9 | 8/9 | 4/9 |
| 24–48 h | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 1/5 | 2/5 | 3/5 | 4/5 | 0/5 |
| 48–72 h | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 1/5 | 2/5 | 0/5 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, A.C.; Cifuentes, J.M.; Bermúdez, R.; Ferreiro, S.F.; Castro, A.R.; Botana, L.M. Heart Alterations after Domoic Acid Administration in Rats. Toxins 2016, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030068
Vieira AC, Cifuentes JM, Bermúdez R, Ferreiro SF, Castro AR, Botana LM. Heart Alterations after Domoic Acid Administration in Rats. Toxins. 2016; 8(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Andres C., José Manuel Cifuentes, Roberto Bermúdez, Sara F. Ferreiro, Albina Román Castro, and Luis M. Botana. 2016. "Heart Alterations after Domoic Acid Administration in Rats" Toxins 8, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030068
APA StyleVieira, A. C., Cifuentes, J. M., Bermúdez, R., Ferreiro, S. F., Castro, A. R., & Botana, L. M. (2016). Heart Alterations after Domoic Acid Administration in Rats. Toxins, 8(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8030068