Venom of the Coral Snake Micrurus clarki: Proteomic Profile, Toxicity, Immunological Cross-Neutralization, and Characterization of a Three-Finger Toxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
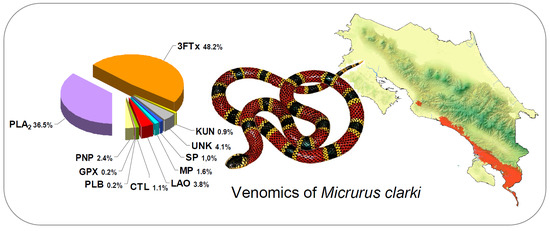
2.1. Proteomic Profile of Micrurus Clarki Venom
2.2. Immunological Properties of Micrurus Clarki Venom
2.3. Lethal Activity of Micrurus Clarki Venom and its Neutralization by Antivenom
2.4. Phospholipase A2 and Myotoxic Activities of Micrurus Clarki Venom
2.5. Lethality Screening of Micrurus Clarki Venom Fractions in Mice
2.6. Characterization of Clarkitoxin-I
2.7. Dichotomy of Venom Types in Micrurus and the Position of Micrurus Clarki
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Venom and Antivenom
4.2. Proteomic Profiling of the Venom
4.3. Quantitative Estimation of the Protein Family Composition of the Venom
4.4. Immunological Cross-Recognition of Venom and its RP-HPLC Fractions
4.5. Mass Determination of Clarkitoxin-I by Electrospray Mass Spectrometry
4.6. Amino Acid Sequencing of Clarkitoxin-I by Tandem Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Venom Lethality and its Neutralization by Antivenom
4.8. Phospholipase A2 and Myotoxic Activities of Micrurus Clarki Venom
4.9. Lethality Screening of Venom Fractions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roze, J.A. Coral Snakes of the Americas. Biology, Identification and Venoms; Krieger Publishing Company: Malabar, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, N.J., Jr.; Sites, J.W. Phylogeny of South American triad coral snakes (Elapidae: Micrurus) based on molecular characters. Herpetologica 2001, 57, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.A.; Lamar, W.W. The Venomous Reptiles of the Western Hemisphere; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- De Roodt, A.R.; de Titto, E.; Dolab, J.A.; Chippaux, J.P. Envenoming by coral snakes (Micrurus) in Argentina during the period between 1979–2003. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2013, 55, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucaretchi, F.; de Capitani, E.M.; Vieira, R.J.; Rodrigues, C.K.; Zannin, M.; da Silva, N.J., Jr.; Casais-e-Silva, L.L.; Hyslop, S. Coral snake bites (Micrurus spp.) in Brazil: A review of literature reports. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solórzano, A. Serpientes de Costa Rica (Snakes of Costa Rica); Instituto Nacional de Biodiversidad (INBio): Heredia, Costa Rica, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Herrera, F.; Vargas-Salinas, F. Anfibios y reptiles en el departamento del Valle del Cauca, Colombia. Biota Colomb. 2013, 9, 251–277. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, K.P. Notes on Central American and Mexican Coral Snakes; Field Museum Natural History: Chicago, IL, USA, 1936; pp. 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lomonte, B.; Fernández, J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J. Venomous snakes of Costa Rica: Biological and medical implications of their venom proteomic profiles analyzed through the strategy of ‘‘snake venomics’‘. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, S.D. Taxonomic distribution and quantitative analysis of free purine and pyrimidine nucleosides in snake venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 140, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Vargas, N.; Pla, D.; Sasa, M.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Sanz, L.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Lomonte, B. Snake venomics of Micrurus alleni and Micrurus mosquitensis from the Caribbean region of Costa Rica reveals two divergent compositional patterns in New World elapids. Toxicon 2015, 107, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aird, S.D. Ophidian envenomation strategies and the role of purines. Toxicon 2002, 40, 335–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Alape-Girón, A.; Angulo, Y.; Sanz, L.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Lomonte, B. Venomic and antivenomic analyses of the Central American coral snake, Micrurus nigrocinctus (Elapidae). J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Núñez, V.; Fernández, J.; Lomonte, B. Integrative characterization of the venom of the coral snake Micrurus dumerilii (Elapidae) from Colombia: Proteome, toxicity, and cross-neutralization by antivenom. J. Proteom. 2016, 136, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lausten, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Lohse, B.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Unveiling the nature of black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) venom through venomics and antivenom immunoprofiling: Identification of key toxin targets for antivenom development. J. Proteom. 2015, 119, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauridsen, L.P.; Laustsen, A.H.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Toxicovenomics and antivenom profiling of the Eastern green mamba (Dendroaspis angusticeps). J. Proteom. 2016, 136, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, J.; Mackessy, S.P.; Sixberry, N.M.; Stura, E.A.; Du, M.H.L.; Ménez, R.; Foo, C.S.; Ménez, A.; Nirthanan, S.; Kini, R.M. Irditoxin, a novel covalently linked heterodimeric three-finger toxin with high taxon-specific neurotoxicity. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Wüster, W.; Kini, R.M.; Brusic, V.; Khan, A.; Venkataraman, D.; Rooney, A.P. Molecular evolution and phylogeny of elapid snake venom three-finger toxins. J. Mol. Evol. 2003, 57, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M. Evolution of three-finger toxins—A versatile mini protein scaffold. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.J.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. In vitro neurotoxic effects of Pseudechis spp. venoms: A comparison of avian and murine skeletal muscle preparations. Toxicon 2013, 63, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margres, M.J.; Aronow, K.; Loyacano, J.; Rokyta, D.R. The venom-gland transcriptome of the eastern coral snake (Micrurus fulvius) reveals high venom complexity in the intragenomic evolution of venoms. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa-Netto, C.; Junqueira-de-Azevedo, I.L.; Silva, D.A.; Ho, P.L.; Leitão-de-Araújo, M.; Alves, M.L.; Sanz, L.; Foguel, D.; Zingali, R.B.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics and venom gland transcriptomic analysis of Brazilian coral snakes, Micrurus altirostris and M. corallinus. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Núñez, V.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Proteomic and biological characterization of the venom of the redtail coral snake, Micrurus mipartitus (Elapidae), from Colombia and Costa Rica. J. Proteom. 2011, 75, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey-Suárez, P.; Stuani-Floriano, R.; Rostelato-Ferreira, S.; Saldarriaga, M.; Núñez, V.; Rodrigues-Simioni, L.; Lomonte, B. Mipartoxin-I, a novel three-finger toxin, is the major neurotoxic component in the venom of the redtail coral snake Micrurus mipartitus (Elapidae). Toxicon 2012, 60, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bénard-Valle, M.; Carbajal-Saucedo, A.; de Roodt, A.; López-Vera, E.; Alagón, A. Biochemical characterization of the venom of the coral snake Micrurus tener and comparative biological activities in the mouse and a reptile model. Toxicon 2014, 77, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, I.; Pedraza-Escalona, M.; Paniagua, D.; Restano-Cassulini, R.; Zamudio, F.; Batista, C.V.; Possani, L.D.; Alagón, A. Eastern coral snake Micrurus fulvius venom toxicity in mice is mainly determined by neurotoxic phospholipases A2. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasa, M.; Smith, E.N. Phylogenetic analysis of monadal coral snakes genus Micrurus from Middle America. In Proceedings of the 2001 Joint Annual Meeting of the Herpetologists League and the Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 27–31 July 2001; pp. 131–132.
- Calvete, J.J. Proteomic tools against the neglected pathology of snake bite envenoming. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2011, 8, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Tsai, W.C.; Ureña-Díaz, J.M.; Sanz, L.; Mora-Obando, D.; Sánchez, E.E.; Fry, B.G.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Gibbs, H.L.; Calvete, J.J. Venomics of New World pit vipers: Genus-wide comparisons of venom proteomes across Agkistrodon. J. Proteom. 2014, 96, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finney, D.J. Statistical Methods in Biological Assay; Charles Griffin and Company Ltd.: London, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]







| Peak | % | Mass, kDa ▼ (Da) | Peptide Ion | MS/MS-Derived Sequence * | Conf (%) | Sc ** | Protein Family; ~ Related Protein and Species *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | z | |||||||
| 1 | 1.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | PNP; adenosine |
| 2–6 | 1.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | PNP |
| 7 | 3.2 | 10 ▼ (6757) | 1707.0 | 1 | FSPGIQTSQTCPAGQK | 99.0 | 11 | 3FTx; ~U3FVH8, 3FTx 4a Micrurus fulvius |
| 8 | 5.9 | 9 ▼ (6638, 7276) | 976.5 | 1 | MFIRTHR | 76.6 | 5 | 3FTx; ~P01414 , toxin FS-2 Dendroaspis polylepis |
| 1322.7 | 1 | ICDDSSIPFLR | 99.0 | 7 | 3FTx; ~U3EPK7, 3FTx 6 Micrurus fulvius | |||
| 9 | 0.2 | 9 ▼ | 1314.7 | 1 | FYFAYQCTSK | man | man | 3FTx; ~C6JUP1, 3FTx Micrurus corallinus |
| 10 | 8.0 | 9 ▼ (6361, 6451) | 2663.2 | 1 | DGFYSVTCTEKENLCFTMFSAR | 99.0 | 11 | 3FTx; ~C6JUP4, 3FTx Micrurus corallinus |
| 1375.6 | 1 | ENLCFTMFSAR | 99.0 | 11 | ||||
| 11 | 0.4 | 9 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | Unknown |
| 12 | 1.8 | 9 ▼ (7045, 7140, 7198) | 1661.8 | 1 | GAYNVCCSTDLCNK | 99.0 | 15 | 3FTx; ~U3FAE1, 3FTx 3a Micrurus fulvius |
| 1374.7 | 1 | KCLEFIYGGCQ | 99.0 | 12 | Kunitz; ~Q6ITB9, mulgin-3 Pseudechis australis | |||
| 13 | 3.6 | 9 ▼ (7071, 7201) | 1786.9 | 1 | VCYTIFLVGPSYPpyEK | 93.5 | 6 | 3FTx; ~AKN63197, 3FTx Micrurus diastema |
| 14 | 6.9 | 9 ▼ (6845) | 1687.8 | 1 | GPYNVCCSTDLCNK | 99 | 7 | 3FTx; ~B3EWF8, mipartoxin-I Micrurus mipartitus |
| 1310.7 | 1 | AIEFGCAASCPK | 99 | 12 | 3FTx; ~AKN63198, 3FTx DK, Micrurus diastema | |||
| 15a | 0.4 | 12 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 15b | 2.5 | 9 ▼ (6843, 7311) | 1314.7 | 1 | FYFAYQCTSK | man | man | 3FTx; ~C6JUP1, 3FTx Micrurus corallinus |
| 16a | 0.3 | 12 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 16b | 0.2 | 10 ▼ | 1373.6 | 1 | CKDFVCNCDR | 99.0 | 7 | PLA2; ~U3FYP8, PLA2 13 Micrurus fulvius |
| 17a | 1.7 | 13 ▼ | 1373.6 | 1 | CKDFVCNCDR | 99.0 | 14 | PLA2; ~U3FYP8, PLA2 13 Micrurus fulvius |
| 1085.4 | 1 | DFVCNCDR | 96.8 | 6 | ||||
| 17b | 1.2 | 9 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 18 | 6.6 | 13 ▼ (13353) | 2969.3 | 1 | HWVSFTNYGCYCGYGGSGTPVDELDK | 99.0 | 12 | PLA2; ~P81167, nigroxin B Micrurus nigrocinctus |
| 1373.5 | 1 | CKDFVCNCDR | 99.0 | 12 | PLA2; ~U3FYP8, PLA2 13 Micrurus fulvius | |||
| 2983.3 | 1 | HWLSFTNYGCYCGYGGSGTPVDELDK | 98.5 | 6 | ||||
| 19 | 11.3 | 13 ▼ (13477) | 1373.6 | 1 | CKDFVCNCDR | 99.0 | 9 | PLA2; ~U3FYN8, PLA2 9 Micrurus fulvius |
| 20 | 1.8 | 13 ▼ | 2855.3 | 1 | SAWDFTNYGCYCGAGGSGTPVDELDR | 99.0 | 15 | PLA2; ~Q8AXW7, PLA2 Micrurus corallinus |
| 21 | 5.3 | 12 ▼ (13331) | 2841.3 | 1 | AWDYNNdaYGCYCGQGGSGTPVDDLDR | 99 | 12 | PLA2; ~R4G7M2, Sut-22 Suta fasciata |
| 1335.7 | 1 | VHDDCYAAAEK | 99 | 18 | PLA2; ~ U3FYP1, PLA2 3b Micrurus fulvius | |||
| 1827.8 | 1 | CCQVHDNCYNEAEK | 99 | 22 | PLA2; ~ A4FS04, natratoxin, Naja atra | |||
| 22a | 2.4 | 20 ▼ | 1278.6 | 1 | VHDDCYAAAEK | 99.0 | 7 | PLA2; ~U3FYP1, PLA2 3b Micrurus fulvius |
| 22b | 4.5 | 13 ▼ | 1373.5 | 1 | CKDFVCNCDR | 99.0 | 8 | PLA2; ~U3FYP8, PLA2 13 Micrurus fulvius |
| 2883.2 | 1 | Sf°AWDFTNYGCYCGAGGSGTPVDELDR | 99.0 | 15 | PLA2; ~Q8AXW7, PLA2 Micrurus corallinus | |||
| 23a | 0.6 | 13 ▼ | 1278.5 | 1 | VHDDCYAAAEK | 99.0 | 8 | PLA2; ~U3FYP1, PLA2 3b Micrurus fulvius |
| 23b | 2.1 | 11 ▼ | 2883.3 | 1 | PWkyIGYVNYGCYCGAGGSGTPVDELDR | 99.0 | 16 | PLA2; ~P00606, PLA2 Bungarus multicinctus |
| 24 | 16.1 | 10 ▼ (7537) | 1478.7 | 1 | RICDDSSIPFLR | 99 | 12 | 3FTx; ~U3EPK7, 3FTx 10a Micrurus fulvius |
| 1322.6 | 1 | ICDDSSIPFLR | 99 | 15 | ||||
| 1108.6 | 1 | KGCASSCPKN | 99 | 13 | ||||
| 25 | 0.9 | 10 ▼ | 1322.6 | 1 | ICDDSSIPFLR | 99.0 | 9 | 3FTx; ~U3EPK7, 3FTx 6 Micrurus fulvius |
| 26 | 1.1 | 22 ▼ | 1183.7 | 1 | NVWIGLNDPR | man | man | CTL; ~ACC67944, mannose-binding 1 Pseudechis porphyriacus |
| 27 | 0.1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 28a | 0.2 | 38 ▼ | 1054.5 | 1 | TYWHYER | 99.0 | 11 | MP; ~U3FWL3, MTP4 Micrurus fulvius |
| 1130.6 | 1 | EVFDGHTIGR | man | man | MP; ~P85314, MP Bothrops moojeni | |||
| 28b | 0.2 | 29 ▼ | 1297.6 | 1 | SAECPTDSFQR | 99.0 | 7 | MP: ~R4G7J1, MP-Hop-13 Hoplocephalus bungaroides |
| 29a | 0.6 | 38 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 29b | 0.2 | 28 ▼ | 1011.6 | 1 | FYVVVDNR | 90.9 | 9 | MP; ~ABQ01135, stephensease-1 Hoplocephalus. stephensii |
| 29c | 0.2 | 25 ▼ | 1011.6 | 1 | FYVVVDNR | man | man | MP; ~ABQ01135, stephensease-1 Hoplocephalus. stephensii |
| 30a | 0.4 | 51 ▼ | 995.6 | 1 | FdhYVVVDNR | man | man | MP; ~ABQ01135, stephensease-1 Hoplocephalus. stephensii |
| 30b | 0.4 | 46 ▼ | 995.6 | 1 | FdhYVVVDNR | man | man | MP; ~ABQ01135, stephensease-1 Hoplocephalus. stephensii |
| 30c | 0.1 | 29 ▼ | 2171.1 | 1 | GDSGGPLICNGQIQGIVSWGR | 99.0 | 7 | SP; ~Q5MCS0, harobin Hydrophis hardwickii |
| 30d | 0.2 | 20 ▼ | 1329.7 | 1 | IHDIKWNFEK | 99.0 | 13 | GPX; ~XP_013914274, glutathione peroxidase 3 Thamnophis sirtalis |
| 31a | 2.2 | 61 ▼ | 1637.8 | 1 | NDLEGWHVNLGPMR | 99.0 | 23 | LAO; ~U3FYQ2, LAAO 1a Micrurus fulvius |
| 1131.5 | 1 | SDDIFSYER | 99.0 | 13 | - | |||
| 1576.9 | 1 | IQDNTENVRVAYRam | 99.0 | 13 | ||||
| 1484.7 | 1 | EADYEEFLEIAR | 99.0 | 19 | ||||
| 31b | 0.5 | 50 ▼ | 1963.1 | 1 | TSGDIVINDLSLIHQLPK | 99.0 | 7 | LAO; ~U3FYQ2, LAAO 1a Micrurus fulvius |
| 2275.1 | 1 | IHFAGEYTANDHGWIDSTIK | 99.0 | 8 | - | |||
| 1484.7 | 1 | EADYEEFLEIAR | 99.0 | 9 | - | |||
| 1310.7 | 1 | RFDEIVGGM°xDR | 99.0 | 10 | LAO; ~A0A0A1WCY6, B variant Echis coloratus | |||
| 1460.8 | 1 | QVVPESLFAWER | 95.0 | 7 | PLB: ~V8ND68, PLB-like 1 Ophiophagus hannah | |||
| 31c | 1.1 | 42 ▼ | 1484.7 | 1 | EADYEEFLEIAR | 99.0 | 13 | LAO; ~U3FYQ2, LAAO 1a Micrurus fulvius |
| 1963.0 | 1 | TSGDIVINDLSLIHQLPK | 99.0 | 17 | ||||
| 2275.0 | 1 | IHFAGEYTANDHGWIDSTIK | 99.0 | 20 | ||||
| 1131.5 | 1 | SDDIFSYER | 99.0 | 11 | ||||
| 1576.8 | 1 | IQDNTENVRVAYRam | 99.0 | 12 | ||||
| 31d | 0.7 | 20 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 31e | 0.2 | 17 ▼ | 1589.8 | 1 | NDLEGWHVNLGPMdtR | 99.0 | 9 | LAO; ~U3FYQ2, LAAO 1a Micrurus fulvius |
| 1466.7 | 1 | EpyADYEEFLEIAR | 99.0 | 11 | ||||
| 1833.8 | 1 | EFVQEDENAWYYIK | 99.0 | 19 | ||||
| 1637.8 | 1 | NDLEGWHVNLGPMR | 99.0 | 12 | ||||
| 1484.7 | 1 | EADYEEFLEIAR | 99.0 | 17 | ||||
| 31f | 0.4 | 14 ▼ | - | - | - | - | - | unknown |
| 32 | 0.9 | 23 ▼ | 1152.6 | 1 | LPFYADWIK | 99.0 | 12 | SP; ~U3FBP8, prostasin-like protein Micrurus fulvius |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lomonte, B.; Sasa, M.; Rey-Suárez, P.; Bryan, W.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Venom of the Coral Snake Micrurus clarki: Proteomic Profile, Toxicity, Immunological Cross-Neutralization, and Characterization of a Three-Finger Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050138
Lomonte B, Sasa M, Rey-Suárez P, Bryan W, Gutiérrez JM. Venom of the Coral Snake Micrurus clarki: Proteomic Profile, Toxicity, Immunological Cross-Neutralization, and Characterization of a Three-Finger Toxin. Toxins. 2016; 8(5):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050138
Chicago/Turabian StyleLomonte, Bruno, Mahmood Sasa, Paola Rey-Suárez, Wendy Bryan, and José María Gutiérrez. 2016. "Venom of the Coral Snake Micrurus clarki: Proteomic Profile, Toxicity, Immunological Cross-Neutralization, and Characterization of a Three-Finger Toxin" Toxins 8, no. 5: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050138
APA StyleLomonte, B., Sasa, M., Rey-Suárez, P., Bryan, W., & Gutiérrez, J. M. (2016). Venom of the Coral Snake Micrurus clarki: Proteomic Profile, Toxicity, Immunological Cross-Neutralization, and Characterization of a Three-Finger Toxin. Toxins, 8(5), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8050138