Aperture Ratio Improvement by Optimizing the Voltage Slope and Reverse Pulse in the Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle of EWD Driving Waveform System
2.1. Electrowetting Equivalent Circuit Model
2.2. Analysis of Ink Distribution in a Pixel
3. Driving Waveform Design
3.1. Testing System
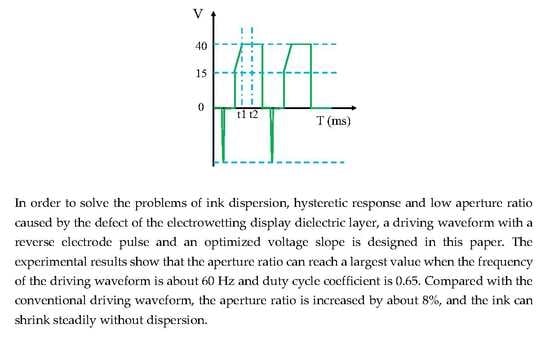
3.2. The Driving Waveform Structure
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. The Frequency of the Driving Waveform
4.2. The Duty Cycle of the Driving Waveform
4.3. The Performance of Driving Waveforms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.Y.; Steckl, A.J. Electrowetting on paper for electronic paper display. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3318–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, A.M.J.; Brown, C.V.; Newton, M.I.; Mchale, G. Dielectrowetting: The Past, Present and Future. Curr. Opin. Colloid 2017, 36, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beni, G.G.; Hackwood, S. Electro-wetting displays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1981, 38, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.S. Droplet morphometry and velocimetry (DMV): A video processing software for time-resolved, label-free tracking of droplet par-ameters. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1892–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.J.; Zhang, W.N.; Liu, L.W.; Xie, S.T.; Zhou, G.F. Portable multi-gray scale video playing scheme for high-performance electrowetting displays. J. Soc. Inf. Display 2016, 24, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.C.; Shui, L.L.; Wang, L.; Jin, M.L.; Hayes, R.A.; Zhou, G.F. A novel driver for active matrix electrowetting displays. Displays 2015, 37, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijk, R.V.; Feenstra, B.J.; Hayes, R.A.; Camps, I.G.J.; Boom, R.G.H.; Wagemans, M.M.H.; Giraldo, A.; Heijden, R.V.D.; Los, R.; Feil, H. Gray Scales for Video Applications on Electrowetting Displays. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2006, 37, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sur, A.; Liu, D.; Pascente, C.; Ruchhoeft, P. Dynamics of droplet motion induced by electrowetting. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 2017, 106, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, Y.H.; Liang, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, W.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Wu, S.H. Accurate-gray-level and quick-responsedriving methods for high-performance electrowetting displays. J. Soc. Inf. Display 2011, 19, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, N.; Xu, R.Q. Effect of driving voltage polarity on dynamic response characteristics of electrowetting liquid lens. Jap. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.M.; Bai, P.F.; Hayes, R.; Shui, L.L.; Jin, M.L.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G.F. Novel Driving Methods for Manipulating Oil Motion in Electrofluidic Display Pixels. J. Disp. Technol. 2015, 12, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquescarmes, T.; Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J.; Schlangen, L. Liquid behavior inside a reflective display pixel based on electrowetting. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquescarmes, T.; Hayes, R.A.; Schlangen, L.J.M. A physical model describing the electro-optic behavior of switchable optical elements based on electrowetting. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 6267–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tang, B.; Dong, B.Q.; Li, H.; Zhou, R.; Guo, Y.Y.; Dou, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.; Groenewold, J.; Alex, H.; et al. Electrowetting on dielectric: Experimental and model study of oil conductivity on rupture voltage. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 195102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Cho, S.K.; Garrell, R.L. Low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, Z.; Feng, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; He, W.; Shui, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, G. Aperture Ratio Improvement by Optimizing the Voltage Slope and Reverse Pulse in the Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines 2019, 10, 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10120862
Yi Z, Feng W, Wang L, Liu L, Lin Y, He W, Shui L, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Zhou G. Aperture Ratio Improvement by Optimizing the Voltage Slope and Reverse Pulse in the Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines. 2019; 10(12):862. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10120862
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Zichuan, Wenyong Feng, Li Wang, Liming Liu, Yue Lin, Wenyao He, Lingling Shui, Chongfu Zhang, Zhi Zhang, and Guofu Zhou. 2019. "Aperture Ratio Improvement by Optimizing the Voltage Slope and Reverse Pulse in the Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays" Micromachines 10, no. 12: 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10120862
APA StyleYi, Z., Feng, W., Wang, L., Liu, L., Lin, Y., He, W., Shui, L., Zhang, C., Zhang, Z., & Zhou, G. (2019). Aperture Ratio Improvement by Optimizing the Voltage Slope and Reverse Pulse in the Driving Waveform for Electrowetting Displays. Micromachines, 10(12), 862. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10120862