1600 Parallel Microchamber Microfluidic Device for Fast Sample Array Preparation Using the Immiscibility of Two Liquids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
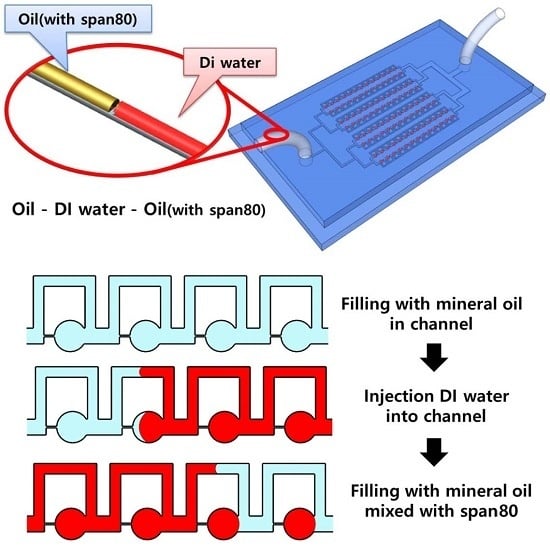
2.1. Sample Array Process in Parallel Microfluidic Device
2.2. Design of Parallel Microfluidic Device
2.3. Fabrication of Parallel Microfluidic Device
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Behavior of Sample Array According to Flow Rate
3.2. Behavior of Sample Array According to Microchamber Position
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, G.; Fang, Q.; den Toonder, J.M.J. Microfluidics for cell-based high throughput screening platforms—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 903, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuži, P.; Giselbrecht, S.; Länge, K.; Huang, T.J.; Manz, A. Revisiting lab-on-a-chip technology for drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Edel, J.B.; DeMello, A.J. Micro- and nanofluidic systems for high-throughput biological screening. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.H. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, V.; Doshi, A.; Kurup, G.K.; Ereifej, E.; Vandevord, P.J.; Basu, A.S. A modular approach for the generation, storage, mixing, and detection of droplet libraries for high throughput screening. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, S.A. High-throughput and ultra-high-throughput screening: Solution- and cell-based approaches. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, Q.; Ai, X.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G. Comprehensive two-dimensional manipulations of picoliter microfluidic droplets sampled from nanoliter samples. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8029–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, C.W.; Rivnak, A.J.; Campbell, T.G.; Piech, T.; Rissin, D.M.; Mösl, M.; Peterça, A.; Niederberger, H.P.; Minnehan, K.A.; Patel, P.P.; et al. Isolation and detection of single molecules on paramagnetic beads using sequential fluid flows in microfabricated polymer array assemblies. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Doberstein, S.K. HTS technologies in biopharmaceutical discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2006, 11, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.L.; Ismagilov, R.F. Microfluidic cartridges preloaded with nanoliter plugs of reagents: An alternative to 96-well plates for screening. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Ullah, A.; Kim, K.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, G.M. Preparation of carbon nanotube-wrapped porous microparticles using a microfluidic device. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 12003–12008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, Y.C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Khong, Y.M.; Chang, S.; Samper, V.D.; van Noort, D.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Yu, H. A novel 3D mammalian cell perfusion-culture system in microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Bithi, S.S.; Vanapalli, S.A. Microfluidic static droplet arrays with tuneable gradients in material composition. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.E.; Schneider, T.; Wang, M.; Chiu, D.T. Self-digitization of sample volumes. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5707–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gansen, A.; Herrick, A.M.; Dimov, I.K.; Lee, L.P.; Chiu, D.T. Digital LAMP in a sample self-digitization (SD) chip. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ahn, B.; Lee, H.; Xu, L.; Lee, K.; Panchapakesan, R.; Oh, K.W. Droplet-based microfluidic device for multiple-droplet clustering. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.M.; Park, S.J.; Kim, G.M. Applications of PLGA microcarriers prepared using geometrically passive breakup on microfluidic chip. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2015, 16, 2545–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.S.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, G.M. Microfluidic array chip with parallel channels for fast preparation of sample droplet array. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 6294–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.M.; Kim, G.M. 1600 Parallel Microchamber Microfluidic Device for Fast Sample Array Preparation Using the Immiscibility of Two Liquids. Micromachines 2017, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8030063
Kim CM, Kim GM. 1600 Parallel Microchamber Microfluidic Device for Fast Sample Array Preparation Using the Immiscibility of Two Liquids. Micromachines. 2017; 8(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chul Min, and Gyu Man Kim. 2017. "1600 Parallel Microchamber Microfluidic Device for Fast Sample Array Preparation Using the Immiscibility of Two Liquids" Micromachines 8, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8030063
APA StyleKim, C. M., & Kim, G. M. (2017). 1600 Parallel Microchamber Microfluidic Device for Fast Sample Array Preparation Using the Immiscibility of Two Liquids. Micromachines, 8(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8030063