Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Intrinsic (Primary, Inherent) TKI-Resistance
2. Clinical and Preclinical Studies Shedding Light on Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-TKIs
2.1. Impact of EGFR-Mutations or -Co-Mutations on Response to EGFR-TKIs
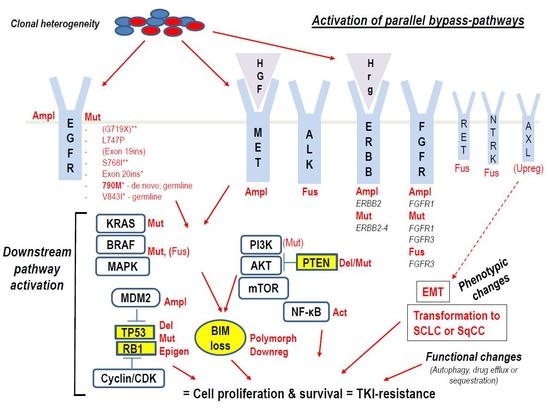
2.2. Role of Co-Mutations in Alternative Cancer-Drivers
2.2.1. Alterations in the TP53 and RB1 Tumor-Suppressor Genes
2.2.2. ALK- and ROS1-Fusions
2.2.3. MET-Alterations
2.2.4. RAS-, BRAF, ERBB-, DDR2-Mutations
2.2.5. PIK3CA- and PTEN-Mutations
2.2.6. CTNNB1-Mutations
2.2.7. SMAD4-Mutations
2.2.8. FGFR-Alterations
2.2.9. Other Gene-Fusions
2.3. Phenotypic Changes
2.3.1. Transformation to SCLC
2.3.2. EMT, BIM Expression, Hypoxia
2.3.3. Conversion to SqCC
2.4. Autophagy, Drug Efflux or Sequestration
2.5. MicroRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs
3. Further Considerations Regarding the 3G EGFR-TKI Osimertinib
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, S.V.; Bell, D.W.; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550, Erratum in Nature 2014, 514, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer: New drugs, new resistance mechanisms, and future treatment options. Cancer J. 2015, 21, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Kondo, N.; Yoneda, K.; Takuwa, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Orui, H.; Okumura, Y.; Tanaka, F.; Kumamoto, K.; Mostafa, M.G.; et al. Frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in Bangladeshi patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Shao, D.; Deng, Q.; Tang, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Guo, F.; Lin, Y.; Mao, M.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiling of lung cancer using a validated panel to explore therapeutic targets in East Asian patients. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Lung cancers: Molecular characterization, clonal heterogeneity and evolution, and cancer stem cells. Cancers 2018, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of squamous cell lung cancers. Nature 2012, 489, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekhtman, N.; Paik, P.K.; Arcila, M.E.; Tafe, L.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Moreira, A.L.; Travis, W.D.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. Clarifying the spectrum of driver oncogene mutations in biomarker-verified squamous carcinoma of lung: Lack of EGFR/KRAS and presence of PIK3CA/AKT1 mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, E.J.; Kim, H.R.; Arcila, M.E.; Barron, D.; Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Chang, M.T.; Ni, A.; Kundra, R.; Jonsson, P.; et al. Prospective comprehensive molecular characterization of lung adenocarcinomas for efficient patient matching to approved and emerging therapies. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; McGranahan, N.; Birkbak, N.J.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Veeriah, S.; Shafi, S.; Johnson, D.H.; Mitter, R.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Watkins, T.B.K.; Wu, W.; Gini, B.; Chabon, J.J.; McCoach, C.E.; McGranahan, N.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Olivas, V.R.; et al. Evolution and clinical impact of co-occurring genetic alterations in advanced-stage EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garinet, S.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Blons, H.; Oudart, J.B. Current and future molecular testing in NSCLC, what can we expect from new sequencing technologies? J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Ding, P.N.; Lord, S.J.; Inoue, A.; Zhou, C.; Mitsudomi, T.; Rosell, R.; Pavlakis, N.; Links, M.; et al. Impact of specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations and clinical characteristics on outcomes after treatment with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors versus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 1033, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackman, D.; Pao, W.; Riely, G.J.; Engelman, J.A.; Kris, M.G.; Jänne, P.A.; Lynch, T.; Johnson, B.E.; Miller, V.A. Clinical definition of acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Pao, W.; Sequist, L.V. Acquired resistance to TKIs in solid tumours: Learning from lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgillo, F.; Della Corte, C.M.; Fasano, M.; Ciardiello, F. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR-targeted drugs: Lung cancer. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetsu, O.; Hangauer, M.J.; Phuchareon, J.; Eisele, D.W.; McCormick, F. Drug resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Chemotherapy 2016, 61, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Buder, A.; Schwab, S.; Burghuber, O.C.; Prosch, H.; Hilbe, W.; Cseh, A.; Fritz, R.; Filipits, M. Liquid-biopsy-based identification of EGFR T790M mutation-mediated resistance to afatinib treatment in patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC, and subsequent response to osimertinib. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Ahn, M.J.; Garassino, M.C.; Han, J.Y.; Katakami, N.; Kim, H.R.; Hodge, R.; Kaur, P.; Brown, A.P.; Ghiorghiu, D.; et al. CNS efficacy of osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Data from a randomized phase III trial (AURA3). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.J.; Tsai, C.M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Sequist, L.V.; Hida, T.; Yang, J.C.H.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Mitsudomi, T.; Jänne, P.A.; et al. Osimertinib in patients with T790M mutation-positive, advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Long-Term follow-up from a pooled analysis of 2 phase 2 studies. Cancer 2019, 125, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auliac, J.B.; Pérol, M.; Planchard, D.; Monnet, I.; Wislez, M.; Doubre, H.; Guisier, F.; Pichon, E.; Greillier, L.; Mastroianni, B.; et al. Real-life efficacy of osimertinib in pretreated patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M mutation. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Cho, B.C.; Cobo, M.; Cho, E.K.; Bertolini, A.; Bohnet, S.; Zhou, C.; Lee, K.H.; Nogami, N.; et al. CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, P.N., Jr.; Haaland, B.; Park, W.; San Tan, P.; Del Giglio, A.; de Lima Lopes, G., Jr. Cost-effectiveness of osimertinib in the first-line treatment of patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulbul, A.; Husain, H. First-line treatment in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer: Is there a best option? Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; Tiseo, M. Third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Review on emerged mechanisms of resistance. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Ho, C.C.; Liao, W.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Tsai, T.H.; Su, K.Y.; Hsieh, M.S.; Chang, Y.L.; et al. Outcomes in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and acquired Thr790Met mutation treated with osimertinib: A genomic study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Niederst, M.J.; Karlovich, C.A.; Wakelee, H.A.; Neal, J.W.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fulton, L.; Hata, A.N.; Lockerman, E.L.; Kalsy, A.; et al. Heterogeneity underlies the emergence of EGFRT790 wild-type clones following treatment of T790M-positive cancers with a third-generation of EGFR inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J.; et al. Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, N.; Ou, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Tong, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, Y.W.; et al. Investigating novel resistance mechanisms to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3097–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, K.; Yamaoka, T.; Ohba, M.; Fujita, K.I.; Arata, S.; Kusumoto, S.; Taki-Takemoto, I.; Kamei, D.; Iwai, S.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. KRAS and EGFR amplifications mediate resistance to rociletinib and osimertinib in acquired afatinib-resistant NSCLC harboring exon 19 deletion/T790M in EGFR. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offin, M.; Somwar, R.; Rekhtman, N.; Benayed, R.; Chang, J.C.; Plodkowski, A.; Lui, A.J.W.; Eng, J.; Rosenblum, M.; Li, B.T.; et al. Acquired ALK and RET gene fusions as mechanisms of resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Isozaki, H.; Lennerz, J.K.; Gainor, J.F.; Lennes, I.T.; Zhu, V.W.; Marcoux, N.; Banwait, M.K.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Su, W.; et al. Landscape of acquired resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant NSCLC and clinical validation of combined EGFR and RET inhibition with osimertinib and BLU-667 for acquired RET fusion. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrock, A.B.; Zhu, V.W.; Hsieh, W.S.; Madison, R.; Creelan, B.; Silberberg, J.; Costin, D.; Bharne, A.; Bonta, I.; Bosemani, T.; et al. Receptor tyrosine kinase fusions and BRAF kinase fusions are rare but actionable resistance mechanisms to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.A.; Suzawa, K.; Jordan, E.; Zehir, A.; Ni, A.; Kim, R.; Kris, M.G.; Hellmann, M.D.; Li, B.T.; Somwar, R.; et al. Concurrent alterations in EGFR-mutant lung cancers associated with resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors and characterization of MTOR as a mediator of resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3108–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Chu, H.; Yao, Y. Intrinsic resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with activating EGFR mutations. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3711–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imielinski, M.; Berger, A.H.; Hammerman, P.S.; Hernandez, B.; Pugh, T.J.; Hodis, E.; Cho, J.; Suh, J.; Capelletti, M.; Sivachenko, A.; et al. Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma with massively parallel sequencing. Cell 2012, 150, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Ding, L.; Griffith, M.; Subramanian, J.; Dees, N.D.; Kanchi, K.L.; Maher, C.A.; Fulton, R.; Fulton, L.; Wallis, J.; et al. Genomic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in smokers and never-smokers. Cell 2012, 150, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, L.; Mengoli, M.C.; Bisagni, A.; Banzi, M.C.; Boni, C.; Rossi, G. Concomitant EGFR mutation and ALK rearrangement in lung adenocarcinoma is more frequent than expected: Report of a case and review of the literature with demonstration of genes alteration into the same tumor cells. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Varghese, A.M.; Ou, S.H.; Kabraji, S.; Awad, M.M.; Katayama, R.; Pawlak, A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Yeap, B.Y.; Riely, G.J.; et al. ALK rearrangements are mutually exclusive with mutations in EGFR or KRAS: An analysis of 1683 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guibert, N.; Barlesi, F.; Descourt, R.; Léna, H.; Besse, B.; Beau-Faller, M.; Mosser, J.; Pichon, E.; Merlio, J.P.; Ouafik, L.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients with lung cancer harboring multiple molecular alterations: Results from the IFCT study biomarkers France. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Lee, B.; Choi, Y.L.; Han, J.; Ahn, M.J.; Um, S.W. Non-small cell lung cancer with concomitant EGFR, KRAS, and ALK mutation: Clinicopathologic features of 12 cases. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildhaus, H.U.; Schultheis, A.M.; Rüschoff, J.; Binot, E.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Fassunke, J.; Schulte, W.; Ko, Y.D.; Schlesinger, A.; Bos, M.; et al. MET amplification status in therapy-naïve adeno- and squamous cell carcinomas of the lung. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholl, L.M.; Aisner, D.L.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Berry, L.D.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Wistuba, I.I.; Chen, H.; Fujimoto, J.; Kugler, K.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Multi-institutional oncogenic driver mutation analysis in lung adenocarcinoma: The lung cancer mutation consortium experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.A.; Aisner, D.L.; Oxnard, G.R. Precision medicine in non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards in pathology and biomarker interpretation. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2018, 38, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated molecular testing guideline for the selection of lung cancer patients for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Guideline from the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemkerian, G.P.; Narula, N.; Kennedy, E.B.; Biermann, W.A.; Donington, J.; Leighl, N.B.; Lew, M.; Pantelas, J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Reck, M.; et al. Molecular testing guideline for the selection of patients with lung cancer for treatment with targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors: American Society of Clinical Oncology Endorsement of the College of American Pathologists/International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/Association for Molecular Pathology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, J.N.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Grauslund, M.; Melchior, L.; Sørensen, J.B. Concomitant driver mutations in advanced EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer and their impact on erlotinib treatment. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26195–26208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Gao, F.; Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L. Concomitant genetic alterations with response to treatment and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachiglio, A.M.; Fenizia, F.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Galetta, D.; Crinò, L.; Vincenzi, B.; Barletta, E.; Pinto, C.; Ferraù, F.; Lambiase, M.; et al. The presence of concomitant mutations affects the activity of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, P.; Chen, H.; Andrews, J.; Naser, R.; Pao, W.; Horn, L. DNA-Mutation Inventory to Refine and Enhance Cancer Treatment (DIRECT): A catalog of clinically relevant cancer mutations to enable genome-directed anticancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1894–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; An, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Bai, H.; Zhu, G.; Duan, J.; Wu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhuo, M.; et al. Patients harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) double mutations had a lower objective response rate than those with a single mutation in non-small cell lung cancer when treated with EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Thorac. Cancer 2014, 5, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnet, M.B.; O’Toole, S.; Horvath, L.G.; Selinger, C.; Yu, B.; Ng, C.C.; Boyer, M.; Cooper, W.A.; Kao, S. EGFR-co-mutated advanced NSCLC and response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T. Emerging paradigms in the development of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, M.; Togashi, Y.; Bannno, E.; Kobayashi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Terashima, M.; De Velasco, M.A.; Sakai, K.; Fujita, Y.; et al. Efficacy of irreversible EGFR-TKIs for the uncommon secondary resistant EGFR mutations L747S, D761Y, and T854A. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thress, K.S.; Paweletz, C.P.; Felip, E.; Cho, B.C.; Stetson, D.; Dougherty, B.; Lai, Z.; Markovets, A.; Vivancos, A.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, H.; Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Primary concomitant EGFR T790M mutation predicted worse prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Cheng, X.; Tang, Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Ye, J.; Chuai, S.; et al. High-throughput sequencing reveals distinct genetic features and clinical implications of NSCLC with de novo and acquired EGFR T790M mutation. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; Ruan, S.Y.; Su, K.Y.; Liao, W.Y.; Yu, K.L.; Ho, C.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR T790M mutation and common activating mutations in pretreatment non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2016, 94, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Suda, K.; Kimura, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Arao, T.; Nagai, T.; Saijo, N.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Nishio, K. Highly sensitive detection of EGFR T790M mutation using colony hybridization predicts favorable prognosis of patients with lung cancer harboring activating EGFR mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciuti, B.; Baglivo, S.; Paglialunga, L.; De Giglio, A.; Bellezza, G.; Chiari, R.; Crinò, L.; Metro, G. Osimertinib in patients with advanced epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Rationale, evidence and place in therapy. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2017, 9, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin-Heymann, N.; Bryant, I.; Rivera, M.N.; Ulkus, L.; Bell, D.W.; Riese, D.J., 2nd; Settleman, J.; Haber, D.A. Oncogenic activity of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase mutant alleles is enhanced by the T790M drug resistance mutation. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7319–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Genetic heterogeneity and cancer drug resistance. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Katakami, N.; Kaji, R.; Yokoyama, T.; Kaneda, T.; Tamiya, M.; Inoue, T.; Kimura, H.; Yano, Y.; Tamura, D.; et al. HANSHIN Oncology Group. Does afatinib plus bevacizumab combination therapy induce positive conversion of T790M in previously-negative patients? Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34765–34771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Grauslund, M.; Melchior, L.C.; Costa, J.C.; Sørensen, J.B.; Urbanska, E.M. Heterogeneous resistance mechanisms in an EGFR exon 19-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patient treated with erlotinib: Persistent FGFR3-mutation, localized transformation to EGFR-mutated SCLC, and acquired T790M EGFR-mutation. Lung Cancer 2017, 113, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Brannon, A.R.; Ferris, L.A.; Campbell, C.D.; Lin, J.J.; Schultz, K.R.; Ackil, J.; Stevens, S.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; et al. Tracking the evolution of resistance to ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors through longitudinal analysis of circulating tumor DNA. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Thress, K.S.; Alden, R.S.; Lawrance, R.; Paweletz, C.P.; Cantarini, M.; Yang, J.C.; Barrett, J.C.; Jänne, P.A. Association between plasma genotyping and outcomes of treatment with osimertinib (AZD9291) in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagita, M.; Redig, A.J.; Paweletz, C.P.; Dahlberg, S.E.; O’Connell, A.; Feeney, N.; Taibi, M.; Boucher, D.; Oxnard, G.R.; Johnson, B.E.; et al. A Prospective evaluation of circulating tumor cells and cell-free DNA in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with erlotinib on a phase II trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 6010–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remon, J.; Caramella, C.; Jovelet, C.; Lacroix, L.; Lawson, A.; Smalley, S.; Howarth, K.; Gale, D.; Green, E.; Plagnol, V.; et al. Osimertinib benefit in EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with T790M-mutation detected by circulating tumour DNA. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, B.S.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Tsai, J.; Weber, B.; Nexo, E.; Meldgaard, P. Monitoring of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-sensitizing and resistance mutations in the plasma DNA of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer during treatment with erlotinib. Cancer 2014, 120, 3896–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baslan, T.; Hicks, J. Unravelling biology and shifting paradigms in cancer with single-cell sequencing. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.H.; Yang, C.T.; Shih, J.Y.; Huang, M.S.; Su, W.C.; Lai, R.S.; Wang, C.C.; Hsiao, S.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Ho, C.L.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment response in advanced lung adenocarcinomas with G719X/L861Q/S768I mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B. Kinase inhibitor-responsive genotypes in EGFR mutated lung adenocarcinomas: Moving past common point mutations or indels into uncommon kinase domain duplications and rearrangements. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.; Reszka, K.; Ramlau, R.; Powrózek, T.; Pankowski, J.; Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Kalinka-Warzocha, E.; Szczęsna, A.; Nicoś, M.; Jarosz, B.; et al. Prevalence of rare EGFR gene mutations in nonsmall-cell lung cancer: A multicenter study on 3856 Polish Caucasian patients. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 358–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventakos, K.; Kipp, B.R.; Rumilla, K.M.; Winters, J.L.; Yi, E.S.; Mansfield, A.S. S768I Mutation in EGFR in patients with lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1798–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund-Iversen, M.; Kleinberg, L.; Fjellbirkeland, L.; Helland, Å.; Brustugun, O.T. Clinicopathological characteristics of 11 NSCLC patients with EGFR-exon 20 mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frega, S.; Lorenzi, M.; Fassan, M.; Indraccolo, S.; Calabrese, F.; Favaretto, A.; Bonanno, L.; Polo, V.; Zago, G.; Lunardi, F.; et al. Clinical features and treatment outcome of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with uncommon or complex epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32626–32638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, I.; Morise, M.; Kodama, Y.; Matsui, A.; Ozawa, N.; Ozone, S.; Goto, D.; Miyazawa, A.; Hase, T.; Hashimoto, N.; et al. Potential for afatinib as an optimal treatment for advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma in patients with uncommon EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Sun, J.M.; Min, Y.J.; Cho, E.K.; Cho, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. Efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer except both exon 19 deletion and exon 21 L858R: A retrospective analysis in Korea. Lung Cancer 2015, 87, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Song, Z.; Cheng, G. Clinical efficacy of first-generation EGFR-TKIs in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 mutations. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 4181–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Minegishi, Y.; Yoshizawa, H.; Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Sugawara, S.; Isobe, H.; Harada, M.; Ishii, Y.; Gemma, A.; et al. Effectiveness of gefitinib against non-small-cell lung cancer with the uncommon EGFR mutations G719X and L861Q. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohinai, Z.; Hoda, M.A.; Fabian, K.; Ostoros, G.; Raso, E.; Barbai, T.; Timar, J.; Kovalszky, I.; Cserepes, M.; Rozsas, A.; et al. Distinct epidemiology and clinical consequence of classic versus rare EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, C.H.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3812–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.Y.; Ke, E.E.; Yang, J.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Yan, H.H.; Zheng, M.Y.; Bai, X.Y.; Wang, Z.; Su, J.; Chen, Z.H.; et al. A comprehensive review of uncommon EGFR mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 114, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, Z.; et al. Efficacy and long-term survival of advanced lung adenocarcinoma patients with uncommon EGFR mutations treated with 1st generation EGFR-TKIs compared with chemotherapy as first-line therapy. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Togashi, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Mizuuchi, H.; Jangchul, P.; Kondo, C.; Shimoji, M.; Sato, K.; Suda, K.; Tomizawa, K.; et al. EGFR exon 18 mutations in lung cancer: Molecular predictors of augmented sensitivity to afatinib or neratinib as compared with first- or third-generation TKIs. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5305–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.; Sequist, L.V.; Geater, S.L.; Tsai, C.M.; Mok, T.S.; Schuler, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yu, C.J.; Ou, S.H.; Zhou, C.; et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: A combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Russo, G.; Imbimbo, M.; Corrao, G.; Proto, C.; Signorelli, D.; Vitali, M.; Ganzinelli, M.; Botta, L.; Zilembo, N.; de Braud, F.; et al. Concomitant EML4-ALK rearrangement and EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A literature review of 100 cases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59889–59900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuzawa, K.; Yasuda, H.; Hamamoto, J.; Nukaga, S.; Hirano, T.; Kawada, I.; Naoki, K.; Soejima, K.; Betsuyaku, T. Characterization of the efficacies of osimertinib and nazartinib against cells expressing clinically relevant epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 105479–105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jänne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasu, S.; Shiroyama, T.; Morita, S.; Takata, S.; Takada, H.; Masuhiro, K.; Tanaka, A.; Morishita, N.; Suzuki, H.; Okamoto, N.; et al. Osimertinib Treatment Was Unsuccessful for Lung Adenocarcinoma with G719S, S768I, and T790M Mutations. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 3643–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricciuti, B.; Baglivo, S.; Ludovini, V.; Sidoni, A.; Metro, G.; Brambilla, M.; Siggillino, A.; Reda, M.S.; Rebonato, A.; Maiettini, D.; et al. Long-term survival with erlotinib in advanced lung adenocarcinoma harboring synchronous EGFR G719S and KRAS G12C mutations. Lung Cancer 2018, 120, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludovini, V.; Bianconi, F.; Pistola, L.; Pistola, V.; Chiari, R.; Colella, R.; Bellezza, G.; Tofanetti, F.R.; Siggillino, A.; Baldelli, E.; et al. Optimization of patient selection for EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer by combined analysis of KRAS, PIK3CA, MET, and non-sensitizing EGFR mutations. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Capelletti, M.; Nafa, K.; Yun, C.H.; Arcila, M.E.; Miller, V.A.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Zhao, B.; Kris, M.G.; Eck, M.J.; et al. EGFR exon 19 insertions: A new family of sensitizing EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1790–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.N.; Wu, S.G.; Yang, J.C.; Shih, J.Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-sensitive exon 19 insertion and exon 20 insertion in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 324–332.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, J. Non-small cell lung cancer harboring a rare EGFR L747P mutation showing intrinsic resistance to both gefitinib and osimertinib (AZD9291): A case report. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.T.; Ning, W.W.; Li, J.; Huang, J.A. Exon 19 L747P mutation presented as a primary resistance to EGFR-TKI: A case report. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E542–E546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xie, X.; Sun, D.; Geng, J.; Fu, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. EGFR mutation L747P led to gefitinib resistance and accelerated liver metastases in a Chinese patient with lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8603–8606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Schumer, S.T.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. Differential responses to erlotinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung cancers with acquired resistance to gefitinib carrying the L747S or T790M secondary mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1182–1184, author reply 1184–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H.; Park, E.; Yun, C.H.; Sng, N.J.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yeo, W.L.; Huberman, M.S.; Cohen, D.W.; Nakayama, S.; Ishioka, K.; et al. Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216ra177, Erratum in Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 225er1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Z.; Kannan, N. Altered conformational landscape and dimerization dependency underpins the activation of EGFR by αC-β4 loop insertion mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8162–E8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorge, S.E.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yasuda, H.; Piotrowska, Z.; Oxnard, G.R.; Rangachari, D.; Huberman, M.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations display sensitivity to Hsp90 inhibition in preclinical models and lung adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6548–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Fintelmann, F.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Jahagirdar, B. Response to osimertinib in an EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive lung adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, e204–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Rocco, G.; Palmer, J.D.; van Zandwijk, N.; Blackhall, F.; Le, X.; Pennell, N.A.; et al. A consensus on the role of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer from the AME lung cancer collaborative group. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3909–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Yasuda, H.; Hamamoto, J.; Masuzawa, K.; Tani, T.; Nukaga, S.; Hirano, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Manabe, T.; Terai, H.; et al. Efficacy of afatinib or osimertinib plus cetuximab combination therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.; Horn, L.; Gettinger, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Riely, G.J.; Wang, B.; Fu, Y.; Chand, V.K.; et al. Dual inhibition of EGFR with afatinib and cetuximab in kinase inhibitor-resistant EGFR-mutant lung cancer with and without T790M mutations. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veggel, B.; de Langen, A.J.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Monkhorst, K.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Thunnissen, E.; Smit, E.F. Afatinib and cetuximab in four patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-positive advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Tan, Z.; Carter, B.W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Poteete, A.; Estrada-Bernal, A.; et al. Mechanisms and clinical activity of an EGFR and HER2 exon 20-selective kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasako, S.; Terasaka, M.; Abe, N.; Uno, T.; Ohsawa, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Fujita, R.; Tanaka, K.; Okayama, T.; Wadhwa, R.; et al. TAS6417, a novel EGFR inhibitor targeting exon 20 insertion mutations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demierre, N.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O.; Stauffer, E.; Zimmermann, D.R.; Betticher, D.C.; Peters, S. A dramatic lung cancer course in a patient with a rare EGFR germline mutation exon 21 V843I: Is EGFR TKI resistance predictable? Lung Cancer 2013, 80, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, S.; Ohtsuka, K.; Ohnishi, H.; Fujiwara, M.; Nakamura, H.; Morii, T.; Kishino, T.; Goto, H.; Watanabe, T. V843I, a lung cancer predisposing EGFR mutation, is responsible for resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Yatabe, Y.; Toyooka, S. Inherited lung cancer syndromes targeting never smokers. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Park, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Koh, Y.; Keam, B.; Min, H.S.; Kim, T.M.; et al. Primary resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring TKI-sensitive EGFR mutations: An exploratory study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bria, E.; Pilotto, S.; Amato, E.; Fassan, M.; Novello, S.; Peretti, U.; Vavalà, T.; Kinspergher, S.; Righi, L.; Santo, A.; et al. Molecular heterogeneity assessment by next-generation sequencing and response to gefitinib of EGFR mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12783–12795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.M.; Kim, H.R.; Cho, E.K.; Min, Y.J.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K.; Cho, B.C.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, H.C.; et al. Targeted sequencing identifies genetic alterations that confer primary resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Korean Lung Cancer Consortium). Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36311–36320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.M.; Lonigro, R.J.; Vats, P.; Cobain, E.; Everett, J.; Cao, X.; Rabban, E.; Kumar-Sinha, C.; Raymond, V.; et al. Integrative clinical genomics of metastatic cancer. Nature 2017, 548, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Petracci, E.; Delmonte, A.; Chiadini, E.; Dazzi, C.; Papi, M.; Capelli, L.; Casanova, C.; De Luigi, N.; Mariotti, M.; et al. Impact of TP53 mutations on outcome in EGFR-mutated patients treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Benavente, S.; Armstrong, E.A.; Li, C.; Wheeler, D.L.; Harari, P.M. p53 modulates acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and radiation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7071–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbé, C.; Cabanero, M.; Korpanty, G.J.; Tomasini, P.; Doherty, M.K.; Mascaux, C.; Jao, K.; Pitcher, B.; Wang, R.; Pintilie, M.; et al. Prognostic and predictive effects of TP53 co-mutation in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Rangachari, D.; Mockus, S.M.; Spotlow, V.; Reddi, H.V.; Malcolm, J.; Huberman, M.S.; Joseph, L.J.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Mutations in TP53, PIK3CA, PTEN and other genes in EGFR mutated lung cancers: Correlation with clinical outcomes. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, B.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.Y.; Choi, Y.L.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. Concurrent genetic alterations predict the progression to target therapy in EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, N.N.; Zhang, X.C.; Chen, H.J.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, L.X.; Xie, Z.; Su, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Tu, H.Y.; Yan, H.H.; et al. Clinical outcomes of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutation, ALK rearrangement and EGFR/ALK co-alterations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65185–65195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulivi, P.; Chiadini, E.; Dazzi, C.; Dubini, A.; Costantini, M.; Medri, L.; Puccetti, M.; Capelli, L.; Calistri, D.; Verlicchi, A.; et al. Nonsquamous, non-small-cell lung cancer patients who carry a double mutation of EGFR, EML4-ALK or KRAS: Frequency, clinical-pathological characteristics, and response to therapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 17, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.K.; Keam, B.; Koh, J.; Cho, H.J.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, D.W.; Chung, D.H. Concomitant ALK translocation and EGFR mutation in lung cancer: A comparison of direct sequencing and sensitive assays and the impact on responsiveness to tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Su, J.; Xu, C.R.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, H.X.; Xie, Z.; Chen, H.J.; Huang, Y.S.; Jiang, B.Y.; et al. Lung cancers with concomitant EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements: Diverse responses to EGFR-TKI and crizotinib in relation to diverse receptors phosphorylation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, H.H.; Grauslund, M.; Urbanska, E.M.; Melchior, L.C.; Rask, C.K.; Costa, J.C.; Skov, B.G.; Sørensen, J.B.; Santoni-Rugiu, E. Concomitant occurrence of EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) and KRAS (V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) mutations in an ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase)-positive lung adenocarcinoma patient with acquired resistance to crizotinib: A case report. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Lin, D.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, L.; Chuai, S.; Fei, K.; Zhou, C.; Hirsch, F.R. Intratumoral heterogeneity of ALK-rearranged and ALK/EGFR coaltered lung adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesweg, M.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Reis, H.; Ting, S.; Savvidou, N.; Skiba, C.; Herold, T.; Christoph, D.C.; Meiler, J.; Worm, K.; et al. High prevalence of concomitant oncogene mutations in prospectively identified patients with ROS1-positive metastatic lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Ali, S.M.; Bailey, M.; Schrock, A.B.; Gainor, J.F.; Ferris, L.A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Miller, V.A.; Iafrate, A.J.; et al. ROS1 fusions rarely overlap with other oncogenic drivers in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Davies, K.D. MET copy number as a secondary driver of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in EGFR-mutant non–small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D. Have we really MET a new target? J. Clin. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Kim, D.W.; Liu, X.; Lee, D.H.; Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Vansteenkiste, J.F.; Su, W.C.; Felip, E.; et al. Phase Ib/II study of capmatinib (INC280) plus gefitinib after failure of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor therapy in patients with EGFR-mutated, MET factor-dysregulated non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3101–3109, Erratum in J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, J.; Brennan, C.; Shih, J.Y.; Riely, G.; Viale, A.; Wang, L.; Chitale, D.; Motoi, N.; Szoke, J.; Broderick, S.; et al. MET amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20932–20937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofalo, M.; Romano, G.; Di Leva, G.; Nuovo, G.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ngankeu, A.; Sun, J.; Lovat, F.; Alder, H.; Condorelli, G.; et al. EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat. Med. 2011, 18, 74–82, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turke, A.B.; Zejnullahu, K.; Wu, Y.L.; Song, Y.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Lifshits, E.; Toschi, L.; Rogers, A.; Mok, T.; Sequist, L.; et al. Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, M.F.; Yan, S.X.; Schiller, J.H. Response to crizotinib/erlotinib combination in a patient with a primary EGFR-mutant adenocarcinoma and a primary c-met-amplified adenocarcinoma of the lung. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Niederst, M.J.; Lennerz, J.K.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Stevens, S.; Shaw, A.T.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. Dramatic response to combination erlotinib and crizotinib in a patient with advanced, EGFR-mutant lung cancer harboring De Novo MET Amplification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noro, R.; Seike, M.; Zou, F.; Soeno, C.; Matsuda, K.; Sugano, T.; Nishijima, N.; Matsumoto, M.; Kitamura, K.; Kosaihira, S.; et al. MET FISH-positive status predicts short progression-free survival and overall survival after gefitinib treatment in lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Tachibana, K.; Minami, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; et al. Hepatocyte growth factor expression in EGFR mutant lung cancer with intrinsic and acquired resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in a Japanese cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, S.A.; Berry, L.; Lu, X.; Gao, D.; Barón, A.E.; Chesnut, P.; Sheren, J.; Aisner, D.L.; Merrick, D.; Doebele, R.C.; et al. Identifying the appropriate FISH criteria for defining MET copy number-driven lung adenocarcinoma through oncogene overlap analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, G.G.Y.; Lim, T.H.; Lim, J.; Liew, P.J.R.; Kwang, X.L.; Nahar, R.; Aung, Z.W.; Takano, A.; Lee, Y.Y.; Lau, D.P.X.; et al. Clonal MET Amplification as a determinant of tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrock, A.B.; Frampton, G.M.; Suh, J.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Rosenzweig, M.; Erlich, R.L.; Halmos, B.; Goldman, J.; Forde, P.; Leuenberger, K.; et al. Characterization of 298 patients with lung cancer harboring MET exon 14 skipping alterations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.D.; Lee, S.E.; Oh, D.Y.; Yu, D.B.; Jeong, H.M.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.; Jung, H.S.; Oh, E.; Song, J.Y.; et al. MET exon 14 skipping mutations in lung adenocarcinoma: Clinicopathologic implications and prognostic values. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigi, M.; McLeer-Florin, A.; Pros, E.; Nadal, E.; Brambilla, E.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M. Genetic screening and molecular characterization of MET alterations in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Leighl, N.B.; Tsao, M.S.; Shepherd, F.A. KRAS mutations as prognostic and predictive markers in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, H.P.; Pranz, K.; Musteanu, M.; Grabner, B.; Hruschka, N.; Mohrherr, J.; Aigner, P.; Stiedl, P.; Brcic, L.; Laszlo, V.; et al. Afatinib restrains K-RAS-driven lung tumorigenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Sequist, L.V.; Arcila, M.E.; Lovly, C.M.; Chen, X.; Rudin, C.M.; Moran, T.; Camidge, D.R.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Berry, L.; et al. Characteristics of lung cancers harboring NRAS mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2584–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pylayeva-Gupta, Y.; Grabocka, E.; Bar-Sagi, D. RAS oncogenes: Weaving a tumorigenic web. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberlein, C.A.; Stetson, D.; Markovets, A.A.; Al-Kadhimi, K.J.; Lai, Z.; Fisher, P.R.; Meador, C.B.; Spitzler, P.; Ichihara, E.; Ross, S.J.; et al. Acquired resistance to mutant-selective EGFR inhibitor AZD9291 is associated with increased dependence on RAS signaling in preclinical models. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takezawa, K.; Pirazzoli, V.; Arcila, M.E.; Nebhan, C.A.; Song, X.; de Stanchina, E.; Ohashi, K.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; Spitzler, P.J.; Melnick, M.A.; et al. HER2 amplification: A potential mechanism of acquired resistance to EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers that lack the second-site EGFRT790M mutation. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, I.J.; Hur, J.Y.; Park, C.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Choi, C.M. Clinical activity of Pan-HER inhibitors against HER2-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e775–e781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazières, J.; Peters, S.; Lepage, B.; Cortot, A.B.; Barlesi, F.; Beau-Faller, M.; Besse, B.; Blons, H.; Mansuet-Lupo, A.; Urban, T.; et al. Lung cancer that harbors an HER2 mutation: Epidemiologic characteristics and therapeutic perspectives. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, D.M.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Won, H.; Rodon, J.; Saura, C.; Shapiro, G.I.; Juric, D.; Quinn, D.I.; Moreno, V.; Doger, B.; et al. HER kinase inhibition in patients with HER2- and HER3-mutant cancers. Nature 2018, 554, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazières, J.; Barlesi, F.; Filleron, T.; Besse, B.; Monnet, I.; Beau-Faller, M.; Peters, S.; Dansin, E.; Früh, M.; Pless, M.; et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: Results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Grève, J.; Teugels, E.; Geers, C.; Decoster, L.; Galdermans, D.; De Mey, J.; Everaert, H.; Umelo, I.; In’t Veld, P.; Schallier, D. Clinical activity of afatinib (BIBW 2992) in patients with lung adenocarcinoma with mutations in the kinase domain of HER2/neu. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torigoe, H.; Shien, K.; Takeda, T.; Yoshioka, T.; Namba, K.; Sato, H.; Suzawa, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Soh, J.; Sakaguchi, M.; et al. Therapeutic strategies for afatinib-resistant lung cancer harboring HER2 alterations. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, T.; Tanizaki, J.; Paranal, R.M.; Endoh, H.; Lydon, C.; Capelletti, M.; Repellin, C.E.; Choi, J.; Ogino, A.; Calles, A.; et al. Response heterogeneity of EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertions to covalent EGFR and HER2 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2712–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ou, S.I.; Schrock, A.B.; Bocharov, E.V.; Klempner, S.J.; Haddad, C.K.; Steinecker, G.; Johnson, M.; Gitlitz, B.J.; Chung, J.; Campregher, P.V.; et al. HER2 transmembrane domain (TMD) mutations (V659/G660) that stabilize homo- and heterodimerization are rare oncogenic drivers in lung adenocarcinoma that respond to afatinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.E.; Narasanna, A.; Perez-Torres, M.; Xiang, B.; Wu, F.Y.; Yang, S.; Carpenter, G.; Gazdar, A.F.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Arteaga, C.L. HER2 kinase domain mutation results in constitutive phosphorylation and activation of HER2 and EGFR and resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koga, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tomizawa, K.; Suda, K.; Kosaka, T.; Sesumi, Y.; Fujino, T.; Nishino, M.; Ohara, S.; Chiba, M.; et al. Activity of a novel HER2 inhibitor, poziotinib, for HER2 exon 20 mutations in lung cancer and mechanism of acquired resistance: An in vitro study. Lung Cancer 2018, 126, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umelo, I.; Noeparast, A.; Chen, G.; Renard, M.; Geers, C.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Giron, P.; De Wever, O.; Teugels, E.; De Grève, J. Identification of a novel HER3 activating mutation homologous to EGFR-L858R in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3068–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, H.; Han, A.; Polsdofer, E.; Liu, S.; Liu, B. Understanding the biology of HER3 receptor as a therapeutic target in human cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Ma, L.; Wong, M.P.; Lee, V.H.; Yan, H. Contribution of EGFR and ErbB-3 heterodimerization to the EGFR mutation-induced gefitinib- and erlotinib-resistance in non-small-cell lung carcinoma treatments. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonesaka, K.; Kudo, K.; Nishida, S.; Takahama, T.; Iwasa, T.; Yoshida, T.; Tanaka, K.; Takeda, M.; Kaneda, H.; Okamoto, I.; et al. The pan-HER family tyrosine kinase inhibitor afatinib overcomes HER3 ligand heregulin-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33602–33611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yonesaka, K.; Hirotani, K.; Kawakami, H.; Takeda, M.; Kaneda, H.; Sakai, K.; Okamoto, I.; Nishio, K.; Jänne, P.A.; Nakagawa, K. Anti-HER3 monoclonal antibody patritumab sensitizes refractory non-small cell lung cancer to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib. Oncogene 2016, 35, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurppa, K.J.; Denessiouk, K.; Johnson, M.S.; Elenius, K. Activating ERBB4 mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.C.; Hao, J.J.; Nagata, Y.; Xu, L.; Shang, L.; Meng, X.; Sato, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Varela, A.M.; Ding, L.W.; et al. Genomic and molecular characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammerman, P.S.; Sos, M.L.; Ramos, A.H.; Xu, C.; Dutt, A.; Zhou, W.; Brace, L.E.; Woods, B.A.; Lin, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Mutations in the DDR2 kinase gene identify a novel therapeutic target in squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, M.; Togashi, Y.; Sato, K.; Mizuuchi, H.; Sakai, K.; Suda, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Banno, E.; Hayashi, H.; De Velasco, M.A.; et al. Functional analyses of mutations in receptor tyrosine kinase genes in non-small cell lung cancer: Double-edged sword of DDR2. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3663–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Plodkowski, A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Chaft, J.E.; Kris, M.G.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M.; Drilon, A. Impact of concurrent PIK3CA mutations on response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers and on prognosis in oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.M.; Song, A.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.O.; Keam, B.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to AZD9291: A mutation-selective, irreversible EGFR inhibitor. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hao, J. Development of anticancer agents targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2344–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Mo, C.; Gong, D.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Li, Y.; Fuller-Pace, F.V.; et al. DDX17 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling promotes acquired gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells via activation of β-catenin. Cancer Lett. 2017, 400, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, S.; Sng, N.; Carretero, J.; Welner, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Tan, A.J.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yasuda, H.; Li, D.; et al. β-catenin contributes to lung tumor development induced by EGFR mutations. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5891–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Terashima, M.; de Velasco, M.A.; Sakai, K.; Fujita, Y.; Tomida, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Nishio, K. Inhibition of β-Catenin enhances the anticancer effect of irreversible EGFR-TKI in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer with a T790M mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massagué, J.; Blain, S.W.; Lo, R.S. TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell 2000, 103, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildhaus, H.U.; Nogova, L.; Wolf, J.; Buettner, R. FGFR1 amplifications in squamous cell carcinomas of the lung: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Sonoda, K.; Nakashima, K.; Tashiro, K.; Watari, K.; Izumi, H.; Kage, M.; Kuwano, M.; Ono, M.; et al. FGFR1 activation is an escape mechanism in human lung cancer cells resistant to afatinib, a pan-EGFR family kinase inhibitor. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5908–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terai, H.; Soejima, K.; Yasuda, H.; Nakayama, S.; Hamamoto, J.; Arai, D.; Ishioka, K.; Ohgino, K.; Ikemura, S.; Sato, T.; et al. Activation of the FGF2-FGFR1 autocrine pathway: A novel mechanism of acquired resistance to gefitinib in NSCLC. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienstmann, R.; Rodon, J.; Prat, A.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Adamo, B.; Felip, E.; Cortes, J.; Iafrate, A.J.; Nuciforo, P.; Tabernero, J. Genomic aberrations in the FGFR pathway: Opportunities for targeted therapies in solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsten, T.; Elkin, S.; Arthur, E.; Tomson, B.N.; Carter, J.; Kurzrock, R. The FGFR landscape in cancer: Analysis of 4853 tumors by next-generation sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; Cai, D.; Li, H.; Ye, T.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Comprehensive investigation of oncogenic driver mutations in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34300–34308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrani, P.; Prabhash, K.; Prasad, R.; Sethunath, V.; Ranjan, M.; Iyer, P.; Aich, J.; Dhamne, H.; Iyer, D.N.; Upadhyay, P.; et al. Drug-sensitive FGFR3 mutations in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelletti, M.; Dodge, M.E.; Ercan, D.; Hammerman, P.S.; Park, S.I.; Kim, J.; Sasaki, H.; Jablons, D.M.; Lipson, D.; Young, L.; et al. Identification of recurrent FGFR3-TACC3 fusion oncogenes from lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6551–6558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Castanaro, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ni, M.; Young, T.M.; Zhang, L.; Burova, E.; Thurston, G. FGFR3-TACC3 fusion proteins act as naturally occurring drivers of tumor resistance by functionally substituting for EGFR/ERK signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.I.; Horn, L.; Cruz, M.; Vafai, D.; Lovly, C.M.; Spradlin, A.; Williamson, M.J.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Johnson, A.; Miller, V.A.; et al. Emergence of FGFR3-TACC3 fusions as a potential by-pass resistance mechanism to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR mutated NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorantes-Heredia, R.; Ruiz-Morales, J.M.; Cano-García, F. Histopathological transformation to small-cell lung carcinoma in non-small cell lung carcinoma tumors. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oser, M.G.; Niederst, M.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. Transformation from non-small-cell lung cancer to small-cell lung cancer: Molecular drivers and cells of origin. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.M.; Zakowski, M.F.; Yu, H.A.; Won, H.H.; Riely, G.J.; Krug, L.M.; Kris, M.G.; Rekhtman, N.; Ladanyi, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Small-cell lung cancers in patients who never smoked cigarettes. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 892–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoux, N.; Gettinger, S.N.; O’Kane, G.; Arbour, K.C.; Neal, J.W.; Husain, H.; Evans, T.L.; Brahmer, J.R.; Muzikansky, A.; Bonomi, P.D.; et al. EGFR-mutant adenocarcinomas that transform to small-cell lung cancer and other neuroendocrine carcinomas: Clinical outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Duan, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Liang, Z. Genetic alterations and protein expression in combined small cell lung cancers and small cell lung cancers arising from lung adenocarcinomas after therapy with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34240–34249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santoni-Rugiu, E. Clinical outcomes provide new insights into transformation to small-cell lung cancer of pulmonary EGFR-mutant adenocarcinoma. Prec. Cancer Med. 2019, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, E.; Gurizzan, C.; Amoroso, V.; Vermi, W.; Ferrari, V.; Berruti, A. Outcome of patients with lung adenocarcinoma with transformation to small-cell lung cancer following tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 59, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, L.; Giaj Levra, M.; Brevet, M.; Antoine, M.; Mazieres, J.; Rossi, G.; Chiari, R.; Westeel, V.; Poudenx, M.; Letreut, J.; et al. A brief report of transformation from NSCLC to SCLC: Molecular and therapeutic characteristics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Youk, J.; Park, S.; An, Y.; Keam, B.; Kim, D.W.; Heo, D.S.; et al. Clonal history and genetic predictors of transformation into small-cell carcinomas from lung adenocarcinomas. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farago, A.F.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V. Unlocking the mystery of small-cell lung cancer transformations in EGFR mutant adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2987–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Cooper, W.; Links, M.; Gebski, V.; Herbst, R.S.; Gralla, R.J.; Mok, T.; Yang, J.C. Clinical and molecular characteristics associated with survival among patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisberg, A.; Cummings, A.; Goldman, J.W.; Bornazyan, K.; Reese, N.; Wang, T.; Coluzzi, P.; Ledezma, B.; Mendenhall, M.; Hunt, J.; et al. A phase II study of pembrolizumab in EGFR-mutant, PD-L1+, tyrosine kinase inhibitor Naïve patients with advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.; Puri, S.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.; Boyle, T.; Hicks, J.K.; Lovinger, K.L.; Roarty, E.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; et al. Landscape of EGFR-dependent and -independent resistance mechanisms to osimertinib and continuation therapy beyond progression in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleczko, E.K.; Heasley, L.E. Mechanisms of rapid cancer cell reprogramming initiated by targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and inherent therapeutic vulnerabilities. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witta, S.E.; Gemmill, R.M.; Hirsch, F.R.; Coldren, C.D.; Hedman, K.; Ravdel, L.; Helfrich, B.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Chan, D.C.; Sugita, M.; et al. Restoring E-cadherin expression increases sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, N.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.C.; Chen, C.; Wang, X. Role of epigenetics in lung cancer heterogeneity and clinical implication. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2017, 64, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; van der Wekken, A.J.; Saber, A.; Terpstra, M.M.; Schuuring, E.; Timens, W.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J.M.; van den Berg, A.; Kok, K. Mutations in EMT-related genes in ALK positive crizotinib resistant non-small cell lung cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.B.; Halmos, B.; Kumar, A.; Schumer, S.T.; Huberman, M.S.; Boggon, T.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Kobayashi, S. BIM mediates EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced apoptosis in lung cancers with oncogenic EGFR mutations. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, A.C.; Corcoran, R.B.; Ebi, H.; Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Chung, E.; Incio, J.; Digumarthy, S.R.; Pollack, S.F.; Song, Y.; et al. BIM expression in treatment-naive cancers predicts responsiveness to kinase inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Oh, Y.T.; Deng, L.; Zhang, G.; Qian, G.; Zhang, S.; Ren, H.; Wu, G.; Legendre, B., Jr.; Anderson, E.; et al. Overcoming acquired resistance to AZD9291, a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, through modulation of MEK/ERK-dependent Bim and Mcl-1 degradation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6567–6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.A.; Niederst, M.J.; Lochmann, T.L.; Hata, A.N.; Kitai, H.; Ham, J.; Floros, K.V.; Hicks, M.A.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition antagonizes response to targeted therapies in lung cancer by suppressing BIM. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.S.; Raffeld, M.; Moon, Y.W.; Xi, L.; Bianco, C.; Pham, T.; Lee, L.C.; Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y.; Okamoto, I.; et al. CRIPTO1 expression in EGFR-mutant NSCLC elicits intrinsic EGFR-inhibitor resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3003–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, S.; Saini, S.; Dar, A.A.; Hirata, H.; Shahryari, V.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamamura, S.; Ueno, K.; Zaman, M.S.; Singh, K.; et al. MicroRNA-205 inhibits Src-mediated oncogenic pathways in renal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2611–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Shang, S.; Shao, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. BIM deletion polymorphism confers resistance to osimertinib in EGFR T790M lung cancer: A case report and literature review. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.P.; Hillmer, A.M.; Chuah, C.T.; Juan, W.C.; Ko, T.K.; Teo, A.S.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Takahashi, N.; Sawada, K.; Fei, Y.; et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; Tao, X.; Wei, H.; Chen, W.S.; Li, B. The BIM deletion polymorphism is a prognostic biomarker of EGFR-TKIs response in NSCLC: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25696–25700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Yamada, T.; Ebi, H.; Sano, T.; Nanjo, S.; Ishikawa, D.; Sato, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sekido, Y.; et al. EGFR-TKI resistance due to BIM polymorphism can be circumvented in combination with HDAC inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Bai, H.; Yan, B.; Li, R.; Shao, M.; Xiong, L.; Han, B. Mimicking the BIM BH3 domain overcomes resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108522–108533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, K.; Yamada, T.; Roca, X.; Ong, S.T.; Yano, S. Histone deacetylase 3 inhibition overcomes BIM deletion polymorphism-mediated osimertinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3139–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Molina, M.A.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Giménez-Capitán, A.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Gervais, R.; Massuti, B.; Wei, J.; Moran, T.; et al. The impact of EGFR T790M mutations and BIM mRNA expression on outcome in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC treated with erlotinib or chemotherapy in the randomized phase III EURTAC trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachaliou, N.; Codony-Servat, J.; Teixidó, C.; Pilotto, S.; Drozdowskyj, A.; Codony-Servat, C.; Giménez-Capitán, A.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; Bertrán-Alamillo, J.; Gervais, R.; et al. BIM and mTOR expression levels predict outcome to erlotinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Chu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Decreased human antigen R expression confers resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer by inhibiting Bim expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 2930–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vouri, M.; Hafizi, S. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2775–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, J.C.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Au, V.; LaFramboise, T.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Wang, X.; Levine, A.D.; Rho, J.K.; et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamichi, S.; Seike, M.; Miyanaga, A.; Chiba, M.; Zou, F.; Takahashi, A.; Ishikawa, A.; Kunugi, S.; Noro, R.; Kubota, K.; et al. Overcoming drug-tolerant cancer cell subpopulations showing AXL activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition is critical in conquering ALK-positive lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27242–27255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and EGFR-TKI resistance of non-small cell lung cancers via HGF/IGF-1/ANXA2 signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, A.; Asselin, M.C.; Reymen, B.; Jackson, A.; Lambin, P.; West, C.M.L.; O’Connor, J.P.B.; Faivre-Finn, C. Targeting hypoxia to improve non-small cell lung cancer outcome. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvold, N.D.; Heidari, P.; Kunawudhi, A.; Sequist, L.V.; Mahmood, U. Tumor hypoxia response after targeted therapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: Proof of concept for FMISO-PET. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 15, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilmar, A.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Cillas, J.G.; Huarriz, M.; Sørensen, J.B. Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1 mRNA expression as a prognostic marker in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2991–2996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murakami, A.; Takahashi, F.; Nurwidya, F.; Kobayashi, I.; Minakata, K.; Hashimoto, M.; Nara, T.; Kato, M.; Tajima, K.; Shimada, N.; et al. Hypoxia increases gefitinib-resistant lung cancer stem cells through the activation of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurwidya, F.; Takahashi, F.; Kobayashi, I.; Murakami, A.; Kato, M.; Minakata, K.; Nara, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Yagishita, S.; Baskoro, H.; et al. Treatment with insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor inhibitor reverses hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Chen, B.; Xie, B.; Zhang, W.M. Implication of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in IGF1R-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44332–44345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 world health organization classification of lung tumors: Impact of genetic, clinical and radiologic advances since the 2004 classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Zhou, S.; Qin, Z.; Yang, L.; Han, X.; Yao, S.; Ji, H. Evidence, mechanism, and clinical relevance of the transdifferentiation from lung adenocarcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fillmore Brainson, C.; Koyama, S.; Redig, A.J.; Chen, T.; Li, S.; Gupta, M.; Garcia-de-Alba, C.; Paschini, M.; Herter-Sprie, G.S.; et al. Erratum: Lkb1 inactivation drives lung cancer lineage switching governed by Polycomb Repressive Complex 2. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roca, E.; Pozzari, M.; Vermi, W.; Tovazzi, V.; Baggi, A.; Amoroso, V.; Nonnis, D.; Intagliata, S.; Berruti, A. Outcome of EGFR-mutated adenocarcinoma NSCLC patients with changed phenotype to squamous cell carcinoma after tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A pooled analysis with an additional case. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassella, E.; Langsch, S.; Dettmer, M.S.; Schlup, C.; Neuenschwander, M.; Frattini, M.; Gugger, M.; Schäfer, S.C. Molecular profiling of lung adenosquamous carcinoma: Hybrid or genuine type? Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23905–23916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; Del Re, M.; Facchinetti, F.; Mazzoni, F.; Barbieri, F.; Camerini, A.; Comin, C.E.; Gnetti, L.; Azzoni, C.; et al. Primary resistance to osimertinib due to SCLC transformation: Issue of T790M determination on liquid re-biopsy. Lung Cancer 2018, 115, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Li, X.F.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.G. Predictive efficacy of (11)C-PD153035 PET imaging for EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdenrieder, S. Biomarkers along the continuum of care in lung cancer. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. Suppl. 2016, 245, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahce, I.; Yaqub, M.; Smit, E.F.; Lammertsma, A.A.; van Dongen, G.A.; Hendrikse, N.H. Personalizing NSCLC therapy by characterizing tumors using TKI-PET and immuno-PET. Lung Cancer 2017, 107, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, C.; Chen, X.; Grandis, J.R.; Duvvuri, U. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition induces autophagy in cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2012, 13, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, W.; Pan, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Ge, W.; Feng, L.; Lin, X.; Wang, X.; et al. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Lam, S.K.; Mak, J.C.; Zheng, C.Y.; Ho, J.C. Erlotinib-induced autophagy in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 81, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, M.C.; Wu, M.Y.; Hwang, M.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Huang, H.J.; Lin, A.M.; Yang, J.C. Chloroquine enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity in gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Yin, W. AZD9291 promotes autophagy and inhibits PI3K/Akt pathway in NSCLC cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Lin, C.; Lu, C.; Zhang, K.; Hu, C.; Ye, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, H.; et al. Protective autophagy decreases osimertinib cytotoxicity through regulation of stem cell-like properties in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 452, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Henson, E.S.; Xiao, W.; Huang, D.; McMillan-Ward, E.M.; Israels, S.J.; Gibson, S.B. Tyrosine kinase receptor EGFR regulates the switch in cancer cells between cell survival and cell death induced by autophagy in hypoxia. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1029–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henson, E.; Chen, Y.; Gibson, S. EGFR family members’ regulation of autophagy is at a crossroads of cell survival and death in cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Klerk, D.J.; Honeywell, R.J.; Jansen, G.; Peters, G.J. Transporter and lysosomal mediated (Multi)drug resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors and potential strategies to overcome resistance. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, K.; Kawahara, H.; Kaji, A.; Katayama, K.; Mitsuhashi, J.; Sugimoto, Y. Substrate-dependent bidirectional modulation of P-glycoprotein-mediated drug resistance by erlotinib. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.M.; Chiu, C.H.; Chang, K.T.; Chen, J.T.; Lai, C.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Hsiao, S.Y. Gefitinib enhances cytotoxicities of antimicrotubule agents in non-small-cell lung cancer cells exhibiting no sensitizing epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.L.; Tsai, Y.M.; Lien, C.T.; Kuo, P.L.; Hung, A.J. The roles of MicroRNA in lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Qu, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, X.; Li, P.; Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, L. The long non-coding RNA, GAS5, enhances gefitinib-induced cell death in innate EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells with wide-type EGFR via downregulation of the IGF-1R expression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, D.D.; Hu, Y.; Yan, D.; Chen, X.; Cao, H.X.; Yu, S.R.; Wang, Z.; Feng, J.F. Genome-wide profiling of long non-coding RNA expression patterns in the EGFR-TKI resistance of lung adenocarcinoma by microarray. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3371–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Garfield, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; Chen, M.; Kuang, P.; et al. MiR-21 overexpression is associated with acquired resistance of EGFR-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhu, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, T.; Pei, D.; Wang, R.; Qian, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z.; et al. Alteration in Mir-21/PTEN expression modulates gefitinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Su, X.; Bai, H.; Zhao, J.; Duan, J.; An, T.; Zhuo, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Identification of plasma microRNA profiles for primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with EGFR activating mutation. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Xu, F.; Zhai, W.; Dong, S.; Yin, L.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z. Role of long non-coding RNA in drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, N.; Cai, W.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Pan, H.; Zhao, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; et al. Long non-coding RNA UCA1 induces non-T790M acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs by activating the AKT/mTOR pathway in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23582–23593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachaliou, N.; Chaib, I.; Cardona, A.F.; Berenguer, J.; Bracht, J.W.P.; Yang, J.; Cai, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C.; Drozdowskyj, A.; et al. Common co-activation of AXL and CDCP1 in EGFR-mutation-positive non-smallcell lung cancer associated with poor prognosis. EBioMedicine 2018, 29, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yamada, T.; Wang, R.; Tanimura, K.; Adachi, Y.; Nishiyama, A.; Tanimoto, A.; Takeuchi, S.; Araujo, L.H.; Boroni, M.; et al. AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Soria, J.C.; Goldman, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Varga, A.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Solomon, B.J.; Oxnard, G.R.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. Rociletinib in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyasu, R.; Nishikawa, S.; Uchibori, K.; Oh-Hara, T.; Yoshizawa, T.; Dotsu, Y.; Koyama, J.; Saiki, M.; Sonoda, T.; Kitazono, S.; et al. High ratio of T790M to EGFR activating mutations correlate with the osimertinib response in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 117, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Re, M.; Bordi, P.; Rofi, E.; Restante, G.; Valleggi, S.; Minari, R.; Crucitta, S.; Arrigoni, E.; Chella, A.; Morganti, R.; et al. The amount of activating EGFR mutations in circulating cell-free DNA is a marker to monitor osimertinib response. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.Y.; Ho, J.C.; Wong, K.H. T790M mutant copy number quantified via ddPCR predicts outcome after osimertinib treatment in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27929–27939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buder, A.; Hochmair, M.J.; Schwab, S.; Bundalo, T.; Schenk, P.; Errhalt, P.; Mikes, R.E.; Absenger, G.; Patocka, K.; Baumgartner, B.; et al. Cell-Free plasma DNA-guided treatment with osimertinib in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederst, M.J.; Hu, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Lockerman, E.L.; Garcia, A.R.; Piotrowska, Z.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. The allelic context of the C797S mutation acquired upon treatment with third-generation EGFR inhibitors impacts sensitivity to subsequent treatment strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3924–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulananda, S.; Do, H.; Musafer, A.; Mitchell, P.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Combination osimertinib and gefitinib in C797S and T790M EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.J.; Huang, J.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Tu, H.Y.; Han-Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.L. Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR T790M and In Trans C797S responds to combination therapy of first- and third-generation EGFR TKIs and shifts allelic configuration at resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Suda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohara, S.; Fujino, T.; Koga, T.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Tomizawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; et al. Effects of secondary EGFR mutations on resistance against upfront osimertinib in cells with EGFR-activating mutations in vitro. Lung Cancer 2018, 126, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Azuma, K.; Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Togashi, Y.; Sesumi, Y.; Chiba, M.; Shimoji, M.; Sato, K.; Tomizawa, K.; et al. Characterization of EGFR T790M, L792F, and C797S mutations as mechanisms of acquired resistance to afatinib in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Fujino, T.; Nishino, M.; Koga, T.; Chiba, M.; Sesumi, Y.; Ohara, S.; Shimoji, M.; Tomizawa, K.; Takemoto, T.; et al. EGFR T790M and C797S mutations as mechanisms of acquired resistance to dacomitinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchibori, K.; Inase, N.; Nishio, M.; Fujita, N.; Katayama, R. Identification of mutation accumulation as resistance mechanism emerging in first-line osimertinib treatment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesaka, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Nakagawa, K. Dual blockade of EGFR tyrosine kinase using osimertinib and afatinib eradicates EGFR-mutant Ba/F3 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.; Rajaram, S.; Steininger, R.J.; Osipchuk, D.; Roth, M.A.; Morinishi, L.S.; Evans, L.; Ji, W.; Hsu, C.H.; Thurley, K.; et al. Diverse drug-resistance mechanisms can emerge from drug-tolerant cancer persister cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.C.; Wells, J.M.; Chow, K.-H.; Huang, H.; Yuan, M.; Saxena, T.; Melnick, M.A.; Politi, K.; Asara, J.M.; Costa, D.B.; et al. miR-147b-mediated TCA cycle dysfunction and pseudohypoxia initiate drug tolerance to EGFR inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohlin, S.; Wigerup, C.; Jögi, A.; Påhlman, S. Hypoxia, pseudohypoxia and cellular differentiation. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 356, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, I.; Takahashi, F.; Nurwidya, F.; Nara, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Murakami, A.; Yagishita, S.; Tajima, K.; Hidayat, M.; Shimada, N.; et al. Oct4 plays a crucial role in the maintenance of gefitinib-resistant lung cancer stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuxen, I.V.; Rohrberg, K.; Østrup, O.; Schmidt, A.Y.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Spanggaard, I.; Hasselby, J.P.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Yde, C.W.; Mau-Soerensen, M.; et al. Copenhagen prospective personalized oncology (CoPPO)—Clinical utility of using molecular profiling to select patients to phase 1 trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlborn, L.B.; Rohrberg, K.S.; Gabrielaite, M.; Tuxen, I.V.; Yde, C.W.; Spanggaard, I.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Nielsen, F.C.; Lassen, U.; Mau-Sorensen, M.; et al. Application of cell-free DNA for genomic tumor profiling: A feasibility study. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yun, C.H.; Park, E.; Ercan, D.; Manuia, M.; Juarez, J.; Xu, C.; Rhee, K.; Chen, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature 2016, 534, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Serrano, A.; Gella, P.; Jiménez, E.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Paz-Ares Rodríguez, L. Targeting EGFR in lung cancer: Current standards and developments. Drugs 2018, 78, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, Z.; Tan, B.; Lin, N. Targeting the cell signaling pathway Keap1-Nrf2 as a therapeutic strategy for adenocarcinomas of the lung. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Pazarentzos, E.; Olivas, V.; Asthana, S.; Yan, J.J.; Tan, I.; Hrustanovic, G.; Chan, E.; Lin, L.; Neel, D.S.; et al. NF-κB-activating complex engaged in response to EGFR oncogene inhibition drives tumor cell survival and residual disease in lung cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivona, T.G.; Hieronymus, H.; Parker, J.; Chang, K.; Taron, M.; Rosell, R.; Moonsamy, P.; Dahlman, K.; Miller, V.A.; Costa, C.; et al. FAS and NF-κB signalling modulate dependence of lung cancers on mutant EGFR. Nature 2011, 471, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, K.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Molina, M.A.; Teixidó, C.; Karachaliou, N.; Pedersen, M.H.; Castellví, J.; Garzón, M.; Codony-Servat, C.; Codony-Servat, J.; et al. Convergent Akt activation drives acquired EGFR inhibitor resistance in lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.M.; Choi, M.K.; Sun, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Ahn, M.J. Acquired resistance to AZD9291 as an upfront treatment is dependent on ERK signaling in a preclinical model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, L.; Jiang, M.; Teng, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Loss of EGFR confers acquired resistance to AZD9291 in an EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer cell line with an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Nakagawa, K. First- and second-generation EGFR-TKIs are all replaced to osimertinib in chemo-naive EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeper, J.; Griesinger, F. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer: What is the preferred first-line therapy? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Somatic Mutation (Amino Acid Position) | Exon | Effect on EGFR-TKIs | Other Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G719X S768I L861Q | 18 20 21 | Reduced response to 1G TKIs in pts. & preclinical models. Sensitive to afatinib. Osimertinib less effective in pts. or cell lines with these mutants than in those with classic EGFR-mutants, regardless of presence of T790M co-mutation. | Significantly less sensitive than L858R & exon 19dels but do show some response to 1G TKIs. Can co-occur together or with sensitizing mutations, especially L858R. The rare variant L861P reported co-existing with L858R in pts. not responding to 1G EGFR-TKIs. | [54,76,81,83,87,89,90,92,94] |
| L747P | 19 | Intrinsic resistance to EGFR-TKIs of all three generations | Very rare, resistance mechanism unclear. The variant L747S occasionally reported both as secondary TKI-resistant mutant in the setting of acquired TKI-resistance and as de novo mutation in cases with co-existing L858R not responding to 1G EGFR-TKIs. | [54,57,58,86,99,101] |
| Exon 19 insertions | 19 | Unclear (very rare, require further investigations) | Some epidemiological evidence for lower TKI-sensitivity than common EGFR-mutations. | [51,97,98] |
| Exon 20 insertions | 20 | Poor response to 1G/2G TKIs; in vitro appear responsive to osimertinib & single cases were reported sensitive to osimertinib. | A763_Y764insFQEA is an exception, as structurally resembles L858R & is sensitive to TKIs. In preclinical models, exon 20ins responded to cetuximab + afatinib or osimertinib. Cases responding to afatinib + cetuximab have been reported. Promising results in vitro and in vivo from new selective TKIs targeting EGFR and ERBB2 exon 20 insertions, such as poziotinib, TAS6417, and TAK-788. Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors also potentially active against NSCLC cells with EGFR exon 20ins. | [83,86,87,103,104,106,108,110,112] |
| T790M | 20 | Resistant to 1G/2G TKIs, sensitive to 3G TKIs. | Present as de novo mutation, either alone or with a common sensitizing mutation such as L858R. Amplification of T790M-positive EGFR may provide further TKI-resistance. High relative abundance of T790M predicts poor response to 1G/2G TKIs but may predict better response to 3G TKIs. | [51,54,57,61,62] |
| Germline T790M | 20 | Resistant to 1G/2G TKIs, sensitive to 3G TKIs. | Predominantly in females, non-smokers with a secondary somatic EGFR-mutation. | [115] |
| Germline V843I | 21 | Resistant to 1G/2G TKIs, possibly sensitive to 3G TKIs. | As T790M sterically hinders TKI-binding to EGFR. | [113,114,115] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Melchior, L.C.; Urbanska, E.M.; Jakobsen, J.N.; de Stricker, K.; Grauslund, M.; Sørensen, J.B. Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2019, 11, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070923
Santoni-Rugiu E, Melchior LC, Urbanska EM, Jakobsen JN, de Stricker K, Grauslund M, Sørensen JB. Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance. Cancers. 2019; 11(7):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070923
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantoni-Rugiu, Eric, Linea C. Melchior, Edyta M. Urbanska, Jan N. Jakobsen, Karin de Stricker, Morten Grauslund, and Jens B. Sørensen. 2019. "Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance" Cancers 11, no. 7: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070923
APA StyleSantoni-Rugiu, E., Melchior, L. C., Urbanska, E. M., Jakobsen, J. N., de Stricker, K., Grauslund, M., & Sørensen, J. B. (2019). Intrinsic Resistance to EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Differences and Similarities with Acquired Resistance. Cancers, 11(7), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070923