TGF-Beta-Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Limit Cetuximab Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
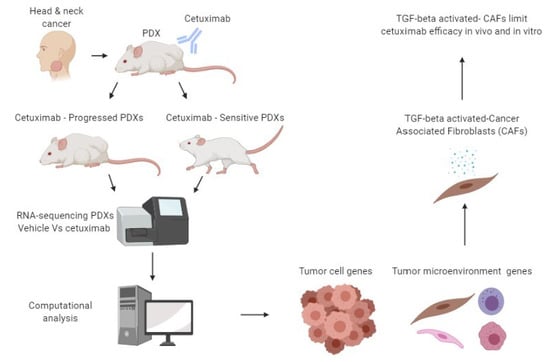
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Diverse Response of HNCs-PDXs to Cetuximab Treatment
2.2. Molecular Characterization of CetuximabSen and CetuximabProg PDXs
2.3. Tumor Progression Under Cetuximab Treatment is Associated with TGF-Beta Activation in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs)
2.4. TGF-Beta-Activated CAFs Reduce Sensitivity to Cetuximab In Vivo and Blocking TGF-Beta Sensitize HNC-PDX to Cetuximab
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Procurement
4.2. Mice and Establishment of Patient-Derived Xenografts (PDXs)
4.3. In-Vivo Experiments
4.4. Chemical Compounds
4.5. Library Preparation and RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq)
4.6. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
4.7. Staining: Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Opal, Immunofluorescence (IF), and Hematoxylin & Eosin Staining (H&E)
4.8. Cell Lines
4.9. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Azarnia, N.; Shin, D.M.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.; Raben, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab for Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.K.; Raben, D.; Baselga, J.; Spencer, S.A.; Zhu, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Trigo, J.; Hitt, R.; Koralewski, P.; Diaz-Rubio, E.; Rolland, F.; Knecht, R.; Amellal, N.; Schueler, A.; Baselga, J. Open-Label, Uncontrolled, Multicenter Phase II Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Toxicity of Cetuximab As a Single Agent in Patients With Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck Who Failed to Respond to Platinum-Based The. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.R.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendelsohn, J. The epidermal growth factor receptor as a target for cancer therapy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2001, 8, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, T.D.; Hill, E.G.; Armeson, K.E.; Gillespie, M.B. Cetuximab Therapy for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review of the Data. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, P.; Resteghini, C.; Paielli, N.; Licitra, L.; Pilotti, S.; Perrone, F. Prognostic and predictive value of EGFR in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 74362–74379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurizi, M.; Almadori, G.; Ferrandina, G.; Distefano, M.; Romanini, M.E.; Cadoni, G.; Benedetti-Panici, P.; Paludetti, G.; Scambia, G.; Mancuso, S. Prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor receptor in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 1253–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kian Ang, K.; Berkey, B.A.; Tu, X.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Katz, R.; Hammond, E.H.; Fu, K.K.; Milas, L. Impact of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression on Survival and Pattern of Relapse in Patients with Advanced Head and Neck Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 7350–7356. [Google Scholar]
- Hitt, R.; Irigoyen, A.; Cortes-Funes, H.; Grau, J.J.; García-Sáenz, J.A.; Cruz-Hernandez, J.J. Phase II study of the combination of cetuximab and weekly paclitaxel in the first-line treatment of patients with recurrent and/or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeeshan, S.; Prasad, M.; Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Gregoire, V.; Saintigny, P.; Elkabets, M. Adaptive Responses to Monotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer: Interventions for Rationale-Based Therapeutic Combinations. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 365–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sok, J.C.; Coppelli, F.M.; Thomas, S.M.; Lango, M.N.; Xi, S.; Hunt, J.L.; Freilino, M.L.; Graner, M.W.; Wikstrand, C.J.; Bigner, D.D.; et al. Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII) contributes to head and neck cancer growth and resistance to EGFR targeting. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5064–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tinhofer, I.; Klinghammer, K.; Weichert, W.; Knödler, M.; Stenzinger, A.; Gauler, T.; Budach, V.; Keilholz, U. Expression of amphiregulin and EGFRvIII affect outcome of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck receiving cetuximab—Docetaxel treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5197–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Costa, A.A.B.A.; Costa, F.D.; Araújo, D.V.; Camandaroba, M.P.G.; de Jesus, V.H.F.; Oliveira, A.; Alves, A.C.F.; Stecca, C.; Machado, L.; de Oliveira, A.C.F.; et al. The roles of PTEN, cMET, and p16 in resistance to cetuximab in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2019, 36, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Huang, S.; Kruser, T.J.; Nechrebecki, M.M.; Armstrong, E.A.; Benavente, S.; Gondi, V.; Hsu, K.T.; Harari, P.M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to cetuximab: Role of HER (ErbB) family members. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3944–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Qian, G.; Zhang, H.; Magliocca, K.R.; Nannapaneni, S.; Amin, A.R.M.R.; Rossi, M.; Patel, M.; El-Deiry, M.; Wadsworth, J.T.; et al. HER3 targeting sensitizes HNSCC to cetuximab by reducing HER3 activity and HER2/HER3 dimerization: Evidence from cell line and patient-derived xenograft models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonard, B.; Brand, T.M.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Lee, E.D.; Zeng, Y.; Kemmer, J.D.; Li, H.; Grandis, J.R.; Bhola, N.E. BET Inhibition Overcomes Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Mediated Cetuximab Resistance in HNSCC. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4331–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brand, T.M.; Iida, M.; Stein, A.P.; Corrigan, K.L.; Braverman, C.M.; Luthar, N.; Toulany, M.; Gill, P.S.; Salgia, R.; Kimple, R.J.; et al. AXL mediates resistance to cetuximab therapy. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5152–5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, A.C.; Ansell, A.; Jerhammar, F.; Lindh, M.B.; Grénman, R.; Munck-Wikland, E.; Östman, A.; Roberg, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce matrix metalloproteinase-mediated cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayuso, J.M.; Vitek, R.; Swick, A.D.; Skala, M.C.; Wisinski, K.B.; Kimple, R.J.; Lambert, P.F.; Beebe, D.J. Effects of culture method on response to EGFR therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, S.; Bindea, G.; Albu, R.I.; Mlecnik, B.; Machiels, J.P. Cetuximab promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer associated fibroblasts in patients with head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34288–34299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Sakai, K.; Arao, T.; Shimoyama, T.; Tamura, T.; Nishio, K. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of cetuximab against tumor cells with wild-type or mutant epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurai, J.; Chikumi, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamasaki, A.; Sako, T.; Touge, H.; Makino, H.; Takata, M.; Miyata, M.; et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by cetuximab against lung cancer cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trédan, O.; Galmarini, C.M.; Patel, K.; Tannock, I.F. Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joyce, J.A. Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bissell, M.J.; Hines, W.C. Why don’t we get more cancer? A proposed role of the microenvironment in restraining cancer progression. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klemm, F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of therapeutic response in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, A.; Chang, X.; Noonan, K.; Pham, V.; Bedi, R.; Fertig, E.J.; Considine, M.; Califano, J.A.; Borrello, I.; Chung, C.H.; et al. Inhibition of TGF-β enhances the in vivo antitumor efficacy of EGF receptor-targeted therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2429–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdollah, S.; Macías-Silva, M.; Tsukazaki, T.; Hayashi, H.; Attisano, L.; Wrana, J.L. TRI Phosphorylation of Smad2 on Ser 465 and Ser 467 Is Required for Smad2-Smad4 Complex Formation and Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27678–27685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shiga, K.; Hara, M.; Nagasaki, T.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, H.; Takeyama, H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: Their characteristics and their roles in tumor growth. Cancers (Basel) 2015, 7, 2443–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Knuechel, R. Tumor-associated fibroblasts (Part I): Active stromal participants in tumor development and progression? Histol. Histopathol. 2002, 17, 599–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Novoplansky, O.; Fury, M.; Prasad, M.; Yegodayev, K.; Zorea, J.; Cohen, L.; Pelossof, R.; Cohen, L.; Katabi, N.; Cecchi, F.; et al. MET activation confers resistance to cetuximab, and prevents HER2 and HER3 upregulation in head and neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 748–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkabets, M.; Pazarentzos, E.; Juric, D.; Sheng, Q.; Pelossof, R.A.; Brook, S.; Oaknin Benzaken, A.; Rodon, J.; Morse, N.; Jiacheng Yan, J.; et al. AXL Mediates Resistance to PI3Kα Inhibition by Activating the EGFR/PKC/mTOR Axis in Head and Neck and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jinnin, M.; Ihn, H.; Tamaki, K. Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and its effect on transforming growth factor-β1-induced extracellular matrix expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjordal, K.; Kaasa, S.; Mastekaasa, A. Quality of life in patients treated for head and neck cancer: A follow-up study 7 to 11 years after radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 28, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.B.; Emerton, S.; Kolbinson, D.A.; Le, N.D.; Phillips, N.; Stevenson-Moore, P.; Osoba, D. Quality of life and oral function following radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Head Neck 1999, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, P.; Bergamini, C.; Siano, M.; Rocca, M.C.; Sponghini, A.P.; Favales, F.; Giannoccaro, M.; Marchesi, E.; Cortelazzi, B.; Perrone, F.; et al. Functional genomics uncover the biology behind the responsiveness of head and neck squamous cell cancer patients to cetuximab. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3961–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Iida, M.; Dunn, E.F.; Ghia, A.J.; Wheeler, D.L. Nuclear EGFR contributes to acquired resistance to cetuximab. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3801–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boeckx, C.; Baay, M.; Wouters, A.; Specenier, P.; Vermorken, J.B.; Peeters, M.; Lardon, F. Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Focus on Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance. Oncologist 2013, 18, 850–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prime, S.S.; Davies, M.; Pring, M.; Paterson, I.C. The role of TGF-β in epithelial malignancy and its relevance to the pathogenesis of oral cancer (part II). Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2004, 15, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. Transforming growth factor-β signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Insights into cellular responses. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4799–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leef, G.; Thomas, S.M. Molecular communication between tumor-associated fibroblasts and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdogan, B.; Webb, D.J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts modulate growth factor signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling to regulate tumor metastasis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Cai, J.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Feng, D.; Wang, Z. Ovarian cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to epithelial ovarian carcinoma metastasis by promoting angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and tumor cell invasion. Cancer Lett. 2011, 303, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, R.F.; Moore, T.; Arumugam, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Amos, K.D.; Rivera, A.; Ji, B.; Evans, D.B.; Logsdon, C.D. Cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts promote pancreatic tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fang, M.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z.; Yu, J. Interleukin-22 secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts regulates the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer cells via the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 4077–4088. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, H.; Liyanarachchi, S.; Davuluri, R.V.; Auer, H.; Martin, E.W.; De La Chapelle, A.; Frankel, W.L. Role of cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts in metastatic colon cancer to the liver and their expression profiles. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7366–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, S.E.; Shi, H.; Lin, F.; Dasari, S.; Bednash, J.; Thorne, S.; Watkins, S.; Joshi, R.; Thomas, S.M. Enhancement of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by tumor-associated fibroblasts in preclinical models. Head Neck 2014, 36, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.P.; Xu, K.; Cui, J.; Yuan, D.Y.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.L.; Li, K.Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, B. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-382-5p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolston, A.; Khan, K.; Spain, G.; Barber, L.J.; Griffiths, B.; Gonzalez-Exposito, R.; Hornsteiner, L.; Punta, M.; Patil, Y.; Newey, A.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Determinants of Therapy Resistance and Immune Landscape Evolution during Anti-EGFR Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Kita, K.; Bando, H.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yano, S. Hepatocyte growth factor induces resistance to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody in lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Yamada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Kayano, Y.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S.; et al. Crosstalk to stromal fibroblasts induces resistance of lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6630–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, T.; Ishii, G.; Goto, K.; Neri, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; Umemura, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; et al. Podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment induce primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, K.L.; Madden, J.M.; Zoratti, G.L.; Kuperwasser, C.; List, K.; Boerner, J.L. Fibroblast-secreted hepatocyte growth factor mediates epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in triple-negative breast cancers through paracrine activation of Met. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knowles, L.M.; Stabile, L.P.; Egloff, A.M.; Rothstein, M.E.; Thomas, S.M.; Gubish, C.T.; Lerner, E.C.; Seethala, R.R.; Suzuki, S.; Quesnelle, K.M.; et al. HGF and c-Met participate in paracrine tumorigenic pathways in head and neck squamous cell cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3740–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, D.; Venè, R.; Benelli, R.; Romairone, E.; Scabini, S.; Catellani, S.; Rebesco, B.; Mastracci, L.; Grillo, F.; Minghelli, S.; et al. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor can counteract the inhibition of natural killer cell function exerted by colorectal tumor-associated fibroblasts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, C.A.; Han, S.J.; Barry, J.J.; Ahn, B.J.; Lanier, L.L.; Parsa, A.T. TGF-β downregulates the activating receptor NKG2D on NK cells and CD8+ T cells in glioma patients. Neuro. Oncol. 2010, 12, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-C.; Lee, K.-M.; Kim, D.-W.; Heo, D.S. Elevated TGF-β1 Secretion and Down-Modulation of NKG2D Underlies Impaired NK Cytotoxicity in Cancer Patients. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7335–7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöss, S.; Chambron, N.; Gardlowski, T.; Weil, S.; Koch, J.; Esser, R.; Von Strandmann, E.P.; Morgan, M.A.; Arseniev, L.; Seitz, O.; et al. Cetuximab reconstitutes pro-inflammatory cytokine secretions and tumor-infiltrating capabilities of sMICA-inhibited NK cells in HNSCC tumor spheroids. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calon, A.; Tauriello, D.V.F.; Batlle, E. TGF-beta in CAF-mediated tumor growth and metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 25, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, C.L. Inhibition of TGFbeta signaling in cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2006, 16, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklarz, M.Y.; Levin, L.; Gordon, M.; Chalifa-Caspi, V. NeatSeq-Flow: A Lightweight High Throughput Sequencing Workflow Platform for Non-Programmers and Programmers alike. bioRxiv 2018, 173005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, J.R.; Farren, M.; Powell, S.J.; Runswick, S.; Weston, S.L.; Brown, H.; Delpuech, O.; Wappett, M.; Smith, N.R.; Carr, T.H.; et al. RNA-Seq Differentiates Tumour and Host mRNA Expression Changes Induced by Treatment of Human Tumour Xenografts with the VEGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cediranib. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMI A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| PDX #18 upregulated | |||
| Description | GeneRatio | p.adjust | |
| mmu04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 12/329 | 0.009162016 |
| mmu04350 | TGF-beta signaling pathway | 10/329 | 0.059661562 |
| mmu05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 16/329 | 0.080670748 |
| mmu05152 | Tuberculosis | 14/329 | 0.113807529 |
| mmu04510 | Focal adhesion | 15/329 | 0.115257749 |
| mmu04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 9/329 | 0.250750449 |
| mmu04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 13/329 | 0.256490746 |
| mmu04360 | Axon guidance | 12/329 | 0.263608253 |
| PDX #20 downregulated | |||
| Description | GeneRatio | p.adjust | |
| mmu05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 153/4199 | 2.71E-13 |
| mmu04360 | Axon guidance | 134/4199 | 9.86E-12 |
| mmu04510 | Focal adhesion | 144/4199 | 3.75E-11 |
| mmu04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 92/4199 | 3.47E-10 |
| mmu04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 70/4199 | 1.51E-05 |
| mmu04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 123/4199 | 1.38E-04 |
| mmu04350 | TGF-beta signaling pathway | 62/4199 | 1.32E-03 |
| mmu05152 | Tuberculosis | 102/4199 | 1.64E-02 |
| PDX #3 downregulated | |||
| Description | GeneRatio | p.adjust | |
| mmu04360 | Axon guidance | 124/3762 | 2.38E-10 |
| mmu05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 137/3762 | 2.82E-10 |
| mmu04510 | Focal adhesion | 126/3762 | 9.95E-08 |
| mmu04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 81/3762 | 2.38E-07 |
| mmu04350 | TGF-beta signaling pathway | 60/3762 | 2.26E-04 |
| mmu05152 | Tuberculosis | 99/3762 | 1.32E-03 |
| mmu04620 | Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | 57/3762 | 6.09E-03 |
| mmu04062 | Chemokine signaling pathway | 105/3762 | 6.69E-03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yegodayev, K.M.; Novoplansky, O.; Golden, A.; Prasad, M.; Levin, L.; Jagadeeshan, S.; Zorea, J.; Dimitstein, O.; Joshua, B.-Z.; Cohen, L.; et al. TGF-Beta-Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Limit Cetuximab Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020339
Yegodayev KM, Novoplansky O, Golden A, Prasad M, Levin L, Jagadeeshan S, Zorea J, Dimitstein O, Joshua B-Z, Cohen L, et al. TGF-Beta-Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Limit Cetuximab Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020339
Chicago/Turabian StyleYegodayev, Ksenia M., Ofra Novoplansky, Artemiy Golden, Manu Prasad, Liron Levin, Sankar Jagadeeshan, Jonathan Zorea, Orr Dimitstein, Ben-Zion Joshua, Limor Cohen, and et al. 2020. "TGF-Beta-Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Limit Cetuximab Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Head and Neck Cancer" Cancers 12, no. 2: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020339
APA StyleYegodayev, K. M., Novoplansky, O., Golden, A., Prasad, M., Levin, L., Jagadeeshan, S., Zorea, J., Dimitstein, O., Joshua, B. -Z., Cohen, L., Khrameeva, E., & Elkabets, M. (2020). TGF-Beta-Activated Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Limit Cetuximab Efficacy in Preclinical Models of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers, 12(2), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020339