Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Accelerates Metastatic Spread and Increases Impairment of Blood Flow in Mouse Mammary Gland Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
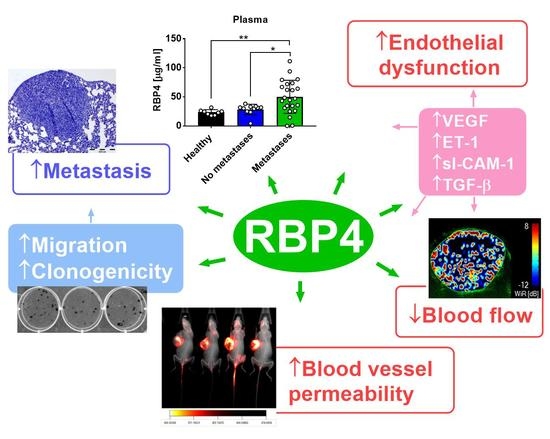
2. Results
2.1. Impaired Angiogenesis in 4T1 Metastatic Tumors Compared to That in Nonmetastatic 67NR Tumors
2.2. Increased RBP4 Protein Level in Young and Aged Mice and in Patients with Breast Cancer with Metastatic and Nonmetastatic Tumors
2.3. Intravenous Injection of RBP4 Increases Settlement of Breast Cancer Cells in the Lungs
2.4. Increase in Metastatic Potential and Tumor Blood Vessel Impairment in Mice Bearing RBP4-transduced Cells
2.5. RBP4 Increases the Invasive Potential of 67NR and 4T1 Mouse Mammary Gland Tumor Cells In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.2. In Vivo Experiments
4.2.1. Cell Transplantation
4.2.2. Tumor Angiogenesis Assessment
4.2.3. Lung Fluorescence Measurement
4.2.4. Blood Morphological Analyses
4.3. Plasma and Tumor Tissue from Patients with Breast Cancer
4.4. In Vitro Experiments
4.4.1. Cell Preparation to Evaluate Proliferation, Migration, Adhesion, and Integrin Expression after Incubation with RBP4
- Proliferation
- Ab—absorbance value measured for cells treated with RBP4
- Ak—absorbance value measured for untreated cells
- Am—absorbance value measured for the culture medium
- Migration
- Adhesion
- Flow cytometry analysis
4.4.2. Proliferation and Migration Evaluation and Clonogenic Assay Using 67NR/RBP4 Cell Line
- Proliferation
- Proliferation of cells treated with anticancer agents
- Migration
- Clonogenic assay
4.5. Tissue and Cell Lysate Preparation for ELISA and Western Blot
4.5.1. ELISA Tests
4.5.2. Western Blot
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DuPré, S.A.; Redelman, D.; Hunter, K.W. The mouse mammary carcinoma 4T1: Characterization of the cellular landscape of primary tumours and metastatic tumour foci. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2007, 88, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslakson, C.J.; Miller, F.R. Selective events in the metastatic process defined by analysis of the sequential dissemination of subpopulations of a mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, G.H.; Miller, F.R.; Shekhar, P.M. Nontransgenic models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2000, 2, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, C.N.; Smith, Y.E.; Cao, Y.; Burrows, A.D.; Cross, R.S.N.; Ling, X.; Redvers, R.P.; Doherty, J.P.; Eckhardt, B.L.; Natoli, A.L.; et al. Functional and molecular characterisation of EO771.LMB tumours, a new C57BL/6-mouse-derived model of spontaneously metastatic mammary cancer. Dis. Model. Mech. 2015, 8, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buczek, E.; Denslow, A.; Mateuszuk, L.; Proniewski, B.; Wojcik, T.; Sitek, B.; Fedorowicz, A.; Jasztal, A.; Kus, E.; Chmura- Skirlinska, A.; et al. Alterations in NO- and PGI2- dependent function in aorta in the orthotopic murine model of metastatic 4T1 breast cancer: Relationship with pulmonary endothelial dysfunction and systemic inflammation. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacia, M.Z.; Mateuszuk, L.; Buczek, E.; Chlopicki, S.; Blazejczyk, A.; Wietrzyk, J.; Baranska, M.; Kaczor, A. Rapid biochemical profiling of endothelial dysfunction in diabetes, hypertension and cancer metastasis by hierarchical cluster analysis of Raman spectra. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeda, M.; Kieronska, A.; Adamski, M.G.; Proniewski, B.; Sternak, M.; Mohaissen, T.; Przyborowski, K.; Derszniak, K.; Kaczor, D.; Stojak, M.; et al. Nitric oxide deficiency and endothelial–Mesenchymal transition of pulmonary endothelium in the progression of 4T1 metastatic breast cancer in mice. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porshneva, K.; Papiernik, D.; Psurski, M.; Nowak, M.; Matkowski, R.; Ekiert, M.; Milczarek, M.; Banach, J.; Jarosz, J.; Wietrzyk, J. Combination Therapy with DETA/NO and Clopidogrel Inhibits Metastasis in Murine Mammary Gland Cancer Models via Improved Vasoprotection. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 5277–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazejczyk, A.; Switalska, M.; Chlopicki, S.; Marcinek, A.; Gebicki, J.; Nowak, M.; Nasulewicz-Goldeman, A.; Wietrzyk, J. 1-methylnicotinamide and its structural analog 1,4-dimethylpyridine for the prevention of cancer metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porshneva, K.; Papiernik, D.; Psurski, M.; Łupicka-Słowik, A.; Matkowski, R.; Ekiert, M.; Nowak, M.; Jarosz, J.; Banach, J.; Milczarek, M.; et al. Temporal inhibition of mouse mammary gland cancer metastasis by CORM-A1 and DETA/NO combination therapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3919–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Kang, E.S.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, B.S. Retinol-binding protein-4 is associated with endothelial dysfunction in adults with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2009, 204, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farjo, K.M.; Farjo, R.A.; Halsey, S.; Moiseyev, G.; Ma, J.X. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Induces Inflammation in Human Endothelial Cells by an NADPH Oxidase- and Nuclear Factor Kappa B-Dependent and Retinol-Independent Mechanism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 5103–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, M.; Martin, A.; Hays, F.; Johnson, J.; Farjo, R.A.; Farjo, K.M. Serum retinol-binding protein-induced endothelial inflammation is mediated through the activation of toll-like receptor 4. Mol. Vis. 2017, 23, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takebayashi, K.; Sohma, R.; Aso, Y.; Inukai, T. Effects of retinol binding protein-4 on vascular endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.; Choi, M.-S.; Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.-S. Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipokines and the Relationship between Obesity, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noy, N.; Li, L.; Abola, M.V.; Berger, N.A. Is retinol binding protein 4 a link between adiposity and cancer? Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 23, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Zheng, L.; Hu, X. RBP4 and THBS2 are serum biomarkers for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92254–92264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karunanithi, S.; Levi, L.; DeVecchio, J.; Karagkounis, G.; Reizes, O.; Lathia, J.D.; Kalady, M.F.; Noy, N. RBP4-STRA6 Pathway Drives Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance and Mediates High-Fat Diet-Induced Colon Carcinogenesis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abola, M.V.; Thompson, C.L.; Chen, Z.; Chak, A.; Berger, N.A.; Kirwan, J.P.; Li, L. Serum levels of retinol-binding protein 4 and risk of colon adenoma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Proteomics Analysis for Finding Serum Markers of Ovarian Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobotka, R.; Čapoun, O.; Kalousová, M.; Hanuš, T.; Zima, T.; Koštířová, M.; Soukup, V. Prognostic Importance of Vitamins A, E and Retinol-binding Protein 4 in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 3801–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Zaghloul, A.S.; Sallam, A.M. Serum retinol binding protein-4 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin are interrelated in pancreatic cancer patients. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2012, 72, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-D.D.; Zhao, Y.-M.M.; Wang, L.; Ren, G.; Wang, F.; Xia, Z.-G.G.; Wang, X.-L.L.; Zhang, T.; Pan, Q.; Dai, Z.; et al. Preoperative serum retinol-binding protein 4 is associated with the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Azman, S.N.; Kerishnan, J.P.; Zain, R.B.; Chen, Y.N.; Wong, Y.L.; Gopinath, S.C.B. Identification of host-immune response protein candidates in the sera of human oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Cui, L.; Ma, A.; Li, N.; Si, H. Elevated serum levels of retinol-binding protein 4 are associated with breast cancer risk: A Case-Control study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Adipokine RBP4 drives ovarian cancer cell migration. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, A.; Titorenko, V.I. The Intricate Interplay between Mechanisms Underlying Aging and Cancer. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 56–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meehan, B.; Dombrovsky, A.; Lau, K.; Lai, T.; Magnus, N.; Montermini, L.; Rak, J. Impact of host ageing on the metastatic phenotype. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2013, 134, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meehan, B.; Garnier, D.; Dombrovsky, A.; Lau, K.; D’Asti, E.; Magnus, N.; Rak, J. Ageing-related responses to antiangiogenic effects of sunitinib in atherosclerosis-prone mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 140, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klement, H.; St Croix, B.; Milsom, C.; May, L.; Guo, Q.; Yu, J.L.; Klement, P.; Rak, J. Atherosclerosis and vascular aging as modifiers of tumor progression, angiogenesis, and responsiveness to therapy. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanotti, G.; Berni, R. Plasma Retinol-Binding Protein: Structure and Interactions with Retinol, Retinoids, and Transthyretin. Vitam. Horm. 2004, 69, 271–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, H.M.; Newcomer, M.E. The structure of human retinol-binding protein (RBP) with its carrier protein transthyretin reveals an interaction with the carboxy terminus of RBP. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazejczyk, A.; Papiernik, D.; Porshneva, K.; Sadowska, J.; Wietrzyk, J. Endothelium and cancer metastasis: Perspectives for antimetastatic therapy. Pharmacol. Reports 2015, 67, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endemann, D.H.; Schiffrin, E.L. Endothelial Dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglarz, M.; Clozel, M. Mechanisms of ET-1-induced endothelial dysfunction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 50, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavazzi, R.; Chirivi, R.G.; Garofalo, A.; Rambaldi, A.; Hemingway, I.; Pigott, R.; Gearing, A.J. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 1 is released by human melanoma cells and is associated with tumor growth in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 2628–2630. [Google Scholar]
- Gho, Y.S.; Kleinman, H.K.; Sosne, G. Angiogenic activity of human soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5128–5132. [Google Scholar]
- Morbidelli, L.; Brogelli, L.; Granger, H.J.; Ziche, M. Endothelial cell migration is induced by soluble P-selectin. Life Sci. 1997, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.E.; Halloran, M.M.; Haskell, C.J.; Shah, M.R.; Polverini, P.J. Angiogenesis mediated by soluble forms of E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Nature 1995, 376, 517–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, E.; Papiernik, D.; Wietrzyk, J. Antiangiogenic cancer treatment: The great discovery and greater complexity (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1773–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, G.; Cook, B.D.; Terushkin, V.; Pintucci, G.; Mignatti, P. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) induces angiogenesis through vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 219, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viñals, F.; Pouysségur, J. Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) promotes endothelial cell survival during in vitro angiogenesis via an autocrine mechanism implicating TGF-alpha signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 7218–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pintavorn, P.; Ballermann, B.J. TGF-β and the endothelium during immune injury. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moustakas, A.; Heldin, C.-H. Signaling networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Tao, D.; Fang, Y.; Deng, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, J. TNF-Alpha Promotes Invasion and Metastasis via NF-Kappa B Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2017, 23, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, T.-X.X.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, N.; Gong, W.; Huang, S. Constitutive NF-κB activity regulates the expression of VEGF and IL-8 and tumor angiogenesis of human glioblastoma. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 725–732. [Google Scholar]
- Sell, H.; Eckel, J. Regulation of retinol binding protein 4 production in primary human adipocytes by adiponectin, troglitazone and TNF-α [2]. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2221–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Graham, T.E.; Mody, N.; Preitner, F.; Peroni, O.D.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Kotani, K.; Quadro, L.; Kahn, B.B. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2005, 436, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.J.; Sargsyan, A.; Lee, S.A.; Yuen, J.J.; Cai, J.; Smalling, R.; Ghyselinck, N.; Mark, M.; Blaner, W.S.; Graham, T.E. Hepatocytes are the principal source of circulating RBP4 in mice. Diabetes 2017, 66, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohd, M.A.; Ahmad Norudin, N.A.; Muhammad, T.S.T. Transcriptional regulation of retinol binding protein 4 by Interleukin-6 via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and CCAAT/Enhancer binding proteins. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2020, 505, 110702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Negishi, M.; Shimomura, Y.; Mori, M. Changes in urinary retinol binding protein excretion and other indices of renal tubular damage in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1992, 18, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, B.; Park, S.I.; Felipe, C.R.; Garcia, R.G.; Machado, P.G.P.; Pereira, A.B.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; Medina-Pestana, J.O. Predictive value of urinary retinol binding protein for graft dysfunction after kidney transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2003, 35, 1341–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.C.; Huang, G.S.; Lin, L.W.; Hong, M.Y.; Se, P.S. Thea sinensis melanin prevents cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchal, P.; Jarkovsky, J.; Hrazdilova, K.; Dvorakova, M.; Struharova, I.; Hernychova, L.; Damborsky, J.; Sova, P.; Vojtesek, B. The new platinum-based anticancer agent LA-12 induces retinol binding protein 4 in vivo. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, S.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, K.; Hu, B.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, K. Kill two birds with one stone: Making multi-transgenic pre-diabetes mouse models through insulin resistance and pancreatic apoptosis pathogenesis. PeerJ 2018, 2018, e4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denslow, A.; Świtalska, M.; Jarosz, J.; Papiernik, D.; Porshneva, K.; Nowak, M.; Wietrzyk, J. Clopidogrel in a combined therapy with anticancer drugs—Effect on tumor growth, metastasis, and treatment toxicity: Studies in animal models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietrzyk, J.; Chodyński, M.; Fitak, H.; Wojdat, E.; Kutner, A.; Opolski, A. Antitumor properties of diastereomeric and geometric analogs of vitamin D3. Anticancer. Drugs 2007, 18, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevozhay, D. Cheburator software for automatically calculating drug inhibitory concentrations from in vitroscreening assays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Cell Line | Route of Transplantation | Age of Mice (weeks) | Time Points of Euthanasia—Days after Cell Transplantation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 67NR, 4T1 | ort. | 6 | 12, 24, 33, “26” |
| 67NR, 4T1 | ort. | 52 | 28 (4, 9, 15, 21) * |
| 67NR, 67NR/0, 67NR/RBP4, 4T1, 4T1/0, 4T1/RBP4 | ort. | 16 | 12, 24, 33 **, “26” |
| 67NR/iRFP and 4T1/iRFP | i.v. | 16 | 48 h after cell transplantation |
| Patients | No. | Age: Median (min-max) | Diabetes | Tumor Diameter: Mean ± SD (mm) | Ki67: Median (min-max) [%] | ER+ | PR+ | HER2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No metastases | 10 | 62 (47–85) | 0/10 | 25 ± 23 | 20 (1–50) | 9/10 | 7/10 | 8/10 |
| Metastases | 24 | 57 (31–83) | 5/24 | 32 ± 21 | 15 (3–60) | 14/24 | 13/24 | 13/24 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papiernik, D.; Urbaniak, A.; Kłopotowska, D.; Nasulewicz-Goldeman, A.; Ekiert, M.; Nowak, M.; Jarosz, J.; Cuprych, M.; Strzykalska, A.; Ugorski, M.; et al. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Accelerates Metastatic Spread and Increases Impairment of Blood Flow in Mouse Mammary Gland Tumors. Cancers 2020, 12, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030623
Papiernik D, Urbaniak A, Kłopotowska D, Nasulewicz-Goldeman A, Ekiert M, Nowak M, Jarosz J, Cuprych M, Strzykalska A, Ugorski M, et al. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Accelerates Metastatic Spread and Increases Impairment of Blood Flow in Mouse Mammary Gland Tumors. Cancers. 2020; 12(3):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030623
Chicago/Turabian StylePapiernik, Diana, Anna Urbaniak, Dagmara Kłopotowska, Anna Nasulewicz-Goldeman, Marcin Ekiert, Marcin Nowak, Joanna Jarosz, Monika Cuprych, Aleksandra Strzykalska, Maciej Ugorski, and et al. 2020. "Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Accelerates Metastatic Spread and Increases Impairment of Blood Flow in Mouse Mammary Gland Tumors" Cancers 12, no. 3: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030623
APA StylePapiernik, D., Urbaniak, A., Kłopotowska, D., Nasulewicz-Goldeman, A., Ekiert, M., Nowak, M., Jarosz, J., Cuprych, M., Strzykalska, A., Ugorski, M., Matkowski, R., & Wietrzyk, J. (2020). Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Accelerates Metastatic Spread and Increases Impairment of Blood Flow in Mouse Mammary Gland Tumors. Cancers, 12(3), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12030623