Applying Tissue Slice Culture in Cancer Research—Insights from Preclinical Proton Radiotherapy
Abstract
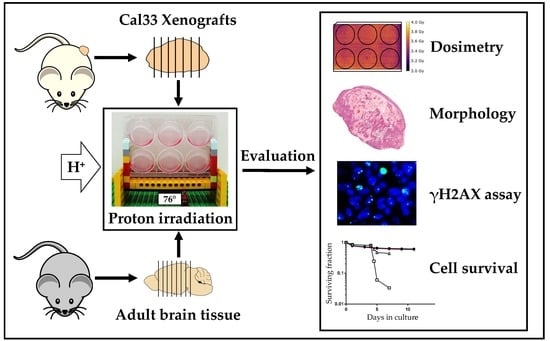
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Optimized Angle for Tissue Slice Irradiation
2.2. Tumor Slice Culture
2.3. Organotypic Brain Slice Culture
3. Discussion
3.1. Tumor Slice Culture
3.2. Organotypic Brain Slice Culture
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Cell Culture Media
4.3. Thin-Cut Tissue Slice Culture
4.4. Irradiation Experiments
4.5. Cytotoxicity, Viability, Inflammation
4.6. Histology
4.7. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, B.; Kraywinkel, K.; Nowossadeck, E.; Schönfeld, I.; Starker, A.; Wienecke, A.; Wolf, U. Bericht zum Krebsgeschehen in Deutschland 2016; Robert Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2016; p. 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Timmermann, B. Paediatric proton therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.C.; Frank, S.J.; Garden, A.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Fuller, C.D.; Gunn, G.B.; Reddy, J.P.; Morrison, W.H.; Williamson, T.D.; Holliday, E.B.; et al. Intensity modulated proton therapy (IMPT)—The future of IMRT for head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2019, 88, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lühr, A.; von Neubeck, C.; Krause, M.; Troost, E.G.C. Relative biological effectiveness in proton beam therapy—Current knowledge and future challenges. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 9, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- PTCOG—Home. Available online: https://www.ptcog.ch/index.php (accessed on 5 March 2020).
- Paganetti, H.; Blakely, E.; Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Carlson, D.J.; Das, I.J.; Dong, L.; Grosshans, D.; Held, K.D.; Mohan, R.; Moiseenko, V.; et al. Report of the AAPM TG-256 on the relative biological effectiveness of proton beams in radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e53–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petr, J.; Platzek, I.; Hofheinz, F.; Mutsaerts, H.J.M.M.; Asllani, I.; van Osch, M.J.P.; Seidlitz, A.; Krukowski, P.; Gommlich, A.; Beuthien-Baumann, B.; et al. Photon vs. proton radiochemotherapy: Effects on brain tissue volume and perfusion. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 128, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubeš, J.; Vondráček, V.; Andrlik, M.; Navrátil, M.; Sláviková, S.; Vítek, P.; Rosina, J.; Abrahámová, J.; Prausová, J.; Grebenyuk, A.; et al. Extreme hypofractionated proton radiotherapy for prostate cancer using pencil beam scanning: Dosimetry, acute toxicity and preliminary results. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 63, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, H.; Allen, A.; Grosshans, D.; McMahon, S.J.; von Neubeck, C.; Wiese, C.; Vikram, B. Toward A variable RBE for proton beam therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 128, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cosper, P.F.; Abel, L.; Lee, Y.-S.; Paz, C.; Kaushik, S.; Nickel, K.P.; Alexandridis, R.; Scott, J.G.; Bruce, J.Y.; Kimple, R.J. Patient Derived Models to Study Head and Neck Cancer Radiation Response. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helbig, L.; Koi, L.; Brüchner, K.; Gurtner, K.; Hess-Stumpp, H.; Unterschemmann, K.; Baumann, M.; Zips, D.; Yaromina, A. BAY 87-2243, a novel inhibitor of hypoxia-induced gene activation, improves local tumor control after fractionated irradiation in a schedule-dependent manner in head and neck human xenografts. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaromina, A.; Krause, M.; Thames, H.; Rosner, A.; Krause, M.; Hessel, F.; Grenman, R.; Zips, D.; Baumann, M. Pre-treatment number of clonogenic cells and their radiosensitivity are major determinants of local tumour control after fractionated irradiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneceur, S.; Löck, S.; Gudziol, V.; Hering, S.; Bütof, R.; Rehm, M.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; von Neubeck, C. Residual gammaH2AX foci in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas as predictors for tumour radiosensitivity: Evaluation in pre-clinical xenograft models and clinical specimens. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Schürer, M.; Neubert, C.; Tillner, F.; Beyreuther, E.; Suckert, T.; Peters, N.; Neubeck, C.; von Lühr, A.; Krause, M.; et al. Multi-modality bedding platform for combined imaging and irradiation of mice. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2020, 6, 037003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpel, C. Neuroscience forefront review organotypic brain slice cultures: A review. Neuroscience 2015, 305, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Humpel, C. Organotypic Brain Slices of ADULT Transgenic Mice: A Tool to Study Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 16, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schommer, J.; Schrag, M.; Nackenoff, A.; Marwarha, G.; Ghribi, O. Method for organotypic tissue culture in the aged animal. MethodsX 2017, 4, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewes, A.; Franke, H.; Singer, D. Organotypic Brain Slice Cultures of Adult Transgenic P301S Mice-A Model for Tauopathy Studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisemann, T.; Costa, B.; Strelau, J.; Mittelbronn, M.; Angel, P.; Peterziel, H. An advanced glioma cell invasion assay based on organotypic brain slice cultures. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadwick, E.J.; Yang, D.P.; Filbin, M.G.; Mazzola, E.; Sun, Y.; Behar, O.; Pazyra-Murphy, M.F.; Goumnerova, L.; Ligon, K.L.; Stiles, C.D.; et al. A brain tumor/organotypic slice co-culture system for studying tumor microenvironment and targeted drug therapies. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 2015, e53304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girdhani, S.; Sachs, R.; Hlatky, L. Biological Effects of Proton Radiation: What We Know and Don’t Know. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaboronok, A.; Isobe, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Sato, E.; Takada, K.; Sakae, T.; Tsurushima, H.; Matsumura, A. Proton beam irradiation stimulates migration and invasion of human U87 malignant glioma cells. J. Radiat. Res. 2013, 55, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konings, K.; Vandevoorde, C.; Belmans, N.; Vermeesen, R.; Baselet, B.; Van Walleghem, M.; Janssen, A.; Isebaert, S.; Baatout, S.; Haustermans, K.; et al. The Combination of Particle Irradiation With the Hedgehog Inhibitor GANT61 Differently Modulates the Radiosensitivity and Migration of Cancer Cells Compared to X-Ray Irradiation. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelants, C.; Pillet, C.; Franquet, Q.; Sarrazin, C.; Peilleron, N.; Giacosa, S.; Guyon, L.; Fontanell, A.; Fiard, G.; Long, J.-A.; et al. Ex-Vivo Treatment of Tumor Tissue Slices as a Predictive Preclinical Method to Evaluate Targeted Therapies for Patients with Renal Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lossi, L.; Merighi, A. The use of ex vivo rodent platforms in neuroscience translational research with attention to the 3RS philosophy. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaira, V.; Fedele, G.; Pyne, S.; Fasoli, E.; Zadra, G.; Bailey, D.; Snyder, E.; Faversani, A.; Coggi, G.; Flavin, R.; et al. Preclinical model of organotypic culture for pharmacodynamic profiling of human tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8352–8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prager, I.; Patties, I.; Himmelbach, K.; Kendzia, E.; Merz, F.; Müller, K.; Kortmann, R.D.; Glasow, A. Dose-dependent short- and long-term effects of ionizing irradiation on neural stem cells in murine hippocampal tissue cultures: Neuroprotective potential of resveratrol. Brain Behav. 2016, 6, e00548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerlach, M.M.; Merz, F.; Wichmann, G.; Kubick, C.; Wittekind, C.; Lordick, F.; Dietz, A.; Bechmann, I. Slice cultures from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A novel test system for drug susceptibility and mechanisms of resistance. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merz, F.; Gaunitz, F.; Dehghani, F.; Renner, C.; Meixensberger, J.; Gutenberg, A.; Giese, A.; Schopow, K.; Hellwig, C.; Schäfer, M.; et al. Organotypic slice cultures of human glioblastoma reveal different susceptibilities to treatments. Neuro. Oncol. 2013, 15, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayin, N.S.; Ma, L.; Thomas, C.; Baitalmal, R.; Sure, A.; Fansiwala, K.; Bustoros, M.; Golfinos, J.G.; Pacione, D.; Snuderl, M.; et al. Patient-Specific Screening Using High-Grade Glioma Explants to Determine Potential Radiosensitization by a TGF-β Small Molecule Inhibitor. Neoplasia (USA) 2016, 18, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Overgaard, J.; Debus, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Daartz, J.; Richter, C.; Zips, D.; Bortfeld, T. Radiation oncology in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, U.; Höhne, K.; Von Neubeck, C.; Thames, H.D.; Yaromina, A.; Dahm-Daphi, J.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M. Residual γh2AX foci predict local tumour control after radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsch, L.; Beyreuther, E.; Eger Passos, D.; Pawelke, J.; Löck, S. Analysing Tumour Growth Delay Data from Animal Irradiation Experiments with Deviations from the Prescribed Dose. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koi, L.; Löck, S.; Linge, A.; Thurow, C.; Hering, S.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Gurtner, K. EGFR-amplification plus gene expression profiling predicts response to combined radiotherapy with EGFR-inhibition: A preclinical trial in 10 HNSCC-tumour-xenograft models. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melissaridou, S.; Wiechec, E.; Magan, M.; Jain, M.V.; Chung, M.K.; Farnebo, L.; Roberg, K. The effect of 2D and 3D cell cultures on treatment response, EMT profile and stem cell features in head and neck cancer 11 Medical and Health Sciences 1112 Oncology and Carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, J.; Seidel, C.; Ebner, R.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Spheroid-based drug screen: Considerations and practical approach. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakis, G.; Timbrell, J.A. In vitro cytotoxicity assays: Comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 160, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassamegevanon, T.; Löck, S.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; von Neubeck, C. Heterogeneity of γH2AX foci increases in ex vivo biopsies relative to in vivo tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rassamegevanon, T.; Löck, S.; Range, U.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M.; von Neubeck, C. Tumor heterogeneity determined with a γH2AX foci assay: A study in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (hHNSCC) models. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willers, H.; Gheorghiu, L.; Liu, Q.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Wirth, L.J.; Krause, M.; von Neubeck, C. DNA Damage Response Assessments in Human Tumor Samples Provide Functional Biomarkers of Radiosensitivity. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 25, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothkamm, K.; Horn, S. γ-H2AX as protein biomarker for radiation exposure. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2009, 45, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Menegakis, A.; De Colle, C.; Yaromina, A.; Hennenlotter, J.; Stenzl, A.; Scharpf, M.; Fend, F.; Noell, S.; Tatagiba, M.; Brucker, S.; et al. Residual γH2AX foci after ex vivo irradiation of patient samples with known tumour-type specific differences in radio-responsiveness. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihatsch, J.; Toulany, M.; Bareiss, P.M.; Grimm, S.; Lengerke, C.; Kehlbach, R.; Rodemann, H.P. Selection of radioresistant tumor cells and presence of ALDH1 activity in vitro. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 99, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkevich, A.; Redon, C.E.; Nakamura, A.J.; Martin, R.F.; Martin, O.A. Use of the γ-H2AX assay to monitor DNA damage and repair in translational cancer research. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moroni, M.; Maeda, D.; Whitnall, H.M.; Bonner, M.W.; Redon, E.C. Evaluation of the Gamma-H2AX Assay for Radiation Biodosimetry in a Swine Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14119–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menegakis, A.; Von Neubeck, C.; Yaromina, A.; Thames, H.; Hering, S.; Hennenlotter, J.; Scharpf, M.; Noell, S.; Krause, M.; Zips, D.; et al. γh2AX assay in ex vivo irradiated tumour specimens: A novel method to determine tumour radiation sensitivity in patient-derived material. In Proceedings of the Radiotherapy and Oncology; Elsevier Ireland Ltd.: Shannon, Ireland, 2015; Volume 116, pp. 473–479. [Google Scholar]
- Rassamegevanon, T.; Löck, S.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; von Neubeck, C. Comparable radiation response of ex vivo and in vivo irradiated tumor samples determined by residual γH2AX. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, W.; Osseiran, A.; Rojec, M.; Liu, Y.; Bombrun, M.; Tang, J.; Costes, S. V Characterizing the DNA Damage Response by Cell Tracking Algorithms and Cell Features Classification Using High-Content Time-Lapse Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidlitz, T.; Merker, S.R.; Rothe, A.; Zakrzewski, F.; von Neubeck, C.; Grützmann, K.; Sommer, U.; Schweitzer, C.; Schölch, S.; Uhlemann, H.; et al. Human gastric cancer modelling using organoids. Gut 2019, 68, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiriac, H.; Belleau, P.; Engle, D.D.; Plenker, D.; Deschênes, A.; Somerville, T.D.D.; Froeling, F.E.M.; Burkhart, R.A.; Denroche, R.E.; Jang, G.-H.; et al. Organoid Profiling Identifies Common Responders to Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1112–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, S.J.; D’Andrea, A.D. Predictive Potential of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Organoids. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béhin, A.; Delattre, J.-Y. Neurologic Sequelae of Radiotherapy on the Nervous System. In Cancer Neurology in Clinical Practice; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake, S.I.; Nonoguchi, N.; Furuse, M.; Yoritsune, E.; Miyata, T.; Kawabata, S.; Kuroiwa, T. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of radiation necrosis in the brain. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2014, 55, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rane, N.; Quaghebeur, G. CNS effects following the treatment of malignancy. Clin. Radiol. 2012, 67, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene-Schloesser, D.; Robbins, M.E.; Peiffer, A.M.; Shaw, E.G.; Wheeler, K.T.; Chan, M.D. Radiation-induced brain injury: A review. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanisch, U.-K.; Kettenmann, H. Microglia: Active sensor and versatile effector cells in the normal and pathologic brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettinger, I.; Thanos, S.; Paulus, W. Microglia promote glioma migration. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 103, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coniglio, S.J.; Segall, J.E. Review: Molecular mechanism of microglia stimulated glioblastoma invasion. Matrix Biol. 2013, 32, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.L.; Mizumatsu, S.; Fike, J.R.; Palmer, T.D. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staal, J.A.; Alexander, S.R.; Liu, Y.; Dickson, T.D.; Vickers, J.C. Characterization of cortical neuronal and glial alterations during culture of organotypic whole brain slices from neonatal and mature mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobner, D. Comparison of the LDH and MTT assays for quantifying cell death: Validity for neuronal apoptosis? J. Neurosci. Methods 2000, 96, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell 2016, 165, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, J.; Pao, G.M.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Verma, I.M. Glioblastoma Model Using Human Cerebral Organoids. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1220–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.I.; Song, H.; Ming, G. li Applications of Human Brain Organoids to Clinical Problems. Dev. Dyn. 2019, 248, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suckert, T.; Müller, J.; Beyreuther, E.; Azadegan, B.; Brüggemann, A.; Bütof, R.; Dietrich, A.; Gotz, M.; Haase, R.; Schürer, M.; et al. High-precision image-guided proton irradiation of mouse brain sub-volumes. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 146, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmbrecht, S.; Baumann, M.; Enghardt, W.; Fiedler, F.; Krause, M.; Lühr, A. Design and implementation of a robust and cost-effective double-scattering system at a horizontal proton beamline. J. Instrum. 2016, 11, T11001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyreuther, E.; Baumann, M.; Enghardt, W.; Helmbrecht, S.; Karsch, L.; Krause, M.; Pawelke, J.; Schreiner, L.; Schürer, M.; Von Neubeck, C.; et al. Research facility for radiobiological studies at the university proton therapy dresden. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2019, 5, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Medium | Reagent | Supplier | Cat.No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSC: DMEM complete | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle Medium | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 61965026 |
| 10% Fetal Bovine Serum | Sigma-Aldrich 2 | F7524 | |
| 2% HEPES Buffer solution | Biochrom 3 | L1613 | |
| 1% non-essential amino acids | Biochrom 3 | K 0293 | |
| 1% sodium pyruvate | VWR 4 | L0473 | |
| 1% Penicillin/Streptomycin | Biochrom 3 | A2213 | |
| OBSC: Dissection buffer | Hibernate A | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | A1247501 |
| 1× Glutamax | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 35050061 | |
| 1× Antibiotic-Antimycotic | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 15240062 | |
| 1× B27 | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 17504044 | |
| OBSC: Cultivation medium | Neurobasal A | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 10888022 |
| 1× Glutamax | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 35050061 | |
| 1× Antibiotic-Antimycotic | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 15240062 | |
| 1× B27 | Thermo Fisher Scientific 1 | 17504044 |
| Endpoint | Dose [Gy] | Time in Culture Before: | Animal Number | Slice Number (Treated/Control) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Harvest | |||||
| TSC | Histology | 0, 4 | 24 h | 48 h | 1 | 8/7 |
| LDH Assay | 0, 10, 20 | 4 d | 13 d | 1 | 3/3 | |
| OBSC | Histology | 0, 10 | 4 d | 5 d | 1 | 3/3 |
| LDH Assay | 0, 10–35 | 4 d | 11 d | 5 | 6/30 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suckert, T.; Rassamegevanon, T.; Müller, J.; Dietrich, A.; Graja, A.; Reiche, M.; Löck, S.; Krause, M.; Beyreuther, E.; von Neubeck, C. Applying Tissue Slice Culture in Cancer Research—Insights from Preclinical Proton Radiotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061589
Suckert T, Rassamegevanon T, Müller J, Dietrich A, Graja A, Reiche M, Löck S, Krause M, Beyreuther E, von Neubeck C. Applying Tissue Slice Culture in Cancer Research—Insights from Preclinical Proton Radiotherapy. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061589
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuckert, Theresa, Treewut Rassamegevanon, Johannes Müller, Antje Dietrich, Antonia Graja, Michael Reiche, Steffen Löck, Mechthild Krause, Elke Beyreuther, and Cläre von Neubeck. 2020. "Applying Tissue Slice Culture in Cancer Research—Insights from Preclinical Proton Radiotherapy" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061589
APA StyleSuckert, T., Rassamegevanon, T., Müller, J., Dietrich, A., Graja, A., Reiche, M., Löck, S., Krause, M., Beyreuther, E., & von Neubeck, C. (2020). Applying Tissue Slice Culture in Cancer Research—Insights from Preclinical Proton Radiotherapy. Cancers, 12(6), 1589. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061589