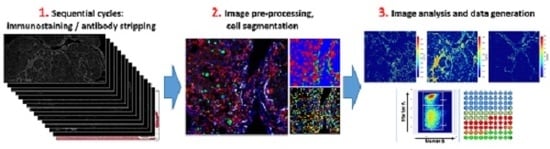
Deciphering the Immune Microenvironment on A Single Archival Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Section by An Immediately Implementable Multiplex Fluorescence Immunostaining Protocol
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In-Depth Tissue and Cell Phenotyping with Multiplex Immunostaining of Archival Mouse and Human Liver
2.2. Generating Detailed Spatial and Phenotypic Information from Large Area Scanning on Different Organs
2.3. Assessing Proliferation of Different Cell Compartments by Unbiased Image Processing and Quantitative Analyses
2.4. Large Scale Tissue Analysis: Characterizing Macrophage Compartment Alterations
2.5. Defining Tissue Regions for Tumoral and Extratumoral Immune Cell Characterization
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tissue Preparation
4.2. Antigen Retrieval
4.3. Blocking
4.4. Primary and Secondary Antibody Incubation
4.5. Nucleus Staining
4.6. Antibody Stripping
4.7. Counterstaining
4.8. Imaging
4.9. Image Preprocessing
4.10. Image Alignment
4.11. Image Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Ben-Moshe, S.; Itzkovitz, S. Spatial heterogeneity in the mammalian liver. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremova, M.; Vento-Tormo, R.; Park, J.E.; Teichmann, S.A.; James, K.R. Immunology in the Era of Single-Cell Technologies. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 727–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yofe, I.; Dahan, R.; Amit, I. Single-cell genomic approaches for developing the next generation of immunotherapies. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hendrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, G.V. History of immunohistochemistry. In Pathobiology of Human Disease; McManus, M.L., Mitchell, N.R., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 3775–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.C.C.; Nerurkar, S.N.; Cai, H.Y.; Ng, H.H.M.; Wu, D.; Wee, Y.T.F.; Lim, J.C.T.; Yeong, J.; Lim, T.K.H. Overview of multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence techniques in the era of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tramu, G.; Pillez, A.; Leonardelli, J. An efficient method of antibody elution for the successive or simultaneous localization of two antigens by immunocytochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1978, 26, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsujikawa, T.; Kumar, S.; Borkar, R.N.; Azimi, V.; Thibault, G.; Chang, Y.H.; Balter, A.; Kawashima, R.; Choe, G.; Sauer, D.; et al. Quantitative Multiplex Immunohistochemistry Reveals Myeloid-Inflamed Tumor-Immune Complexity Associated with Poor Prognosis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefere, S.; Puengel, T.; Hundertmark, J.; Penners, C.; Frank, A.K.; Guillot, A.; de Muynck, K.; Heymann, F.; Adarbes, V.; Defrêne, E.; et al. Differential effects of selective- and pan-PPAR agonists on experimental steatohepatitis and hepatic macrophages. J. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenkel, O.; Tacke, F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A.; Buch, C.; Jourdan, T. Kupffer Cell and Monocyte-Derived Macrophage Identification by Immunofluorescence on Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Mouse Liver Sections. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2164, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, A.; Tacke, F. Liver Macrophages: Old Dogmas and New Insights. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, K.; Marzioni, M.; Meng, F.; Francis, H.; Glaser, S.; Alpini, G. Ductular Reaction in Liver Diseases: Pathological Mechanisms and Translational Significances. Hepatology 2019, 69, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartneck, M.; Schrammen, P.L.; Möckel, D.; Govaere, O.; Liepelt, A.; Krenkel, O.; Ergen, C.; McCain, M.V.; Eulberg, D.; Luedde, T.; et al. The CCR2+ Macrophage Subset Promotes Pathogenic Angiogenesis for Tumor Vascularization in Fibrotic Livers. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rehg, J.E.; Bush, D.; Ward, J.M. The utility of immunohistochemistry for the identification of hematopoietic and lymphoid cells in normal tissues and interpretation of proliferative and inflammatory lesions of mice and rats. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 40, 345–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapiro, D.; Jackson, H.W.; Raghuraman, S.; Fischer, J.R.; Zanotelli, V.R.; Schulz, D.; Giesen, C.; Catena, R.; Varga, Z.; Bodenmiller, B. histoCAT: Analysis of cell phenotypes and interactions in multiplex image cytometry data. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gendusa, R.; Scalia, C.R.; Buscone, S.; Cattoretti, G. Elution of High-affinity (>10−9 KD) Antibodies from Tissue Sections: Clues to the Molecular Mechanism and Use in Sequential Immunostaining. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolognesi, M.M.; Manzoni, M.; Scalia, C.R.; Zannella, S.; Bosisio, F.M.; Faretta, M.; Cattoretti, G. Multiplex Staining by Sequential Immunostaining and Antibody Removal on Routine Tissue Sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2017, 65, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, D.K.; Jelinek, D.F. Multiplex Immunofluorescence of Bone Marrow Core Biopsies: Visualizing the Bone Marrow Immune Contexture. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2020, 68, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdes, M.J.; Sevinsky, C.J.; Sood, A.; Adak, S.; Bello, M.O.; Bordwell, A.; Can, A.; Corwin, A.; Dinn, S.; Filkins, R.J.; et al. Highly multiplexed single-cell analysis of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cancer tissue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11982–11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wizenty, J.; Schumann, T.; Theil, D.; Stockmann, M.; Pratschke, J.; Tacke, F.; Aigner, F.; Wuensch, T. Recent Advances and the Potential for Clinical Use of Autofluorescence Detection of Extra-Ophthalmic Tissues. Molecules 2020, 25, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wizenty, J.; Ashraf, M.I.; Rohwer, N.; Stockmann, M.; Weiss, S.; Biebl, M.; Pratschke, J.; Aigner, F.; Wuensch, T. Autofluorescence: A potential pitfall in immunofluorescence-based inflammation grading. J. Immunol. Methods 2018, 456, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenkel, O.; Hundertmark, J.; Abdallah, A.T.; Kohlhepp, M.; Puengel, T.; Roth, T.; Branco, D.P.P.; Mossanen, J.C.; Luedde, T.; Trautwein, C.; et al. Myeloid cells in liver and bone marrow acquire a functionally distinct inflammatory phenotype during obesity-related steatohepatitis. Gut 2020, 69, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.; Dobie, R.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Dora, E.F.; Henderson, B.E.P.; Luu, N.T.; Portman, J.R.; Matchett, K.P.; Brice, M.; Marwick, J.A.; et al. Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature 2019, 575, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesen, C.; Wang, H.A.; Schapiro, D.; Zivanovic, N.; Jacobs, A.; Hattendorf, B.; Schüffler, P.J.; Grolimund, D.; Buhmann, J.M.; Brandt, S.; et al. Highly multiplexed imaging of tumor tissues with subcellular resolution by mass cytometry. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braubach, P.; Lippmann, T.; Raoult, D.; Lagier, J.C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Zender, S.; Länger, F.P.; Kreipe, H.H.; Kühnel, M.P.; Jonigk, D. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for Diagnosis of Whipple’s Disease in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. Front. Med. 2017, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, R.; Almeida, C.; Azevedo, N.F. Influence of the fixation/permeabilization step on peptide nucleic acid fluorescence in situ hybridization (PNA-FISH) for the detection of bacteria. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Togobo, C.; Pedersen, M.Ø.; Jensen, S.G.; Duduyemi, B.; Gyasi, R.K.; Ofori, M.F.; Paintsil, V.; Renner, L.; Nørgaard, P.; Hviid, L. Reliable cell and tissue morphology-based diagnosis of endemic Burkitt lymphoma in resource-constrained settings in Ghana. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sternberg, S.R. Biomedical Image Processing. Computer 1983, 16, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeffner, F.; Zarella, M.D.; Buchbinder, N.; Bui, M.M.; Goodman, M.R.; Hartman, D.J.; Lujan, G.M.; Molani, M.A.; Parwani, A.V.; Lillard, K.; et al. Introduction to Digital Image Analysis in Whole-slide Imaging: A White Paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. Inform. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.R.; Izar, B.; Wang, S.; Yapp, C.; Mei, S.; Shah, P.M.; Santagata, S.; Sorger, P.K. Highly multiplexed immunofluorescence imaging of human tissues and tumors using t-CyCIF and conventional optical microscopes. Elife 2018, 7, e31657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliceiri, K.W.; Berthold, M.R.; Goldberg, I.G.; Ibáñez, L.; Manjunath, B.S.; Martone, M.E.; Murphy, R.F.; Peng, H.; Plant, A.L.; Roysam, B.; et al. Biological imaging software tools. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berg, S.; Kutra, D.; Kroeger, T.; Straehle, C.N.; Kausler, B.X.; Haubold, C.; Schiegg, M.; Ales, J.; Beier, T.; Rudy, M.; et al. Ilastik: Interactive machine learning for (bio)image analysis. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamprecht, M.R.; Sabatini, D.M.; Carpenter, A.E. CellProfiler: Free, versatile software for automated biological image analysis. Biotechniques 2007, 42, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, T.R.; Kang, I.H.; Wheeler, D.B.; Lindquist, R.A.; Papallo, A.; Sabatini, D.M.; Golland, P.; Carpenter, A.E. CellProfiler Analyst: Data exploration and analysis software for complex image-based screens. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Timeline | Steps Performed |
|---|---|
| Day 1 | Deparaffinization |
| Antigen retrieval | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Nonspecific fluorescence elimination | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Nonspecific binding blocking | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Primary antibody incubation | |
| Days 2 to x | Rinse once in PBS-T 0.1% |
| Rinse 2 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Secondary antibody incubation | |
| Rinse once in PBS-T 0.1% | |
| Rinse 2 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Nucleus staining | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in DI water | |
| Aqueous mounting | |
| Imaging | |
| Slides immerged in DI water and cover glass removal | |
| Antibody stripping | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in DI water | |
| Antigen retrieval | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Primary antibody incubation | |
| Final day | Rinse once in PBS-T 0.1% |
| Rinse 2 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Secondary antibody incubation | |
| Rinse once in PBS-T 0.1% | |
| Rinse 2 × 5 min in PBS | |
| Nucleus staining | |
| Rinse 3 × 5 min in DI water | |
| Aqueous mounting | |
| Imaging | |
| Slides immerged in DI water and cover glass removal | |
| Masson’s trichrome | |
| Permanent mounting | |
| Imaging |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guillot, A.; Kohlhepp, M.S.; Bruneau, A.; Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Deciphering the Immune Microenvironment on A Single Archival Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Section by An Immediately Implementable Multiplex Fluorescence Immunostaining Protocol. Cancers 2020, 12, 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092449
Guillot A, Kohlhepp MS, Bruneau A, Heymann F, Tacke F. Deciphering the Immune Microenvironment on A Single Archival Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Section by An Immediately Implementable Multiplex Fluorescence Immunostaining Protocol. Cancers. 2020; 12(9):2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092449
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuillot, Adrien, Marlene S. Kohlhepp, Alix Bruneau, Felix Heymann, and Frank Tacke. 2020. "Deciphering the Immune Microenvironment on A Single Archival Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Section by An Immediately Implementable Multiplex Fluorescence Immunostaining Protocol" Cancers 12, no. 9: 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092449
APA StyleGuillot, A., Kohlhepp, M. S., Bruneau, A., Heymann, F., & Tacke, F. (2020). Deciphering the Immune Microenvironment on A Single Archival Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Section by An Immediately Implementable Multiplex Fluorescence Immunostaining Protocol. Cancers, 12(9), 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092449