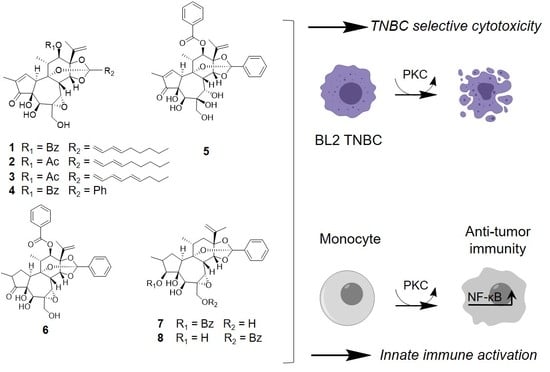
Yuanhuacine Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Basal-Like 2 Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer with Immunogenic Potential
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Reagents
2.3. Isolation of 1 and Other Daphnane Type Diterpenoids
2.4. Sulforhodamine B and Caspase 3/7 Viability Assays
2.5. THP-1 Differentiation Assay
2.6. Quantitative Real Time-PCR
2.7. Athymic Nude Mice Antitumor Xenograft Studies
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Dual Immunogenic and TNBC Subtype Selective Activities of Yuanhuacine
3.2. The Epoxide in Daphnane Type Diterpenoids Is an Important Pharmacophore for Bioactivity
3.3. Protein Kinase C Agonists Can Induce Selective Cytotoxicity against BL2 TNBC Cells and Promote THP-1 Differentiation
3.4. Yuanhuacine Cytotoxicity against BL2 TNBC Is Mediated by Protein Kinase C
3.5. Yuanhuacine Promotes the Expression of Antitumor Cytokines
3.6. Yuanhuacine Exhibits Potent In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy against BL2 Tumors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghasemi, F.; Sarabi, P.; Athari, S.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. Therapeutics strategies against cancer stem cell in breast cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 109, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezi, S.; Botticelli, A.; Pomati, G.; Cerbelli, B.; Scagnoli, S.; Amirhassankhani, S.; d’Amati, G.; Marchetti, P. Standard of Care and Promising New Agents for the Treatment of Mesenchymal Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahba, H.; El-Hadaad, H. Current approaches in treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Lin, N.U.; Polyak, K. Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Minckwitz, G.; Untch, M.; Blohmer, J.-U.; Costa, S.D.; Eidtmann, H.; Fasching, P.A.; Gerber, B.; Eiermann, W.; Hilfrich, J.; Huober, J.; et al. Definition and Impact of Pathologic Complete Response on Prognosis After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Various Intrinsic Breast Cancer Subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masuda, H.; Baggerly, K.A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Valero, V.; Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; et al. Differential Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Among 7 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5533–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, B.A.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification and use of biomarkers in treatment strategies for triple-negative breast cancer subtypes. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Jovanović, B.; Chen, X.; Estrada, M.V.; Johnson, K.N.; Shyr, Y.; Moses, H.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Pietenpol, J.A. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157368. [Google Scholar]
- Robles, A.J.; Du, L.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Mooberry, S.L. Maximiscin Induces DNA Damage, Activates DNA Damage Response Pathways, and Has Selective Cytotoxic Activity against a Subtype of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1822–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robles, A.J.; McCowen, S.; Cai, S.; Glassman, M.; Ruiz, F.; Cichewicz, R.H.; McHardy, S.F.; Mooberry, S.L. Structure–Activity Relationships of New Natural Product-Based Diaryloxazoles with Selective Activity against Androgen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 9275–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, Y.-S.; Risinger, A.L.; Petersen, C.L.; Mooberry, S.L.; Cichewicz, R.H. Leucinostatins from Ophiocordyceps spp. and Purpureocillium spp. Demonstrate Selective Antiproliferative Effects in Cells Representing the Luminal Androgen Receptor Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2010–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pederson, P.J.; Cai, S.; Carver, C.; Powell, D.R.; Risinger, A.L.; Grkovic, T.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mooberry, S.L.; Cichewicz, R.H. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Exhibit Differential Sensitivity to Cardenolides from Calotropis gigantea. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.V.; Cai, S.; Risinger, A.L.; Liang, H.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Doench, J.G.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Mooberry, S.L. CRISPR-Cas9 Genome-Wide Knockout Screen Identifies Mechanism of Selective Activity of Dehydrofalcarinol in Mesenchymal Stem-like Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3080–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X. A Comprehensive Immunologic Portrait of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 11, 311–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Rugo, H.S.; Adams, S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Henschel, V.; Molinero, L.; Chui, S.Y.; et al. Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130): Updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Kalinsky, K.; Kaklamani, V.; D’Adamo, D.R.; Aktan, G.; Tsai, M.L.; O’Regan, R.M.; Kaufman, P.A.; Wilks, S.T.; Andreopoulou, E.; et al. Eribulin Plus Pembrolizumab in Patients With Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (ENHANCE 1): A Phase 1b/2 Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3061–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Gao, P.Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Wu, C.F.; Zhang, Y.; Song, S.J. Daphnane-Type Diterpenoids from the Flower Buds of Daphne genkwa. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.-S.; Minh, N.; Choi, H.-Y.; Byun, J.-S.; Kim, W.-G. Daphnane and Phorbol Diterpenes, Anti-neuroinflammatory Compounds with Nurr1 Activation from the Roots and Stems of Daphne genkwa. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, R.-R.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.-B.; Zhao, L.; Ye, Y.; Song, Y.-N.; Zhang, M.; Tie, H.-Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Daphnane Diterpenoids from Daphne genkwa Inhibit PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling and Induce Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Colon Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuki, K.; Li, W.; Miura, K.; Asada, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Koike, K. Isolation, Structural Elucidation, and Anti-HIV Activity of Daphnane Diterpenoids from Daphne odora. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3270–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.-X.; Shi, L.-L.; Zhang, D.-P.; Wei, H.-Y.; Si, Y.; Ma, G.-X.; Zhang, J. A Review on Daphnane-Type Diterpenoids and Their Bioactive Studies. Molecules 2019, 24, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, P.; Gao, X.; Song, Q. Preparation of yuanhuacine and relative daphne diterpene esters from Daphne genkwa and structure–activity relationship of potent inhibitory activity against DNA topoisomerase I. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.H.; Kasai, R.; Wu, R.Y.; Tagahara, K.; Lee, K.H. Antitumor agents LV: Effects of genkwadaphnin and yuanhuacine on nucleic acid synthesis of P-388 lymphocytic leukemia cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Piao, Y.; Choi, D.-K.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Sohn, K.-C.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.-H. Genkwadaphnin induces reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated apoptosis of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wender, P.A.; Buschmann, N.; Cardin, N.B.; Jones, L.R.; Kan, C.; Kee, J.-M.; Kowalski, J.A.; Longcore, K.E. Gateway synthesis of daphnane congeners and their protein kinase C affinities and cell-growth activities. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, W.-X.; Ni, H.-M.; Li, M.; Liao, Y.; Chen, X.; Stolz, D.B.; Dorn, G.W.; Yin, X.-M. Nix Is Critical to Two Distinct Phases of Mitophagy, Reactive Oxygen Species-mediated Autophagy Induction and Parkin-Ubiquitin-p62-mediated Mitochondrial Priming*. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27879–27890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isakov, N. Protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms in cancer, tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 48, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.E.; Parker, P.J.; Nixon, J.S. Isoenzyme specificity of bisindolylmaleimides, selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. Biochem. J. 1993, 294, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Hyman, T.; Blumberg, P.M. Differential Effect of Bryostatin 1 and Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate on HOP-92 Cell Proliferation Is Mediated by Down-regulation of Protein Kinase Cδ. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7261–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.-B.; Ahn, K.-S.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, J. Genkwadaphnin Induces IFN-γ via PKD1/NF-κB/STAT1 Dependent Pathway in NK-92 Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, J.; Cao, Y.; Gao, X. The signaling pathways and targets of traditional Chinese medicine and natural medicine in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 264, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Sun, Q.; Hong, L.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Xia, M.; Ikejima, T.; Peng, Y.; Song, S. Daphnane-type diterpenes with inhibitory activities against human cancer cell lines from Daphne genkwa. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2500–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Hong, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Bae, S.; Jung, C.; Park, H.; Lee, S. Anti-Tumor Activity of Yuanhuacine by Regulating AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway and Actin Cytoskeleton Organization in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144368. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Shang, X.Y.; Hou, X.W.; Li, L.Z.; Wang, W.; Hayashi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, G.D.; Song, S.J. Yuanhuatine from Daphne genkwa selectively induces mitochondrial apoptosis in estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer cells in vitro. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Z.-J.; Fan, C.-Q.; Ding, J.; Yue, J.-M. Novel diterpenoids with potent inhibitory activity against endothelium cell HMEC and cytotoxic activities from a well-known TCM plant Daphne genkwa. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turban, S.; Hajduch, E. Protein kinase C isoforms: Mediators of reactive lipid metabolites in the development of insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sourbier, C.; Scroggins, B.T.; Ratnayake, R.; Prince, T.L.; Lee, S.; Lee, M.-J.; Nagy, P.; Lee, Y.H.; Trepel, J.B.; Beutler, J.A.; et al. Englerin A Stimulates PKCθ to Inhibit Insulin Signaling and to Simultaneously Activate HSF1: Pharmacologically Induced Synthetic Lethality. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsherniak, A.; Vazquez, F.; Montgomery, P.G.; Weir, B.A.; Kryukov, G.; Cowley, G.S.; Gill, S.; Harrington, W.F.; Pantel, S.; Krill-Burger, J.M.; et al. Defining a Cancer Dependency Map. Cell 2017, 170, 564–1916796928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boudreault, P.-L.; Mattler, J.K.; Wender, P.A. Studies on the regio- and diastereo-selective epoxidation of daphnanes and tiglianes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyle, G.M.; D’Souza, M.M.A.; Pierce, C.J.; Adams, R.A.; Cantor, A.S.; Johns, J.P.; Maslovskaya, L.; Gordon, V.A.; Reddell, P.W.; Parsons, P.G. Intra-Lesional Injection of the Novel PKC Activator EBC-46 Rapidly Ablates Tumors in Mouse Models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, J.K.; Boyle, G.M.; Yap, P.-Y.; Elmlinger, S.; Simmons, J.L.; Broit, N.; Johns, J.; Ferguson, B.; Maslovskaya, L.A.; Savchenko, A.I.; et al. Activation of PKC supports the anticancer activity of tigilanol tiglate and related epoxytiglianes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panizza, B.J.; de Souza, P.; Cooper, A.; Roohullah, A.; Karapetis, C.S.; Lickliter, J.D. Phase I dose-escalation study to determine the safety, tolerability, preliminary efficacy and pharmacokinetics of an intratumoral injection of tigilanol tiglate (EBC-46). EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- A Trial of Tigilanol Tiglate in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Stage IIIB to IV M1c-Melanoma. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04834973 (accessed on 5 March 2021).






| Cells | IC50 ± SEM (nM) | EC50 ± SEM (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| HCC1806 (BL2) | 1.6 ± 0.4 | - |
| HCC70 (BL2) | 9.4 ± 1.6 | - |
| MDA-MB-231 (M) | >3000 | - |
| HCC1937 (BL1) | >3000 | - |
| MDA-MB-453 (LAR) | >3000 | - |
| BT-549 (M) | >3000 | - |
| THP-1 | - | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| Compound | HCC1806 IC50 ± SEM (nM) | HCC70 IC50 ± SEM (nM) | THP-1 EC50 ± SEM (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.6 ± 0.4 | 9 ± 1 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| 2 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.1 |
| 3 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 12 ± 1 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| 4 | 2.7 ± 0.6 | 15 ± 1 | 2.2 ± 0.4 |
| 5 | 149 ± 31 | 1612 ± 472 | 149 ± 1 |
| 6 | 7 ± 1 | 22 ± 2 | 8.6 ± 0.4 |
| 7 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 6 ± 1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| 8 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 10 ± 1 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fermaintt, C.S.; Peramuna, T.; Cai, S.; Takahashi-Ruiz, L.; Essif, J.N.; Grant, C.V.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mooberry, S.L.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Risinger, A.L. Yuanhuacine Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Basal-Like 2 Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer with Immunogenic Potential. Cancers 2021, 13, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112834
Fermaintt CS, Peramuna T, Cai S, Takahashi-Ruiz L, Essif JN, Grant CV, O’Keefe BR, Mooberry SL, Cichewicz RH, Risinger AL. Yuanhuacine Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Basal-Like 2 Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer with Immunogenic Potential. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112834
Chicago/Turabian StyleFermaintt, Charles S., Thilini Peramuna, Shengxin Cai, Leila Takahashi-Ruiz, Jacob Nathaniel Essif, Corena V. Grant, Barry R. O’Keefe, Susan L. Mooberry, Robert H. Cichewicz, and April L. Risinger. 2021. "Yuanhuacine Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Basal-Like 2 Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer with Immunogenic Potential" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112834
APA StyleFermaintt, C. S., Peramuna, T., Cai, S., Takahashi-Ruiz, L., Essif, J. N., Grant, C. V., O’Keefe, B. R., Mooberry, S. L., Cichewicz, R. H., & Risinger, A. L. (2021). Yuanhuacine Is a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Basal-Like 2 Subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer with Immunogenic Potential. Cancers, 13(11), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112834