The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Female Oriented Cancers
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Incidence of Female-Oriented Cancers
2.1. Breast Cancer (BC)
2.2. Gynecological Cancers
2.2.1. Endometrial Cancer (EC)
2.2.2. Cervical Cancer (CC)
2.2.3. Ovarian Cancer (OC)
2.2.4. Primary Fallopian Tube Carcinoma (PFTC)
2.2.5. Vaginal Cancer (VC)
2.2.6. Vulvar Cancer (VC)
2.2.7. Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
3. LncRNAs: Classification and Biogenesis
3.1. Classification
- 1.
- Linear lncRNAsLinear lncRNAs are classified based on their genomic localization and interaction with protein-coding genes, presence of accompanying repeat elements, the likeness with mRNA as well as function. Based on their genomic location and their direction of transcription to complementary protein-coding genes, lncRNAs are classified into the following categories [50]:
- (A)
- Intronic lncRNA
- (i)
- Sense intronic lncRNAs are located inside the intron of the protein-coding gene and transcribed from a coding strand of the respective gene. For example, lncGHRL3:3 is believed to be an intronic and sense overlapping lncRNA. It is located at chromosome 3 within the ghrelin gene, probably involved in the regulation of T2DM, and can be presumed as a potential biomarker of T2DM [14].
- (ii)
- Antisense intronic lncRNAs also exist in the intron region of a protein-coding gene but are transcribed from the opposite direction of the coding strand of that gene. For example, ANRASSF1 is an intronic antisense lncRNA that inhibits the function of the tumor suppressor gene RASSF1A by targeting its promoter region [51].
- (B)
- Intergenic lncRNA
- (i)
- Sense intergenic lncRNAs are sited between two protein-coding genes with overlapping sense strands of the coding gene. LincRNA-p21 is an important example induced during DNA damage by p53 (a tumor suppressor protein) to relay its anti-oncogenic functions [52].
- (ii)
- Antisense intergenic lncRNAs are located between two coding genes while transcribed from the antisense strand of a protein-coding gene, e.g., HOTAIR lncRNA. It belongs to a subclass of lincRNA that can decrease radiosensitivity in laryngeal cancer patients by regulating miR-454-3p [53].
- (C)
- Exonic lncRNA
- (i)
- Sense exonic lncRNAs are synthesized by transcribing lncRNA sequence from the sense strand of protein-coding gene and comprise the exons of that gene. For example, NONHSAG044354 is a sense exonic lncRNA associated with inflammatory bowel diseases gene BACH2 [54].
- (ii)
- Antisense exonic lncRNA is produced if its transcript is derived from the intron of the protein-coding gene on the opposite strand, e.g., Tsix lncRNA. Tsix lncRNA is an anti-sense lncRNA to the Xist gene, known to orchestrate the X-inactivation during dosage compensation by inhibiting the expression of Xist RNA and thus influences the random choice of which X will be inactivated [55].
- (D)
- Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs)
- 2.
- Circular lncRNAs (circRNAs)
3.2. Biogenesis
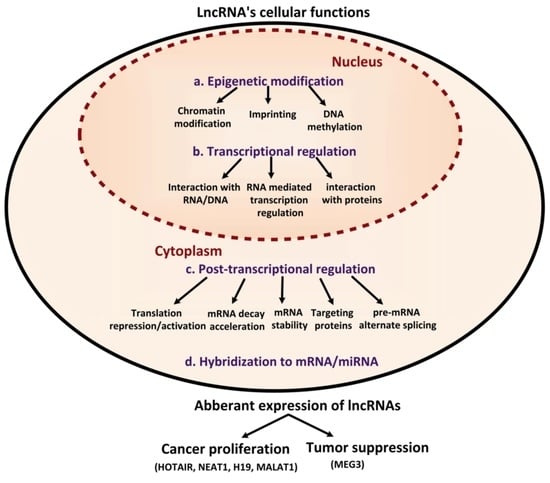
4. LncRNAs and Regulatory Implications
5. LncRNAs and Diagnosis of Cancer
6. LncRNAs and Therapy Resistance in Cancer
7. Current Clinical Applications of lncRNAs
8. LncRNAs in Female-Oriented Cancers
8.1. HOTAIR
8.2. NEAT1
8.3. H19
8.4. MALAT1
8.5. MEG3
9. Closing Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| p54nrb | 54 KDa nuclear RNA and DNA-binding proteins |
| AMP | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ANGPTL1 | Angiopoietin-related protein 1 |
| BTG1 | BTG anti-proliferation factor 1 |
| CDC42 | Cell division cycle 42 |
| DVL2 | Disheveled Segment Polarity Protein 2 |
| DUSP5 | Dual-specific phosphatase 5 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ER+ BC | Estrogen receptor-positive BC |
| Fbxw8 | F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 8 |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| FDA | Food and drug administration |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead Box O1 |
| HES-1 | Hairy and enhancer of split homolog-1 |
| HMGA2 | High-mobility group AT-hook 2 |
| HOXA10 | homeobox gene A10 |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| FIGO | International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics |
| KIF1B | Kinesin Family Member 1B |
| LAMA4 | Laminin Subunit Alpha 4 |
| lincRNA | Long intergenic non-coding RNA |
| KDM5B | Lysine-specific demethylase 5B protein |
| NEAT2 | Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 2 |
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| PSPC1 | Paraspeckle component 1 |
| PBLD | Phenazine biosynthesis like protein domain-containing |
| PDGFRA | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor Alpha |
| PARP1 | Poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase 1 |
| 2PRC2 | Poly comb recessive complex |
| RALGAPA2 | Ral GTPase Activating Protein Catalytic Subunit Alpha 2 |
| RBFOX2 | RNA Binding Fox-1 Homolog 2 |
| RBPs | RNA-binding proteins |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| SNHG3 | Small nucleolar host gene 3 |
| SFPQ | Splicing factor proline/glutamine-rich |
| STC1 | Stanniocalcin-1 |
| TIMD4 | T cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain 4 |
| TJP3 | Tight junction protein 3 expression |
| TGFβ | Transforming growth factor β |
| TAK1 | Transforming growth factor-β activated kinase 1 |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-β |
| TEF1A1 | Translation elongation factor 1-alpha 1 gene |
| TM | Tumor microenvironment |
| TNFAIP8 | Tumor necrosis factorα-induced protein 8 |
| XBP1-HIF-1α | X-box binding protein 1- hypoxia-inducible factor |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
References
- Zampetaki, A.; Albrecht, A.; Steinhofel, K. Long non-coding RNA structure and function: Is there a link? Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczyk, M.; Kasprowicz, M.K.; Kasprzyk, M.E.; Wrzesinski, J. Human long noncoding RNA interactome: Detection, characterization and function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, N.; McGrath, A.; Chen, Y.-P.P. Evaluation of deep learning in non-coding RNA classification. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Ferreira, A.-M.; Johnson, R.; Jungreis, I.; Loveland, J.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.; Armstrong, J. GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D766–D773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, M.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, T. Long noncoding RNA and its role in virus infection and pathogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2019, 24, 777–789. [Google Scholar]
- Uszczynska-Ratajczak, B.; Lagarde, J.; Frankish, A.; Guigó, R.; Johnson, R. Towards a complete map of the human long non-coding RNA transcriptome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahariya, S.; Paddibhatla, I.; Kumar, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Pallepati, A.; Gutti, R.K. Long non-coding RNA: Classification, biogenesis and functions in blood cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, H.; Wang, L.; Zhan, H.; Dai, J.; Chang, Y.; Wu, F.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Gao, C.; Li, L. A long noncoding RNA distributed in both nucleus and cytoplasm operates in the PYCARD-regulated apoptosis by coordinating the epigenetic and translational regulation. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.E.; Trevino, A.E.; Chang, H.Y. Diverse lncRNA mechanisms in brain development and disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2020, 65, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aillaud, M.; Schulte, L.N. Emerging Roles of Long Noncoding RNAs in the Cytoplasmic Milieu. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guh, C.-Y.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Chu, H.-P. Functions and properties of nuclear lncRNAs—From systematically mapping the interactomes of lncRNAs. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, J.; Kretz, M. From structure to function: Route to understanding lncRNA mechanism. BioEssays 2020, 42, 2000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karner, H.; Webb, C.-H.; Carmona, S.; Liu, Y.; Lin, B.; Erhard, M.; Chan, D.; Baldi, P.; Spitale, R.C.; Sun, S. Functional conservation of lncRNA JPX despite sequence and structural divergence. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbari, D.M.; Al-Harithy, R.N. Ghrelin intronic lncRNAs, lnc-GHRL-3: 2 and lnc-GHRL-3: 3, as novel biomarkers in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Tao, M.; Shen, X.; Ju, S. Translatable circRNAs and lncRNAs: Driving mechanisms and functions of their translation products. Cancer Lett. 2020, 483, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzi, L.; Avila Cobos, F.; Decock, A.; Everaert, C.; Helsmoortel, H.; Lefever, S.; Verboom, K.; Volders, P.J.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. Long noncoding RNA expression profiling in cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Islami, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ward, E.M.; Jemal, A. Global cancer in women: Burden and trends. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2017, 26, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, P.; Frenk, J.; Knaul, F.M.; Shulman, L.N.; Alleyne, G.; Armstrong, L.; Atun, R.; Blayney, D.; Chen, L.; Feachem, R. Expansion of cancer care and control in countries of low and middle income: A call to action. Lancet 2010, 376, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, L.; Shi, W.; Zeng, F.; Zhuo, R.; Hao, X.; Fan, P. Trends of female and male breast cancer incidence at the global, regional, and national levels, 1990–2017. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nero, C.; Ciccarone, F.; Pietragalla, A.; Scambia, G. PTEN and gynecological cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bin, X.; Hongjian, Y.; Xiping, Z.; Bo, C.; Shifeng, Y.; Binbin, T. Research progresses in roles of LncRNA and its relationships with breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Zhao, L.; Liang, H.; Zhen, Y.; Han, L. Recent advances in unraveling the molecular mechanisms and functions of HOXA11-AS in human cancers and other diseases. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1737–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costantino, C.; Alba, D.; Cimino, L.; Conforto, A.; Mazzucco, W. The Role of Vaccination and Screening in Limiting the Worldwide Disease Burden of Preventable Female Cancers: A Review. Women 2021, 1, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnenschein, C.; Soto, A.M. Carcinogenesis explained within the context of a theory of organisms. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2016, 122, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dumars, C.; Ngyuen, J.-M.; Gaultier, A.; Lanel, R.; Corradini, N.; Goudin, F.; Heymann, D. Dysregulation of macrophage polarization is associated with the metastatic process in osteosarcoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78343–78354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basse, C.; Arock, M. The increasing roles of epigenetics in breast cancer: Implications for pathogenicity, biomarkers, prevention and treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2785–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, J.S.; Miele, L. Breast cancer stem cells. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, R.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Lastra, R.R.; Lee, N.K.; Moroney, J.W.; Son, C.H.; Tatebe, K.; Veneris, J.L. Current recommendations and recent progress in endometrial cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 258–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A. International patterns and trends in endometrial cancer incidence, 1978–2013. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, P.; Leary, A.; Creutzberg, C.; Abu-Rustum, N.; Darai, E. Endometrial cancer. Lancet 2016, 387, 1094–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörk, T.; Hillemanns, P.; Tempfer, C.; Breu, J.; Fleisch, M.C. Genetic susceptibility to endometrial cancer: Risk factors and clinical management. Cancers 2020, 12, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbyn, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bruni, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Saraiya, M.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet Global Health 2020, 8, e191–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, J.; Ploner, A.; Elfström, K.M.; Wang, J.; Roth, A.; Fang, F.; Sundström, K.; Dillner, J.; Sparén, P. HPV vaccination and the risk of invasive cervical cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small Jr, W.; Bacon, M.A.; Bajaj, A.; Chuang, L.T.; Fisher, B.J.; Harkenrider, M.M.; Jhingran, A.; Kitchener, H.C.; Mileshkin, L.R.; Viswanathan, A.N. Cervical cancer: A global health crisis. Cancer 2017, 123, 2404–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sachan, P.L.; Singh, M.; Patel, M.L.; Sachan, R. A study on cervical cancer screening using pap smear test and clinical correlation. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2018, 5, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessmon, P.; Boulanger, T.; Zhou, W.; Patwardhan, P. Epidemiology and treatment patterns of epithelial ovarian cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Trabert, B.; DeSantis, C.E.; Miller, K.D.; Samimi, G.; Runowicz, C.D.; Gaudet, M.M.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, Z.; Menon, U. Ovarian cancer screening: Current status and future directions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 65, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrar, R.; Muhammad, S. Primary Fallopian Tube Carcinoma: A Case Report. Andalas Obstet. Gynecol. J. 2021, 5, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lv, F. MRI can be used to differentiate between primary fallopian tube carcinoma and epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin. Radiol. 2020, 75, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, T.S.; Cuello, M.A. Cancer of the vagina. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2018, 143, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mantovani, G.; Fragomeni, S.M.; Inzani, F.; Fagotti, A.; Della Corte, L.; Gentileschi, S.; Tagliaferri, L.; Zannoni, G.F.; Scambia, G.; Garganese, G. Molecular pathways in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma: Implications for target therapeutic strategies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1647–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, D.; Gomez-Martinez, R.A. Vulvar cancer. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. 2019, 46, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, S.; Zhao, X.; Ouyang, L. Long non-coding RNA expression profile in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical significance. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2571–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, S.; Sorosky, J. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020.
- Sharami, S.R.Y.; Saffarieh, E. A review on management of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2020, 9, 1287. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.J.; Slater, S.; Seckl, M.J. Treatment of gestational trophoblastic disease in the 2020s. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 33, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, K.-Q. Structure, regulation, and function of linear and circular long Non-Coding RNAs. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pathania, A.S.; Challagundla, K.B. Exosomal long non-coding RNAs: Emerging players in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 8, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckedorff, F.C.; Ayupe, A.C.; Crocci-Souza, R.; Amaral, M.S.; Nakaya, H.I.; Soltys, D.T.; Menck, C.F.; Reis, E.M.; Verjovski-Almeida, S. The intronic long noncoding RNA ANRASSF1 recruits PRC2 to the RASSF1A promoter, reducing the expression of RASSF1A and increasing cell proliferation. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarte, M.; Guttman, M.; Feldser, D.; Garber, M.; Koziol, M.J.; Kenzelmann-Broz, D.; Khalil, A.M.; Zuk, O.; Amit, I.; Rabani, M. A large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene repression in the p53 response. Cell 2010, 142, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mozdarani, H.; Ezzatizadeh, V.; Rahbar Parvaneh, R. The emerging role of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in breast cancer development and treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zacharopoulou, E.; Gazouli, M.; Tzouvala, M.; Vezakis, A.; Karamanolis, G. The contribution of long non-coding RNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayen, S.; Maclary, E.; Buttigieg, E.; Hinten, M.; Kalantry, S. A primary role for the Tsix lncRNA in maintaining random X-chromosome inactivation. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, J.C.; Acuña, S.M.; Aoki, J.I.; Floeter-Winter, L.M.; Muxel, S.M. Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of gene expression: Physiology and disease. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shigeyasu, K.; Toden, S.; Ozawa, T.; Matsuyama, T.; Nagasaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Sahoo, D.; Ghosh, P.; Uetake, H.; Fujiwara, T. The PVT1 lncRNA is a novel epigenetic enhancer of MYC, and a promising risk-stratification biomarker in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-K.; Hemberg, M.; Gray, J.M. Enhancer RNAs: A class of long noncoding RNAs synthesized at enhancers. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sartorelli, V.; Lauberth, S.M. Enhancer RNAs are an important regulatory layer of the epigenome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.M.; Kim, S.O.; Inoue, K.; Smola, M.J.; Lee, D.M.; Schertzer, M.D.; Wooten, J.S.; Baker, A.R.; Sprague, D.; Collins, D.W. Functional classification of long non-coding RNAs by k-mer content. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Ren, J. Long noncoding RNAs in renal diseases. ExRNA 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Wang, P.; Sun, D.; Gan, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. LincSNP 3.0: An updated database for linking functional variants to human long non-coding RNAs, circular RNAs and their regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1244–D1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ren, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q.; Song, H. LncRNA, a novel target biomolecule, is involved in the progression of colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2515. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, I.; Munita, R.; Agirre, E.; Dittmer, T.A.; Gysling, K.; Misteli, T.; Luco, R.F. A lncRNA regulates alternative splicing via establishment of a splicing-specific chromatin signature. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanoa, J.K.; Sethi, R.S.; Verma, R.; Arora, J.S.; Mukhopadhyay, C.S. Long non-coding RNA: Its evolutionary relics and biological implications in mammals: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2018, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Shen, L.; Chen, K.N. Association between H3K4 methylation and cancer prognosis: A meta-analysis. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Zhao, J.; Hu, G. Genome-wide methods for investigating long noncoding RNAs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandwani, A.; Rathore, S.; Datta, M. LncRNAs in cancer: Regulatory and therapeutic implications. Cancer Lett. 2021, 501, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xia, L.Q.; Lu, W.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.S. LncRNAs and cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Begolli, R.; Sideris, N.; Giakountis, A. LncRNAs as chromatin regulators in cancer: From molecular function to clinical potential. Cancers 2019, 11, 1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, H.; Xi, H.; Wu, X.; Cui, J.; Gao, Y.; Liang, W.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Genome-wide lncRNA microarray profiling identifies novel circulating lncRNAs for detection of gastric cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Ai, F.Y.; Zhang, D.C.; Tian, L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, S.J. LncRNA NEAT1 knockdown attenuates autophagy to elevate 5e 5iling identifies novel circulating lncRNAs fong miR-34a. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pisani, G.; Baron, B. NEAT1 and paraspeckles in cancer development and chemoresistance. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xiao, H.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Lou, G. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR knockdown inhibits autophagy and epithelial–mesenchymal transition through the Wnt signaling pathway in radioresistant human cervical cancer HeLa cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 3478–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ai, H.; Fan, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reverses cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells through inhibiting miR-138-5p-regulated EZH2 and SIRT1. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Jiang, J.; Tang, B.; Nice, E.C.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Xie, N. Managing therapeutic resistance in breast cancer: From the lncRNAs perspective. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, D.-H.; Liu, G.-F.; Yu, S.-N.; Li, L.-Y.; Zhao, G.-Q.; Liu, L.; Li, X.-F. Long non-coding RNA LINC00968 attenuates drug resistance of breast cancer cells through inhibiting the Wnt2/β-catenin signaling pathway by regulating WNT2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kladi-Skandali, A.; Michaelidou, K.; Scorilas, A.; Mavridis, K. Long noncoding RNAs in digestive system malignancies: A novel class of cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets? Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 319861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arriaga-Canon, C.; De La Rosa-Velázquez, I.A.; González-Barrios, R.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Oliva-Rico, D.; Jiménez-Trejo, F.; Cortés-González, C.; Herrera, L.A. The use of long non-coding RNAs as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Y. Aberrant LncRNA expression in leukemia. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzel, E.; Okyay, T.M.; Yalcinkaya, B.; Karacaoglu, S.; Gocmen, M.; Akcakuyu, M.H. Tumor suppressor and oncogenic role of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. North. Clin. Istanb. 2020, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Sun, L.; Song, H.; Yin, H.; He, F. lncRNA SNHG3 acts as a novel Tumor Suppressor and regulates Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis via AKT/mTOR/ERK pathway in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, L. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 inhibits metastasis by targeting miR-182/ANGPTL1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, N.; Zhang, W.; Shen, L.; Ding, R.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Du, Y. lncRNA SNHG3 promotes breast cancer progression by acting as a miR-326 sponge. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.W.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, T.; Wen, L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Shen, S.C.; Zhang, J.; Ma, T.; Chen, W.; Ni, L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, F.; Zhan, H.; Chen, L.; Deng, Q.; Xiong, T.; Li, Y.; Ye, J. lncRNA CASC9 sponges miR-758-3p to promote proliferation and EMT in bladder cancer by upregulating TGF-β2. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.D.; Tian, Z.B.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.P.; Liu, F.G.; Sun, X.G.; Han, Y.; Sun, L.J.; Chen, L. Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00908 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by regulating KLF5 expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Yao, X.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L. LncRNA CRNDE attenuates chemoresistance in gastric cancer via SRSF6-regulated alternative splicing of PICALM. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.; Wu, M.; Peng, D.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z.; Ke, H.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, A.P. LncRNA DANCR represses Doxorubicin-induced apoptosis through stabilizing MALAT1 expression in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, Z.; Hu, H.; Luo, M.-L.; Song, E. Non-coding RNAs rewire cancer metabolism networks. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 75, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Liu, C.; Lin, P.; Xie, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, S.; Shi, J.; Yu, X. LncRNA AC245100. 4 binds HSP90 to promote the proliferation of prostate cancer. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, J.; Nie, S.; Tang, Z.; Kang, A.; Fu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liao, Q.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y. Long noncoding RNA EPB41L4A-AS1 functions as an oncogene by regulating the Rho/ROCK pathway in colorectal cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Maheronnaghsh, M.; Molaei, F.; Mashouri, L.; Aref, A.R.; Momeny, M.; Alahari, S.K. Long noncoding RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: Classification, and mechanisms in breast cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Oncogene 2020, 39, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-y.; Lu, A.-q.; Chen, L.-j. LncRNAs in ovarian cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 490, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Hu, X.-X.; Liu, X.-X.; Wang, H.-J.; Lin, K.; Pan, Y.-Q.; Sun, H.-L.; Peng, H.-X.; Chen, X.-X.; Wang, S.-K. Association between SNPs in long non-coding RNAs and the risk of female breast cancer in a Chinese population. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mansoori, Y.; Tabei, M.B.; Askari, A.; Izadi, P.; Daraei, A.; Bastami, M.; Naghizadeh, M.M.; NarimanmanWang, S.-K. Association bn bcRNAs: Classification, and mechanisms in breast cancer metastasis and drug resis5 lnc RNA s in cancer-free breast tissue: Molecular associations with age at menarche and obesity. Breast J. 2018, 24, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerardi, A.N.; Sullivan, I.E. Research on Long-Chain Non-Coding RNA and Breast Cancer: A Review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. Res. 2020, 8, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wen, T.; Li, Z.; Feng, L.; Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, L.; Shi, S.; Hou, K.; Shen, J. Cross-talk between the ER pathway and the lncRNA MAFG-AS1/miR-339-5p/CDK2 axis promotes progression of ER+ breast cancer and confers tamoxifen resistance. Aging 2020, 12, 20658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantile, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Cerrone, M.; Collina, F.; De Laurentiis, M.; Botti, G. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in breast cancer therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Ning, Y.; Pan, Y. Emerging roles of HOTAIR in human cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 3235–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, H.I.; Okmen, D.; Kontou, P.I.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Pavlopoulou, A. HOTAIR as a prognostic predictor for diverse human cancers: A meta-and bioinformatics analysis. Cancers 2019, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obaid, M.; Udden, S.N.; Alluri, P.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates glucose transporter Glut1 expression and glucose uptake in macrophages during inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashoji, A.; Hayashida, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kawai, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Yokoe, T.; Nagayama, A.; Seki, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kitagawa, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the homeobox family genes in breast cancer demonstrates their similar roles in cancer and development. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshi, A.; Raeisi, F.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohajerani, F.; Kabiri, H.; Fazel, R.; Zabihian-Langeroudi, M.; Jusic, A. A Comparative Study of HOTAIR Expression in Breast Cancer Patient Tissues and Cell Lines. Cell J. 2020, 22, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Geng, D.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M. Lnc RNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA 2 axis in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, G.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, S. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes breast cancer development by targeting ZEB1 via sponging miR-601. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Xiao, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, M.; Fan, S. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances breast cancer radioresistance through facilitating HSPA1A expression via sequestering miR-449b-5p. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1801–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-X.; Wang, C.; Mao, L.-W.; Wang, Y.-L.; Xia, L.-Q.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J.; Chen, J. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR mediates the estrogen-induced metastasis of endometrial cancer cells via the miR-646/NPM1 axis. Am. J. Physiol-Cell Physiol. 2018, 314, C690–C701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Hu, P.; Xie, Y.-Q.; Kang, Y.-J.; Li, M. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation by binding to PTEN via the activating phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00251-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Feng, D.; Xiao, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Knockdown of long non-coding HOTAIR enhances the sensitivity to progesterone in endometrial cancer by epigenetic regulation of progesterone receptor isoform B. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 83, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-H.; Cui, Y.-H.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in cervical cancer: Molecular marker, mechanistic insight, and therapeutic target. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 97, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Chao, X.; Shi, S.; Liang, M.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Z. HOTAIR contributes to cell proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer via targetting miR-23b/MAPK1 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fan, R. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating BCL2 via targeting miR-143-3p. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, N.; Ghorbian, S. Analysis of clinical important of LncRNA-HOTAIR gene variations and ovarian cancer susceptibility. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 7421–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, N.; Umer, M.; Kashaninejad, N.; Kasetsirikul, S.; Kline, R.; Salomon, C.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Shiddiky, M.J. PCR-Free Detection of Long Non-Coding HOTAIR RNA in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines and Plasma Samples. Cancers 2020, 12, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Chu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zuo, J. miR-200c overexpression inhibits the invasion and tumorigenicity of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by suppressing lncRNA HOTAIR in mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Cai, E.; Cai, J.; Wen, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, X.; Han, Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, T. HOTAIR maintains the stemness of ovarian cancer stem cells via the miR-206/TBX3 axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 395, 112218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Han, L.; Xie, L.; Han, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, X. HOTAIR promotes paclitaxel resistance by regulating CHEK1 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Cheng, R.; Ouyang, L. Effects of Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR on the Biological Behaviors of Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma A431 Cells. J. China Med. Univ. 2017, 46, 990–994. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, K.; Huang, W. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1-centric gene regulation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3769–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Lei, Y.-Y.; Ding, M.-G.; Luo, L.-H.; Xie, Y.-C.; Liu, X.-L. LncRNA NEAT1 interacted with DNMT1 to regulate malignant phenotype of cancer cell and cytotoxic T cell infiltration via epigenetic inhibition of p53, cGAS, and STING in lung cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, B. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer by regulating ACSL4 via sponging miR-34a-5p and miR-204-5p. Cell. Signal. 2020, 65, 109422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, V.Y.; Chen, J.; Cheuk, I.W.-Y.; Siu, M.-T.; Ho, C.-W.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Kwong, A. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 confers oncogenic role in triple-negative breast cancer through modulating chemoresistance and cancer stemness. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, X.; Li, Y. lncRNA NEAT1 facilitates cell proliferation, invasion and migration by regulating CBX7 and RTCB in breast cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, D.; Chen, K.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.; Lv, L. Identification of lncRNA NEAT1/miR-21/RRM2 axis as a novel biomarker in breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3372–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hao, J.; Hong, Y.; Mai, J.; Huang, W. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes the proliferation, migration, and metastasis of human breast-cancer cells by inhibiting miR-146b-5p expression. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhong, R.; He, X.; Deng, Q.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Luo, X. Investigations on the mechanism of progesterone in inhibiting endometrial cancer cell cycle and viability via regulation of long noncoding RNA NEAT1/microRNA-146b-5p mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Zhai, J.; Fu, Y. Overexpression of Nuclear Enriched Autosomal Transcript 1 Facilitates Cell Proliferation, Migration Invasion, and Suppresses Apoptosis in Endometrial Cancer by Targeting MicroRNA-202-3p/T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain 4 Axis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ge, L.; Xu, X.-J.; Yang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-H. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes endometrial cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by regulating the miR-144-3p/EZH2 axis. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J.; Xu, D.; Ihira, K.; Konno, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Todo, Y.; Watari, H. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 drives aggressive endometrial cancer progression via miR-361-regulated networks involving STAT3 and tumor microenvironment-related genes. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, B. Long non-coding RNA-NEAT1 promotes cell migration and invasion via regulating miR-124/NF-κB pathway in cervical cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Guo, R.; Wang, C. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 accelerates cell progression in cervical cancer by regulating the miR-889-3p/E2F7 axis through the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 34627–34635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, L.Y.; Zhou, M.; Lv, H.; Qin, X.; Zhou, J.; Mao, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, H. Involvement of NEAT1/miR/mi3a axis in promoting cervical cancer progression via targeting SOX4. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18985–18993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Lin, S.; Zheng, M.; Cai, Q.; Tu, Y. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes the growth of cervical cancer cells via sponging miR-9-5p. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Xu, D.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Watari, H. 320 LncRNA NEAT1-mediated miR-361 downregulation contributes to EMT and sphere formation of cervical cancer cells via increasing HSP90 expression. BMJ J. 2020, 30, A128–A129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yi, K.; Yang, L. LncRNA NEAT1 promotes proliferation of ovarian cancer cells and angiogenesis of co-incubated human umbilical vein endothelial cells by regulating FGF9 through sponging miR-365: An experimental study. Medicine 2021, 100, e23423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, H.; Luo, K.; Qing, C. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes ovarian cancer cell invasion and migration by interacting with miR-1321 and regulating tight junction protein 3 expression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3429–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.; Si, Q.; Li, M. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 modifies cell proliferation, colony formation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via the miR-4500/BZW1 axis in ovarian cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 3347–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Yu, D.; Jun, Z.; Yachen, D.; Weiwei, W.; Midie, X.; Xingzhu, J.; Xiaohua, W. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1, regulated by LIN28B, promotes cell proliferation and migration through sponging miR-506 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, X. NEAT1 Knockdown Suppresses the Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian Cancer by Regulating miR-770-5p/PARP1 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Z. 321 Comparison of two types of triple incision technique in the treatment of patients with locally advanced vulvar cancer. IJGC 2020, 30, A129–A130. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi, M.; Moazeni-Roodi, A.; Sarabandi, S.; Karami, S.; Ghavami, S. Association between genetic polymorphisms of long noncoding RNA H19 and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. J. Genet. 2019, 98, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, L.; Kessler, S.M. The Good, the Bad, the Question–H19 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kamiya, S.; Ishiwata, T. Expression and role of long non-coding RNA H19 in carcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 614–625. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, E.-R.; Chou, Y.-E.; Liu, Y.-F.; Hsueh, K.-C.; Lee, H.-L.; Yang, S.-F.; Su, S.-C. Association of lncRNA H19 gene polymorphisms with the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Genes 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.; You, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, B.; Chen, M. Association between lncRNA H19 polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility based on a meta-analysis from 25 studies. Gene 2020, 729, 144317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Xu, P.; Lyu, L. Associations of lncRNA H19 polymorphisms at microrna binding sites with glioma susceptibility and prognosis. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.W.S.; Xiang, X.; Garg, M.; Le, M.T.; Wong, A.L.-A.; Wang, L.; Goh, B.-C. The double-edged sword of H19 lncRNA: Insights into cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2020, 500, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Alipoor, B.; Parvar, S.N.; Sabati, Z.; Ghaedi, H.; Ghasemi, H. An updated review of the H19 lncRNA in human cancer: Molecular mechanism and diagnostic and therapeutic importance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 6357–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peperstraete, E.; Lecerf, C.; Collette, J.; Vennin, C.; Raby, L.; Völkel, P.; Angrand, P.-O.; Winter, M.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P. Enhancement of Breast Cancer Cell Aggressiveness by lncRNA H19 and its Mir-675 Derivative: Insight into Shared and Different Actions. Cancers 2020, 12, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias-Rizk, T.; El Hajj, J.; Segal-Bendirdjian, E.; Hilal, G. The long non coding RNA H19 as a biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis in Lebanese women. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Xie, B.; Jia, Y.; Jayasinghe, U.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Xie, S. H19/let-7/Lin28 ceRNA network mediates autophagy inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ma, H.-Y.; Hu, X.-W.; Qu, Y.-Y.; Wen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.-Y. LncRNA H19 promotes triple-negative breast cancer cells invasion and metastasis through the p53/TNFAIP8 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Yu, P. LncRNA H19 regulates the expression of its target gene HOXA10 in endometrial carcinoma through competing with miR-612. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4820–4827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhai, W.; Pan, J.; Pang, H.; Li, X. H19 promotes endometrial cancer progression by modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J.; JB Hanley, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Todo, Y.; Watari, H. Exploring lncRNA-mediated regulatory networks in endometrial cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment: Advances and challenges. Cancers 2019, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Jin, Y.-M.; Lyu, X.-M.; Fan, L.-M.; Wu, F. Long noncoding RNA H19 regulates HIF-1α/AXL signaling through inhibiting miR-20b-5p in endometrial cancer. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, A.; Samadder, S.; Das, P.; Mazumder, D.I.; Chatterjee, A.; Addya, S.; Mondal, R.; Roy, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Panda, C.K. Deregulation of H19 is associated with cervical carcinoma. Genomics 2020, 112, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, S.J.; Na, J.Y.; Park, C.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, I.H.; Oh, Y.K. Alterations in promoter usage and expression levels of insulin-like growth factor-II and H19 genes in cervical and endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 35, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Q.; Hua, F. Decreased expression of miR-138-5p by lncRNA H19 in cervical cancer promotes tumor proliferation. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-L.; Ip, S.-M.; Cheng, D.; Wong, L.-C.; Ngan, H.Y. Loss of imprinting of the IGF-II and H19 genes in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Deng, X.; Luo, M.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhong, M. Long noncoding RNA H19 promotes transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-370-3p in ovarian cancer cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sajadpoor, Z.; Amini-Farsani, Z.; Teimori, H.; Shamsara, M.; Sangtarash, M.H.; Ghasemi-Dehkordi, P.; Yadollahi, F. Valproic acid promotes apoptosis and cisplatin sensitivity through downregulation of H19 noncoding RNA in ovarian A2780 cells. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2018, 185, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Li, T.-L.; Zhang, H.-B.; Deng, J.-L.; Zhang, R.; Sun, H.; Wan, Z.-R.; Liu, Y.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-S.; Wang, G. Polymorphisms in IGF2/H19 gene locus are associated with platinum-based chemotherapeutic response in Chinese patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, T.; Matsuda, T.; Takagi, N.; Wake, N. Association of IGF2 and H19 imprinting with choriocarcinoma development. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1997, 93, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.-L.; Chang, K.; Lu, L.-S.; Zhao, D.; Han, J.; Zheng, Y.-R.; Yan, Y.-H.; Yi, P.; Guo, J.-X.; Zhou, Y.-G. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference targeting the H19 gene inhibits cell proliferation and apoptosis in human choriocarcinoma cell line JAR. BMC Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Wu, C.; Tan, Q.; Liu, H. Long noncoding RNA H19 promotes chemotherapy resistance in choriocarcinoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 15131–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, L. New insights into long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer and metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arun, G.; Aggarwal, D.; Spector, D.L. MALAT1 long non-coding RNA: Functional implications. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, J.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Vukadin, L.; Richard, A.; Giannini, H.K.; Lim, S.-T.S.; Tan, M.; Ahn, E.-Y.E. Hypoxia induces cancer cell-specific chromatin interactions and increases MALAT1 expression in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11213–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Kong, L.; Hou, M.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC2: A fast and accurate coding potential calculator based on sequence intrinsic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W12–W16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fei, J.; Jadaliha, M.; Harmon, T.S.; Li, I.T.; Hua, B.; Hao, Q.; Holehouse, A.S.; Reyer, M.; Sun, Q.; Freier, S.M. Quantitative analysis of multilayer organization of proteins and RNA in nuclear speckles at super resolution. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 4180–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y. The oncogenic and tumor suppressive functions of the long noncoding RNA MALAT1: An emerging controversy. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arun, G.; Diermeier, S.D.; Spector, D.L. Therapeutic targeting of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; He, H.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y. MALAT1 promotes osteosarcoma development by targeting TGFA via MIR376A. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. lncRNA MALAT1 modulates oxaliplatin resistance of gastric cancer via sponging miR-22-3p. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, P.; Diederichs, S.; Wang, W.; Böing, S.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Tidow, N.; Brandt, B.; Buerger, H.; Bulk, E. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin β 4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8031–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Fang, X.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J. MiR-146b-5p Regulates the Expression of Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 and Its Effect on the Invasion and Proliferation of Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 36, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pa, M.; Naizaer, G.; Seyiti, A.; Kuerbang, G. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 functions as a sponge of MiR-200c in ovarian cancer. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, X. Pioglitazone up-regulates MALAT1 and promotes the proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells through increasing c-Myc expression in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aging Pathobiol. Ther. 2020, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, A.; Hu, S.; Wang, N.; Luo, X.-G.; Ma, W.; Zhang, T.-C.; He, H. IL-6/STAT3 mediates the HPV18 E6/E7 stimulated upregulation of MALAT1 gene in cervical cancer HeLa cells. Virus Res. 2020, 281, 197907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Gao, X. Meta-analysis of the association between MALAT1 rs619586 A > G polymorphism and cancer risk. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060520941969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Piao, H.-L.; Kim, B.-J.; Yao, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Siverly, A.N.; Lawhon, S.E.; Ton, B.N. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. The expression of lncRNA-MALAT1 in breast cancer patients and its influences on prognosis. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2020, 66, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, B.; Yadav, S.R.M.; Awasthee, N.; Gupta, S.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Gupta, S.C. Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic significance of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2021, 1875, 188502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Wang, B.; Zheng, T.; Li, X.; Zheng, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, Y.; Xi, T. MALAT1 induced migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by competitively binding miR-1 with cdc42. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 472, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamodu, O.A.; Huang, W.-C.; Lee, W.-H.; Wu, A.; Wang, L.S.; Hsiao, M.; Yeh, C.-T.; Chao, T.-Y. Aberrant KDM5B expression promotes aggressive breast cancer through MALAT1 overexpression and downregulation of hsa-miR-448. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dolatabadi, N.F.; Dehghani, A.; Shahand, E.; Yazdanshenas, M.; Tabatabaeian, H.; Zamani, A.; Azadeh, M.; Ghaedi, K. The interaction between MALAT1 target, miR-143-3p, and RALGAPA2 is affected by functional SNP rs3827693 in breast cancer. Human Cell 2020, 33, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.J.; Xia, Y.; He, G.F.; Zheng, L.L.; Cai, Y.P.; Yin, Y.; Wu, Q. MALAT1 promotes angiogenesis of breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, N.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Wen, X.; Jia, L.; Cui, J.; Hoffman, A.R.; Hu, J.-F.; Li, W. Genome-wide target interactome profiling reveals a novel EEF1A1 epigenetic pathway for oncogenic lncRNA MALAT1 in breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiping, Z.; Bo, C.; Shifeng, Y.; Feijiang, Y.; Hongjian, Y.; Qihui, C.; Binbin, T. Roles of MALAT1 in development and migration of triple negative and Her-2 positive breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Sarkissyan, M.; Ogah, O.; Kim, J.; Vadgama, J.V. Expression of MALAT1 Promotes Trastuzumab Resistance in HER2 Overexpressing Breast Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.-q.; You, S.; Zhang, C.-m.; Wu, L.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.-m. Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 as a Detection and Diagnostic Molecular Marker in Various Human Cancers: A Pooled Analysis Based on 3255 Subjects. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, M.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.; He, J.; Hua, W.; Duan, P. Association of polymorphisms in MALAT1 with the risk of endometrial cancer in Southern Chinese women. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R.; Xiong, H.; Qiu, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Disrupting MALAT1/miR-200c sponge decreases invasion and migration in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 383, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Trovik, J.; Sun, K.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, P.; Lau, T.-S.; Hoivik, E.A.; Salvesen, H.B.; Sun, H. A novel wnt regulatory axis in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5103–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Mengjun, S.; Lin, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y. MALAT1 plays important role in MEK inhibitor, RG7420, on the proliferation and migration of endometrial cancer cell through sponging miR-129-5p/TAK1. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; McCown, P.J.; Schiefelbein, G.E.; Brown, J.A. Secondary Structural Model of MALAT1 Becomes Unstructured in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Undergoes Structural Rearrangement in Cervical Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; He, Y.; Lin, L.; Qi, Z.; Ma, L.; Li, L.; Su, Y. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 modulates radiosensitivity of HR-HPV+ cervical cancer via sponging miR-145. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W. Long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1/microRNA-202-3p/periostin axis modulates invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human cervical cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14170–14180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Xu, X. Overexpression of MALAT1 contributes to cervical cancer progression by acting as a sponge of miR-429. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 11219–11226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ding, N.; Zhang, H.; Lu, M.; Cui, X.; Yu, X. MicroRNA-625-5p sponges lncRNA MALAT1 to inhibit cervical carcinoma cell growth by suppressing NF-κB signaling. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 78, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Hou, M.; Zhan, Y.; Shen, X.; Xue, H. MALAT1 promotes cisplatin resistance in cervical cancer by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7653–7659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Cheng, H.; Tian, Z. The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 enhances ovarian cancer cell stemness by inhibiting YAP translocation from nucleus to cytoplasm. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e922012-1–e922012-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X. Knockdown of MALAT1 enhances chemosensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through inhibiting the Notch1 signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 366, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Guan, W.; Ren, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, G. MALAT1 affects ovarian cancer cell behavior and patient survival. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 2644–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Q.; Xie, F. LncRNA-MALAT1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells by targeting miR-503-5p. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, M.A.; Babbs, B.; Cochrane, D.R.; Bitler, B.G.; Richer, J.K. The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating RBFOX2-mediated alternative splicing. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, X. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3703–3712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, J. Reflections on the Role of Malat1 in Gynecological Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, J.; Pei, S.; Ding, S.; Kang, L.; Xiao, R.; Zeng, Q. Functions and regulatory mechanisms of metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 134–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, R.; Zhang, Y. The long non-coding RNA MALAT1 interacted with miR-218 modulates choriocarcinoma growth by targeting Fbxw8. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yang, W.; Yang, J.; Ding, J.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, Y.; Teng, L.; Yang, J. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 negatively regulates proliferation and angiogenesis in vascular endothelial cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Peng, G.; Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Mao, G.; Ning, X.; Yang, H.; Deng, J. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 is involved in osteogenic differentiation and bone diseases. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 13, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.C.; Widagdo, J.; Chau, Y.Q.; Zhu, T.; Wong, J.J.-L.; Cheung, A.; Anggono, V. The activity-induced long non-coding RNA Meg3 modulates AMPA receptor surface expression in primary cortical neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benetatos, L.; Vartholomatos, G.; Hatzimichael, E. MEG3 imprinted gene contribution in tumorigenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, C.; Smyth, D.J.; Maisuria-Armer, M.; Walker, N.M.; Todd, J.A.; Clayton, D.G. The imprinted DLK1-MEG3 gene region on chromosome 14q32. 2 alters susceptibility to type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goovaerts, T.; Steyaert, S.; Vandenbussche, C.A.; Galle, J.; Thas, O.; Van Criekinge, W.; De Meyer, T. A comprehensive overview of genomic imprinting in breast and its deregulation in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Zhang, B.; Miao, L.; Ji, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Ma, H.; Yuan, H. Association of long non-coding RNA MEG3 polymorphisms with oral squamous cell carcinoma risk. Oral Dis. 2019, 25, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rugeebah, A.; Alanazi, M.; Parine, N.R. MEG3: An oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2019, 25, 859–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.-l.; Sun, K.-x.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.-g.; Zong, Z.-H. Upregulation of the lncRNA Meg3 induces autophagy to inhibit tumorigenesis and progression of epithelial ovarian carcinoma by regulating activity of ATG3. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Xu, P.; Deng, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, N.; Liu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Z. LncRNA MEG3 rs3087918 was associated with a decreased breast cancer risk in a Chinese population: A case-control study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Jing, H.; Huang, G.; Sun, Z.; Xu, S. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 inhibits breast cancer growth via upregulating endoplasmic reticulum stress and activating NF S. Long no. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6789–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarmaa, B.; Wu, Z.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yan, T.; Yin, W.; Lu, J.; Zhou, L. Association of LncRNA MEG3 polymorphisms with efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, F.; Mi, H.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Han, M.; Gu, Y. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 suppresses cell proliferation, migration and invasion, induces apoptosis and paclitaxel-resistance via miR-4513/PBLD axis in breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 3277–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Shaker, O.G.; Alazrak, M.; AbdelHafez, M.N.; Khalefa, A.A.; Hemeda, N.F.; Abdelmoktader, A.; Ahmed, F.A. Association analyses of a genetic variant in long non-coding RNA MEG3 with breast cancer susceptibility and serum MEG3 expression level in the Egyptian population. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 28, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Ding, J.; Kang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, J.; Pan, G. Hypermethylation of lncRNA MEG3 impairs chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zou, L. Downregulation of LncRNA-MEG3 promotes HTR8/SVneo cells apoptosis and attenuates its migration by repressing Notch1 signal in preeclampsia. Reproduction 2020, 160, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Qian, Z.; Yan, D.; Li, L.; Huang, L. LncRNA-MEG3 inhibits cell proliferation of endometrial carcinoma by repressing Notch signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 82, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.-X.; Wu, D.-D.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zong, Z.-H. LncRNA MEG3 inhibit endometrial carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression through PI3K pathway. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, R.; Konno, Y.; Ihira, K.; Yue, J.; Watari, H. PD-L1 is a tumor suppressor in aggressive endometrial cancer cells and its expression is regulated by miR-216a and lncRNA MEG3. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 598205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Zhao, H. Analysis of diagnostic and prognostic value of lncRNA MEG3 in cervical cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornesello, M.L.; Faraonio, R.; Buonaguro, L.; Annunziata, C.; Starita, N.; Cerasuolo, A.; Pezzuto, F.; Tornesello, A.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. The role of microRNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and circular RNAs in cervical cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, T.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 is downregulated in cervical cancer and affects cell proliferation and apoptosis by regulating miR-21. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.; Cao, Y.-M.; Liu, J.-H.; Ding, J.; Xie, X.-Y.; Cao, P.-G. MEG3 Induces Cervical Carcinoma Cell’s Apoptosis Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by miR-7-5p/STC1 Axis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, Y. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits cervical cancer cell growth by promoting degradation of P-STAT3 protein via ubiquitination. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Han, S. Lidocaine inhibits cervical cancer cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis by modulating the lncRNA-MEG3/miR-421/BTG1 pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 5404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buttarelli, M.; De Donato, M.; Raspaglio, G.; Babini, G.; Ciucci, A.; Martinelli, E.; Baccaro, P.; Pasciuto, T.; Fagotti, A.; Scambia, G. Clinical value of lncRNA MEG3 in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.; He, Y.; Xia, Q.; Liu, S. LncRNA MEG3 impacts proliferation, invasion, and migration of ovarian cancer cells through regulating PTEN. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, M.; Zhao, S. lncRNA MEG3 modified epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ovarian cancer cells by sponging miR-219a-5p and regulating EGFR. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 17709–17722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Yang, B.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W. The overexpression of lncRNA MEG3 inhibits cell viability and invasion and promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer by sponging miR-205-5p. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ding, L.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B.; Wei, D. LncRNA MEG3 suppressed the progression of ovarian cancer via sponging miR-30e-3p and regulating LAMA4 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Ni, Z.; Yicheng, S.; Pan, H.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, T. Anisomycin inhibits angiogenesis in ovarian cancer by attenuating the molecular sponge effect of the lncRNA-Meg3/miR-421/PDGFRA axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 1296–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Li, X. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 is a tumor suppressor in choriocarcinoma by upregulation of microRNA-211. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 22911–22920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Ma, L. MEG3 is restored by schisandrin A and represses tumor growth in choriocarcinoma cells. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, Y.; Meng, Q.; Lyu, Y. The role of EMT-related lncRNA in the process of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20203121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Dashti, S.; Taheri, M. The HOTTIP (HOXA transcript at the distal tip) lncRNA: Review of oncogenic roles in human. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 127, 110158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Sun, S.-g.; Yue, Z.-Q.; Bai, F. Role of lncRNA LUCAT1 in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Bian, E.; Zhao, B. LncRNA-ATB in cancers: What do we know so far? Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4077–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourramezan, Z.; Attar, F.A.; Yusefpour, M.; Azizi, M.; Oloomi, M. Circulating LncRNAs Landscape as Potential Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Duan, S. The role of long non-coding RNA NNT-AS1 in neoplastic disease. Cancers 2020, 12, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, P.; Meeran, S.M. Long non-coding rnas in breast cancer metastasis. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ge, X.; Li, Q.; Miao, L. Long noncoding RNA DANCR regulates proliferation and migration by epigenetically silencing FBP1 in tumorigenesis of cholangiocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Xie, Z.; Lei, X.; Gan, R. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 in human cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shen, N.; Fu, S. Involvement of lncRNA-mediated signaling pathway in the development of cervical cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3672–3687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Wen, F.; Liu, J.; Zou, L.; Zhang, J. Regulatory role of long non-coding RNA UCA1 in signaling pathways and its clinical applications. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Ren, X.; He, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. The value of LncRNA BCAR4 as a prognostic biomarker on clinical outcomes in human cancers. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Fu, Y.; Zeng, N.; Yin, J.; Li, Q. LncRNA FAM83H-AS1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression by regulating the miR-136-5p/metadherin axis. Aging 2020, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hu, H.; Yao, M.; Song, Y.; Yang, A.; Xu, X.; Zhang, N.; Gao, J.; Liu, B. PCAT-1 facilitates breast cancer progression via binding to RACK1 and enhancing oxygen-independent stability of HIF-1α. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Kamali, M.J.; Abak, A.; Shoorei, H.; Taheri, M. LncRNA ZFAS1: Role in tumorigenesis and other diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Tan, Y.Q.; Wu, M.M.; Ma, L.; Zhu, T.; Lobie, P.E.; Pandey, V. Long non-coding RNAs in recurrent ovarian cancer: Theranostic perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2021, 502, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piergentili, R.; Zaami, S.; Cavaliere, A.F.; Signore, F.; Scambia, G.; Mattei, A.; Marinelli, E.; Gulia, C.; Perelli, F. Non-Coding RNAs as Prognostic Markers for Endometrial Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Qiu, M.; Jiang, L.; Liu, K. Long noncoding RNA HOXB-AS1 is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma and sponged miR-149-3p to upregulate Wnt10b. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820967462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Taheri, M. UCA1 long non-coding RNA: An update on its roles in malignant behavior of cancers. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shen, F.; Zhao, L. The relationship between lncRNA PCGEM1 and STAT3 during the occurrence and development of endometrial carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 918–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Kong, M.; Liu, S.; Hu, J. Linc-ROR promotes endometrial cell proliferation by activating the PI3K-Akt pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Dashti, S.; Taheri, M. PCAT1: An oncogenic lncRNA in diverse cancers and a putative therapeutic target. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 114, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, J.; Shen, Z.; Hu, W.; Li, M.; Shi, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, D. LncRNA DCST1-AS1 was upregulated in endometrial carcinoma and may sponge miR-92a-3p to upregulate Notch1. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Meng, X.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, S.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, P. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 impairs the proliferation and invasion of endometrial carcinoma induced by high glucose via targeting miR-222-3p/p27. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 2413. [Google Scholar]
- Aalijahan, H.; Ghorbian, S. Long non-coding RNAs and cervical cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 106, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Yan, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, H. LncRNA SNHG20 promotes cell proliferation and invasion via miR-140-5p-ADAM10 axis in cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, J.; Kang, Y. Long noncoding RNA XIST contributes to cervical cancer development through targeting miR-889-3p/SIX1 axis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, F.C.B.; Mathias, C.; Garcia, L.E.; Gradia, D.F.; de Araújo Souza, P.S.; Cipolla, G.A.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Malheiros, D. Comprehensive Analysis of ceRNA Networks in HPV16-and HPV18-mediated Cervical Cancers Reveals XIST as a Pivotal Competing Endogenous RNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Feng, J.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.; Xi, J.; Yang, J. LncRNA SBF2-AS1 promotes the progression of cervical cancer by regulating miR-361-5p/FOXM1 axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, X.; Mao, C.; Guo, G.; Ye, S.; Xu, J.; Zou, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Duan, P. Upregulation of long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation and migration. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamaraev, A.V.; Volik, P.I.; Sukhikh, G.T.; Kopeina, G.S.; Zhivotovsky, B. Long non-coding RNAs: A view to kill ovarian cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Liu, K. Long non-coding RNA DANCR upregulates IGF2 expression and promotes ovarian cancer progression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López-Camarillo, C.; Ruíz-García, E.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; Hernández-de la Cruz, O.N.; Marchat, L.A.; Gallardo-Rincón, D. Deciphering the Long Non-Coding RNAs and MicroRNAs Coregulation Networks in Ovarian Cancer Development: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamini-Montemurri, M.; Lamas-Maceiras, M.; Barreiro-Alonso, A.; Vizoso-Vázquez, Á.; Rodríguez-Belmonte, E.; Quindós-Varela, M.; Cerdán, M.E. The challenges and opportunities of lncRNAs in ovarian cancer research and clinical use. Cancers 2020, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Leng, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Nie, X.; Yang, L. Sanguinarine inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer development via regulating long non-coding RNA CASC2-EIF4A3 axis and/or inhibiting NF-κB signaling or PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Gao, S.; Xuan, L.; Liu, X. Long non non.; Yang, L. Sanguinarine inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer development via regulating4 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 4275–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Xia, R.; Gong, H.; Yang, P.; Chen, T.; Wu, D.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J. The pseudogene derived from long non-coding RNA DUXAP10 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through epigenetically silencing of p21 and PTEN. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Hu, Y.-B.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, C. Long non-coding RNA ASAP1-IT1 suppresses ovarian cancer progression by regulating Hippo/YAP signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Yang, P.; Gao, Y. Long non-coding RNA EPB41L4A-AS2 suppresses progression of ovarian cancer by sequestering microRNA-103a to upregulate transcription factor RUNX1T1. Exp. Physiol. 2020, 105, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Feng, L.; Tian, C.; Tang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Hu, F. Long noncoding RNA-JPX predicts the poor prognosis of ovarian cancer patients and promotes tumor cell proliferation, invasion and migration by the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8135–8144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Clinical significance and oncogene function of long noncoding RNA HAGLROS overexpression in ovarian cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 300, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, G.; Chen, C.; Bai, L.; Wang, G.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Xiao, Y. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA DLEU1 suppresses the progression of renal cell carcinoma by downregulating the Akt pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4551–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cui, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Tian, T. Linc-ROR induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer by increasing W.nt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, C.; Ren, X.; He, J.; Li, S.; Qi, L.; Duan, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. The predictive value of lncRNA MIR31HG expression on clinical outcomes in patients with solid malignant tumors. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, E.M.; Lavorato-Rocha, A.M.; de Melo Maia, B.; Rodrigues, I.S.; Carvalho, K.C.; Stiepcich, M.M.; Baiocchi, G.; Sato-Kuwabara, Y.; Rogatto, S.R.; Soares, F.A. ROCK1 as a novel prognostic marker in vulvar cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Q.; Fang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. Exosomal lncRNA UCA1 from cancerng, X.; ted fibroblasts enhances chemoresistance in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fiore, R.; Suleiman, S.; Felix, A.; O’Toole, S.A.; O’Leary, J.J.; Ward, M.P.; Beirne, J.; Sabol, M.; Ozretić, P.; Yordanov, A. An Overview of the Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Human Choriocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Jiang, S.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Ao, L.; Zhang, Y. The increased lncRNA MIR503HG in preeclampsia modulated trophoblast cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via regulating matrix metalloproteinases and NF-κB signaling. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, T. Long Non-Coding RNAs: The regulatory mechanisms, research strategies, and future directions in cancers. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| LncRNAs | Locus | Status | Target/Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOXA11-AS | 7p15.2 | Oncogenic | EMT process | [22] |
| CCAT2 | 8q24.21 | Oncogenic | OCT4-PG1, Wnt/B-catenin, Notch signaling pathway | [249] |
| HOTTIP | 7p15.2 | Oncogenic | miR-615−3p/HMGB3, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Snail, twist, PI3K/AKT, Wnt/β-catenin pathway | [250] |
| NEAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | RTCB, CBX7, EMT process, miR-21/RRM2, miR-146b-5p | [128,129] |
| LUCAT1 | 5q14.3 | Oncogenic | miR-5702, miR-7-5p, SOX2 | [251] |
| Linc-ROR | 18q21.31 | Oncogenic | EMT process via miR-205 | [96] |
| lncRNA-ATB | chr 13, | Oncogenic | EMT process via targeting miR-141-3p | [252] |
| LINP1 | 10p14 | Oncogenic | EMT process by anti-metastatic effects of P53 | [96] |
| Z38 | 3q12.1 | Oncogenic | N/A, silencing promotes apoptosis in breast cancer | [253] |
| SKAI1BC | - | Oncogenic | KAI1/CD82 metastasis suppressor gene | [96] |
| NNT-AS1 | 5p12 | Oncogenic | miR-142-3p/ZEB1 axis | [254] |
| AK058003 | 10q22 | Oncogenic | gamma-synuclein gene (SNCG) | [253] |
| LINC00628 | 1q32.1 | Tumor suppressor | BCL-2/BAX/Caspase-3 signaling pathway | [255] |
| ANCR | 4q12 | Tumor suppressor | EMT via E2H2 | [96,256] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | miR-1/CDC42, miR-143-3p/RALGAPA2, EEF1A1, XBP1-HIF-1α, HER-2 pathway | [191,193,194] |
| GAS5 | 1q25.1 | Tumor suppressor | miR-23a, PTEN, miR-21 | [257,258] |
| BANCR | 9q21.11 | Oncogenic | MMPs, EMT, BAX, Caspase 3, PARP | [96] |
| H19 | 11p15.5 | Oncogenic | c-myc, miR-675, Let-7/Lin28, EMT via TNFAIP8/p53 | [155,156] |
| UCA1 | 19p13.12 | Oncogenic | SATB1, ARID1A/CEBPα, EMT by TGF-β, p27 (Kip1), miR-122-5p, Wnt/β-catenin pathway | [259] |
| BCAR4 | 16p13.13 | Oncogenic | Wnt/β-catenin, YAP/Hh signaling pathways, ERBB2, EMT via mTOR signaling | [260] |
| HOTAIR | 12q13.13 | Oncogenic | miR-206/BCL-W, miR-34a/SOX2, c-Myc/BRCA1,many othr miRNA | [53,103,107] |
| FAM83H-AS1 | 8q24.3 | Oncogenic | miR-136-5p/MTDH axis | [261] |
| NBAT1 | 6p22. 3 | Tumor suppressor | DKK1, EZH2, PRC2 | [255] |
| XIST | Xq13 | Tumor suppressor | miR-155/CDX1 axis, c-Met pathway | [255] |
| GHET1 | 7q36.1 | Oncogenic | N-cadherin, Vimentin, E-cadherin | [255] |
| PCAT1 | 8q24 | Oncogenic | HIF-1a/RACK1 pathway | [262] |
| ZFAS1 | 20q13.13 | Oncogenic | miR-589, MMP9, MMP2, BCL-2, Caspase-3, PTEN, BAX, N-cadherin, E-cadherin, Vimentin PI3K/AKT pathway | [263] |
| HOST2 | 10q23.1 | Oncogenic | miR Let-7b pathway | [255,264] |
| CASC2 | 10q26 | Tumor suppressor | miR-96-5p/SYVN1 pathway | [255] |
| MEG3 | 14q32.3 | Tumor suppressor | NF-Κb/p53 pathway, miR-4513/PBLD | [226,228] |
| LncRNAs | Locus | Status | Target/Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTTIP | 7p15.2 | Oncogenic | PI3K/AKT pathway | [250] |
| NEAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | Wnt/β-catenin signaling, miR-202-3p/TIMD4, miR-144-3p/EZH2, miR-361/STAT3 | [130,131,133] |
| ASlnc04080 | - | Oncogenic | Unknown | [265] |
| H19 | 11p15.5 | Oncogenic | EMT via Let-7 targets Imp3, c-myc, HMGA2, miR-20b-5p/AXL/HIF-1α | [159,160] |
| HOXB-AS1 | _ | Oncogenic | miR-149-3p/Wnt10b, c-Myc, β-catenin, cyclinD1 | [266] |
| BANCR | 9q21.11 | Oncogenic | MMP1/2, MAPK, MEK/ERK signaling | [159] |
| UCA1 | 19p13.12 | Oncogenic | AMOTp130, YAP, Hippo-YAP, miR-143, FOSL2 | [267] |
| PCGEM1 | 2q32 | Oncogenic | miR-129/STAT3 | [268] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | miR-200c/TGFβ, PCDH10–Wnt/b-catenin axis, RG7420, miR-129-5p/TAK1 | [198,199,200] |
| MEG3 | 14q32.3 | Tumor suppressor | Notch1, PI3K, BCL-XL, VEGF-A, P70S6K, mTOR | [231,233] |
| HOTAIR | 12q13.13 | Oncogenic | miR-646/NPM1, PTEN, PI3K/Akt signaling | [111,112] |
| CCAT2 | 8q24.21 | Oncogenic | miR-216b/PI3K/AKT pathway, BCL-2 | [265] |
| SRA | 5q31.3 | Oncogenic | Wnt/β-catenin, EIF4E-BP1 | [265] |
| Linc-RoR | 18q21.31 | Oncogenic | miR-145, PI3K-Akt pathway | [269] |
| PCAT1 | 8q24 | Oncogenic | BCL-2, vimentin, N-cadherin, E-cadherin | [270] |
| DLEU1 | 13q14.3 | Oncogenic | miR-490, BAX, N-cadherin, E-cadherin, Snail, CASP-3, vimentin, SP1, PI3K, mTOR, AKT1, p70S6K, GSK3B, STAT3, BCL--2, BCL-xl, | [265] |
| TUG1 | 22q12.2 | Oncogenic | VEGF-A, miR-34a, miR-299 | [159] |
| DCST1-AS1 | _ | Oncogenic | miR-92a-3p/Notch1 | [271] |
| ZFAS1 | 20q13.13 | Oncogenic | CDK4, Cyclin-D1, Ecadherin, Ncadherin, EMT | [263] |
| GAS5 | 1q25.1 | Tumor suppressor | P27/PTEN, miR-103/PTEN, miR-222-3p | [272] |
| FER1L4 | Chr. 20 | Tumor suppressor | PTEN, AKT | [159] |
| SNHG8 | Chr. 4 | Oncogenic | miR-152/c-MET | [265] |
| LncRNAs | Locus | Status | Target/Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTAIR | 12q13.13 | Oncogenic | MMP-9, VEGF, EMT-related genes, miR-23b/MAPK1, miR-143-3p/BCL-2 axis | [77,114,115,116] |
| NNT-AS1 | 5p12 | Oncogenic | Wnt/β–catenin pathway, miR-186/HMGB1 axis | [254] |
| ANRIL | 9p21.3 | Oncogenic | p15, miR-186, PI3K/Akt pathway | [273] |
| BCAR4 | 16p13.13 | Oncogenic | EMT process | [260] |
| H19 | 11p15.5 | Oncogenic | miR-138-5p | [163] |
| GAS5 | 1q25.1 | Tumor suppressor | Akt, miR-106b, IER3 | [257,258] |
| SNHG20 | 17q25.2 | Oncogenic | miR-140-5p/ADAM10 axis | [274] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | IL-6/STAT3, HPV18 E6/E7, PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, miR-145/Cyclin D1, miR-625-5p/NF-κB | [184,202,205,206] |
| XIST | Xq13 | Oncogenic | miR-889-3p/SIX1 axis, miR-23a-3p/LGR4 miR-30b-5p, miR-30c-5p, miR-30e-5p I ADAM9 | [275,276] |
| UCA1 | 19p13.12 | Oncogenic | VEGF, miR-206 | [267] |
| LET | _ | Tumor suppressor | Unknown | [273] |
| MEG3 | 14q32.3 | Tumor suppressor | miR-21-5p, miR-7-5p/SCT1, miR-421/BTG1, P-STAT3 | [237,238,239,240] |
| CCAT2 | 8q24.21 | Oncogenic | TCF7L2, MYC, miR-17-5p, miR20a, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | [258] |
| SBF2-AS1 | 11p15.1 | Oncogenic | miR-361-5p/FOXM1 axis | [277] |
| EBIC | 16q | Oncogenic | E-cadherin/EZH2, | [258,273] |
| LUCAT1 | 5q14.3 | Oncogenic | MTA1, miR-181a, miR-199b-5p | [251] |
| PVT1 | 8q24 | Oncogenic | miR-200b/EZH2, miR-128-3p, miR-424 | [258,277] |
| CCHE1 | 10q21.1 | Oncogenic | PCNA | [273] |
| TUG1 | 22q12.2 | Oncogenic | miR-138-5p/SIRT1, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | [278] |
| NEAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | miR-124/NF-κB, miR-889-3p/E2F7/PI3K/AKT, miR-361/HSP90 | [134,135,138] |
| PCAT1 | 8q24 | Oncogenic | Unknown | [270] |
| LncRNA-ATB | chr 13, 14 and 22 | Oncogenic | miR-144/ITGA6 axis | [252] |
| SPRY4-IT1 | _ | Oncogenic | MiR-101-3p, E-cadherin, vimentin, ZEB1, EMT | [236] |
| ZFAS1 | 20q13.13 | Oncogenic | Unknown | [263] |
| LncRNAs | Locus | Status | Target/Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTTIP | 7p15.2 | Oncogenic | Wnt/β-catenin, STAT3 signaling pathways, IL-6/PD-L1, c-jun | [250] |
| NEAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | EMT via miR-365/FGF9, miR-1321/TJP3, miR-4500/BZW1 axis, miR-770-5p/PARP1 | [139,140,141,143] |
| HOXA11-AS | 7p15.2 | Tumor suppressor | Unknown | [22] |
| PVT1 | 8q24 | Oncogenic | miRNA133a, miR-140, s TGF-β1, p-SMAD4, CASPASE-3 | [264] |
| AB073614 | 3q24 | Oncogenic | p-Akt, PTEN, PI3K/Akt, ERK pathways, BCL-2, BAK, BAX, N-cadherin, vimentin, MMP2, EMT | [279] |
| ABHD11-AS1 | 7 q11. 23. | Oncogenic | RhoC/PI3K/Akt signaling, RhoC/P70s6k, RhoC/BCL-xL | [279] |
| DANCR | 4q12 | Oncogenic | IGF2 | [256,280] |
| FAS-AS1 | 10q23.31 | Oncogenic | Unknown | [281] |
| aHIF | _ | Oncogenic | Unknown | [282] |
| FAM83H-AS1 | 8q24.3 | Oncogenic | HuR protein | [261,282] |
| HOST2 | 10q23.1 | Oncogenic | miRNA let-7 | [264] |
| ADAMTS9-AS2 | 3p14. 1 | Tumor suppressor | miR-182-5p/FOXF2 signaling pathway | [279] |
| CASC2 | 10q26 | Tumor suppressor | EIF4A3, PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, NF-κB signaling | [282,283] |
| ANRIL | 9p21.3 | Oncogenic | let-7a, HMGA2, MMP3, MET, cyclin D1-CDK4/6 | [264] |
| FEZF1-AS1 | 7q31.32 | Oncogenic | miR-130a-5p/SOX4 axis. | [284] |
| DUXAP10 | 14q11.2 | Oncogenic | VEGF, MMP-9, E-cadherin, B-catenin, Snail, vimentin, Twist | [97,285] |
| ASAP1-IT1 | _ | Tumor suppressor | Hippo/YAP signaling | [286] |
| GAS5 | 1q25.1 | Tumor suppressor | miR-196a-5p | [257] |
| EPB41L4A-AS2 | _ | Tumor suppressor | microRNA-103a/RUNX1T1 | [287] |
| GHET1 | 7q36.1 | Oncogenic | HIF1a/VEGF | [282] |
| JPX | _ | Oncogenic | PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | [288] |
| CCAT1 | 8q24.21 | Oncogenic | miR-490-3p, miR-1290, miR-3679, TGFβR1 | [264] |
| CCAT2 | 8q24.21 | Oncogenic | Wnt/beta-catenin pathway miR-424 | [97,264] |
| HAGLROS | 2q31.1 | Oncogenic | miR-100/mTOR, miR-100/ZNRF2 | [289] |
| CPS1-IT1 | _ | Tumor Suppressor | BAX, caspase-9, BCL-2 | [279] |
| LUCAT1 | 5q14.3 | Oncogenic | miR-612/HOXA13 axis, miR-612/HOXA13, miR-199a-5p | [251,281] |
| HOTAIR | 12q13.13 | Oncogenic | EMT-related genes, MMPs, miR-206/TBX3 axis, miR-138-5p/CHEK1 | [117,118,120,121] |
| DLEU1 | 13q14.3 | Oncogenic | miR-490-3p/CDK1 expression | [282,290] |
| EIBC | _ | Oncogenic | Wnt/β-catenin | [97] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | YAP, Notch1 signaling pathway, miR-143-3p/CMPK, miR-503-5p/JAK2-STAT3, miR-200c, EMT via RBFOX2, KIF1B, β-catenin, DVL2, cyclin D1, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | [182,207,208,209,210,211,212] |
| MNX1-AS1 | _ | Oncogenic | CDK4, cyclin D, BCL-2, BAX | [97] |
| MEG3 | 14q32.3 | Tumor suppressor | PTEN, miR-205-5p, miR-219a-5p/EGFR axis, miR-421/PDGFRA axis, Notch1 pathway | [242,243,244,245,246] |
| SNHG15 | 7p13 | Oncogenic | miR-18a, AKT/mTOR signalling pathway | [264] |
| XIST1 | Xq13.2 | Tumor suppressor | miR-150-5p | [264] |
| Linc-ROR | 18q21.31 | Oncogenic | EMT via Wnt/β-catenin signaling | [291] |
| NBAT1 | 6p22. 3 | Tumor suppressor | ERK1/2, Akt pathways | [279] |
| UCA1 | 19p13.12 | Oncogenic | miR-129/ABCB1 axis, SRPK1 | [259] |
| lncBRM | _ | Oncogenic | Sox4, miR-204 | [97] |
| H19 | 11p15.5 | Oncogenic | EMT via miR-370-3p/TGF-β pathway, IGF2 | [165,167] |
| ZFAS1 | 20q13.13 | Oncogenic | miR-548e, let-7a, E-cadherin, N-cadherin CXCR4, Vimentin, MMP-2, BCLXL, miR-150-5p, KLF2, | [263] |
| PCAT1 | 8q24 | Oncogenic | miR-129-5p, cyclin D1/CDK4, NEK2/Wnt pathway, miR-124-3p/cyclin D1, CDK6, p53, BAX, cleaved caspase-3, metallopeptidases, vimentin, Wnt3a, β-catenin | [270] |
| LncRNAs | Locus | Status | Target/Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HOTAIR | 12q13.13 | Oncogenic | Unknown | [122] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | Unknown | [213,214] |
| MIR31HG | 9p21.3 | Oncogenic | p16INK4A | [292] |
| NEAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | Unknown | [144] |
| ROCK1 | _ | Oncogenic | Unknown | [293] |
| UCA1 | 19p13.12 | Oncogenic | miR-103a/WEE1 | [294] |
| LncRNAs | Locus | Status | Target/Function | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OGFRP1 | 22q13.2 | Oncogenic | AKT/mTOR | [295] |
| LINC00261 | 20p11.21 | Tumor suppressor | Unknown | [295] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | Oncogenic | miR-218/Fbxw8 | [215] |
| PCA3 | 9q21-22 | Oncogenic | miR-106b | [295] |
| MEG3 | 14q32.3 | Tumor suppressor | miR-211/PI3K/AKT and AMPK pathways, PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway | [247,248] |
| MIR503HG | Xq26 | Tumor suppressor | Unknown | [295] |
| H19 | 11p15.5 | Oncogenic | PI3K/AKT/mTOR | [170] |
| LOXL1-AS1 | _ | Tumor suppressor | miR-515-5p/NF-κB signaling pathway | |
| SPRY4-IT1 | _ | Oncogenic | EMT process | [296] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naz, F.; Tariq, I.; Ali, S.; Somaida, A.; Preis, E.; Bakowsky, U. The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Female Oriented Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236102
Naz F, Tariq I, Ali S, Somaida A, Preis E, Bakowsky U. The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Female Oriented Cancers. Cancers. 2021; 13(23):6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236102
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaz, Faiza, Imran Tariq, Sajid Ali, Ahmed Somaida, Eduard Preis, and Udo Bakowsky. 2021. "The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Female Oriented Cancers" Cancers 13, no. 23: 6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236102
APA StyleNaz, F., Tariq, I., Ali, S., Somaida, A., Preis, E., & Bakowsky, U. (2021). The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in Female Oriented Cancers. Cancers, 13(23), 6102. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13236102