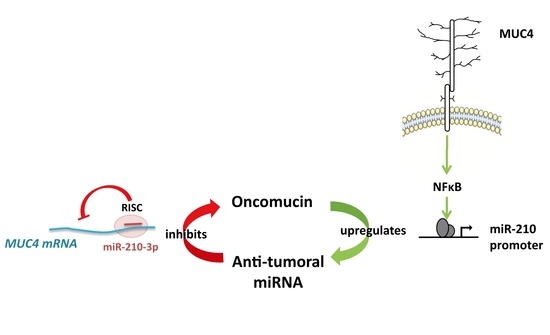
Antagonistic Roles of the Tumor Suppressor miR-210-3p and Oncomucin MUC4 Forming a Negative Feedback Loop in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MiR-210-3p Is Overexpressed in PDAC
2.2. MiR-210-3p Expression Is Positively Correlated with Muc4 Expression during Pancreatic Carcinogenesis
2.3. MUC4 Regulates miR-210 Expression at the Transcriptional Level
2.4. MiR-210-3p Represses MUC4 Expression in PDAC-Derived Cells
2.5. MiR-210-3p Inhibits PDAC-Derived Cell Proliferation and Migration In Vitro
2.6. MiR-210-3p Inhibits Pancreatic Tumor Growth In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Pancreatic Ductal Tumor Sample
4.2. Pdx1-Cre; LSL-KrasG12D Mouse Model
4.3. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.4. Gene Expression Omnibus Microarray
4.5. Cell Transient Transfection
4.6. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.7. Establishment of miR-210 Stable Cell Lines by CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.10. Immunoblotting
4.11. Analysis of Cell Properties
4.12. Subcutaneous Xenografts
4.13. Immunohistochemistry
4.14. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Herman, J.; Schulick, R.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2011, 378, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting Cancer Incidence and Deaths to 2030: The Unexpected Burden of Thyroid, Liver, and Pancreas Cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hruban, R.H.; Maitra, A.; Goggins, M. Update on pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2008, 1, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swartz, M.J.; Batra, S.K.; Varshney, G.C.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Yeo, C.J.; Cameron, J.L.; Wilentz, R.E.; Hruban, R.H.; Argani, P. MUC4 expression increases progressively in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2002, 117, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonckheere, N.; Van Seuningen, I. The membrane-bound mucins: How large O-glycoproteins play key roles in epithelial cancers and hold promise as biological tools for gene-based and immunotherapies. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2008, 14, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberelle, M.; Jonckheere, N.; Melnyk, P.; Van Seuningen, I.; Lebegue, N. EGF-Containing Membrane-Bound Mucins: A Hidden ErbB2 Targeting Pathway? J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5074–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonckheere, N.; Skrypek, N.; Merlin, J.; Dessein, A.F.; Dumont, P.; Leteurtre, E.; Harris, A.; Desseyn, J.L.; Susini, C.; Frenois, F.; et al. The mucin MUC4 and its membrane partner ErbB2 regulate biological properties of human CAPAN-2 pancreatic cancer cells via different signalling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32232. [Google Scholar]
- Skrypek, N.; Duchene, B.; Hebbar, M.; Leteurtre, E.; van Seuningen, I.; Jonckheere, N. The MUC4 mucin mediates gemcitabine resistance of human pancreatic cancer cells via the Concentrative Nucleoside Transporter family. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1714–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Large, T.Y.; Meijer, L.L.; Prado, M.M.; Kazemier, G.; Frampton, A.E.; Giovannetti, E. Circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Link, A.; Becker, V.; Goel, A.; Wex, T.; Malfertheiner, P. Feasibility of fecal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sohrabi, E.; Rezaie, E.; Heiat, M.; Sefidi-Heris, Y. An Integrated Data Analysis of mRNA, miRNA and Signaling Pathways in Pancreatic Cancer. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 1326–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, A.; Gurlich, R.; Liberko, M.; Soumarova, R.; Vernerova, Z.; Mandys, V.; Popov, A. Expression of selected microRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Is there a relation to tumor morphology, progression and patient’s outcome? Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greither, T.; Grochola, L.F.; Udelnow, A.; Lautenschlager, C.; Wurl, P.; Taubert, H. Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Chang, P.; LeBlanc, A.; Li, D.; Abbruzzesse, J.L.; Frazier, M.L.; Killary, A.M.; Sen, S. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, C.; Yuan, W.; Wang, C.; Zhao, P.; Chen, L.; Ma, J. Evaluation of Plasma MicroRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: miR-196a and miR-210 Could Be Negative and Positive Prognostic Markers, Respectively. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6495867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Shao, C.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Li, J. Diagnostic Value of Plasma miR-181b, miR-196a, and miR-210 Combination in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 6073150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhou, W.B.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H.M.; Liu, X.D.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, W.; Ye, L.; Yao, L.C.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as novel potential detection biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahdaoui, F.; Delpu, Y.; Vincent, A.; Renaud, F.; Messager, M.; Duchene, B.; Leteurtre, E.; Mariette, C.; Torrisani, J.; Jonckheere, N.; et al. miR-219-1-3p is a negative regulator of the mucin MUC4 expression and is a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, S.; Arora, S.; Wang, B.; Grizzle, W.E.; Singh, A.P. MicroRNA-150 directly targets MUC4 and suppresses growth and malignant behavior of pancreatic cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, C.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Canamero, M.; Grippo, P.J.; Verdaguer, L.; Perez-Gallego, L.; Dubus, P.; Sandgren, E.P.; Barbacid, M. Chronic pancreatitis is essential for induction of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by K-Ras oncogenes in adult mice. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasseur, R.; Skrypek, N.; Duchene, B.; Renaud, F.; Martinez-Maqueda, D.; Vincent, A.; Porchet, N.; Van Seuningen, I.; Jonckheere, N. The mucin MUC4 is a transcriptional and post-transcriptional target of K-ras oncogene in pancreatic cancer. Implication of MAPK/AP-1, NF-kappaB and RalB signaling pathways. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, M.A.; Swanson, B.J. Mucins in cancer: Protection and control of the cell surface. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonckheere, N.; Skrypek, N.; Van Seuningen, I. Mucins and pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 1794–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Singh, A.P.; Moniaux, N.; Senapati, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Meza, J.L.; Batra, S.K. MUC4 mucin potentiates pancreatic tumor cell proliferation, survival, and invasive properties and interferes with its interaction to extracellular matrix proteins. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workman, H.C.; Sweeney, C.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd. The membrane mucin Muc4 inhibits apoptosis induced by multiple insults via ErbB2-dependent and ErbB2-independent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giannakakis, A.; Sandaltzopoulos, R.; Greshock, J.; Liang, S.; Huang, J.; Hasegawa, K.; Li, C.; O’Brien-Jenkins, A.; Katsaros, D.; Weber, B.L.; et al. miR-210 links hypoxia with cell cycle regulation and is deleted in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Ding, L.; Bennewith, K.L.; Tong, R.T.; Welford, S.M.; Ang, K.K.; Story, M.; Le, Q.T.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia-inducible mir-210 regulates normoxic gene expression involved in tumor initiation. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jonckheere, N.; Vincent, A.; Neve, B.; Van Seuningen, I. Mucin expression, epigenetic regulation and patient survival: A toolkit of prognostic biomarkers in epithelial cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerondakis, S.; Grumont, R.; Gugasyan, R.; Wong, L.; Isomura, I.; Ho, W.; Banerjee, A. Unravelling the complexities of the NF-kappaB signalling pathway using mouse knockout and transgenic models. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6781–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Evans, D.B.; Larry, L.; Cleary, K.R.; Chiao, P.J. The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fei, M.; Xue, G.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, Y.; Li, L.; Xin, H.; Sun, S. Elevated levels of hypoxia-inducible microRNA-210 in pre-eclampsia: New insights into molecular mechanisms for the disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, A.; Ducourouble, M.P.; Van Seuningen, I. Epigenetic regulation of the human mucin gene MUC4 in epithelial cancer cell lines involves both DNA methylation and histone modifications mediated by DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 3035–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrais, M.; Pigny, P.; Ducourouble, M.P.; Petitprez, D.; Porchet, N.; Aubert, J.P.; Van Seuningen, I. Characterization of human mucin gene MUC4 promoter: Importance of growth factors and proinflammatory cytokines for its regulation in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 30923–30933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrianifahanana, M.; Agrawal, A.; Singh, A.P.; Moniaux, N.; van Seuningen, I.; Aubert, J.P.; Meza, J.; Batra, S.K. Synergistic induction of the MUC4 mucin gene by interferon-gamma and retinoic acid in human pancreatic tumour cells involves a reprogramming of signalling pathways. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6143–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonckheere, N.; Perrais, M.; Mariette, C.; Batra, S.K.; Aubert, J.P.; Pigny, P.; Van Seuningen, I. A role for human MUC4 mucin gene, the ErbB2 ligand, as a target of TGF-beta in pancreatic carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 5729–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, W.; Cen, F.; Yan, Q. Mechanism of miR-210 involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells under hypoxia. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2019, 39, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.B.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.J.; Gao, J.; Han, B.; Zhang, C.S. MiR-210 knockdown promotes the development of pancreatic cancer via upregulating E2F3 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8640–8648. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trehoux, S.; Lahdaoui, F.; Delpu, Y.; Renaud, F.; Leteurtre, E.; Torrisani, J.; Jonckheere, N.; Van Seuningen, I. Micro-RNAs miR-29a and miR-330-5p function as tumor suppressors by targeting the MUC1 mucin in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853 Pt A, 2392–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Q.; Regan, S.N.; Xia, Y.; Oostrom, L.A.; Cowan, C.A.; Musunuru, K. Enhanced efficiency of human pluripotent stem cell genome editing through replacing TALENs with CRISPRs. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 393–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daneshvar, K.; Pondick, J.V.; Kim, B.M.; Zhou, C.; York, S.R.; Macklin, J.A.; Abualteen, A.; Tan, B.; Sigova, A.A.; Marcho, C.; et al. DIGIT Is a Conserved Long Noncoding RNA that Regulates GSC Expression to Control Definitive Endoderm Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mali, P.; Yang, L.; Esvelt, K.M.; Aach, J.; Guell, M.; DiCarlo, J.E.; Norville, J.E.; Church, G.M. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 2013, 339, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jonckheere, N.; Fauquette, V.; Stechly, L.; Saint-Laurent, N.; Aubert, S.; Susini, C.; Huet, G.; Porchet, N.; Van Seuningen, I.; Pigny, P. Tumour growth and resistance to gemcitabine of pancreatic cancer cells are decreased by AP-2alpha overexpression. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Seuningen, I.; Ostrowski, J.; Bustelo, X.R.; Sleath, P.R.; Bomsztyk, K. The K protein domain that recruits the interleukin 1-responsive K protein kinase lies adjacent to a cluster of c-Src and Vav SH3-binding sites. Implications that K protein acts as a docking platform. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26976–26985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Block | Sense | Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| miR-scamble | Forward | 5′-CCGGTACACCATGTTGCCAGTCTCTAGGTGGGCGTATAGACGTGTTACACTGTGAAGCCACAGATGTGTAACACGTCTATACGCCCATGGCGTCTGGCCCAACCACACTTTTTG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-AATTCAAAAAGTGTGGTTGGGCCAGACGCCATGGGCGTATAGACGTGTTACACATCTGTGGCTTCACAGTGTAACACGTCTATACGCCCACCTAGAGACTGGCAACATGGTGTA-3′ | |
| miR-210 | Forward | 5′-CCGGTACACCATGTTGCCAGTCTCTAGGAGCCCCTGCCCACCGCACACTGTGTGAAGCCACAGATCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGATGGCGTCTGGCCCAACCACACTTTTTG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-AATTCAAAAAGTGTGGTTGGGCCAGACGCCATCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGATCTGTGGCTTCACACAGTGTGCGGTGGGCAGGGGCTCCTAGAGACTGGCAACATGGTGTA-3′ | |
| Anti-miR-control | Forward | 5′-CCGGTAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAAGTGAAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAACGCGTAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAAATCGAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAACGCGTAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAAGTGAAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAACGCGTAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAAATCGAGAGCTCCCTTCAATCCAATTTTTG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-AATTCAAAAATTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTCGATTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTACGCGTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTTCACTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTACGCGTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTCGATTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTACGCGTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTTCACTTGGATTGAAGGGAGCTCTA-3′ | |
| Anti-miR-210-3p | Forward | 5′-CCGGTTCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGGTGATCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGCGCGTTCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGATCGTCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGCGCGTTCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGGTGATCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGCGCGTTCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGATCGTCAGCCGCTGTCACACGCACAGTTTTTG-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-AATTCAAAAACTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGACGATCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGAACGCGCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGATCACCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGAACGCGCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGACGATCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGAACGCGCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGATCACCTGTGCGTGTGACAGCGGCTGAA-3′ | |
| SgRNA AAVS1 | 5′-GGGGCCACTAGGGACAGGATTGG-3′ |
| Position from TSS | Orientation | Sequences (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| −159/−282 | Forward | 5′-GACCACCTCGGGCCGTACCAT-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CTTTTCTGCACGTCTGCCCG-3 | |
| −262/−419 | Forward | 5′-CGGGAAGAGGGGCAGCTC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-ATGGTACGGCCCGAGGTGGTC-3′ | |
| −1061/−1170 | Forward | 5′-CATGGGCTGGTTCGGAAGCTC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-CATGACCTCCCTGCCTCGG-3′ | |
| −1475/−1596 | Forward | 5′-GGTGCCTGTGAAATTGGCAGGAC-3′ |
| Reverse | 5′-GGGACAAGAAGGGGCAAGAGGAC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boukrout, N.; Souidi, M.; Lahdaoui, F.; Duchêne, B.; Neve, B.; Coppin, L.; Leteurtre, E.; Torrisani, J.; Van Seuningen, I.; Jonckheere, N. Antagonistic Roles of the Tumor Suppressor miR-210-3p and Oncomucin MUC4 Forming a Negative Feedback Loop in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246197
Boukrout N, Souidi M, Lahdaoui F, Duchêne B, Neve B, Coppin L, Leteurtre E, Torrisani J, Van Seuningen I, Jonckheere N. Antagonistic Roles of the Tumor Suppressor miR-210-3p and Oncomucin MUC4 Forming a Negative Feedback Loop in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(24):6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246197
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoukrout, Nihad, Mouloud Souidi, Fatima Lahdaoui, Belinda Duchêne, Bernadette Neve, Lucie Coppin, Emmanuelle Leteurtre, Jérôme Torrisani, Isabelle Van Seuningen, and Nicolas Jonckheere. 2021. "Antagonistic Roles of the Tumor Suppressor miR-210-3p and Oncomucin MUC4 Forming a Negative Feedback Loop in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 24: 6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246197
APA StyleBoukrout, N., Souidi, M., Lahdaoui, F., Duchêne, B., Neve, B., Coppin, L., Leteurtre, E., Torrisani, J., Van Seuningen, I., & Jonckheere, N. (2021). Antagonistic Roles of the Tumor Suppressor miR-210-3p and Oncomucin MUC4 Forming a Negative Feedback Loop in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 13(24), 6197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13246197