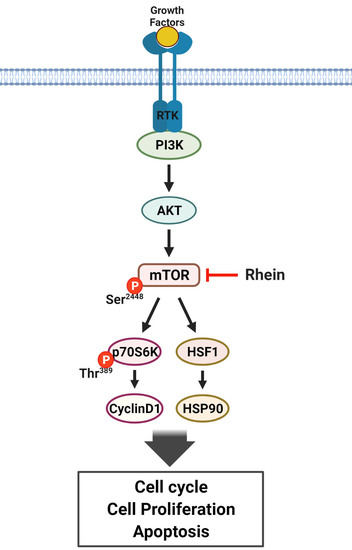
Rhein Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the mTOR Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Anchorage-Independent Cell Growth
2.5. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Analysis
2.6. Wound-Healing Assay
2.7. Migration and Invasion Assays
2.8. In Vitro Pull-Down Assay
2.9. Protein Stability and Ubiquitination
2.10. Establishment of Stable mTOR Overexpressing Cell Lines
2.11. Lentiviral Production and Infection
2.12. Western Blotting Assay
2.13. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.14. In Vivo Xenograft Experiments
2.15. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.16. Tissue Microarray
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rhein Inhibits the Growth of CRC Cells
3.2. Rhein Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of CRC Cells
3.3. Rhein Induces S-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis of CRC Cells
3.4. Rhein Directly Targets mTOR and Suppresses mTOR Signaling in CRC Cells
3.5. Rhein Promotes mTOR Protein Degradation by the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway
3.6. Overexpression of mTOR Promotes the Proliferation, Anchorage-Independent Colony Formation, Migration, and Invasion of CRC Cells
3.7. Knockdown of mTOR Suppresses the Proliferation, Anchorage-Independent Colony Formation, Migration, and Invasion of CRC Cells
3.8. Rhein Suppresses HCT116 CRC Tumor Growth in a Xenograft Mouse Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manfredi, S.; Benhamiche, A.M.; Meny, B.; Cheynel, N.; Rat, P.; Faivre, J. Population-based study of factors influencing occurrence and prognosis of local recurrence after surgery for rectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2001, 88, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.E.; Womeldorph, C.M.; Johnson, E.K.; Maykel, J.A.; Brucher, B.; Stojadinovic, A.; Avital, I.; Nissan, A.; Steele, S.R. Early detection of colorectal cancer recurrence in patients undergoing surgery with curative intent: Current status and challenges. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fearon, E.R. Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conciatori, F.; Bazzichetto, C.; Falcone, I.; Pilotto, S.; Bria, E.; Cognetti, F.; Milella, M.; Ciuffreda, L. Role of mTOR signaling in tumor microenvironment: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, N.; Ao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; et al. Targeting mTOR suppressed colon cancer growth through 4EBP1/eIF4E/PUMA pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2019, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. mTOR signaling in cancer and mTOR inhibitors in solid tumor targeting therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponnurangam, S.; Standing, D.; Rangarajan, P.; Subramaniam, D. Tandutinib inhibits the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to inhibit colon cancer growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, S.; Li, W.; Guan, Y. Tunicamycin inhibits colon carcinoma growth and aggressiveness via modulation of the ERK-JNK-mediated AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4203–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklemichael, A.A.; Mizukami, S.; Toume, K.; Mosaddeque, F.; Kamel, M.G.; Kaneko, O.; Komatsu, K.; Karbwang, J.; Huy, N.T.; Hirayama, K. Anti-malarial activity of traditional Kampo medicine Coptis rhizome extract and its major active compounds. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Shen, M.; Zhao, X.; Xie, J.; He, X.; Li, C. A Review of traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological properties of the genus saururus. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomford, N.E.; Senthebane, D.A.; Rowe, A.; Munro, D.; Seele, P.; Maroyi, A.; Dzobo, K. Natural Products for Drug Discovery in the 21st Century: Innovations for Novel Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Xia, W.; Yue, W.; Peng, C.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, H. Rhein: A review of pharmacological activities. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2015, 2015, 578107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, C. Pharmacokinetic analysis of rhein in Rheum undulatum L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 84, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.J.; Pu, Z.J.; Tang, Y.P.; Shen, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Kang, A.; Zhou, G.S.; Duan, J.A. Advances in bio-active constituents, pharmacology, and clinical applications of rhubarb. Chin. Med. 2017, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Xiang, Y.; Dai, X.; Liang, G.; Huang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, C. Rhein shows potent efficacy against non-small-cell lung cancer through inhibiting the STAT3 pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, L.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Yang, C.; Leng, X.; Wang, W.; Ni, J. Rhein induces cell death in heparg cells through cell cycle arrest and apoptotic pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.J.; Zhen, Y.S. Rhein lysinate suppresses the growth of breast cancer cells and potentiates the inhibitory effect of Taxol in athymic mice. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2009, 20, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Guo, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, W. Rhein inhibits the migration of ovarian cancer cells through downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Tian, W.; Hua, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, F. Rhein enhances the cytotoxicity of effector lymphocytes in colon cancer under hypoxic conditions. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 5350–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, L.; Hu, W.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, H. Rhein sensitizes human colorectal cancer cells to EGFR inhibitors by inhibiting STAT3 pathway. Oncotargets Ther. 2019, 12, 5281–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilella-Bach, M.; Nuzzi, P.; Fang, Y.; Chen, J. The FKBP12-rapamycin-binding domain is required for FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein kinase activity and G1 progression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 4266–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steeg, P.S. Targeting metastasis. Nature reviews. Cancer 2016, 16, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.T.; Yang, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Averous, J.; Fonseca, B.D.; Proud, C.G. Regulation of cyclin D1 expression by mTORC1 signaling requires eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Chien, C.Y.; Huang, W.T.; Luo, S.D.; Su, Y.Y.; Tien, W.Y.; Lan, Y.C.; Chen, C.H. Prognostic significance and function of mammalian target of rapamycin in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, P.; Garcia, P.; Sandoval, A.; Letelier, P.; Brebi, P.; Ili, C.; Alvarez, H.; Tapia, O.; Roa, J.C. Immunohistochemical expression of phospho-mTOR is associated with poor prognosis in patients with gallbladder adenocarcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas, N. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bu, T.; Wang, C.; Jin, H.; Meng, Q.; Huo, X.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. Organic anion transporters and PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway mediate the synergistic anticancer effect of pemetrexed and rhein. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3309–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Gu, L.; Chen, D.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.; Hu, H.; Wan, Y.; Sun, W. Rhein inhibits autophagy in rat renal tubular cells by regulation of AMPK/mTOR signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendillo, M.L.; Santagata, S.; Koeva, M.; Bell, G.W.; Hu, R.; Tamimi, R.M.; Fraenkel, E.; Ince, T.A.; Whitesell, L.; Lindquist, S. HSF1 drives a transcriptional program distinct from heat shock to support highly malignant human cancers. Cell 2012, 150, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, S.D.; Prince, T.; Gong, J.; Calderwood, S.K. mTOR is essential for the proteotoxic stress response, HSF1 activation and heat shock protein synthesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, S.D.; Hanley, S.E.; Beishke, T.; Tati, P.D.; Cooper, K.F. Ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated cyclin C degradation promotes cell survival following nitrogen starvation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2020, 31, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhu, G.; Yao, X.; Wang, N.; Hu, R.; Kong, Q.; Zhou, D.; Long, L.; Cai, J.; Zhou, W. Celastrol induces ubiquitin-dependent degradation of mTOR in breast cancer cells. Oncotargets Ther. 2018, 11, 8977–8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.H. Non-thermal plasma induces antileukemic effect through mTOR ubiquitination. Cells 2020, 9, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Tian, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, K.; Fan, X.Y.; Wang, K.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.E.; Chen, C.; et al. FBXW7-induced mTOR degradation forces autophagy to counteract persistent prion infection. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Choi, B.Y.; Wei, L.; Fredimoses, M.; Yin, F.; Fu, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, K.; Kundu, J.K.; Dong, Z.; et al. Acetylshikonin suppressed growth of colorectal tumour tissue and cells by inhibiting the intracellular kinase, T-lymphokine-activated killer cell-originated protein kinase. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2303–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Liu, K.; Liu, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Zu, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, T.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Gossypetin is a novel MKK3 and MKK6 inhibitor that suppresses esophageal cancer growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2019, 442, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Yin, S.; Zhao, R.; Liu, K.; Kundu, J.K.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; Dong, Z. (S)-10-Hydroxycamptothecin inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth in vitro and in vivo via decreasing Topoisomerase I enzyme activity. Cancers 2019, 11, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell 2017, 169, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Tao, T.; Li, H.; Zhu, X. mTOR signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: Progress and challenges. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurangan, A.K.; Ismail, S.; Esa, N.M.; Munusamy, M.A. Inositol-6 phosphate inhibits the mTOR pathway and induces autophagy-mediated death in HT-29 colon cancer cells. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2018, 14, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, D.L.; Hornberger, T.A.; Lincoln, H.C.; Bamman, M.M. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2B epsilon induces cap-dependent translation and skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 3023–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, W.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Zhai, E.; Cai, S.; et al. Increased expression of heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) is associated with poor survival in gastric cancer patients. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, S.; Hu, R.; Lin, N.U.; Mendillo, M.L.; Collins, L.C.; Hankinson, S.E.; Schnitt, S.J.; Whitesell, L.; Tamimi, R.M.; Lindquist, S.; et al. High levels of nuclear heat-shock factor 1 (HSF1) are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18378–18383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertoli, C.; Skotheim, J.M.; de Bruin, R.A. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Echalier, A.; Endicott, J.A.; Noble, M.E. Recent developments in cyclin-dependent kinase biochemical and structural studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seim, J.; Graff, P.; Amellem, O.; Landsverk, K.S.; Stokke, T.; Pettersen, E.O. Hypoxia-induced irreversible S-phase arrest involves downregulation of cyclin A. Cell Prolif. 2003, 36, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, K.M.; Eastman, A. Variations in Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 status and DNA damage-induced S-phase arrest in the cell lines of the NCI60 panel. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Bai, C.; Yao, C.; Zhong, H.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. Sophoridine induces apoptosis and S-phase arrest via ROS-dependent JNK and ERK activation in human pancreatic cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2017, 36, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.; Hu, H.; Tong, X.; Li, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Yuan, H.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The mTOR-S6K pathway links growth signalling to DNA damage response by targeting RNF168. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Craene, B.; Berx, G. Regulatory networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nature reviews. Cancer 2013, 13, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Yi, J.-K.; Huang, H.; Park, S.; Park, S.; Kwon, W.; Kim, E.; Jang, S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Choi, S.-K.; et al. Rhein Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the mTOR Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers 2021, 13, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092176
Zhang H, Yi J-K, Huang H, Park S, Park S, Kwon W, Kim E, Jang S, Kim S-Y, Choi S-K, et al. Rhein Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the mTOR Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers. 2021; 13(9):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092176
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haibo, Jun-Koo Yi, Hai Huang, Song Park, Sijun Park, Wookbong Kwon, Eungyung Kim, Soyoung Jang, Si-Yong Kim, Seong-Kyoon Choi, and et al. 2021. "Rhein Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the mTOR Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo" Cancers 13, no. 9: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092176
APA StyleZhang, H., Yi, J. -K., Huang, H., Park, S., Park, S., Kwon, W., Kim, E., Jang, S., Kim, S. -Y., Choi, S. -K., Kim, S. -H., Liu, K., Dong, Z., Ryoo, Z. Y., & Kim, M. O. (2021). Rhein Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the mTOR Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers, 13(9), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13092176