Enhanced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Advanced Retinoblastoma Tumors Is Driven by miR-181a
Abstract
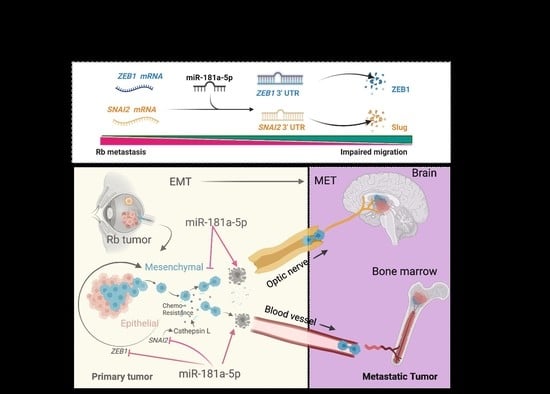
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Tumor miRNA and mRNA Profiling
2.3. Cell Lines
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Histopathology and Light Microscopy
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. FACS Analysis of MDR1 Surface Staining
2.9. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.10. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
2.11. Colony Formation/Tumor Spheroid Assay
2.12. Chemosensitivity Assay
2.13. miRNA–mRNA Target Prediction and Network Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Transcriptomic Profiling Identified Differentially Regulated miRNAs, EMT, and Drug-Resistant Genes in the Rb Tumor Subtype
3.2. Validation of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Chemo-Drug Resistance Proteins in Rb Tumors and Their Interaction with miR-181a-5p
3.3. Chemotherapy-Resistant Rb Cells Conferred a High EMT Program and Metastasis
3.4. Resistant Cells Elicited a Transition through ZEB1 and Resistance through Cathepsin L
3.5. Resistance Depletion by miR-181a-5p Conferred Sensitivity to Chemotherapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gupta, H.; Malaichamy, S.; Mallipatna, A.; Murugan, S.; Jeyabalan, N.; Suresh Babu, V.; Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, A.; Santhosh, S.; Seshagiri, S.; et al. Retinoblastoma genetics screening and clinical management. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancona-Lezama, D.; Dalvin, L.A.; Shields, C.L. Modern treatment of retinoblastoma: A 2020 review. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2356–2365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vempuluru, V.S.; Jakati, S.; Kaliki, S. Delayed metastasis in patients with intraocular retinoblastoma: A review of three cases. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honavar, S.G.; Manjandavida, F.P.; Reddy, V.A.P. Orbital retinoblastoma: An update. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canturk, S.; Qaddoumi, I.; Khetan, V.; Ma, Z.; Furmanchuk, A.; Antoneli, C.B.; Sultan, I.; Kebudi, R.; Sharma, T.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; et al. Survival of retinoblastoma in less-developed countries impact of socioeconomic and health-related indicators. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 94, 1432–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, C.L.; Shields, J.A. Retinoblastoma management: Advances in enucleation, intravenous chemoreduction, and intra-arterial chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 21, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosaleh, A.; Sampor, C.; Solernou, V.; Fandino, A.; Dominguez, J.; de Davila, M.T.; Chantada, G.L. Outcome of children with retinoblastoma and isolated choroidal invasion. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shields, C.L.; Shields, J.A.; Baez, K.; Cater, J.R.; De Potter, P. Optic nerve invasion of retinoblastoma. Metastatic potential and clinical risk factors. Cancer 1994, 73, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rootman, J.; Ellsworth, R.M.; Hofbauer, J.; Kitchen, D. Orbital extension of retinoblastoma: A clinicopathological study. Can. J Ophthalmol. 1978, 13, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Finger, P.T.; Harbour, J.W.; Karcioglu, Z.A. Risk factors for metastasis in retinoblastoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2002, 47, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namouni, F.; Doz, F.; Tanguy, M.L.; Quintana, E.; Michon, J.; Pacquement, H.; Bouffet, E.; Gentet, J.C.; Plantaz, D.; Lutz, P.; et al. High-dose chemotherapy with carboplatin, etoposide and cyclophosphamide followed by a haematopoietic stem cell rescue in patients with high-risk retinoblastoma: A SFOP and SFGM study. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, C.L.; Shelil, A.; Cater, J.; Meadows, A.T.; Shields, J.A. Development of new retinoblastomas after 6 cycles of chemoreduction for retinoblastoma in 162 eyes of 106 consecutive patients. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, H.S.; Thorner, P.S.; Haddad, G.; Gallie, B.L. Multidrug-resistant phenotype in retinoblastoma correlates with P-glycoprotein expression. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.W.; Fraga, C.H.; Fuller, C.E.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Mancini, J.; Hagedorn, N.; Leggas, M.L.; Stewart, C.F. Immunohistochemical detection of multidrug-resistant protein expression in retinoblastoma treated by primary enucleation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1269–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Yun, P.Y. Upregulation of MDR- and EMT-Related Molecules in Cisplatin-Resistant Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxena, M.; Stephens, M.A.; Pathak, H.; Rangarajan, A. Transcription factors that mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition lead to multidrug resistance by upregulating ABC transporters. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Lopez, A.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Cano, A. Role of microRNA in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis and clinical perspectives. Cancer Manag. Res. 2014, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kandalam, M.M.; Beta, M.; Maheswari, U.K.; Swaminathan, S.; Krishnakumar, S. Oncogenic microRNA 17-92 cluster is regulated by epithelial cell adhesion molecule and could be a potential therapeutic target in retinoblastoma. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.; Wan, W.; Long, Y.; Li, Q.; Jin, X.; Wan, G.; Zhang, F.; Lv, Y.; Zheng, G.; Li, Z.; et al. Corrigendum to “MiR-25-3p promotes malignant phenotypes of retinoblastoma by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway” [Biomed. Pharmacother. 118 (2019) 109111]. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L. MiR-200c suppresses the migration of retinoblastoma cells by reversing epithelial mesenchymal transition. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallipatna, A.; Gallie, B.; Chévez-Barrios, P.; Rouic, L.; Chantada, G.; Doz, F.; Brisse, H.; Munier, F.; Albert, D.; Català, J.; et al. Retinoblastoma. In AJCC Cancer Staging Manual; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 819–831. [Google Scholar]
- Murphree, A.L. Intraocular retinoblastoma: The case for a new group classification. Ophthalmol. Clin. North Am. 2005, 18, 41–53, viii. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, U.; Mahmud, N.M.; Kay, P.; Yang, Y.C.; Harding, S.P.; Grierson, I.; Kamalden, T.A.; Jackson, M.J.; Paraoan, L. Advanced glycation end products-related modulation of cathepsin L and NF-kappaB signalling effectors in retinal pigment epithelium lead to augmented response to TNFalpha. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dykes, S.S.; Fasanya, H.O.; Siemann, D.W.; Cathepsin, L. Secretion by host and neoplastic cells potentiates invasion. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 5560–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cicinelli, M.V.; Kaliki, S. Orbital relapse of retinoblastoma in patients with high-risk histopathology features. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2019, 11, 2515841419844080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berry, J.L.; Kogachi, K.; Aziz, H.A.; McGovern, K.; Zolfaghari, E.; Murphree, A.L.; Jubran, R.; Kim, J.W. Risk of metastasis and orbital recurrence in advanced retinoblastoma eyes treated with systemic chemoreduction versus primary enucleation. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapela, S.; Bouchal, J.; Jolly, M.K.; Culig, Z.; Soucek, K. ZEB1: A. Critical Regulator of Cell Plasticity, DNA Damage Response, and Therapy Resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, K.; Yamashita, H.; Mogi, A.; Takenoshita, S.; Miyazono, K. Lack of transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor expression in human retinoblastoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 175, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaghi, L.; White, D.T.; Key, N.; Choi, J.; Mahale, A.; Alkatan, H.; Edward, D.P.; Elkhamary, S.M.; Al-Mesfer, S.; Maktabi, A.; et al. ACVR1C/SMAD2 signaling promotes invasion and growth in retinoblastoma. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2056–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceru, S.; Konjar, S.; Maher, K.; Repnik, U.; Krizaj, I.; Bencina, M.; Renko, M.; Nepveu, A.; Zerovnik, E.; Turk, B.; et al. Stefin B interacts with histones and cathepsin L in the nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10078–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Zhai, X.; Ge, T.; Yang, C.; Lou, G. miR-181a-5p Promotes Proliferation and Invasion and Inhibits Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells via Regulating Inositol Polyphosphate-5-Phosphatase A (INPP5A). Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Rui, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, Y.H.; Qu, Y.Q. Serum miR-1228-3p and miR-181a-5p as Noninvasive Biomarkers for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9601876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kuscu, C.; Banach, A.; Zhang, Q.; Pulkoski-Gross, A.; Kim, D.; Liu, J.; Roth, E.; Li, E.; Shroyer, K.R.; et al. miR-181a-5p Inhibits Cancer Cell Migration and Angiogenesis via Downregulation of Matrix Metalloproteinase-14. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2674–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Du, Y.; Hu, X.; Xia, W. LncRNA LUCAT1/miR-181a-5p axis promotes proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via targeting KLF6 and KLF15. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Yao, Y.; Yuan, F.; Xie, B. Overexpression of miR-181a-5p inhibits retinal neovascularization through endocan and the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 9323–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastushenko, I.; Brisebarre, A.; Sifrim, A.; Fioramonti, M.; Revenco, T.; Boumahdi, S.; Van Keymeulen, A.; Brown, D.; Moers, V.; Lemaire, S.; et al. Identification of the tumour transition states occurring during EMT. Nature 2018, 556, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and opportunities. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, D.; Villen, J.; Shin, C.; Camargo, F.D.; Gygi, S.P.; Bartel, D.P. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008, 455, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krech, T.; Scheuerer, E.; Geffers, R.; Kreipe, H.; Lehmann, U.; Christgen, M. ABCB1/MDR1 contributes to the anticancer drug-resistant phenotype of IPH-926 human lobular breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 315, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Chu, F.; Chou, P.M.; Gallati, C.; Dier, U.; Mirkin, B.L.; Mousa, S.A.; Rebbaa, A. Cathepsin L inhibition suppresses drug resistance in vitro and in vivo: A putative mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 296, C65–C74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.M.; Nikolic, I.; Yang, J.; Castillo, L.; Deng, N.; Chan, C.L.; Yeung, N.K.; Dodson, E.; Elsworth, B.; Spielman, C.; et al. MicroRNAs as potential therapeutics to enhance chemosensitivity in advanced prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Weng, X.D.; Liu, X.H.; Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Diao, C.H. miR-181a-5p is downregulated and inhibits proliferation and the cell cycle in prostate cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3969–3976. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, M.; Liu, G.; Xiong, C.; Rao, J. microRNA-181a-5p impedes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of retinoblastoma cells by targeting the NRAS proto-oncogene. Clinics 2022, 77, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.V.; Conroy, S.; Tomar, T.; Eggens-Meijer, E.; Bhat, K.; Copray, S.; Walenkamp, A.M.; Boddeke, E.; Balasubramanyian, V.; Wagemakers, M.; et al. TGF-beta is an inducer of ZEB1-dependent mesenchymal transdifferentiation in glioblastoma that is associated with tumor invasion. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siebzehnrubl, F.A.; Silver, D.J.; Tugertimur, B.; Deleyrolle, L.P.; Siebzehnrubl, D.; Sarkisian, M.R.; Devers, K.G.; Yachnis, A.T.; Kupper, M.D.; Neal, D.; et al. The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonci, D.; Coppola, V.; Musumeci, M.; Addario, A.; Giuffrida, R.; Memeo, L.; D’Urso, L.; Pagliuca, A.; Biffoni, M.; Labbaye, C.; et al. The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ID | Sex | Laterality | Age at Presentation | Clinical Risk | IIRC Group | AJCC Staging |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | M | Bilateral | 15 months | Advanced | Group E | cT3b |
| P2 | F | Unilateral | 20 months | Advanced | Group E | cT3b |
| P3 | M | Unilateral | 24 months | Advanced | Group E | cT3a |
| P4 | F | Bilateral | 4 months | Advanced | Group E | cT3b |
| P5 | M | Bilateral | 30 months | Advanced | Group E | cT3b |
| P6 | F | Bilateral | 21 months | Non-advanced | Group D | cT2b |
| P7 | F | Unilateral | 28 months | Non-advanced | Group D | cT2b |
| P8 | M | Unilateral | 20 months | Non-advanced | Group D | cT2b |
| P9 | M | Unilateral | 21 months | Non-advanced | Group D | cT2a |
| Control 1 | F | NA | 3 months | Cardiac arrest (no ocular complications) | ||
| Control 2 | F | NA | 2 months | Multiple organ dysfunction (no ocular complications) | ||
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Tm (F/R) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 | GCCTCCTATAGCTCACACATAAG | TGCTGGAAGAGACGGTGAA | 56.67/56.8 |
| SNAI2 | GTGATTATTTCCCCGTATCTCTAT | TCAATGGCATGGGGTCTGA | 55.6/60.2 |
| CDH1 (E-cadherin) | GAAGGTGACAGAGCCTCTGGAT | GATCGGTTACCGTGATCAA | 57.2/58.4 |
| CDH2 (N-cadherin) | CGAGCCGCCTGCGCTGCCAC | CGCTGCTCTCCGCTCCCCGC | 56.5/57.3 |
| ACVRC1 | AGGAGTTTCGACCCCAGTAA | GTAGCACTTACCGTAGCACC | 57.9/58.2 |
| CTSL | AGGCCTGGACTCTGAGGAAT | AGCCGGTGTCATTAGCAACA | 57.8/57 |
| SMAD2 | CCGCCAGTTGTGAAGAGACT | CTGCCCATTCTGCTCTCCTC | 59.9/60.1 |
| ABCB1 | GAGCAGTCATCTGTGGTCTT | CCCCTTCAAGATCCATTCCG | 57.2/58.0 |
| β-Actin | TCCCTGGAGAAGAGCTACGA | AGGAAGGAAGGCTGGAAGAG | 56.9/55.2 |
| S. No. | Systematic Name | Regulation | Mirbase Accession No | Active Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa-miR-331-3p | Down | MIMAT0000760 | TTCTAGGATAGGCCCAGGG |
| 2 | hsa-miR-181a-5p | Down | MIMAT0000256 | ACTCACCGACAGCGT |
| 3 | hsa-miR-574-5p | Up | MIMAT0004795 | ACACACTCACACACACAC |
| 4 | hsa-miR-1290 | Up | MIMAT0005880 | TCCCTGATCCAAAAATCC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suresh Babu, V.; Bisht, A.; Mallipatna, A.; SA, D.; Dudeja, G.; Kannan, R.; Shetty, R.; Guha, N.; Heymans, S.; Ghosh, A. Enhanced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Advanced Retinoblastoma Tumors Is Driven by miR-181a. Cancers 2022, 14, 5124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205124
Suresh Babu V, Bisht A, Mallipatna A, SA D, Dudeja G, Kannan R, Shetty R, Guha N, Heymans S, Ghosh A. Enhanced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Advanced Retinoblastoma Tumors Is Driven by miR-181a. Cancers. 2022; 14(20):5124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205124
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuresh Babu, Vishnu, Anadi Bisht, Ashwin Mallipatna, Deepak SA, Gagan Dudeja, Ramaraj Kannan, Rohit Shetty, Nilanjan Guha, Stephane Heymans, and Arkasubhra Ghosh. 2022. "Enhanced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Advanced Retinoblastoma Tumors Is Driven by miR-181a" Cancers 14, no. 20: 5124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205124
APA StyleSuresh Babu, V., Bisht, A., Mallipatna, A., SA, D., Dudeja, G., Kannan, R., Shetty, R., Guha, N., Heymans, S., & Ghosh, A. (2022). Enhanced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Chemoresistance in Advanced Retinoblastoma Tumors Is Driven by miR-181a. Cancers, 14(20), 5124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205124