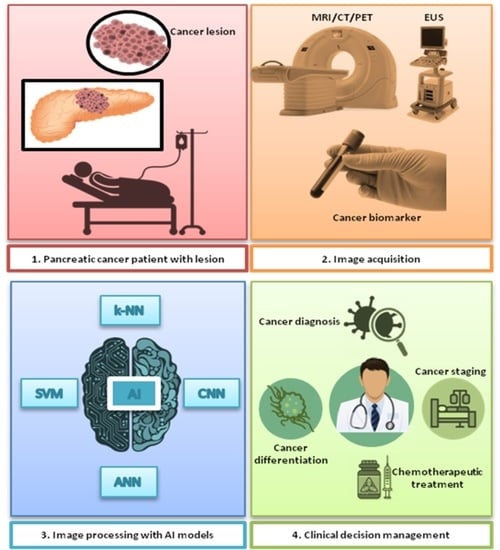
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Artificial Intelligence for Diagnostic Applications
3. AI Models for the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer
4. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)
5. MRI
6. Computed Tomography
7. Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
8. Pancreatic Cancer Risk Prediction Using AI
9. AI-Driven Diagnosis Based on Cancer Biomarkers
10. Ethics of Using AI for Diagnosis
11. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, M. In Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: The Value and Significance of Interventional Therapy. J. Interv. Med. 2020, 3, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon-Dseagu, V.L.; Devesa, S.S.; Goggins, M.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R. Pancreatic Cancer Incidence Trends: Evidence from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Population-Based Data. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 47, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: An Update. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic Cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.-T.; Zhou, Y.-P.; Zhang, Z.-D.; Li, S.; Lu, Y. Establishment and Application of an Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis System for Pancreatic Cancer with a Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 2795–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.D.; Clarke, S.E.; Costa, A.F. Factors Associated with Missed and Misinterpreted Cases of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2422–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Yoon, S.N. Application of Artificial Intelligence-Based Technologies in the Healthcare Industry: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González García, C.; Núñez-Valdez, E.; García-Díaz, V.; Pelayo G-Bustelo, C.; Cueva-Lovelle, J.M. A Review of Artificial Intelligence in the Internet of Things. Int. J. Interact. Multimed. Artif. Intell. 2019, 5, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S. The Evolution of Machine Learning: Past, Present, and Future. In Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning in Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1–12. ISBN 978-0-323-67538-3. [Google Scholar]
- Luchini, C.; Pea, A.; Scarpa, A. Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: Current Applications and Future Perspectives. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Induja, S.N.; Raji, C.G. Computational Methods for Predicting Chronic Disease in Healthcare Communities. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Data Science and Communication (IconDSC), Bangalore, India, 1–2 March 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, U. Applications of Machine Learning in Disease Pre-screening. In Research Anthology on Artificial Intelligence Applications in Security; Information Resources Management Association, Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 1052–1084. ISBN 978-1-79987-705-9. [Google Scholar]
- Noori, A.; Alfi, A.; Noori, G. An Intelligent Control Strategy for Cancer Cells Reduction in Patients with Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia Using the Reinforcement Learning and Considering Side Effects of the Drug. Expert Syst. 2021, 38, e12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kosorok, M.R.; Zeng, D. Reinforcement Learning Design for Cancer Clinical Trials. Statist. Med. 2009, 28, 3294–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Xie, L.; Han, J.; Guo, X. The Application of Deep Learning in Cancer Prognosis Prediction. Cancers 2020, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vial, A.; Stirling, D.; Field, M.; Ros, M.; Ritz, C.; Carolan, M.; Holloway, L.; Miller, A.A. The Role of Deep Learning and Radiomic Feature Extraction in Cancer-Specific Predictive Modelling: A Review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Azam, S.; Hasib, K.M.; Karim, A.; Jonkman, M.; Anwar, A. A Performance Based Study on Deep Learning Algorithms in the Effective Prediction of Breast Cancer. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Chien, T.-W.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-L.; Su, S.-B. An App to Classify a 5-Year Survival in Patients with Breast Cancer Using the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in Microsoft Excel: Development and Usability Study. Medicine 2022, 101, e28697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakasa, W.; Viriri, S. Pancreatic Cancer Survival Prediction: A Survey of the State-of-the-Art. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 1188414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capobianco, E. High-Dimensional Role of AI and Machine Learning in Cancer Research. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, L.; Saeed, S.; Awan, I.A.; Idris, A.; Nadeem, M.S.A.; Chaudhry, Q.-A. Detecting Brain Tumor Using Machines Learning Techniques Based on Different Features Extracting Strategies. CMIR 2019, 15, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassenmaier, S.; Afat, S.; Nickel, D.; Mostapha, M.; Herrmann, J.; Othman, A.E. Deep Learning–Accelerated T2-Weighted Imaging of the Prostate: Reduction of Acquisition Time and Improvement of Image Quality. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 137, 109600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Javed, Z.; Sadia, H.; Qureshi, I.A.; Irshad, A.; Ahmed, R.; Malik, K.; Raza, S.; Abbas, A.; Pezzani, R.; et al. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cancer Diagnosis: Looking into the Future. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Jing, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, X. A Review of Medical Image Detection for Cancers in Digestive System Based on Artificial Intelligence. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davatzikos, C.; Sotiras, A.; Fan, Y.; Habes, M.; Erus, G.; Rathore, S.; Bakas, S.; Chitalia, R.; Gastounioti, A.; Kontos, D. Precision Diagnostics Based on Machine Learning-Derived Imaging Signatures. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 64, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chen, Q.; Parker, R.A.; Zhou, Y.; Lustigova, E.; Wu, B.U. Risk Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients with Abnormal Morphologic Findings Related to Chronic Pancreatitis: A Machine Learning Approach. Gastro Hep Adv. 2022, 1, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avuçlu, E.; Elen, A. Evaluation of Train and Test Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms and Parkinson Diagnosis with Statistical Measurements. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2020, 58, 2775–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, N.; Kursun, O.; Ucan, O.N. Classification of the Colonic Polyps in CT-Colonography Using Region Covariance as Descriptor Features of Suspicious Regions. J. Med. Syst. 2010, 34, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.J.; Arun Prasath, T.; PallikondaRajasekaran, M.; Vishnuvarthanan, G. Brain and Pancreatic Tumor Classification Based on GLCM—K-NN Approaches. In International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Applications; Bhaskar, M.A., Dash, S.S., Das, S., Panigrahi, B.K., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 846, pp. 293–302. ISBN 9789811321818. [Google Scholar]
- Jamshidi, M.; Zilouchian, A. Intelligent Control Systems Using Soft Computing Methodologies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-8493-1875-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-G.; Jun, S.; Cho, Y.-W.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.B.; Seo, J.B.; Kim, N. Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: General Overview. Korean J. Radiol. 2017, 18, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Janssen, J.; Hocke, M.; Larsen, M.; Iglesias–Garcia, J.; Arcidiacono, P.; Will, U.; Giovannini, M.; et al. Efficacy of an Artificial Neural Network–Based Approach to Endoscopic Ultrasound Elastography in Diagnosis of Focal Pancreatic Masses. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 84–90.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.V. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Artificial Neural Networks versus Logistic Regression for Predicting Medical Outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkoum, H.; Idri, A.; Abnane, I. Assessing and Comparing Interpretability Techniques for Artificial Neural Networks Breast Cancer Classification. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2021, 9, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, D.M.; Jacyna, G.M. Support Vector Machine Regularization. WIREs Comp. Stat. 2011, 3, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H. A Reduced Support Vector Machine Approach for Interval Regression Analysis. Inf. Sci. 2012, 217, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-M.; Yang, H.; Jin, Z.-D.; Yu, J.-G.; Cai, Z.-Y.; Li, Z.-S. Differential Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer from Normal Tissue with Digital Imaging Processing and Pattern Recognition Based on a Support Vector Machine of EUS Images. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Rao, N.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Luo, C.; Li, Z.; Gan, T.; Zeng, B. Review on the Applications of Deep Learning in the Analysis of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 142053–142069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P. Convolutional Neural Network. In MATLAB Deep Learning; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 121–147. ISBN 978-1-4842-2844-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H. Feature Extraction and Image Recognition with Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1087, 062032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kim, J.; Lyndon, D.; Fulham, M.; Feng, D. An Ensemble of Fine-Tuned Convolutional Neural Networks for Medical Image Classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddique, N.; Paheding, S.; Elkin, C.P.; Devabhaktuni, V. U-Net and Its Variants for Medical Image Segmentation: A Review of Theory and Applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82031–82057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özyurt, F. A Fused CNN Model for WBC Detection with MRMR Feature Selection and Extreme Learning Machine. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 8163–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Zerbe, N.; Klempert, I.; Hellwich, O.; Hufnagl, P. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Automatic Classification of Gastric Carcinoma Using Whole Slide Images in Digital Histopathology. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2017, 61, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.; Qadir, H.A.; Aabakken, L.; Bergsland, J.; Balasingham, I. Automatic Colon Polyp Detection Using Region Based Deep CNN and Post Learning Approaches. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 40950–40962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, M.; Shimizu, N.; Oda, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Kitasaka, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; Roth, H.R. Towards Dense Volumetric Pancreas Segmentation in CT Using 3D Fully Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2018: Image Processing, Houston, TX, USA, 2 March 2018; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, L.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M.; Sonka, M.; Yao, J. Deep LOGISMOS: Deep Learning Graph-Based 3D Segmentation of Pancreatic Tumors on CT Scans. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 1230–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Luthra, A.K.; Evans, J.A. Review of Current and Evolving Clinical Indications for Endoscopic Ultrasound. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo-Marin, J. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munroe, C.A.; Fehmi, S.M.A.; Savides, T.J. Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Expert Opin. Med. Diagn. 2013, 7, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, M.; Koduru, P.; Joshi, V.; Saxena, P.; Suzuki, R.; Irisawa, A.; Yamao, K. The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Pancreatic Cancer Screening. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeWitt, J.; Devereaux, B.M.; Lehman, G.A.; Sherman, S.; Imperiale, T.F. Comparison of Endoscopic Ultrasound and Computed Tomography for the Preoperative Evaluation of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausawasdi, N.; Hongsrisuwan, P.; Chalermwai, W.V.; Butt, A.S.; Maipang, K.; Charatchareonwitthaya, P. The Diagnostic Performance of Combined Conventional Cytology with Smears and Cell Block Preparation Obtained from Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Intra-Abdominal Mass Lesions. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Uemura, N.; Matsumura, K.; Zhao, L.; Sato, H.; Shiraishi, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Baba, H. Recent Advances in Artificial Intelligence for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 7480–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herth, F.J.F.; Rabe, K.F.; Gasparini, S.; Annema, J.T. Transbronchial and Transoesophageal (Ultrasound-Guided) Needle Aspirations for the Analysis of Mediastinal Lesions. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 28, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazacu, I.; Udristoiu, A.; Gruionu, L.; Iacob, A.; Gruionu, G.; Saftoiu, A. Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Cancer: Toward Precision Diagnosis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2019, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, I.D.; Zheng, Y.; Wiersema, M.S.; Greenleaf, J.; Clain, J.E.; DiMagno, E.P. Neural Network Analysis of EUS Images to Differentiate between Pancreatic Malignancy and Pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 54, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Xu, C.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Jin, Z.; Li, Z. Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer and Chronic Pancreatitis Using Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Images: A Diagnostic Test. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, A.; Nguyen, C.C.; Li, F.; Li, B. Digital Image Analysis of EUS Images Accurately Differentiates Pancreatic Cancer from Chronic Pancreatitis and Normal Tissue. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 67, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, M.; Cakiroglu, M.; Kocaman, O.; Kurt, M.; Yilmaz, B.; Can, G.; Korkmaz, U.; Dandil, E.; Eksi, Z. Age-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis Approach for Pancreatic Cancer on Endoscopic Ultrasound Images. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Gheonea, D.I.; Gorunescu, M.; Ciurea, T.; Popescu, G.L.; Iordache, A.; Hassan, H.; Iordache, S. Neural Network Analysis of Dynamic Sequences of EUS Elastography Used for the Differential Diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2008, 68, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonozuka, R.; Itoi, T.; Nagata, N.; Kojima, H.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Nagakawa, Y.; Mukai, S. Deep Learning Analysis for the Detection of Pancreatic Cancer on Endosonographic Images: A Pilot Study. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Sci. 2021, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Okuno, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Obata, M.; Kurita, Y.; Koda, H.; Toriyama, K.; Onishi, S.; et al. Usefulness of Deep Learning Analysis for the Diagnosis of Malignancy in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, E.A.; Ungureanu, B.S.; Cazacu, I.M.; Florescu, L.M.; Streba, L.; Croitoru, V.M.; Sur, D.; Croitoru, A.; Turcu-Stiolica, A.; Lungulescu, C.V. Diagnostic Value of Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viard, A.; Eustache, F.; Segobin, S. History of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Trip Down Memory Lane. Neuroscience 2021, 474, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Cui, H. Functional Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 814–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanada, K.; Shimizu, A.; Kurihara, K.; Ikeda, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Okuda, Y.; Tazuma, S. Endoscopic Approach in the Diagnosis of High-grade Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enriquez, J.S.; Chu, Y.; Pudakalakatti, S.; Hsieh, K.L.; Salmon, D.; Dutta, P.; Millward, N.Z.; Lurie, E.; Millward, S.; McAllister, F.; et al. Hyperpolarized Magnetic Resonance and Artificial Intelligence: Frontiers of Imaging in Pancreatic Cancer. JMIR Med. Inform. 2021, 9, e26601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaissis, G.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohöfer, F.; Algül, H.; Eiber, M.; Weichert, W.; Schmid, R.; Friess, H.; Rummeny, E.; Ankerst, D.; et al. A Machine Learning Model for the Prediction of Survival and Tumor Subtype in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma from Preoperative Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X. Performance of Deep Learning for Differentiating Pancreatic Diseases on Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Preliminary Study. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Qu, S.; Zhang, H. Support Vector Machine Combined with Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Accurate Diagnosis of Paediatric Pancreatic Cancer. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, A.D.; Murugan, P.R.; Thiyagarajan, A.P. Analysis and Classification of Malignancy in Pancreatic Magnetic Resonance Images Using Neural Network Techniques. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2019, 29, 399–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, J.E.; Hussein, S.; Kandel, P.; Bolan, C.W.; Bagci, U.; Wallace, M.B. Deep Learning to Classify Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pancreas 2019, 48, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ruan, D.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, B.; Saouaf, R.; Yang, W.; Li, D.; Fan, Z. Fully Automated Multiorgan Segmentation in Abdominal Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Deep Neural Networks. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 4971–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.L. Computed Tomography. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 1993, 37, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.P.; Horton, K.M.; Fishman, E.K. Multimodality Imaging of Pancreatic Cancer—Computed Tomography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Positron Emission Tomography. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Múnera, F.; Cohn, S.; Rivas, L.A. Penetrating Injuries of the Neck: Use of Helical Computed Tomographic Angiography. J. Trauma Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2005, 58, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.T.; Sofka, C.M.; Zhang, P.; Khurana, J.S. Systematic Approach to Tumors and Tumor-Like Conditions of Soft Tissue. In Diagnostic Imaging of Musculoskeletal Diseases; Bonakdarpour, A., Reinus, W.R., Khurana, J.S., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 313–349. ISBN 978-1-58829-947-5. [Google Scholar]
- Willemink, M.J.; Persson, M.; Pourmorteza, A.; Pelc, N.J.; Fleischmann, D. Photon-Counting CT: Technical Principles and Clinical Prospects. Radiology 2018, 289, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razzak, M.I.; Naz, S.; Zaib, A. Deep Learning for Medical Image Processing: Overview, Challenges and the Future. In Classification in BioApps; Dey, N., Ashour, A.S., Borra, S., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 26, pp. 323–350. ISBN 978-3-319-65980-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dhruv, B.; Mittal, N.; Modi, M. Early and Precise Detection of Pancreatic Tumor by Hybrid Approach with Edge Detection and Artificial Intelligence Techniques. EAI Endorsed Trans. Pervasive Health Technol. 2021, 7, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, A.M.; van Veldhuisen, C.L.; Bellin, M.D.; Besselink, M.G.; Bouwense, S.A.; Olesen, S.S.; van Santvoort, H.; Vase, L.; Windsor, J.A. Assessment of Pain Associated with Chronic Pancreatitis: An International Consensus Guideline. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 1256–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Z.-X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Wu, F.-T.; Xu, C.-F.; Shen, Z.; Yu, C.-H.; Li, Y.-M. Construction of a Convolutional Neural Network Classifier Developed by Computed Tomography Images for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5156–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y. A Novel and Efficient Tumor Detection Framework for Pancreatic Cancer via CT Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020; pp. 1160–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.-T.; Wu, T.; Wang, P.; Chang, D.; Liu, K.-L.; Wu, M.-S.; Roth, H.R.; Lee, P.-C.; Liao, W.-C.; Wang, W. Pancreatic Cancer Detection on CT Scans with Deep Learning: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Radiology 2022, 2022, 220152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barat, M.; Chassagnon, G.; Dohan, A.; Gaujoux, S.; Coriat, R.; Hoeffel, C.; Cassinotto, C.; Soyer, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Critical Review of Current Applications in Pancreatic Imaging. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2021, 39, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandland, J.; Malatesti, N.; Boyle, R. Porphyrins and Related Macrocycles: Combining Photosensitization with Radio- or Optical-Imaging for next Generation Theranostic Agents. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 23, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Ghosh, A. 18F-AlF Labeled Peptide and Protein Conjugates as Positron Emission Tomography Imaging Pharmaceuticals. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 953–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, O.; Chen, X. PET Designated Flouride-18 Production and Chemistry. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buchmann, I.; Ganten, T.; Haberkorn, U. [18F]-FDG-PET in der Diagnostik gastrointestinaler Tumoren. Z. Gastroenterol. 2008, 46, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, S.J.; Lind, T.; Antoch, G.; Bockisch, A. False-Positive FDG PET Uptake—The Role of PET/CT. Eur. Radiol. 2006, 16, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakzad, F.; Groves, A.M.; Ell, P.J. The Role of Positron Emission Tomography in the Management of Pancreatic Cancer. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2006, 36, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, S. [18F]2-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose PET/CT in Mediastinal Masses. Cancer Imaging 2010, 10, S156–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yao, Y. An Effective Computer Aided Diagnosis Model for Pancreas Cancer on PET/CT Images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 165, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, Y.; Hotta, M.; Motoi, F.; Takanami, K.; Minamimoto, R.; Takase, K. Prognostic Value of FDG-PET Radiomics with Machine Learning in Pancreatic Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.D.; Lyman, W.B.; Passeri, M.J.; Murphy, K.J.; Sarantou, J.P.; Iannitti, D.A.; Martinie, J.B.; Vrochides, D.; Baker, E.H. Use of Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning to Determine the Malignant Potential of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms with Preoperative Computed Tomography Imaging. Am. Surg. 2021, 87, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.A.; Gaddam, S.; Wachsman, A.M.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Asadpour, V.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, B.; Pandol, S.J.; et al. Predicting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Artificial Intelligence Analysis of Pre-Diagnostic Computed Tomography Images. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, Y.-H.; Kim, D.; Kim, K.G.; Lee, D.-H. Automated Pancreas Segmentation and Volumetry Using Deep Neural Network on Computed Tomography. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Ge, J.; He, W.; Xu, X.; He, J. Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based Computerized Tomography Image Features Combined with Serum Tumor Markers for Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 8979404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Liu, C.; Gao, F.; Qi, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Ji, R.Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. Prediction of Clinically Relevant Pancreatico-Enteric Anastomotic Fistulas after Pancreatoduodenectomy Using Deep Learning of Preoperative Computed Tomography. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9779–9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogan, M.T.; Lo, J.Y.; Freed, K.S.; Raptopoulos, V.; Blake, S.; Kamel, I.R.; Weisinger, K.; Rosen, M.P.; Nelson, R.C. Outcome Analysis of Patients with Acute Pancreatitis by Using an Artificial Neural Network. Acad. Radiol. 2002, 9, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, W.; Duan, N.; Chen, X.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Machine Learning–Based Quantitative Computed Tomography Texture Analysis for Prediction of Histopathological Grade. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 9253–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.-L.; Wu, T.; Chen, P.-T.; Tsai, Y.M.; Roth, H.; Wu, M.-S.; Liao, W.-C.; Wang, W. Deep Learning to Distinguish Pancreatic Cancer Tissue from Non-Cancerous Pancreatic Tissue: A Retrospective Study with Cross-Racial External Validation. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e303–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.C.; Park, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xie, L.; Liu, F.; et al. Application of Deep Learning to Pancreatic Cancer Detection: Lessons Learned from Our Initial Experience. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2019, 16, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, K.; Xue, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Gong, W.; Liang, T.; Duan, S. Fully End-to-End Deep-Learning-Based Diagnosis of Pancreatic Tumors. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Hart, G.R.; Nartowt, B.; Farrell, J.J.; Johung, K.; Liang, Y.; Deng, J. Pancreatic Cancer Prediction Through an Artificial Neural Network. Front. Artif. Intell. 2019, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Schott, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Nasief, H.; Paulson, E.; Hall, W.; Knechtges, P.; Erickson, B.; Li, X.A. Auto-Segmentation of Pancreatic Tumor in Multi-Parametric MRI Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 145, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna Devi, B.; PallikondaRajasekaran, M. Performance Evaluation of MRI Pancreas Image Classification Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN). In Smart Intelligent Computing and Applications; Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Satapathy, S.C., Bhateja, V., Das, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 104, pp. 671–681. ISBN 9789811319204. [Google Scholar]
- Marya, N.B.; Powers, P.D.; Chari, S.T.; Gleeson, F.C.; Leggett, C.L.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Iyer, P.G.; Majumder, S.; Pearson, R.K.; et al. Utilisation of Artificial Intelligence for the Development of an EUS-Convolutional Neural Network Model Trained to Enhance the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Gut 2021, 70, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Săftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Dietrich, C.F.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Hocke, M.; Seicean, A.; Ignee, A.; Hassan, H.; Streba, C.T.; Ioncică, A.M.; et al. Quantitative Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic EUS in Differential Diagnosis of Focal Pancreatic Masses (with Videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, T.A.; Javed, S.; Sarmadi, T.; Pandol, S.J.; Li, D. Artificial Intelligence and Imaging for Risk Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer: A Narrative Review. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.-S.; Chen, W.-L.; Guo, W.-J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, W.-H.; Peng, C.-H.; Zhang, S.-D.; Li, H.-W.; et al. Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer by Serum Biomarkers Using Surface-Enhanced Laser Desorption/Ionization-Based Decision Tree Classification. Oncology 2005, 68, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezgyte, G.; Shah, V.; Jach, D.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Earlier Detection of Pancreatic Cancer—A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Ma, Q.; Tan, Y.; Du, W.; Lv, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, H. Pancreatic Cancer Biomarker Detection by Two Support Vector Strategies for Recursive Feature Elimination. Biomark. Med. 2019, 13, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ou, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, R.; Yu, S.; Zhao, M.; Tai, S. Advances in Biomarkers and Techniques for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Ren, B.; You, L. Early Screening and Diagnosis Strategies of Pancreatic Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1257–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Bhagwat, N.; Yee, S.S.; Ortiz, N.; Sahmoud, A.; Black, T.; Aiello, N.M.; McKenzie, L.; O’Hara, M.; Redlinger, C.; et al. Combining Machine Learning and Nanofluidic Technology to Diagnose Pancreatic Cancer Using Exosomes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11182–11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.Y.; Mukherjee, I. A Novel Neural Network to Predict Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Using 4 Urinary Biomarkers: REG1A/1B, LYVE1, and TFF1. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2022, 235, S144–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.N.N.; He, Z.; Leung, K.L.; To, C.C.K.; Wong, C.Y.; Wong, S.C.C.; Yoo, J.S.; Chan, C.K.R.; Chan, A.Z.; Lacambra, M.D.; et al. Current Developments of Artificial Intelligence in Digital Pathology and Its Future Clinical Applications in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Cancers 2022, 14, 3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausar, T.; Kausar, A.; Ashraf, M.A.; Siddique, M.F.; Wang, M.; Sajid, M.; Siddique, M.Z.; Haq, A.U.; Riaz, I. SA-GAN: Stain Acclimation Generative Adversarial Network for Histopathology Image Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidinekoo, A.; Denton, E.; Rampun, A.; Honnor, K.; Zwiggelaar, R. Deep Learning in Mammography and Breast Histology, an Overview and Future Trends. Med. Image Anal. 2018, 47, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Lin, X.; Shen, Q.; Qian, X. Combined Spiral Transformation and Model-Driven Multi-Modal Deep Learning Scheme for Automatic Prediction of TP53 Mutation in Pancreatic Cancer. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Marklund, H.; Blaha, O.; Desai, M.; Martin, B.; Bingham, D.; Berry, G.J.; Gomulia, E.; Ng, A.Y.; Shen, J. Deep Learning Assistance for the Histopathologic Diagnosis of Helicobacter Pylori. Intell. Based Med. 2020, 1–2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrung, M.; Crispin-Ortuzar, M.; Berman, A.G.; O’Donovan, M.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Markowetz, F. Triage-Driven Diagnosis of Barrett’s Esophagus for Early Detection of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Using Deep Learning. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.M.; Rogers, W.; Win, K.T.; Frazer, H.; Richards, B.; Houssami, N. The Ethical, Legal and Social Implications of Using Artificial Intelligence Systems in Breast Cancer Care. Breast 2020, 49, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shreve, J.T.; Khanani, S.A.; Haddad, T.C. Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: Current Capabilities, Future Opportunities, and Ethical Considerations. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Technique | Merit(s) | Demerit(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) |
|
|
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) |
|
|
| Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with or without fine needle aspiration (FNA) |
|
|
| Positron emission tomography (PET) |
|
|
| Modality | AI Model | Study Population | Purpose | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT | CNN | 27 | Pancreatic cystic neoplasm malignancy prediction | - | - | 92.9 | Watson et al., 2021 [102] |
| CT | Naïve Bayer classifier | 72 | PDAC identification | - | - | 86 | Ahamed et al., 2022 [103] |
| CT | CNN | 1006 | Pancreas segmentation | - | - | - | Lim et al., 2022 [104] |
| CT | CNN | 68 | Serum tumor marker analysis | 89.31 | 92.31 | - | Qiao et al., 2022 [105] |
| CT | CNN | 513 | Pancreatico enteric Anastomotic Fistulas prediction after a pancreatoduodenectomy | 86.7 | 87.3 | 87.1 | Mu et al., 2020 [106] |
| CT | ANN | 62 | Acute pancreatitis risk prediction | - | - | - | Keogan et al., 2002 [107] |
| CT | Support vector machine | 56 | PDAC histopathological grade discrimination | 78 | 95 | 86 | Qiu et al., 2019 [108] |
| CT | CNN | 370 patients, 320 controls | PC detection | 97.3 (Test set 1) 99 (Test set 2) | 100 (Test set 1) 98.9 (Test set 2) | 98.6(Test set 1) 98.9 (Test set 2) | Liu et al., 2020 [109] |
| CT | Deep learning | 750 patients 575 controls | PDAC detection | - | - | 87.8 | Chu et al., 2019 [110] |
| CT | CNN | 222 patients 190 controls | PC diagnosis | 91.58 | 98.27 | 95.47 | Ma et al., 2020 [89] |
| CT | DCNN | 2890 CT images | Pancreatic cancer detection | 83.76 | 91.79 | 94 | Zhang et al., 2020 [90] |
| CT | Deep learning | 319 | Preoperative pancreatic cancer diagnosis | 86.8 | 69.5 | 87.1 | Si et al., 2021 [111] |
| CT | ANN | 898 | Cancer risk prediction | 80.7 | 80.7 | - | Muhammad et al., 2019 [112] |
| CT | CNN | 669 patients 804 controls | PC differentiation | 89.7 | 92.8 | - | Chen et al., 2022 [91] |
| MRI | CNN | 139 | Identification of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia | 75 | 78 | - | Juan et al., 2019 [78] |
| MRI | CNN | 27 | Automatic image segmentation | - | - | - | Liang et al., 2020 [113] |
| MRI | ANN | 168 | PDAC differentiation | - | - | 96 | Devi et al., 2018 [114] |
| EUS | CNN | 583 | Autoimmune pancreatitis from PDAC | 90 | 85 | - | Marya et al., 2021 [115] |
| EUS | CAD | 920 (Validation) +470 (test) | PDAC detection | - | - | - | Tonozuka et al., 2021 [67] |
| EUS | ANN | 202 (cancerous) & 130 (Non-cancerous) | Computer-aided pancreatic cancer diagnosis using image processing | 83.3 | 93.3 | 87.5 | Ozkan et al., 2019 [65] |
| EUS | ANN | 258 | Pancreatic lesion characterization | - | - | 91 | Saftoiu et al., 2012 [34] |
| EUS | ANN | 388 | PDAC and CP differentiation | 96 | 93 | 94 | Zhu et al., 2013 [63] |
| EUS | ANN | 167 | PDAC and CP differentiation | 94 | 94 | - | Saftoiu et al., 2015 [116] |
| EUS | ANN | 56 | Normal, CP and PDAC differentiation | - | - | 93 | Das et al., 2008 [64] |
| EUS | ANN | 21 | PDAC and CP differentiation | - | - | 89 | Norton et al., 2001 [62] |
| PET/CT | SVM | 80 | Pancreatic cancer segmentation | 95.23 | 97.51 | 96.47 | Li et al., 2018 [100] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hameed, B.S.; Krishnan, U.M. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215382
Hameed BS, Krishnan UM. Artificial Intelligence-Driven Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215382
Chicago/Turabian StyleHameed, Bahrudeen Shahul, and Uma Maheswari Krishnan. 2022. "Artificial Intelligence-Driven Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215382
APA StyleHameed, B. S., & Krishnan, U. M. (2022). Artificial Intelligence-Driven Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 14(21), 5382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215382