Targeted Deletion of Kindlin-2 in Mouse Mammary Glands Inhibits Tumor Growth, Invasion, and Metastasis Downstream of a TGF-β/EGF Oncogenic Signaling Pathway
Abstract
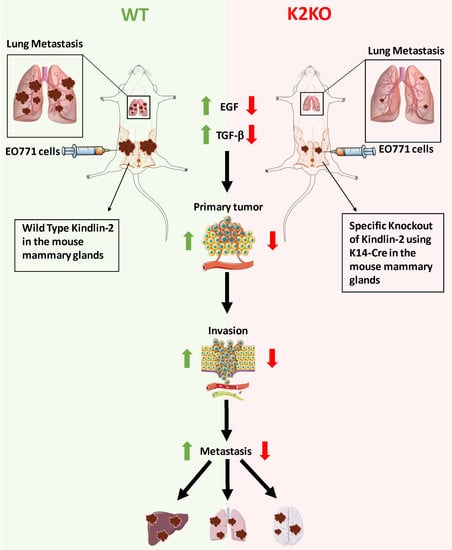
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell Lines and Reagents
2.3. Generation of the Fermt2 Conditional Knockout Mouse Strain
2.4. Primary Tumor Growth and Metastasis Assays
2.5. Mammary Glands Whole Mounts
2.6. Isolation of Mammary Epithelial Cells
2.7. Immunofluorescence Assays and Confocal Microscopy Analyses
2.8. Three-Dimensional Tumorsphere Growth and Invasion Assays
2.9. Antibodies
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Generation of the Fermt2 Floxed Mouse
3.2. Tissue Specific Deletion of Fermt2 in Mammary Glands
3.3. Loss of Kindlin-2 in Basal Mammary Epithelial Cells Has No Deleterious Effects on Mammary Gland Development, Mouse Development and Fertility
3.4. Loss of Kindlin-2 Inhibits the Oncogenic Behavior of E0771 TNBC Cells In Vitro and In Vivo
3.5. Kindlin-2 Regulates the TGF-β/EGF Signaling Axis in MECs to Support Breast Cancer Tumor Growth in Mammary Glands
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Fukuda, K.; Xu, Z.; Ma, Y.Q.; Hirbawi, J.; Mao, X.; Wu, C.; Plow, E.F.; Qin, J. Structural basis of phosphoinositide binding to kindlin-2 protein pleckstrin homology domain in regulating integrin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43334–43342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, S.; Zhang, R. Crystal structure of kindlin-2 PH domain reveals a conformational transition for its membrane anchoring and regulation of integrin activation. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perera, H.D.; Ma, Y.Q.; Yang, J.; Hirbawi, J.; Plow, E.F.; Qin, J. Membrane binding of the N-terminal ubiquitin-like domain of kindlin-2 is crucial for its regulation of integrin activation. Structure 2011, 19, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metcalf, D.G.; Moore, D.T.; Wu, Y.; Kielec, J.M.; Molnar, K.; Valentine, K.G.; Wand, A.J.; Bennett, J.S.; DeGrado, W.F. NMR analysis of the alphaIIb beta3 cytoplasmic interaction suggests a mechanism for integrin regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22481–22486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larjava, H.; Plow, E.F.; Wu, C. Kindlins: Essential regulators of integrin signalling and cell-matrix adhesion. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, M.; Nieswandt, B.; Ussar, S.; Pozgajova, M.; Fassler, R. Kindlin-3 is essential for integrin activation and platelet aggregation. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinin, N.L.; Plow, E.F.; Byzova, T.V. Kindlins in FERM adhesion. Blood 2010, 115, 4011–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussar, S.; Moser, M.; Widmaier, M.; Rognoni, E.; Harrer, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; Fassler, R. Loss of Kindlin-1 causes skin atrophy and lethal neonatal intestinal epithelial dysfunction. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moser, M.; Bauer, M.; Schmid, S.; Ruppert, R.; Schmidt, S.; Sixt, M.; Wang, H.V.; Sperandio, M.; Fassler, R. Kindlin-3 is required for beta2 integrin-mediated leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, J.J.; Gibbs, E.; Russell, M.; Goldman, D.; Minarcik, J.; Golden, J.A.; Feldman, E.L. Kindlin-2 is an essential component of intercalated discs and is required for vertebrate cardiac structure and function. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pluskota, E.; Dowling, J.J.; Gordon, N.; Golden, J.A.; Szpak, D.; West, X.Z.; Nestor, C.; Ma, Y.Q.; Bialkowska, K.; Byzova, T.; et al. The integrin coactivator kindlin-2 plays a critical role in angiogenesis in mice and zebrafish. Blood 2011, 117, 4978–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, J.; Luan, W.; Lu, L.; Zhang, S.; Qi, F. Knockdown of the KINDLIN-2 Gene and Reduced Expression of Kindlin-2 Affects Vascular Permeability in Angiogenesis in a Mouse Model of Wound Healing. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5376–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Jiao, H.; Lai, Y.; Zheng, W.; Chen, K.; Qu, H.; Deng, W.; Song, P.; Zhu, K.; Cao, H.; et al. Kindlin-2 controls TGF-beta signalling and Sox9 expression to regulate chondrogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cattaneo, P.; Veevers, J.; Peter, A.K.; Manso, A.M.; Knowlton, K.U.; Zhou, X.; et al. Kindlin-2 Is Essential for Preserving Integrity of the Developing Heart and Preventing Ventricular Rupture. Circulation 2019, 139, 1554–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluskota, E.; Ma, Y.; Bledzka, K.M.; Bialkowska, K.; Soloviev, D.A.; Szpak, D.; Podrez, E.A.; Fox, P.L.; Hazen, S.L.; Dowling, J.J.; et al. Kindlin-2 regulates hemostasis by controlling endothelial cell-surface expression of ADP/AMP catabolic enzymes via a clathrin-dependent mechanism. Blood 2013, 122, 2491–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pluskota, E.; Bledzka, K.M.; Bialkowska, K.; Szpak, D.; Soloviev, D.A.; Jones, S.V.; Verbovetskiy, D.; Plow, E.F. Kindlin-2 interacts with endothelial adherens junctions to support vascular barrier integrity. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 6443–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, D.H.; Ashton, G.H.; Penagos, H.G.; Lee, J.V.; Feiler, H.S.; Wilhelmsen, K.C.; South, A.P.; Smith, F.J.; Prescott, A.R.; Wessagowit, V.; et al. Loss of kindlin-1, a human homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans actin-extracellular-matrix linker protein UNC-112, causes Kindler syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mory, A.; Feigelson, S.W.; Yarali, N.; Kilic, S.S.; Bayhan, G.I.; Gershoni-Baruch, R.; Etzioni, A.; Alon, R. Kindlin-3: A new gene involved in the pathogenesis of LAD-III. Blood 2008, 112, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malinin, N.L.; Zhang, L.; Choi, J.; Ciocea, A.; Razorenova, O.; Ma, Y.Q.; Podrez, E.A.; Tosi, M.; Lennon, D.P.; Caplan, A.I.; et al. A point mutation in KINDLIN3 ablates activation of three integrin subfamilies in humans. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plow, E.F.; Das, M.; Bialkowska, K.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. Of Kindlins and Cancer. Discoveries (Craiova) 2016, 4, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Kansakar, U.; Markovic, V.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. Role of Kindlin-2 in cancer progression and metastasis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Zhang, H. Kindlins: Roles in development and cancer progression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2018, 98, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Pluskota, E.; Szpak, D.; Plow, E.F. The Kindlin2-p53-SerpinB2 signaling axis is required for cellular senescence in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Pluskota, E.; Szpak, D.; Schiemann, W.P.; Plow, E.F. The Kindlin-2 regulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer metastasis is mediated through miR-200b. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Pluskota, E.; Bialkowska, K.; Szpak, D.; Parker, Y.; Morrison, C.D.; Lindner, D.J.; Schiemann, W.P.; Plow, E.F. Kindlin-2 Regulates the Growth of Breast Cancer Tumors by Activating CSF-1-Mediated Macrophage Infiltration. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5129–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Kato, Y.; Brownlie, D.; Soong, D.Y.H.; Sugano, G.; Kippen, N.; Li, J.; Doughty-Shenton, D.; Carragher, N.; Pollard, J.W. Mammary Tumor Cells with High Metastatic Potential Are Hypersensitive to Macrophage-Derived HGF. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 2052–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, G.W.; McKnight, R.A.; Smith, G.H.; Hennighausen, L. Mammary epithelial cells undergo secretory differentiation in cycling virgins but require pregnancy for the establishment of terminal differentiation. Development 1995, 121, 2079–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, P.S.; Kurokawa, M.; Model, M.A. Evidence for macromolecular crowding as a direct apoptotic stimulus. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs243931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialkowska, K.; Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Pluskota, E.; Izem, L.; Qin, J.; Plow, E.F. Site-specific phosphorylation regulates the functions of kindlin-3 in a variety of cells. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 3, e201900594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansakar, U.; Wang, W.; Markovic, V.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. Phosphorylation of the proline-rich domain of WAVE3 drives its oncogenic activity in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kansakar, U.; Markovic, V.; Wang, B.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. WAVE3 phosphorylation regulates the interplay between PI3K, TGF-beta, and EGF signaling pathways in breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, A.E.; Laster, W.R., Jr.; Ross, G.L. Sustained enhanced growth of carcinoma EO771 in C57 black mice. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1951, 77, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, C.N.; Smith, Y.E.; Cao, Y.; Burrows, A.D.; Cross, R.S.; Ling, X.; Redvers, R.P.; Doherty, J.P.; Eckhardt, B.L.; Natoli, A.L.; et al. Functional and molecular characterisation of EO771.LMB tumours, a new C57BL/6-mouse-derived model of spontaneously metastatic mammary cancer. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Plow, E.F. miR-138-Mediated Regulation of KINDLIN-2 Expression Modulates Sensitivity to Chemotherapeutics. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bledzka, K.; Bialkowska, K.; Sossey-Alaoui, K.; Vaynberg, J.; Pluskota, E.; Qin, J.; Plow, E.F. Kindlin-2 directly binds actin and regulates integrin outside-in signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 213, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guy, C.T.; Cardiff, R.D.; Muller, W.J. Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: A transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992, 12, 954–961. [Google Scholar]
- Sinn, E.; Muller, W.; Pattengale, P.; Tepler, I.; Wallace, R.; Leder, P. Coexpression of MMTV/v-Ha-ras and MMTV/c-myc genes in transgenic mice: Synergistic action of oncogenes in vivo. Cell 1987, 49, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, A.S.; Grosschedl, R.; Guzman, R.C.; Parslow, T.; Varmus, H.E. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell 1988, 55, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.J.; Massague, J. Contextual determinants of TGFbeta action in development, immunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Schiemann, W.P. The TGF-beta paradox in human cancer: An update. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bierie, B.; Moses, H.L. Tumour microenvironment: TGFbeta: The molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godbout, E.; Son, D.O.; Hume, S.; Boo, S.; Sarrazy, V.; Clement, S.; Kapus, A.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Has, C.; et al. Kindlin-2 Mediates Mechanical Activation of Cardiac Myofibroblasts. Cells 2020, 9, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschberg, R. Kindlin-2: A new player in renal fibrogenesis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1339–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, H.; Tu, Y.; Shi, X.; Larjava, H.; Saleem, M.A.; Shattil, S.J.; Fukuda, K.; Qin, J.; Kretzler, M.; Wu, C. Kindlin-2 regulates podocyte adhesion and fibronectin matrix deposition through interactions with phosphoinositides and integrins. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, J.; Song, J.; Wang, P.; Chi, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fang, W.; Zhang, H. Kindlin-2 induced by TGF-beta signaling promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through downregulation of transcriptional factor HOXB9. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Xia, Y.; Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Nie, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hou, F.F. Kindlin-2 mediates activation of TGF-beta/Smad signaling and renal fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Primer Name | Primer Sequence | PCR Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| K2 Floxed 5′ F | 5′-CTT CCC TCA GTG ATG GAG TGT GAT CTG AG-3′ | 230/264 |
| K2 Floxed 5′ R | 5′-GGA GTC AGA GAG AAT GGG CAC TCT AGG TG-3′ | |
| K2 Floxed 3′ F | 5′-CTA AAG CAG GCA GGT TGC CTG GAC-3′ | 288/322 |
| K2 Floxed 3′ R | 5′-CTC TTA CCC ACT GAG CCA TCT CAC C-3′ | |
| K2 Del F | 5′-CCC TCA GTG ATG GAG TGT GAT-3′ | 404 |
| K2 Del R | 5′-AAG AGG GCG TCA GAT TTC GTT-3′ | |
| K14 Cre Tg F | 5′-GCG GTC TGG CAG TAA AAA CTA TC-3′ | 100 |
| K14 Cre Tg R | 5′-GTG AAA CAG CAT TGC TGT CAC TT-3′ | |
| K2 RT Ex1 F | 5′-CGG GAC TCC ATT AGC AGC G-3′ | 2201/457 |
| K2 RT Ex 15 R | 5′-TTC CTA TTC ACA CCC AAC CAC T-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Rana, P.S.; Alkrekshi, A.; Bialkowska, K.; Markovic, V.; Schiemann, W.P.; Plow, E.F.; Pluskota, E.; Sossey-Alaoui, K. Targeted Deletion of Kindlin-2 in Mouse Mammary Glands Inhibits Tumor Growth, Invasion, and Metastasis Downstream of a TGF-β/EGF Oncogenic Signaling Pathway. Cancers 2022, 14, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030639
Wang W, Rana PS, Alkrekshi A, Bialkowska K, Markovic V, Schiemann WP, Plow EF, Pluskota E, Sossey-Alaoui K. Targeted Deletion of Kindlin-2 in Mouse Mammary Glands Inhibits Tumor Growth, Invasion, and Metastasis Downstream of a TGF-β/EGF Oncogenic Signaling Pathway. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030639
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wei, Priyanka S. Rana, Akram Alkrekshi, Katarzyna Bialkowska, Vesna Markovic, William P. Schiemann, Edward F. Plow, Elzbieta Pluskota, and Khalid Sossey-Alaoui. 2022. "Targeted Deletion of Kindlin-2 in Mouse Mammary Glands Inhibits Tumor Growth, Invasion, and Metastasis Downstream of a TGF-β/EGF Oncogenic Signaling Pathway" Cancers 14, no. 3: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030639
APA StyleWang, W., Rana, P. S., Alkrekshi, A., Bialkowska, K., Markovic, V., Schiemann, W. P., Plow, E. F., Pluskota, E., & Sossey-Alaoui, K. (2022). Targeted Deletion of Kindlin-2 in Mouse Mammary Glands Inhibits Tumor Growth, Invasion, and Metastasis Downstream of a TGF-β/EGF Oncogenic Signaling Pathway. Cancers, 14(3), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030639