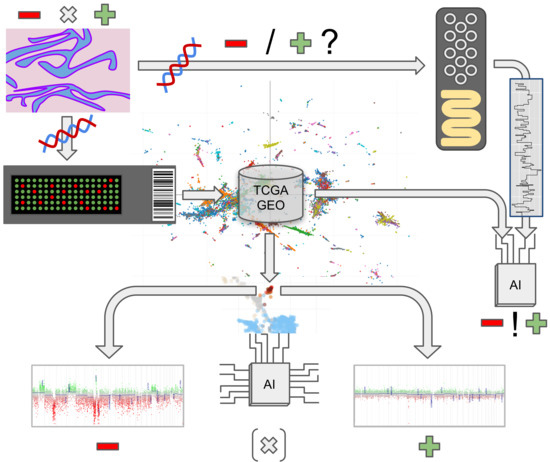
An Integrated Epigenomic and Genomic View on Phyllodes and Phyllodes-like Breast Tumors
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Collection
2.2. Methylation and Copy Number Analysis
2.3. Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.4. Nanopore Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Patient Outcome
3.3. DNA Methylation and Copy Number Changes
3.4. Overlapping Methylation Patterns of Phyllodes Tumors and Fibroadenomas
3.5. Copy Number Alterations in Phyllodes Tumors and Fibroadenomas
3.6. Proof-of-Concept Experiment Using Nanopore Sequencing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Kleer, C.G. Phyllodes Tumor of the Breast: Histopathologic Features, Differential Diagnosis, and Molecular/Genetic Updates. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer. WHO Classification of Tumours. In Breast Tumours, 5th ed.; Lokuhetty, D., White, V.A., Watanabe, R., Cree, I.A., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2019; ISBN 978-92-832-4500-1. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.Y.; Acs, G.; Apple, S.K.; Badve, S.; Bleiweiss, I.J.; Brogi, E.; Calvo, J.P.; Dabbs, D.J.; Ellis, I.O.; Eusebi, V.; et al. Phyllodes Tumours of the Breast: A Consensus Review. Histopathology 2016, 68, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdalla, H.M.; Sakr, M.A. Predictive Factors of Local Recurrence and Survival Following Primary Surgical Treatment of Phyllodes Tumors of the Breast. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 18, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Sill, M.; Hovestadt, V.; Schrimpf, D.; Sturm, D.; Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Chavez, L.; Reuss, D.E.; et al. DNA Methylation-Based Classification of Central Nervous System Tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euskirchen, P.; Bielle, F.; Labreche, K.; Kloosterman, W.P.; Rosenberg, S.; Daniau, M.; Schmitt, C.; Masliah-Planchon, J.; Bourdeaut, F.; Dehais, C.; et al. Same-Day Genomic and Epigenomic Diagnosis of Brain Tumors Using Real-Time Nanopore Sequencing. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, S.; Martínez-Cardús, A.; Sayols, S.; Musulén, E.; Balañá, C.; Estival-Gonzalez, A.; Moutinho, C.; Heyn, H.; Diaz-Lagares, A.; de Moura, M.C.; et al. Epigenetic Profiling to Classify Cancer of Unknown Primary: A Multicentre, Retrospective Analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djirackor, L.; Halldorsson, S.; Niehusmann, P.; Leske, H.; Capper, D.; Kuschel, L.P.; Pahnke, J.; Due-Tønnessen, B.J.; Langmoen, I.A.; Sandberg, C.J.; et al. Intraoperative DNA Methylation Classification of Brain Tumors Impacts Neurosurgical Strategy. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Classification of Tumours, Revised 4th ed. In WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System; Louis, D.N., Ohgaki, H., Wiestler, O.D., Cavenee, W.K., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2016; ISBN 978-92-832-4492-9. [Google Scholar]
- Koelsche, C.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Sill, M.; Sahm, F.; Reuss, D.E.; Blattner, M.; Worst, B.; Heilig, C.E.; Beck, K.; et al. Sarcoma Classification by DNA Methylation Profiling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuschel, L.P.; Hench, J.; Frank, S.; Hench, I.B.; Girard, E.; Blanluet, M.; Masliah-Planchon, J.; Misch, M.; Onken, J.; Czabanka, M.; et al. Robust Methylation-Based Classification of Brain Tumors Using Nanopore Sequencing. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, J.; Hultschig, C. NanoDiP—Nanopore Digital Pathology. Available online: https://github.com/neuropathbasel/nanodip (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.03426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing Data Using T-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger, S.; Tzankov, A.; Frank, S.; Bihl, M.; Vallejo, A.; Stebler, J.; Hench, J. NUT Midline Carcinomas and Their Differentials by a Single Molecular Profiling Method: A New Promising Diagnostic Strategy Illustrated by a Case Report. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2020, 478, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, C.; Jaszczuk, P.; Hund-Georgiadis, M.; Frank, S.; Cordier, D.; Hench, I.B.; Todea, A.; Wasilewski, A.; Wilmes, S.; Grigioni, G.; et al. Differentiation of Rare Brain Tumors through Unsupervised Machine Learning: Clinical Significance of in-Depth Methylation and Copy Number Profiling Illustrated through an Unusual Case of IDH Wildtype Glioblastoma. Clin. Neuropathol. 2020, 40, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, J.; Frank, S. EpiDiP Server. Available online: http://www.epidip.org (accessed on 27 May 2021).
- Jurmeister, P.; Schöler, A.; Arnold, A.; Klauschen, F.; Lenze, D.; Hummel, M.; Schweizer, L.; Bläker, H.; Pfitzner, B.M.; Mamlouk, S.; et al. DNA Methylation Profiling Reliably Distinguishes Pulmonary Enteric Adenocarcinoma from Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurmeister, P.; Bockmayr, M.; Seegerer, P.; Bockmayr, T.; Treue, D.; Montavon, G.; Vollbrecht, C.; Arnold, A.; Teichmann, D.; Bressem, K.; et al. Machine Learning Analysis of DNA Methylation Profiles Distinguishes Primary Lung Squamous Cell Carcinomas from Head and Neck Metastases. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahm, F.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Jones, D.T.; Hielscher, T.; Schefzyk, S.; Okonechnikov, K.; Koelsche, C.; Reuss, D.E.; Capper, D.; et al. DNA Methylation-Based Classification and Grading System for Meningioma: A Multicentre, Retrospective Analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweizer, L.; Thierfelder, F.; Thomas, C.; Soschinski, P.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jödicke, R.; Woltering, N.; Förster, A.; Teichmann, D.; Siewert, C.; et al. Molecular Characterisation of Sporadic Endolymphatic Sac Tumours and Comparison to von Hippel-Lindau Disease-Related Tumours. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2021, 47, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maros, M.E.; Capper, D.; Jones, D.T.W.; Hovestadt, V.; von Deimling, A.; Pfister, S.M.; Benner, A.; Zucknick, M.; Sill, M. Machine Learning Workflows to Estimate Class Probabilities for Precision Cancer Diagnostics on DNA Methylation Microarray Data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 479–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Stichel, D.; Sahm, F.; Jones, D.T.W.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Schmid, S.; Hovestadt, V.; Reuss, D.E.; Koelsche, C.; et al. Practical Implementation of DNA Methylation and Copy-Number-Based CNS Tumor Diagnostics: The Heidelberg Experience. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 181–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Stichel, D.; Hielscher, T.; Sievers, P.; Berghoff, A.S.; Schrimpf, D.; Sill, M.; Euskirchen, P.; Blume, C.; Patel, A.; et al. Integrated Molecular-Morphologic Meningioma Classification: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis, Retrospectively and Prospectively Validated. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3839–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, N.; Hübschmann, D.; Toprak, U.H.; Ishaque, N.; Neidert, M.; Schrimpf, D.; Stichel, D.; Reuss, D.; Sievers, P.; Reinhardt, A.; et al. Mutational Patterns and Regulatory Networks in Epigenetic Subgroups of Meningioma. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, E.; Capper, D. Invited Review: DNA Methylation-based Classification of Paediatric Brain Tumours. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2020, 46, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortin, J.-P.; Triche, T.J.; Hansen, K.D. Preprocessing, Normalization and Integration of the Illumina HumanMethylationEPIC Array with Minfi. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksimovic, J.; Gordon, L.; Oshlack, A. SWAN: Subset-Quantile Within Array Normalization for Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChips. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hovestadt, V.; Zapatka, M. Conumee (R 3.6.3), Bioconductor; German Cancer Research Center: Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stichel, D. CNsummaryplots. Available online: https://github.com/dstichel/CNsummaryplots (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- Mohd Ali, N.A.; Nasaruddin, A.F.; Mohamed, S.S.; Wan Rahman, W.F. Ki67 and P53 Expression in Relation to Clinicopathological Features in Phyllodes Tumour of the Breast. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2020, 21, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitus, J.; Adamczyk, A.; Majchrzyk, K.; Kowalik, A.; Rys, J.; Niemiec, J. Comparison of Mutation Profile between Primary Phyllodes Tumors of the Breast and Their Paired Local Recurrences. Pol. J. Pathol. 2020, 71, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.J.; Lai, J.C.; Thike, A.A.; Lim, J.C.T.; Tan, S.Y.; Koh, V.C.Y.; Lim, T.H.; Bay, B.H.; Tan, M.-H.; Tan, P.H. Novel Genetic Aberrations in Breast Phyllodes Tumours: Comparison between Prognostically Distinct Groups. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 145, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, C.; Kuijper, A.; Schmidt, H.; Packeisen, J.; Liedtke, C.; Tidow, N.; Gustmann, C.; Hinrichs, B.; Wülfing, P.; Tio, J.; et al. Amplifications of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene (Egfr) Are Common in Phyllodes Tumors of the Breast and Are Associated with Tumor Progression. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2006, 86, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| GEO ID | Sentrix ID | Histology | Methylation Category | Age at Diagnosis | Follow-Up (Months) | Recurrent Disease | CNV Aberrations | Confirmed by FISH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSM5418497 | 203293640041_R07C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 50 | 6 | yes | 1 gain | |
| GSM5418498 | 203271740040_R08C01 | PT NOS | PHYT_NOS | 64 | NA | 1q gain | ||
| GSM5418499 | 203259060045_R04C01 | benign PT | PHYT_NOS | 59 | 81 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418500 | 203259600099_R07C01 | borderline PT | PHYT_BOR | 65 | 30 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418501 | 203259600099_R06C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 72 | 91 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418502 | 203271740040_R01C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 21 | NA | 1q gain | ||
| GSM5418503 | 203257020148_R07C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_NOS | 66 | 48 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418504 | 203253040182_R07C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 50 | 135 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418505 | 203293640041_R06C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 50 | 122 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418506 | 203244490194_R06C01 | borderline PT | PHYT_NOS | 83 | 60 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418507 | 203946830053_R07C01 | benign PT | PHYT_NOS | 40 | 15 | no | 1q gain | |
| GSM5418508 | 203836210043_R03C01 | benign PT | PHYT_BEN | 54 | 1q gain | |||
| GSM5418509 | 203836210043_R04C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 51 | NA | 1q gain, EGFR amp., RB1 del. | RB1 del., EGFR ampl. | |
| GSM5418510 | 203836210043_R07C01 | benign or borderline PT | PHYT_NOS | 51 | NA | 1q gain, MDM4 amplification, EGFR amp. | EGFR ampl. | |
| GSM5418511 | 203259600099_R05C01 | benign PT | PHYT_BEN | 69 | NA | 1q/MDM4 gain | ||
| GSM5418512 | 203259060045_R01C01 | benign PT | PHYT_BEN | 60 | NA | CDKN2a/b deletion | ||
| GSM5418513 | 203271740040_R07C01 | benign PT | PHYT_MAL | 50 | NA | CDKN2a/b deletion | ||
| GSM5418514 | 203808570131_R05C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 48 | 36 | yes | CDKN2a/b deletion | CDKN2a/b deletion |
| GSM5418515 | 203271740040_R02C01 | benign PT | PHYT_BEN | 42 | NA | MDM4 gain | ||
| GSM5418516 | 203271740040_R03C01 | benign PT | PHYT_BEN | 46 | NA | MDM4 gain | ||
| GSM5418517 | 203259060045_R02C01 | borderline PT | PHYT_NOS | 82 | NA | MDM4 gain, CDKN2a/b deletion | ||
| GSM5418518 | 203271740040_R06C01 | benign PT | PHYT_BEN | 36 | 65 | yes | MDM4 gain, CDKN2a/b deletion | CDKN2a/b deletion |
| GSM5418519 | 203271740040_R05C01 | FA | BR_FAD | 38 | MDM4 gain, malignant-looking CNV | |||
| GSM5418520 | 203293640041_R03C01 | benign PT | PHYT_MAL | 64 | 204 | no | RB1 deletion | RB1 deletion |
| GSM5418521 | 203253040182_R08C01 | malignant PT | PHYT_MAL | 83 | NA | susp. 1q gain (bad DNA) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hench, J.; Vlajnic, T.; Soysal, S.D.; Obermann, E.C.; Frank, S.; Muenst, S. An Integrated Epigenomic and Genomic View on Phyllodes and Phyllodes-like Breast Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030667
Hench J, Vlajnic T, Soysal SD, Obermann EC, Frank S, Muenst S. An Integrated Epigenomic and Genomic View on Phyllodes and Phyllodes-like Breast Tumors. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030667
Chicago/Turabian StyleHench, Juergen, Tatjana Vlajnic, Savas Deniz Soysal, Ellen C. Obermann, Stephan Frank, and Simone Muenst. 2022. "An Integrated Epigenomic and Genomic View on Phyllodes and Phyllodes-like Breast Tumors" Cancers 14, no. 3: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030667
APA StyleHench, J., Vlajnic, T., Soysal, S. D., Obermann, E. C., Frank, S., & Muenst, S. (2022). An Integrated Epigenomic and Genomic View on Phyllodes and Phyllodes-like Breast Tumors. Cancers, 14(3), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030667