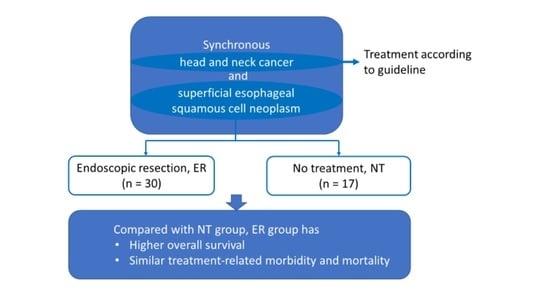
Synchronous Head and Neck Cancer and Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasm: Endoscopic Treatment or No Treatment for the Superficial Esophageal Neoplasm
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Clinical Staging
2.3. Treatments
2.4. Follow-Up
2.5. Definitions in This Study
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Treatment-Related Complications
3.2. The Outcomes of the Patients
3.3. Factors Associated with Poor Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, H.; Brown, R.E. Field effect in cancer-an update. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 39, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-C.; Huang, W.-C.; Chan, C.H.; Chen, P.-T.; Lee, K.-D. Impact of second primary esophageal or lung cancer on survival of patients with head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2010, 46, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.S.; Lo, W.C.; Chen, K.C.; Lin, C.L.; Wen, M.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, S.C.; Liao, L.J. Clinical benefits from endoscopy screening of esophageal second primary tumor for head and neck cancer patients: Analysis of a hospital-based registry. Oral Oncol. 2019, 96, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, H.Y.; Gong, E.J.; Na, H.K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.S.; Choi, K.D.; et al. Clinical significance of early detection of esophageal cancer in patients with head and neck cancer. Gut Liver 2015, 9, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Lu, H.I.; Chien, C.Y.; Lo, C.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Chou, S.Y.; Su, Y.Y.; Shih, L.H.; Li, S.H. Treatment Outcomes of Patients with Locally Advanced Synchronous Esophageal and Head/Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Receiving Curative Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shen, C.; Hu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, X. Long-term treatment results and prognostic factors of synchronous and metachronous squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck and esophagus. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Chuang, H.C.; Guo, C.S.; Lin, Y.T.; Luo, S.D.; Fang, F.M.; Chien, C.Y. Effect of routine esophageal screening in patients with head and neck cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, E.J.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Choi, K.S.; Jung, K.W.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.D.; Song, H.J.; Lee, G.H.; Jung, H.Y.; et al. Routine endoscopic screening for synchronous esophageal neoplasm in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective study. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Chang, C.Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Tai, C.M.; Wang, W.L.; Tseng, P.H.; Hwang, J.C.; Hwang, T.Z.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, J.T. Narrow-band imaging with magnifying endoscopy for the screening of esophageal cancer in patients with primary head and neck cancers. Endoscopy 2010, 42, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, C.L.; Iriya, K.; Baba, E.R.; Navarro-Rodriguez, T.; Zerbini, M.C.; Eisig, J.N.; Barbuti, R.; Chinzon, D.; Moraes-Filho, J.P. Lugol’s dye spray chromoendoscopy establishes early diagnosis of esophageal cancer in patients with primary head and neck cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, B.; Machiels, J.P.; Kim, H.R.; Licitra, L.; Golusinski, W.; Gregoire, V.; Lee, Y.G.; Belka, C.; Guo, Y.; Rajappa, S.J.; et al. Pan-Asian adaptation of the EHNS-ESMO-ESTRO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, Y.; Uno, T.; Oyama, T.; Kato, K.; Kato, H.; Kawakubo, H.; Kawamura, O.; Kusano, M.; Kuwano, H.; Takeuchi, H.; et al. Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2017 edited by the Japan esophageal society: Part 2. Esophagus 2019, 16, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.H.; Ou, C.Y.; Lee, W.T.; Lee, Y.; Chang, T.; Yen, Y.T. Treatment outcomes for one-stage concurrent surgical resection and reconstruction of synchronous esophageal and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 2929–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chen, B.H.; Lee, C.H.; Le, P.H.; Tsou, Y.K.; Lin, C.H. cT1N0M0 Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invades the Muscularis Mucosa or Submucosa: Comparison of the Results of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection and Esophagectomy. Cancers 2022, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.W.; Lee, H.; Song, B.G.; Min, B.H.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, N.Y.; Carriere, K.C.; Rhee, P.L.; et al. Comparison of endoscopic submucosal dissection and surgery for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A propensity score-matched analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 88, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.F.; Li, Q.; Yao, L.; Korrapati, P.; Jin, X.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; et al. Outcomes of Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection vs Esophagectomy for T1 Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Real-World Cohort. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 73–81.e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Fujita, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Kato, M.; Asaka, M. Long-term outcome after endoscopic mucosal resection in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma invading the muscularis mucosae or deeper. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, Y.K.; Chuang, W.Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Ohata, K.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, M.S.; Cheng, H.T.; Chiu, C.T. Learning curve for endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal neoplasms. Dis. Esophagus 2016, 29, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, R.; Mitani, H.; Yonekawa, H.; Fukushima, H.; Sasaki, T.; Shimbashi, W.; Seto, A.; Koizumi, Y.; Ebina, A.; Kawabata, K. A Clinical Study of Pharyngolaryngectomy with Total Esophagectomy: Postoperative Complications, Countermeasures, and Prognoses. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 153, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Watanabe, M.; Mine, S.; Nishida, K.; Shigaki, H.; Kawabata, K.; Yanaga, K.; Sano, T. Comparison of synchronous versus staged surgeries for patients with synchronous double cancers of the esophagus and head-and-neck. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoto, M.; Shioyama, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Nakamura, K.; Ohura, H.; Toh, Y.; Higaki, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ohnishi, K.; Atsumi, K.; et al. Clinical results of definitive chemoradiotherapy for patients with synchronous head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and esophageal cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 34, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Ogino, I.; Inayama, Y.; Sugiura, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Kokawa, A.; Kunisaki, C.; Inoue, T. Impact of the early detection of esophageal neoplasms in hypopharyngeal cancer patients treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 13, e3–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, R.N.; Arantes, V.N.; Ribeiro, T.M.L.; Guimarães, R.G.; de Oliveira, J.F.; Kulcsar, M.A.V.; Sallum, R.A.A.; Ribeiro-Junior, U.; Maluf-Filho, F. Does a history of head and neck cancer affect outcome of endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma? Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E900–E910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Watanabe, M.; Shigaki, H.; Nishida, K.; Mine, S.; Sano, T.; Yanaga, K. Efficacy of Staged Treatment Strategy for Patients with Synchronous Double Cancers of the Esophagus and Head and Neck: A Retrospective Study. World J. Surg. 2016, 40, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Overall (n = 47) | ER Group (n = 30) | No-Treatment Group (n = 17) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range), years | 53 (35–71) | 52 (45–68) | 53 (35–71) | 0.061 |
| Sex, male | 46 (97.9%) | 30 (100%) | 16 (94.1%) | 0.362 |
| CCI score, median (range) | 3 (2–8) | 3 (2–6) | 3 (2–8) | 0.041 |
| ECOG PS score | 0.042 | |||
| ≤1, n | 44 (93.6%) | 30 (100.0%) | 14 (82.4%) | |
| >2, n | 3 (6.4%) | 0 | 3 (17.6) | |
| Location of HNC | 0.412 | |||
| Oropharynx, n | 9 (19.1%) | 5 (16.7%) | 4 (23.5%) | |
| Hypopharynx, n | 21 (44.7%) | 14 (46.7%) | 7 (41.2%) | |
| Larynx, n | 1 (2.1%) | 0 | 1 (5.9%) | |
| Oral cavity, n | 10 (21.3%) | 8 (26.7%) | 2 (11.8%) | |
| Multicentric, n | 5 (10.6%) | 3 (10.0%) | 2 (11.8%) | |
| Unknown of primary, n | 1 (2.1%) | 0 | 1 (5.9%) | |
| Location of SESCN | 0.094 | |||
| Cervical, n | 1 (2.1%) | 1 (3.3%) | 0 | |
| Upper third, n | 5 (10.6%) | 4 (13.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | |
| Middle third, n | 18 (38.3%) | 13 (43.3%) | 5 (29.4%) | |
| Lower third, n | 16 (34.0%) | 6 (20.2%) | 10 (58.8%) | |
| Multiple, n | 7 (14.9%) | 6 (20.2%) | 1 (5.9%) | |
| Clinical stage of HNC | 0.752 | |||
| Stage I + II, n | 13 (27.7%) | 9 (30.0%) | 4 (23.5%) | |
| Stage III + IV, n | 34 (72.3%) | 21 (70.0%) | 13 (76.5%) | |
| Stage III/IV, n | 4/30 | 3/18 | 1/12 | |
| Clinical T-stage of SESCN | 1.000 | |||
| Tis or T1a, n | 43 (91.5%) | 27 (90.0%) | 16 (94.1%) | |
| T1b, n | 4 (8.5%) | 3 (10.0%) | 1 (5.9%) | |
| Initial treatment for HNC | 0.074 | |||
| Surgery | 16 (34.0%) | 13 (43.3%) | 3 (17.6%) | |
| CCRT | 31 (66.0%) | 17 (56.7%) | 14 (82.4%) |
| Overall (n = 47) | ER Group (n = 30) | No-Tx Group (n = 17) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment-related complications | ||||
| Hospitalized with complications, n | 7 (14.9%) | 3 (10.0%) | 4 (23.5%) | 0.235 |
| Grade 5 †, n | 2 (4.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1.000 |
| Mucositis Grade 3–4 †, n | 6 (12.8%) | 2 (6.7%) | 4 (23.5%) | 0.170 |
| Dermatitis Grade 3–4 †, n | 8 (17.0%) | 5 (16.7%) | 3 (17.6%) | 1.000 |
| Neutropenia Grade 3–4 †, n | 5 (10.6%) | 4 (13.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0.640 |
| Anemia Grade 3–4 †, n | 8 (17.0%) | 3 (10.0%) | 5 (29.4%) | 0.118 |
| Thrombocytopenia Grade 3–4 †, n | 1 (2.1%) | 0 | 1 (5.9%) | 0.362 |
| Upper aerodigestive tract stricture | 8 (17.0%) | 7 (23.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0.228 |
| Outcomes | ||||
| Disease progression-HNC | 15 (31.9%) | 6 (20.0%) | 9 (52.9%) | 0.027 |
| Disease progression-SESCN | 4 (8.5%) | 1 (3.3%) | 3 (17.6%) | 0.128 |
| Died of HNC, n | 14 (29.8%) | 6 (20.0%) | 8 (47.1%) | 0.095 |
| Died of SESCN, n | 2 (4.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 1 |
| All-cause mortality, n | 28 (59.6%) | 16 (53.3%) | 12 (70.6%) | 0.356 |
| 1-year overall survival | 74.5% | 83.3% | 58.8% | 0.047 |
| 3-year overall survival | 55.3% | 66.7% | 35.3% | 0.019 |
| 5-year overall survival | 31.9% | 43.3% | 11.8% | 0.044 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Age, per year increase | 0.996 (0.947–1.048) | 0.892 | ||
| CCI score, per score increase | 1.417 (1.067–1.883) | 0.016 | 1.111 (0.809–1.525) | 0.516 |
| ECOG PS score | ||||
| ≤1 | 1 | |||
| >1 | 12.541 (3.034–51.095) | 0.001 | 11.745 (1.786–77.251) | 0.010 |
| Multicentric HNC at diagnosis | ||||
| Single | 1 | |||
| Multiple | 2.375 (0.813–6.940) | 0.114 | ||
| Clinical stage of HNC | ||||
| Stage I + II | 1 | |||
| Stage III + IV | 1.890 (0.764–4.678) | 0.169 | ||
| Clinical T-stage of SESCN | ||||
| Tis + T1a | 1 | |||
| T1b | 2.869 (0.966–8.515) | 0.058 | 2.324 (0.708–7.631) | 0.164 |
| Treatment for HNC | ||||
| Surgery | 1 | |||
| CCRT | 1.707 (0.720–4.045) | 0.224 | ||
| Treatment for SESCN | ||||
| ER | 1 | |||
| No treatment | 2.106 (0.980–4.522) | 0.056 | 1.080 (0.438–2.667) | 0.867 |
| HNC disease progression | ||||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 5.191 (2.302–11.705) | 0.001 | 4.492 (1.753–11.509) | 0.002 |
| SESCN disease progression | ||||
| No | 1 | |||
| Yes | 1.340 (0.403–4.459) | 0.663 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.-W.; Chen, B.-H.; Yeh, C.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Le, P.-H.; Tsou, Y.-K.; Chiu, C.-T. Synchronous Head and Neck Cancer and Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasm: Endoscopic Treatment or No Treatment for the Superficial Esophageal Neoplasm. Cancers 2023, 15, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041079
Liu C-W, Chen B-H, Yeh C-J, Lee C-H, Le P-H, Tsou Y-K, Chiu C-T. Synchronous Head and Neck Cancer and Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasm: Endoscopic Treatment or No Treatment for the Superficial Esophageal Neoplasm. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041079
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chung-Wei, Bo-Huan Chen, Chi-Ju Yeh, Cheng-Han Lee, Puo-Hsien Le, Yung-Kuan Tsou, and Cheng-Tang Chiu. 2023. "Synchronous Head and Neck Cancer and Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasm: Endoscopic Treatment or No Treatment for the Superficial Esophageal Neoplasm" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041079
APA StyleLiu, C. -W., Chen, B. -H., Yeh, C. -J., Lee, C. -H., Le, P. -H., Tsou, Y. -K., & Chiu, C. -T. (2023). Synchronous Head and Neck Cancer and Superficial Esophageal Squamous Cell Neoplasm: Endoscopic Treatment or No Treatment for the Superficial Esophageal Neoplasm. Cancers, 15(4), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041079