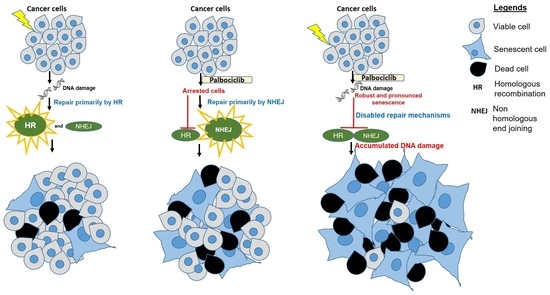
CDK4/6 Inhibition Induces Senescence and Enhances Radiation Response by Disabling DNA Damage Repair in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Palbociclib
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Gamma Irradiator
2.5. Culture Treatment
2.6. Clonogenic Survival Assay
2.7. Determination of Drug-Radiation Combination Index Using Compusyn Analysis
2.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.9. Senescence Associated (SA)-β-Galactosidase Staining
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Transient Knockdowns-siRNA Transfections
2.12. RNA Isolation
2.13. Real Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.14. Spheroid Models for Immortalized Lines
2.15. Establishing Patient-Derived Tumor Cell Culture via Conditional Reprogramming
2.16. Treatment Validation in Patient-Derived Tumor Organoid Models
2.17. Culture Treatment of Immortalized and CR Organoid Models
2.18. Trypan Blue Assay
2.19. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Palbociclib Reduces Cell Proliferation and Results in Synergy When Combined with Radiation in HNSCC
3.2. Palbociclib Induces G1 Arrest and Potentiates Senescence When Combined with Radiation
3.3. A Concurrent Palbociclib and Radiation Treatment Induces DNA Damage and Diminishes DDR Activity
3.4. CDK4/CDK6 Knockdown Combined with Radiation Leads to Senescence and Synergism
3.5. Palbociclib Combined with Radiation Reduces Proliferation and Size of OCSCC 3D Culture Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pignon, J.P.; Bourhis, J.; Domenge, C.; Designé, L. Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: Three meta-analyses of updated individual data. MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-Analysis of Chemotherapy on Head and Neck Cancer. Lancet 2000, 355, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, J.S.; Pajak, T.F.; Forastiere, A.A.; Jacobs, J.; Campbell, B.H.; Saxman, S.B.; Kish, J.A.; Kim, H.E.; Cmelak, A.J.; Rotman, M.; et al. Postoperative concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy for high-risk squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferris, R.L.; Blumenschein, G.; Fayette, J.; Guigay, J.; Colevas, A.D.; Licitra, L.; Harrington, K.; Kasper, S.; Vokes, E.E.; Even, C.; et al. Nivolumab for Recurrent Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Burtness, B.; Mehra, R.; Weiss, J.; Berger, R.; Eder, J.P.; Heath, K.; McClanahan, T.; Lunceford, J.; Gause, C.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, L.; Lam, T.; Chen, A.; Jensen, C.; Duncan, L.; Kong, F.-C.; Kurago, Z.B.; Shay, C.; Teng, Y. Circumventing AKT-Associated Radioresistance in Oral Cancer by Novel Nanoparticle-Encapsulated Capivasertib. Cells 2020, 9, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, N.; Frederick, M.J.; Pickering, C.R.; Bettegowda, C.; Chang, K.; Li, R.J.; Fakhry, C.; Xie, T.-X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Exome Sequencing of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Reveals Inactivating Mutations in NOTCH1. Science 2011, 333, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stransky, N.; Egloff, A.M.; Tward, A.D.; Kostic, A.D.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lawrence, M.S.; Sougnez, C.; McKenna, A.; et al. The mutational landscape of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Science 2011, 333, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.-L.; Yang, L.-Y.; Hsieh, J.C.-H.; Lin, T.-C.; Lu, M.-Y.J.; Liao, C.-T. Prognostic Genetic Biomarkers Based on Oncogenic Signaling Pathways for Outcome Prediction in Patients with Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leemans, C.R.; Braakhuis, B.J.M.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Münger, K.; Basile, J.R.; Duensing, S.; Eichten, A.; Gonzalez, S.L.; Grace, M.; Zacny, V.L. Biological activities and molecular targets of the human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7888–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Münger, K. The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Virology 2009, 384, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, L.; Ke, N.; Hydbring, P.; Choi, Y.J.; Widlund, H.R.; Chick, J.M.; Zhai, H.; Vidal, M.; Gygi, S.P.; Braun, P.; et al. A systematic screen for CDK4/6 substrates links FOXM1 phosphorylation to senescence suppression in cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 2011, 20, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Mann, D.; Sinha, U.K.; Kokot, N.C. The molecular mechanisms of increased radiosensitivity of HPV-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC): An extensive review. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 47, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forastiere, A.A.; Goepfert, H.; Maor, M.; Pajak, T.F.; Weber, R.; Morrison, W.; Glisson, B.; Trotti, A.; Ridge, J.A.; Chao, C.; et al. Concurrent Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Organ Preservation in Advanced Laryngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2091–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernier, J.; Domenge, C.; Ozsahin, M.; Matuszewska, K.; Lefèbvre, J.-L.; Greiner, R.H.; Giralt, J.; Maingon, P.; Rolland, F.; Bolla, M.; et al. Postoperative Irradiation with or without Concomitant Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seiwert, T.Y.; Cohen, E.E.W. State-of-the-art management of locally advanced head and neck cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marur, S.; D’Souza, G.; Westra, W.H.; Forastiere, A.A. HPV-associated head and neck cancer: A virus-related cancer epidemic. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ettl, J.; Harbeck, N. The safety and efficacy of palbociclib in the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2017, 17, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Scott, L.J. Palbociclib: A Review in HR-Positive, HER2-Negative, Advanced or Metastatic Breast Cancer. Target Oncol. 2017, 12, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Leu, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-S.; Lian, J.-H.; Hsieh, H.-L.; Chen, C.-Y. Palbociclib induces DNA damage and inhibits DNA repair to induce cellular senescence and apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadsden, N.J.; Fulcher, C.D.; Li, D.; Shrivastava, N.; Thomas, C.; Segall, J.E.; Prystowsky, M.B.; Schlecht, N.F.; Gavathiotis, E.; Ow, T.J. Palbociclib Renders Human Papilloma Virus–Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Vulnerable to the Senolytic Agent Navitoclax. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Zheng, W.; Chen, T.; Lin, W.; Liao, Z.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y. CDK4/6 Inhibitor Palbociclib Amplifies the Radiosensitivity to Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells via Mediating Apoptosis and Suppressing DNA Damage Repair. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11107–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Göttgens, E.-L.; Bussink, J.; Leszczynska, K.B.; Peters, H.; Span, P.N.; Hammond, E.M. Inhibition of CDK4/CDK6 Enhances Radiosensitivity of HPV Negative Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 105, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Patel, N.H.; Saleh, T.; Cudjoe, E.K.; Alotaibi, M.; Wu, Y.; Lima, S.; Hawkridge, A.M.; Gewirtz, D.A. Differential Radiation Sensitivity in p53 Wild-Type and p53-Deficient Tumor Cells Associated with Senescence but not Apoptosis or (Nonprotective) Autophagy. Radiat. Res. 2018, 190, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, R.; Pilpel, N.; Tokarsky-Amiel, R.; Biran, A.; Ovadya, Y.; Cohen, S.; Vadai, E.; Dassa, L.; Shahar, E.; Condiotti, R.; et al. Directed elimination of senescent cells by inhibition of BCL-W and BCL-XL. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkarah, A.R.; Ali-Fehmi, R.; Jiang, J.Z.; Elhammady, E.; Malone, J.M.; Saed, G.M. The effects of combining docetaxel and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on proliferation and apoptosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2007, 18, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Alexander, P.B.; Wang, X.-F. Cellular senescence: From anti-cancer weapon to anti-aging target. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Feng, W.; Li, H.; Gardner, D.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Meng, A.; Sharpless, N.E.; Zhou, D. Total body irradiation causes long-term mouse BM injury via induction of HSC premature senescence in an Ink4a- and Arf-independent manner. Blood 2014, 123, 3105–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarrard, D.F.; Sarkar, S.; Shi, Y.; Yeager, T.R.; Magrane, G.; Kinoshita, H.; Nassif, N.; Meisner, L.; Newton, M.A.; Waldman, F.M.; et al. p16/pRb pathway alterations are required for bypassing senescence in human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Sano, D.; Pickering, C.R.; Jasser, S.A.; Henderson, Y.C.; Clayman, G.L.; Sturgis, E.M.; Ow, T.J.; Lotan, R.; Carey, T.E.; et al. Assembly and initial characterization of a panel of 85 genomically validated cell lines from diverse head and neck tumor sites. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7248–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, K.; Peters, T.; Nawroth, T.; Sänger, M.; Schmidberger, H.; Langguth, P. Determination of cell survival after irradiation via clonogenic assay versus multiple MTT Assay—A comparative study. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leonard, C.E.; Chan, D.C.; Chou, T.C.; Kumar, R.; Bunn, P.A. Paclitaxel enhances in vitro radiosensitivity of squamous carcinoma cell lines of the head and neck. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 5198–5204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Fu, J.-N.; Chou, T.-C. Synergistic combination of microtubule targeting anticancer fludelone with cytoprotective panaxytriol derived from panax ginseng against MX-1 cells in vitro: Experimental design and data analysis using the combination index method. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, T.-C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Thomas, C.; Shrivastava, N.; Gersten, A.; Gadsden, N.; Schlecht, N.; Kawachi, N.; Schiff, B.A.; Smith, R.V.; Rosenblatt, G.; et al. Establishment of a diverse head and neck squamous cancer cell bank using conditional reprogramming culture methods. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28388. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.28388 (accessed on 23 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Correa, B.R.S.; Hu, J.; Penalva, L.O.F.; Schlegel, R.; Rimm, D.L.; Galante, P.A.F.; Agarwal, S. Patient-derived conditionally reprogrammed cells maintain intra-tumor genetic heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlik, T.M.; Keyomarsi, K. Role of cell cycle in mediating sensitivity to radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2004, 59, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billard-Sandu, C.; Tao, Y.-G.; Sablin, M.-P.; Dumitrescu, G.; Billard, D.; Deutsch, E. CDK4/6 inhibitors in P16/HPV16-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; DeCristo, M.J.; McAllister, S.S.; Zhao, J.J. CDK4/6 Inhibition in Cancer: Beyond Cell Cycle Arrest. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 911–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, H.D.; Sandulache, V.C.; Ow, T.J.; Meyn, R.E.; Yordy, J.S.; Beadle, B.M.; Fitzgerald, A.L.; Giri, U.; Ang, K.K.; Myers, J.N. TP53 Disruptive Mutations Lead to Head and Neck Cancer Treatment Failure through Inhibition of Radiation-Induced Senescence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ewald, J.A.; Desotelle, J.A.; Wilding, G.; Jarrard, D.F. Therapy-Induced Senescence in Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campisi, J.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. Cellular senescence: When bad things happen to good cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P. Sensing and repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, B.H.; Powell, S.N. Molecular Pathways: Understanding the Role of Rad52 in Homologous Recombination for Therapeutic Advancement. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6400–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Segura, A.; Nehme, J.; Demaria, M. Hallmarks of Cellular Senescence. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 436–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, J.; Hall, E.J.; Giaccia, A. Radiation oncology: A century of achievements. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasin, M.; Rothstein, R. Repair of Strand Breaks by Homologous Recombination. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherr, C.J.; Beach, D.; Shapiro, G.I. Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From Discovery to Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasch, C.A.; Favreau, P.F.; Yueh, A.E.; Babiarz, C.P.; Gillette, A.A.; Sharick, J.T.; Karim, M.R.; Nickel, K.P.; DeZeeuw, A.K.; Sprackling, C.M.; et al. Patient-Derived Cancer Organoid Cultures to Predict Sensitivity to Chemotherapy and Radiation. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5376–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drost, J.; Clevers, H. Organoids in cancer research. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrivastava, N.; Chavez, C.G.; Li, D.; Mehta, V.; Thomas, C.; Fulcher, C.D.; Kawachi, N.; Bottalico, D.M.; Prystowsky, M.B.; Basu, I.; et al. CDK4/6 Inhibition Induces Senescence and Enhances Radiation Response by Disabling DNA Damage Repair in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072005
Shrivastava N, Chavez CG, Li D, Mehta V, Thomas C, Fulcher CD, Kawachi N, Bottalico DM, Prystowsky MB, Basu I, et al. CDK4/6 Inhibition Induces Senescence and Enhances Radiation Response by Disabling DNA Damage Repair in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072005
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrivastava, Nitisha, Claudia Gutierrez Chavez, Daniel Li, Vikas Mehta, Carlos Thomas, Cory D. Fulcher, Nicole Kawachi, Danielle M. Bottalico, Michael B. Prystowsky, Indranil Basu, and et al. 2023. "CDK4/6 Inhibition Induces Senescence and Enhances Radiation Response by Disabling DNA Damage Repair in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072005
APA StyleShrivastava, N., Chavez, C. G., Li, D., Mehta, V., Thomas, C., Fulcher, C. D., Kawachi, N., Bottalico, D. M., Prystowsky, M. B., Basu, I., Guha, C., & Ow, T. J. (2023). CDK4/6 Inhibition Induces Senescence and Enhances Radiation Response by Disabling DNA Damage Repair in Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 15(7), 2005. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072005