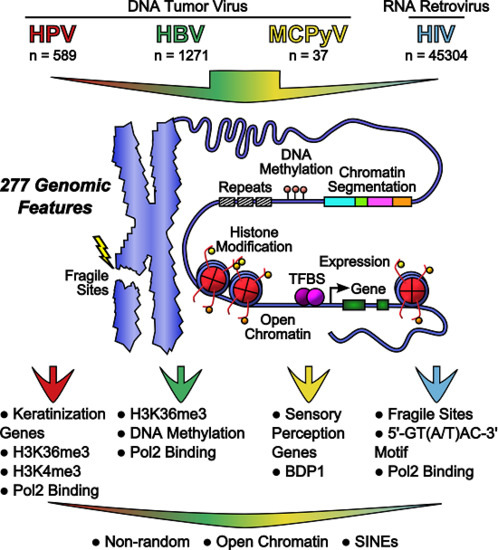
Meta-Analysis of DNA Tumor-Viral Integration Site Selection Indicates a Role for Repeats, Gene Expression and Epigenetics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Catalog of Viral Integration Sites
2.2. Viral Integration Hotspots

2.3. Evidence of Viral Integration Bias in Functional Genes

2.4. No Evidence for Preferential Integration of DNA Tumor Viruses in CFSs
2.5. Tumor Viral Integration Did Not Require Sequence Preference
2.6. Feature Scoring and Data Integration

2.7. Genomic Features Were Associated with Integration
| Category | Gene Presence | Gene Expression | Open Chromatin | Histone Modifications | DNA Methylation | TF and Other Protein Binding | Chromatin Segmentation | Repeats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Type | GENCODE, COSMIC Cancer Gene Census | RNA-seq | DNase-seq, FAIRE-seq | ChIP-seq | Methyl-RRBS | ChIP-seq | Hoffman et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. | UCSC repeat masker |
| Data Source | hg19 | HeLa *, SiHa, NHEK *, HepG2 *, GM12878 * | HeLa *, NHEK *, HepG2 *, GM12878 * | HeLa *, NHEK *, HepG2 *, GM12878 * | HeLa *, HepG2 *, GM12878 * | HeLa *, NHEK *, HepG2 *, GM12878 * | HeLa *, HepG2 *, GM12878 * | hg19 |
| Scoring Method | Number of genes | Sum of RPKM | Number of peaks | Number of peaks | Percent Methylated | Number of peaks | Length of segment | Length of repeat |
| Number of Features | 2 | 5 | 8 | 44 | 3 | 178 | 21 | 16 |

2.8. Genomic Features Predicted Integration

2.9. HPV and HBV Integrations Differ among Classes

3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Detection of HPV-16 Integration in Oral Cancer
4.2. Catalog of Viral Integration Sites
4.3. Hotspots
4.4. GO Term Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Fragile Sites
4.6. Random Sites
4.7. Motif Finding
4.8. Genomic Feature Scoring
4.9. Statistical Analysis
4.10. Selection of Features to Classify Integration and Random Sites
4.11. Cell Culture
4.12. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.13. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Quantification via qPCR
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berry, C.; Hannenhalli, S.; Leipzig, J.; Bushman, F.D. Selection of target sites for mobile DNA integration in the human genome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, J.; Akhtar, W.; Badhai, J.; Rust, A.G.; Rad, R.; Hilkens, J.; Berns, A.; van Lohuizen, M.; Wessels, L.F.A.; de Ridder, J. Chromatin landscapes of retroviral and transposon integration profiles. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, N.; Dong, B.; Boren, D.; Lee, S.A.; Das Gupta, J.; Gaughan, C.; Klein, E.A.; Lee, C.; Silverman, R.H.; et al. Integration site preference of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus, a new human retrovirus associated with prostate cancer. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9964–9977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, T.; Agosto, L.; Malani, N. HIV integration site distributions in resting and activated CD4+ T cells infected in culture. AIDS 2009, 23, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martel, C.; Ferlay, J.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Plummer, M. Global burden of cancers attributable to infections in 2008: A review and synthetic analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Engels, E.A.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Xiao, W.; Kim, E.; Jiang, B.; Goodman, M.T.; Sibug-Saber, M.; Cozen, W.; et al. Human papillomavirus and rising oropharyngeal cancer incidence in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4294–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feitelson, M.A.; Lee, J. Hepatitis B virus integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Chen, P.-J.; Hou, J.; McCrae, M.A.; et al. Re-evaluation of the carcinogenic significance of hepatitis B virus integration in hepatocarcinogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Jantin, C.; Filippone, C.; Cassar, O.; Peter, M.; Tomasic, G.; Vielh, P.; Brière, J.; Petrella, T.; Aubriot-Lorton, M.H.; Mortier, L.; et al. Genetic variability and integration of Merkel cell polyomavirus in Merkel cell carcinoma. Virology 2012, 426, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P. Clonal integration of a polyomavirus in human Merkel cell carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Lambert, P.F. Integration of human papillomavirus type 16 DNA into the human genome leads to increased stability of E6 and E7 mRNAs: Implications for cervical carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1654–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Bonura, C.; Giannini, C.; Mouly, H.; Soussan, P.; Kew, M.; Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Brechot, C.; Kremsdorf, D. Biological impact of natural COOH-terminal deletions of hepatitis B virus X protein in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7803–7810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shuda, M.; Feng, H.; Kwun, H.J.; Rosen, S.T.; Gjoerup, O.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. T antigen mutations are a human tumor-specific signature for Merkel cell polyomavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16272–16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, M.; Rosty, C.; Couturier, J.; Radvanyi, F.; Teshima, H.; Sastre-Garau, X. MYC activation associated with the integration of HPV DNA at the MYC locus in genital tumors. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5985–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, W.-K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.-C.; Sun, T.; Ching, A.K.K.; He, M.; Li, J.-W.; Wong, A.M.; Co, N.N.; Chan, A.W.H.; Li, P.-S.; Lung, R.W.M.; et al. Viral-human chimeric transcript predisposes risk to liver cancer development and progression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lace, M.J.; Anson, J.R.; Klussmann, J.P.; Wang, D.H.; Smith, E.M.; Haugen, T.H.; Turek, L.P. Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16) genomes integrated in head and neck cancers and in HPV-16-immortalized human keratinocyte clones express chimeric virus-cell mRNAs similar to those found in cervical cancers. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, K.; Li, J.; Broutian, T.R.; Padilla-Nash, H.; Xiao, W.; Jiang, B.; Rocco, J.W.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, B.; Wangsa, D.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of HPV integration in human cancers reveals recurrent, focal genomic instability. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorland, E.C.; Myers, S.L.; Gostout, B.S.; Smith, D.I. Common fragile sites are preferential targets for HPV16 integrations in cervical tumors. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1225–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, M.J.; Thorland, E.C.; Brink, A.A.; Rapp, A.K.; Phillips, L.A.; McGovern, R.; Gostout, B.S.; Cheung, T.H.; Chung, T.K.; Fu, W.Y.; et al. Preferential integration of human papillomavirus type 18 near the c-myc locus in cervical carcinoma. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7233–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentzensen, N.; Vinokurova, S.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M. Systematic review of genomic integration sites of human papillomavirus genomes in epithelial dysplasia and invasive cancer of the female lower genital tract. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3878–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, C.M.; Hall, B.K.; Hoge, A.; Paradee, W.; Smith, D.I.; Glover, T.W. FRA3B extends over a broad region and contains a spontaneous HPV16 integration site: Direct evidence for the coincidence of viral integration sites and fragile sites. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimov, E.; Vinokourova, S.; Moisjak, E.; Rakhmanaliev, E.; Kobseva, V.; Laimins, L.; Kisseljov, F.; Sulimova, G. Human papilloma viruses and cervical tumours: Mapping of integration sites and analysis of adjacent cellular sequences. BMC Cancer 2002, 2, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.P.; Ciuffi, A.; Leipzig, J.; Berry, C.C.; Bushman, F.D. HIV integration site selection: Analysis by massively parallel pyrosequencing reveals association with epigenetic modifications. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferber, M.J.; Montoya, D.P.; Yu, C.; Aderca, I.; McGee, A.; Thorland, E.C.; Nagorney, D.M.; Gostout, B.S.; Burgart, L.J.; Boix, L.; et al. Integrations of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human papillomavirus (HPV) into the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene in liver and cervical cancers. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3813–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, J.; Sastre-Garau, X.; Schneider-Maunoury, S.; Labib, A.; Orth, G. Integration of papillomavirus DNA near myc genes in genital carcinomas and its consequences for proto-oncogene expression. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 4534–4538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Kang, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; Li, M.; Lv, Q.; Chen, X.; et al. The function of targeted host genes determines the oncogenicity of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, T.A.; McLaughlin, S.; Garg, K.; Cheung, C.Y.K.; Larsen, B.B.; Styrchak, S.; Huang, H.C.; Edlefsen, P.T.; Mullins, J.I.; Frenkel, L.M. Proliferation of cells with HIV integrated into cancer genes contributes to persistent infection. Science 2014, 345, 570–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterlini-Bréchot, P.; Saigo, K.; Murakami, Y.; Chami, M.; Gozuacik, D.; Mugnier, C.; Lagorce, D.; Bréchot, C. Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis occurs frequently in human liver cancers and recurrently targets human telomerase gene. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3911–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegert, C.; Wentzensen, N.; Vinokurova, S.; Kisseljov, F.; Einenkel, J.; Hoeckel, M.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M. A comprehensive analysis of HPV integration loci in anogenital lesions combining transcript and genome-based amplification techniques. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3977–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luft, F.; Klaes, R.; Nees, M.; Dürst, M.; Heilmann, V.; Melsheimer, P.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M. Detection of integrated papillomavirus sequences by ligation-mediated PCR (DIPS-PCR) and molecular characterization in cervical cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Lou, X.; Hua, D.; Yu, W.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, F.; Zhao, N.; Ren, G.; Li, L.; et al. Recurrent targeted genes of hepatitis B virus in the liver cancer genomes identified by a next-generation sequencing-based approach. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1003065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, M.; Driesch, C.; Jansen, L.; Runnebaum, I.B.; Dürst, M. Non-random integration of the HPV genome in cervical cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandegraaff, N.; Engelman, A. Molecular mechanisms of HIV integration and therapeutic intervention. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2007, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presson, A.P.; Kim, N.; Xiaofei, Y.; Chen, I.S.; Kim, S. Methodology and software to detect viral integration site hot-spots. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraus, I.; Driesch, C.; Vinokurova, S.; Hovig, E.; Schneider, A.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M.; Dürst, M. The majority of viral-cellular fusion transcripts in cervical carcinomas cotranscribe cellular sequences of known or predicted genes. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigo, K.; Yoshida, K.; Ikeda, R.; Sakamoto, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Urashima, T.; Asano, T.; Kenmochi, T.; Inoue, I. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL4) gene and rearrangements of MLL4 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Crise, B.; Burgess, S.M.; Munroe, D.J. Weak palindromic consensus sequences are a common feature found at the integration target sites of many retroviruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 5211–5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, A.G.; Coffin, J.M. Symmetrical base preferences surrounding HIV-1, avian sarcoma/leukosis virus, and murine leukemia virus integration sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6103–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentzensen, N.; Ridder, R.; Klaes, R. Characterization of viral-cellular fusion transcripts in a large series of HPV16 and 18 positive anogenital lesions. Oncogene 2002, 21, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shimazaki, N.; Lieber, M.R. Histone methylation and V(D)J recombination. Int. J. Hematol. 2014, 100, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieci, G.; Fiorino, G.; Castelnuovo, M.; Teichmann, M.; Pagano, A. The expanding RNA polymerase III transcriptome. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Liu, J.; Haverty, P.M.; Kennemer, M.I.; Guan, Y.; Lee, W.; Carnevali, P.; Stinson, J.; Johnson, S.; et al. The effects of hepatitis B virus integration into the genomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldarelli, F.; Wu, X.; Su, L.; Simonetti, F.R.; Shao, W.; Hill, S.; Spindler, J.; Ferris, A.L.; Mellors, J.W.; Kearney, M.F.; et al. Specific HIV integration sites are linked to clonal expansion and persistence of infected cells. Science 2014, 345, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall, K.L.; Scarpini, C.G.; Roberts, I.; Winder, D.M.; Stanley, M.A.; Muralidhar, B.; Herdman, M.T.; Pett, M.R.; Coleman, N. Characterization of naturally occurring HPV16 integration sites isolated from cervical keratinocytes under noncompetitive conditions. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8249–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Maunakea, A.K.; Martin, M.M.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ryan, M.; Kim, R.; Lin, C.M.; Zhao, K.; Aladjem, M.I. Methylation of histone H3 on lysine 79 associates with a group of replication origins and helps limit DNA replication once per cell cycle. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, D.B.; Oda, H.; Shen, S.S.; Reinberg, D. PR-Set7 and H4K20me1: At the crossroads of genome integrity, cell cycle, chromosome condensation, and transcription. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Lu, Z.; Kurosawa, A.; Klemm, L.; Bagshaw, A.T.; Tsai, A.G.; Gemmell, N.; Müschen, M.; Adachi, N.; Hsieh, C.-L.; et al. Both CpG methylation and activation-induced deaminase are required for the fragility of the human bcl-2 major breakpoint region: Implications for the timing of the breaks in the t(14;18) translocation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, D.-M.; Petersen-Mahrt, S.K. AID and APOBEC deaminases: Balancing DNA damage in epigenetics and immunity. Epigenomics 2014, 6, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Takashima, H.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Bréchot, C.; Paterlini-Bréchot, P. Large scaled analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2005, 54, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonilla Guerrero, R.; Roberts, L.R. The role of hepatitis B virus integrations in the pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 760–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, W.J. BLAT—The BLAST-Like Alignment Tool. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Durinck, S.; Moreau, Y.; Kasprzyk, A.; Davis, S.; de Moor, B.; Brazma, A.; Huber, W. BioMart and Bioconductor: A powerful link between biological databases and microarray data analysis. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3439–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durinck, S.; Spellman, P.T.; Birney, E.; Huber, W. Mapping identifiers for the integration of genomic datasets with the R/Bioconductor package biomaRt. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. topGO: Enrichment analysis for Gene Ontology, R package version 2.14.0. 2010.
- Lukusa, T.; Fryns, J.P. Human chromosome fragility. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, S.; Benner, C.; Spann, N.; Bertolino, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Laslo, P.; Cheng, J.X.; Murre, C.; Singh, H.; Glass, C.K. Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrow, J.; Frankish, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Diekhans, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Aken, B.L.; Barrell, D.; Zadissa, A.; Searle, S.; et al. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futreal, P.A.; Coin, L.; Marshall, M.; Down, T.; Hubbard, T.; Wooster, R.; Rahman, N.; Stratton, M.R. A census of human cancer genes. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.M.; Ernst, J.; Wilder, S.P.; Kundaje, A.; Harris, R.S.; Libbrecht, M.; Giardine, B.; Ellenbogen, P.M.; Bilmes, J.A.; Birney, E.; et al. Integrative annotation of chromatin elements from ENCODE data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Liaw, W.H.A.; Lumley, T.; Maechler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Moeller, S.; Schwartz, M.; et al. gplots: Various R Programming Tools for Plotting Data. 2015; R package version 2.6.0. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M.; Wing, J.; Weston, S.; Williams, A.; Keefer, C.; Engelhardt, A.; Cooper, T.; Mayer, Z.; the R Core Team. caret: Classification and Regression Training. Astrophysics Source Code Library, 2014; R package version 6.0-30. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doolittle-Hall, J.M.; Cunningham Glasspoole, D.L.; Seaman, W.T.; Webster-Cyriaque, J. Meta-Analysis of DNA Tumor-Viral Integration Site Selection Indicates a Role for Repeats, Gene Expression and Epigenetics. Cancers 2015, 7, 2217-2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7040887
Doolittle-Hall JM, Cunningham Glasspoole DL, Seaman WT, Webster-Cyriaque J. Meta-Analysis of DNA Tumor-Viral Integration Site Selection Indicates a Role for Repeats, Gene Expression and Epigenetics. Cancers. 2015; 7(4):2217-2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7040887
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoolittle-Hall, Janet M., Danielle L. Cunningham Glasspoole, William T. Seaman, and Jennifer Webster-Cyriaque. 2015. "Meta-Analysis of DNA Tumor-Viral Integration Site Selection Indicates a Role for Repeats, Gene Expression and Epigenetics" Cancers 7, no. 4: 2217-2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7040887
APA StyleDoolittle-Hall, J. M., Cunningham Glasspoole, D. L., Seaman, W. T., & Webster-Cyriaque, J. (2015). Meta-Analysis of DNA Tumor-Viral Integration Site Selection Indicates a Role for Repeats, Gene Expression and Epigenetics. Cancers, 7(4), 2217-2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers7040887