Radiation-Induced Changes of microRNA Expression Profiles in Radiosensitive and Radioresistant Leukemia Cell Lines with Different Levels of Chromosome Abnormalities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Viability
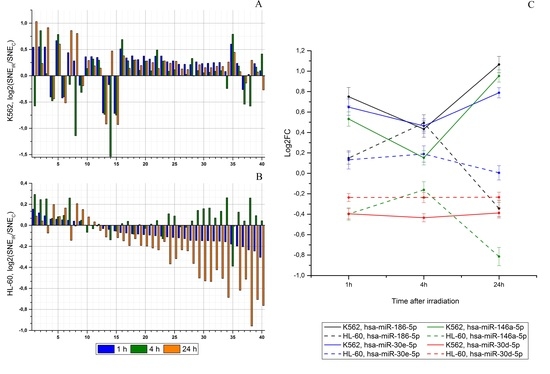
2.2. Radiation-Induced Changes in microRNA Expression
2.3. microRNA Effects on Signaling Pathway Activity
2.4. An Effect of Chromosome Abnormality on microRNA Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
- (1)
- the HL-60 cell line, a radiosensitive human promyelocytic leukemia cells (karyotype 44,X,−Х,−5,dic(5;17)(q11;p11),del(7)(p?),der(7)t(5;7)(q11;q?31),t(5;16)(q11;q?),add(8)(q?),der(9)del(9)(p2?),t(9;14)(q2?;q2?),del(10)(p?),ins(11;8)(q13?;?),der(14)t(14;15)(q1?;q?),−15,der(16)t(5;16)(q?;q?22~24),der(16)t(7;16)(?;q?22~24),+18) [26];
- (2)
- the К562 cell line, a radioresistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells (karyotype 67,X,−X,+1,der(2)add(2)(q33),+4,+5,der(?)t(5;6),dup(6)(p12~p22),−7,inv(7),del(7)(p15),der(7)readel(7),+8,−9,−9,dup(9)(q34),del(9)(p12),der(10)t(3;10),der(10,17)t(3;10;17),+11,der(?)t(6;11),−12,der(12)t(12;19),der(12)t(12;21),der(?)t(12;19),−13,der(13)t(9;13),+15,+16,−17,der(17)t(9;17)×2,−19,der(19)t(2;19),der(?)t(19;20),der(22)(q11.2),del(X)(p11)) [25].
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaliberov, S.; Buchsbaum, D. Cancer Treatment with Gene Therapy and Radiation Therapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2012, 115, 221–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, S.M.; Butz, L.; Stegen, B.; Klumpp, D.; Braun, N.; Ruth, P.; Eckert, F. Ionizing radiation, ion transports, and radioresistance of cancer cells. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomax, M.E.; Folkes, L.K.; O’Neill, P. Biological Consequences of Radiation-induced DNA Damage: Relevance to Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 25, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyn, R.E.; Stephens, C.; Milas, L. Programmed cell death and radioresistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1996, 15, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.V.; Leblanc, M.; Wade, M.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Wahl, G.M. Increased Radioresistance and Accelerated B Cell Lymphomas in Mice with Mdmx Mutations that Prevent Modifications by DNA-Damage-Activated Kinases. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Koyama-Saegusa, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Ishikawa, A.; Kawai, S.; Yasuda, K.; Suga, T.; Michikawa, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Iwakawa, M.; et al. Gene expression profile changes correlating with radioresistance in human cell lines. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 65, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, M.D.; Lund, A.H. microRNA and cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metheetrairut, C.; Slack, F.J. microRNAs in the Ionizing Radiation Response and in Radiotherapy. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013, 23, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Qiu, Y.; Su, Z.; Ren, S.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Y. Genome-wide analyses of radioresistance-associated miRNA expression profile in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using next generation deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Ren, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, T.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; et al. A specific miRNA signature promotes radioresistance of human cervical cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Deng, X.; Shen, L.; Fang, Y.; Xie, C. Identification of microRNAs involved in the radioresistance of esophageal cancer cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Moskwa, P.; Zinn, P.O.; Hirshman, B.R.; Choi, Y.E.; Shukla, S.A.; Fendler, W.; Lu, J.; Golub, T.R.; Hjelmeland, A.; et al. A Functional Screen IdentifiesmiRNAs that Induce Radioresistance in Glioblastomas. Neurosurgery 2016, 63, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Su, Z.; Ren, S.; Zhu, G.; Tian, Y.; Qiu, Y. microRNA-324–3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by directly targeting WNT2B. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, C.; Liang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, R.; Su, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Lee, M.; Yang, H. MiR-205 determines the radioresistance of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma by directly targeting PTEN. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 785–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.S.; Kim, J.J.; Byun, J.Y.; Kim, I.A. Lin28-let7 modulates radiosensitivity of human cancer cells with activation of K-Ras. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, H.; Gao, F.; Xu, D.; Li, Q. MiR-21 modulates radiosensitivity of cervical cancer through inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/Akt/HIF-1alpha feedback loop and the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 12161–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, W.A.; Chen, M.S.; Behbod, F.; Alfaro, M.P.; Buchholz, T.A.; Rosen, J.M. WNT/beta-catenin mediates radiation resistance of mouse mammary progenitor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roses, R.E.; Xu, M.; Koski, G.K.; Czerniecki, B.J. Radiation therapy and Toll-like receptor signaling: Implications for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellini, F.; Morganti, A.G.; Genovesi, D.; Silvestris, N.; Valentini, V. Role of microRNA in Response to Ionizing Radiations: Evidences and Potential Impact on Clinical Practice for Radiotherapy. Molecules 2014, 19, 5379–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertson, D.G.; Collins, C.; McCormick, F.; Gray, J.W. Chromosome aberrations in solid tumors. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, N.; Greshock, J.; Megraw, M.S.; Giannakakis, A.; Liang, S.; Naylor, T.L.; Barchetti, A.; Ward, M.R.; et al. microRNAs exhibit high frequency genomic alterations in human cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9136–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lages, E.; Ipas, H.; Guttin, A.; Nesr, H.; Berger, F.; Issartel, J.-P. microRNAs: Molecular features and role in cancer. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2508–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, S.; Reutzel, D.; Speicher, M.; Decker, H.-J. Complete karyotype characterization of the K562 cell line by combined application of G-banding, multiplex-fluorescence in situ hybridization, fluorescence in situ hybridization, and comparative genomic hybridization. Leuk. Res. 2001, 25, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.C.; Ning, Y.; Wang, R.Y.; Padilla-Nash, H.M.; Schröck, E.; Soenksen, D.; Nagarajan, L.; Ried, T. SpectralKaryotypic Study of the HL-60 cell line: Detection of complex rearrangements involving chromosomes 5, 7, and 16 and delineation of critical region of deletion on 5q31.1. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1999, 113, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Cha, H.J.; Lee, E.M.; Lee, S.J.; Seo, S.K.; Jin, H.O.; Park, I.C.; Lin, Y.W.; An, S. Alteration of miRNA profiles by ionizing radiation in A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, R.; Hussey, D.J.; Haier, J. microRNAs: Predictors and modifiers of chemo- and radiotherapy in different tumour types. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Rao, E.Y.; Meng, N.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.J. microRNA-17-92 significantly enhances radioresistance in human mantle cell lymphoma cells. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorai, A.; Ghosh, U. miRNA gene counts in chromosomes vary widely in a species and biogenesis of miRNA largely depends on transcription or post-transcriptional processing of coding genes. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsafrir, D.; Bacolod, M.; Selvanayagam, Z.; Tsafrir, I.; Shia, J.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; Krier, C.; Stengel, R.F.; Barany, F.; et al. Relationship of gene expression and chromosomal abnormalities in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2129–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocana, A.; Vera-Badillo, F.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Templeton, A.J.; Corrales-Sanchez, V.; Diez-Gonzalez, L.; Cuenca-Lopez, M.D.; Seruga, B.; Pandiella, A.; Amir, E. Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT pathway and survival in solid tumors: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brechbiel, J.; Miller-Moslin, K.; Adjei, A.A. Crosstalk between hedgehog and other signaling pathways as a basis for combination therapies in cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Li, J.J. NF-κB-mediated adaptive resistance to ionizing radiation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Cozzi, P.; Hao, J.; Beretov, J.; Chang, L.; Duan, W.; Shigdar, S.; Delprado, W.; Graham, P.; Bucci, J.; et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is associated with prostate cancer metastasis and chemo/radioresistance via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Int. J. Biоchem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2736–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knizetova, P.; Ehrmann, J.; Hlobilkova, A.; Vancova, I.; Kalita, O.; Kolar, Z.; Bartek, J. Autocrine regulation of glioblastoma cell cycle progression, viability and radioresistance through the VEGF-VEGFR2 (KDR) interplay. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhane, H.; Epperly, M.W.; Goff, J.; Kalash, R.; Cao, S.; Franicola, D.; Zhang, X.; Shields, D.; Houghton, F.; Wang, H.; et al. Radiologic Differences between Bone Marrow Stromal and Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Lines from Fanconi Anemia (Fancd2–/–) Mice. Radiat. Res. 2014, 181, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstung, M.; Pellagatti, A.; Malcovati, L.; Giagounidis, A.; Della Porta, M.G.; Jädersten, M.; Dolatshad, H.; Verma, A.; Cross, N.; Vyas, P.; et al. Combining gene mutation with gene expression data improves outcome prediction in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; McConechy, M.K.; Horlings, H.M.; Ha, G.; Chun Chan, F.; Funnell, T.; Mullaly, S.C.; Reimand, J.; Bashashati, A.; Bader, G.D.; et al. Systematic analysis of somatic mutations impacting gene expression in 12 tumour types. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehan, E.; Ben-Dor, A.; Liao, W.; Lipson, D.; Frimer, H.; Rienstein, S.; Simansky, D.; Krupsky, M.; Yaron, P.; Friedman, E.; et al. Chromosomal aberrations and gene expression profiles in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2007, 56, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyle, R.; Gehrig, C.; Neergaard-Henrichsen, C.; Deutsch, S.; Antonarakis, S.E. Gene Expression from the Aneuploid Chromosome in a Trisomy Mouse Model of Down Syndrome. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoch, C.; Kohlmann, A.; Dugas, M.; Kern, W.; Hiddemann, W.; Schnittger, S.; Haferlach, T. Genomic gains and losses influence expression levels of genes located within the affected regions: A study on acute myeloid leukemias with trisomy 8, 11, or 13, monosomy 7, or deletion 5q. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascotti, K.; McCullough, J.; Burger, S.R. HPC viability measurement: Trypan blue versus acridine orange and propidium iodide. Transfusion 2000, 40, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| microRNA | Chromosome Localization | Number of Signaling Pathways | |
|---|---|---|---|
| K562 (67, X) | HL-60 (44, X) | ||
| hsa-miR-101-3p | 1,+1 (1p31.3); м7 (9p24.1) | 1 (1p31.3); 9 (9p24.1) | 2 |
| hsa-miR-103a-3p | 5,+5 (5q34); 20 (20p13) | 5,−5 (5q34); 20 (20p13) | 1 |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | 13,−13 (13q14.2); 3 (3q25.33); м15 (13q14.2) | 13 (13q14.2); 3 (3q25.33) | 29 |
| hsa-miR-181a-5p | 1,+1 (1q32.1); м19 (1q32.1); м8 (9q33.3) | 1 (1q32.1); 9 (9q33.3) | 5 |
| hsa-miR-181b-5p | 1,+1 (1q32.1); м19 (1q32.1); м8 (9q33.3) | 1 (1q32.1); 9 (9q33.3) | 3 |
| hsa-miR-24-3p | 19,−19 (19p13.12); м7(9q22.32); м8 (9q22.32); м17 (19p13.12); м18 (19p13.12) | 9 (9q22.32); 19 (19p13.12) | 22 |
| hsa-miR-7-5p | 15,+15 (15q26.1); 19,−19 (19p13.3); м7 (9q21.32); м8 (9q21.32) | 9 (9q21.32); 15,−15 (15q26.1); 19 (19p13.3) | 22 |
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | 13,−13 (13q31.3); м15 (13q31.3) | 13 (13q31.3) | 5 |
| hsa-miR-9-5p | 1,+1 (1q22); 5,+5 (5q14.3); 15,+15 (15q26.1) | 1 (1q22); 5,−5 (5q14.3); 15,−15 (15q26.1) | 22 |
| hsa-miR-17-5p | 13,−13 (13q31.3); м15 (13q31.3) | 13 (13q31.3) | 26 |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 13,−13 (13q31.3); м15 (13q31.3) | 13 (13q31.3) | 8 |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 17,−17 (17q23.1); м16 (17q23.1), м16 (17q23.1) | 17 (17q23.1) | 3 |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | 19,−19 (19p13.12); м17 (19p13.12); м18 (19p13.12) | 19 (19p13.12) | 3 |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | 19,−19 (19p13.12); м17 (19p13.12); м18 (19p13.12) | 19 (19p13.12) | 5 |
| hsa-miR-186-5p | 1,+1 (1p31.1) | 1 (1p31.1) | 5 |
| hsa-miR-30e-5p | 1,+1 (1p34.2) | 1 (1p34.2) | 2 |
| hsa-miR-99a-5p | 21 (21q21.1); м13 (21q21.1); м19 (21q21.1) | 21 (21q21.1) | 8 |
| hsa-miR-155-5p | 21 (21q21.3); м13 (21q21.3); м19 (21q21.3) | 21 (21q21.1) | 33 |
| hsa-miR-185-5p | 22 (22q11.21) | 22 (22q11.21) | 18 |
| hsa-miR-146a-5p | 5,+5 (5q33.3) | 5,−5 (5q33.3) | 12 |
| hsa-miR-106b-5p | 7,−7 (7q22.1); м4 (7q22.1); м5 (7q22.1) | 7 (7q22.1) | 8 |
| hsa-miR-93-5p | 7,−7 (7q22.1); м4 (7q22.1); м5 (7q22.1) | 7 (7q22.1) | 1 |
| hsa-miR-29a-3p | 7,−7 (7q32.3); м4 (7q32.3); м5 (7q32.3) | 7 (7q32.3) | 28 |
| hsa-miR-30d-5p | 8,+8 (8q24.22) | 8 (8q24.22) | 7 |
| hsa-miR-27b-3p | м7 (9q22.32), м8 (9q22.32) | 9 (9q22.32) | 1 |
| hsa-miR-199b-5p | м7 (9q34.11); м8 (9q34.11) | 9 (9q34.11) | 2 |
| hsa-miR-126-3p | м7 (9q34.3); м8 (9q34.3) | 9 (9q34.3) | 3 |
| hsa-miR-221-3p | X,−X (Xp11.3) | X,−X (Xp11.3) | 12 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liamina, D.; Sibirnyj, W.; Khokhlova, A.; Saenko, V.; Rastorgueva, E.; Fomin, A.; Saenko, Y. Radiation-Induced Changes of microRNA Expression Profiles in Radiosensitive and Radioresistant Leukemia Cell Lines with Different Levels of Chromosome Abnormalities. Cancers 2017, 9, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9100136
Liamina D, Sibirnyj W, Khokhlova A, Saenko V, Rastorgueva E, Fomin A, Saenko Y. Radiation-Induced Changes of microRNA Expression Profiles in Radiosensitive and Radioresistant Leukemia Cell Lines with Different Levels of Chromosome Abnormalities. Cancers. 2017; 9(10):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9100136
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiamina, Daria, Wladimir Sibirnyj, Anna Khokhlova, Viacheslav Saenko, Eugenia Rastorgueva, Aleksandr Fomin, and Yury Saenko. 2017. "Radiation-Induced Changes of microRNA Expression Profiles in Radiosensitive and Radioresistant Leukemia Cell Lines with Different Levels of Chromosome Abnormalities" Cancers 9, no. 10: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9100136
APA StyleLiamina, D., Sibirnyj, W., Khokhlova, A., Saenko, V., Rastorgueva, E., Fomin, A., & Saenko, Y. (2017). Radiation-Induced Changes of microRNA Expression Profiles in Radiosensitive and Radioresistant Leukemia Cell Lines with Different Levels of Chromosome Abnormalities. Cancers, 9(10), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9100136