Polyoxometalate Dicationic Ionic Liquids as Catalyst for Extractive Coupled Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization
Abstract
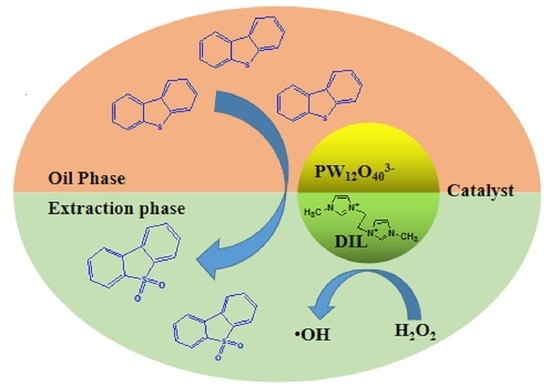
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Catalyst
2.2. Catalytic Activity of Catalyst
| Catalyst | Reaction Conditions | S-Removal (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| [C2(MIM)2]PW12O40 | n(catalyst)/n(S) = 0.025; n(H2O2)/n(S) = 6; 50 °C; 60 min; acetonitrile = 0.5 mL; V(model oil) = 5 mL | 98.4 | This work |
| [C4(MIM)2]PW12O40 | n(catalyst)/n(S) = 0.025; n(H2O2)/n(S) = 6; 50 °C; 60 min; acetonitrile = 0.5 mL; V(model oil) = 5 mL | 97.0 | This work |
| [C6(MIM)2]PW12O40 | n(catalyst)/n(S) = 0.025; n(H2O2)/n(S) = 6; 50 °C; 60 min; acetonitrile = 0.5 mL; V(model oil) = 5 mL | 95.5 | This work |
| [C4mim]3PW12O40 | m(catalyst) = 0.03 g, 60 °C, 30 min, n(H2O2)/n(DBT) = 3 | 11.4 | [45] |
| [C8mim]3PW12O40 | m(catalyst) = 0.03 g, 60 °C, 30 min, n(H2O2)/n(DBT) = 3 | 10.3 | [45] |
| [C16mim]3PW12O40 | m(catalyst) = 0.03 g, 60 °C, 30 min, n(H2O2)/n(DBT) = 3 | 12.5 | [45] |
| Cs2.5H0.5PW12O40 | 60 min; 60 °C; O/S = 15; acetonitrile = 60 mL | 70.5 | [46] |
| [C16mim]3PW12O40 | m(catalyst) = 0.01 g; 60 °C; 1 h; O/S = 3; [Bmim]BF4 = 1 mL | 21.4 | [47] |
2.3. Recycling of Catalysts
2.4. Oxidation Product and Reaction Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Catalyst
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Oxidative Desulfurization Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, M.; Wang, D. Generational differences in attitudes towards car, car ownership and car use in Beijing. Transp. Res. D Transp. Environ. 2019, 72, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, J.C.; Baron, K. The effects of SO2 on the performance of noble metal catalysts in automobile exhaust. J. Catal. 1979, 57, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.C. An evaluation of desulfurization technologies for sulfur removal from liquid fuels. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 759–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Q.L.; Yang, G. Strong affinity of mineral dusts for sulfur dioxide and catalytic mechanisms towards acid rain formation. Catal. Commun. 2018, 114, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Ma, X. New design approaches to ultra-clean diesel fuels by deep desulfurization and deep dearomatization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 41, 207–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C. An overview of new approaches to deep desulfurization for ultra-clean gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel. Catal. Today 2003, 86, 211–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislaus, A.; Marafi, A.; Rana, M.S. Recent advances in the science and technology of ultra low sulfur diesel (ULSD) production. Catal. Today 2010, 153, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimu, A.; Alhooshani, K. Advanced hydrodesulfurization catalysts: A review of design and synthesis. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 2810–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankov, D.S.V.; Shishkova, I.; Chavdarov, I.; Petkov, P.; Palichev, T. Opportunity to Produce Near Zero Sulphur Gasoline and Improve Refining Profitability by Combining FCC Feed Hydrotreatment and Gasoline Post Treatment. Oil Gas Eur. Mag. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, Y.B.; Zhang, D.Q.; Chu, Y.; Gao, X.D. Development of RSDS-III Technology for Ultra-Low-Sulfur Gasoline Production. China Pet. Process Petrochem. Technol. 2015, 17, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, O.Y.; Singh, S.; Schachtl, E.; Kim, J.; Kondratieva, E.; Hein, J.; Lercher, J.A. Effects of the support on the performance and promotion of (Ni) MoS2 catalysts for simultaneous hydrodenitrogenation and hydrodesulfurization. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Guo, Z.; Lv, Z. Synthesis of Convertible {PO4[WO3⇌W(O)2(O2)]4}-DMA16 in SBA-15 Nanochannels and Its Catalytic Oxidation Activity. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 2794–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaji, A.K.; Mortaheb, H.R.; Mokhtarani, B. Extractive-catalytic oxidative desulfurization with graphene oxide-based heteropolyacid catalysts: Investigation of affective parameters and kinetic modeling. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertleff, B.; Goebel, R.; Claußnitzer, J.; Korth, W.; Skiborowski, M.; Wasserscheid, P.; Jess, A.; Albert, J. Investigations on catalyst stability and product isolation in the extractive oxidative desulfurization of fuels using polyoxometalates and molecular oxygen. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 4602–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, H.H.; Hua, M.Q.; Chen, L.L.; Wei, Y.C.; Wang, C.; Wu, P.W.; Zhu, F.X.; Chu, X.Z.; Li, H.M.; et al. Extraction combined catalytic oxidation desulfurization of petcoke in ionic liquid under mild conditions. Fuel 2020, 260, 116200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, S.H.; Yu, Z.D.; He, M.Q.; Wei, Y.C.; Li, X.W.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.S.; Li, H.M. Supported phosphotungstic-based ionic liquid as an heterogeneous catalyst used in the extractive coupled catalytic oxidative desulfurization in diesel. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2019, 45, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaji, A.K.; Mokhtarani, B.; Mortaheb, H.R. Deep and fast oxidative desulfurization of fuels using graphene oxide-based phosphotungstic acid catalysts. Fuel 2019, 236, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, Z.E.A.; Li, B.S.; Asma, T. Direct synthesis of mesoporous (C19H42N)4H3(PW11O39)/SiO2 and its catalytic performance in oxidative desulfurization. Colloid Surf. A. 2009, 341, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Lu, Y.Z.; Meng, H.; Li, C.X. Lipophilicity of amphiphilic phosphotungstates matters in catalytic oxidative desulfurization of oil by H2O2. Fuel 2019, 253, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, X.N.; Van Doan, H. Activity and stability of amino-functionalized SBA-15 immobilized 12-tungstophosphoric acid in the oxidative desulfurization of a diesel fuel model with H2O2. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 206, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andevary, H.H.; Akbari, A.; Omidkhah, M. High efficient and selective oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel using dual-function [Omim]FeCl4 as catalyst/extractant. Fuel Process Technol. 2019, 185, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, K.Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Xu, W. Ti-modified hierarchical mordenite as highly active catalyst for oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Fuel 2016, 174, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Made, M.; Liu, J.F.; Pang, L. Environmental application, fate, effects, and concerns of ionic liquids: A review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12611–12627. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.W.; Gao, R.M.; Zhao, J.S. Deep oxidative desulfurization of fuel catalyzed by modified heteropolyacid: The comparison performance of three kinds of ionic liquids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 15858–15866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.L.; Zhu, W.S.; Li, H.M.; Shi, H.; Zhu, G.P.; Liu, H.; Chen, G.Y. Heteropolyanion-based ionic liquid for deep desulfurization of fuels in ionic liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8998–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Hu, B.; Hu, C.Q. Deep desulfurization of fuels by heteropolyanion-based ionic liquid. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, 34, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, J.Z.; Hu, B.; Tan, J.J.; Jin, X.Y. Deep oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene with molybdovanadophosphoric heteropolyacid-based catalysts. Transit. Metal. Chem. 2014, 39, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, E.; Mirnezami, F. Keggin-structured polyoxometalate-based ionic liquid salts: Thermoregulated catalysts for rapid oxidation of sulfur-based compounds using H2O2 and extractive oxidation desulfurization of sulfur-containing model oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 199, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.W.; Sun, L.L.; Su, T.; Hao, D.M.; Liao, W.P.; Deng, C.L.; Ren, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.M.; Lü, H.Y. Polyoxometalate-based ionic liquid catalyst with unprecedented activity and selectivity for oxidative desulfurization of diesel in [Omim]BF4. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyan, A.; Eseva, E.; Polikarpova, P.; Kedalo, A.; Vutolkina, A.; Glotov, A. Deep oxidative desulfurization of fuels in the presence of brönsted acidic polyoxometalate-based ionic liquids. Molecules 2020, 25, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montalbán, M.G.; Villora, G.; Licence, P. Ecotoxicity assessment of dicationic versus monocationic ionic liquids as a more environmentally friendly alternative. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindri, I.M.; Siddiqui, D.A.; Bhardwaj, P.; Rodriguez, L.C.; Palmer, K.L.; Frizzo, C.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Rodrigues, D.C. Dicationic imidazolium-based ionic liquids: A new strategy for non-toxic and antimicrobial materials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62594–62602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Kang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Sheng, K. Chemically tunable DILs: Physical properties and highly efficient capture of low-concentration SO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Ren, P. Synthesis, characterization, and properties of imidazole dicationic ionic liquids and their application in esterification. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 221, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.A.; Hou, Y.C.; Ren, S.H.; Yao, C.F.; Wu, W.Z. Highly efficient separation of phenolic compounds from oil mixtures by imidazolium-based dicationic ionic liquids via forming deep eutectic solvents. Energ. Fuel. 2017, 31, 10274–10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, M.A.; Ivanov, A.S.; Arkhipova, E.A.; Desyatov, A.V.; Savilov, S.V.; Lunin, V.V. Structure and properties of new dicationic ionic liquid DBTMEDA(BF4)2. Struct. Chem. 2019, 30, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.Y.; Yue, Z.; Ma, Q.; Dunya, H.; Mandal, B.K.; Dunya, H.; Mandal, B.K. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of new dicationic ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Lei, X.J.; Tang, X.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Wang, Z.Y. Acid dicationic ionic liquids as extractants for extractive desulfurization. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4079–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yu, W.H.; Li, T.X.N.; Wang, Y.T.; Tan, J.J.; Hu, B.; Nie, L.H. Synthesis of novel magnetic ionic liquids as high efficiency catalysts for extraction-catalytic oxidative desulfurization in fuel oil. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 19232–19241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, P.A.; Faiz, M.; Tabet, N.; Hamdan, N.M.; Hussain, Z. A study of the stability of tungstophosphoric acid, H3PW12O40, using synchrotron XPS, XANES, hexane cracking, XRD, and IR spectroscopy. J. Catal. 2003, 217, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, B.L.; Osmari, B.F.; Heinen, T.M.; Bonacorso, H.G.; Zanatta, N.; Nielsen, S.O.; Ranathunga, D.T.S.; Villetti, M.A.; Frizzo, C.P. Dicationic imidazolium-based dicarboxylate ionic liquids: Thermophysical properties and solubility. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, S.H.; Zheng, D.; Yin, S.; Qin, Y.J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, W.S.; Li, H.M. TiO2 microspheres supported polyoxometalate-based ionic liquids induced catalytic oxidative deep-desulfurization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42402–42412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Li, X.Y.; Qu, Z.P.; Zhao, Q.D.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Chen, G.H. Correlations of WO3 species and structure with the catalytic performance of the selective oxidation of cyclopentene to glutaraldehyde on WO3/TiO2 catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.S.; Zhu, G.P.; Li, H.M.; Chao, Y.H.; Zhang, M.; Du, D.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z. Catalytic kinetics of oxidative desulfurization with surfactant-type polyoxometalate-based ionic liquids. Fuel Process Technol. 2013, 106, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.D.; Huang, X.Y.; Xun, S.H.; He, M.Q.; Zhu, L.H.; Wu, L.L.; Yuan, M.M.; Zhu, W.S.; Li, H.M. Synthesis of carbon nitride supported amphiphilic phosphotungstic acid based ionic liquid for deep oxidative desulfurization of fuels. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 308, 113059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Wei, A.M.; Zhu, W.S.; Xun, S.H.; Li, Y.N.; Li, H.P.; Li, H.M. Facile synthesis of amphiphilic polyoxometalate-based ionic liquid supported silica induced efficient performance in oxidative desulfurization. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 406, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, G.F.; Zhao, H.X. Polyoxometalate as effective catalyst for the deep desulfurization of diesel oil. Catal. Today 2010, 149, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; Jiang, B.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, L.H.; Sun, Z.N.; Wang, J.Y.; Tantai, X.W. Polymeric cation and isopolyanion ionic self-assembly: Novel thin-layer mesoporous catalyst for oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.Q.; Zeng, Y.N.; Chen, J.; Lin, R.G.; Zhuang, W.E.; Cao, R.; Lin, Z.J. Zr-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks with Intrinsic Peroxidase-Like Activity for Ultradeep Oxidative Desulfurization: Mechanism of H2O2 Decomposition. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 6983–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, J.S. Highly effective oxidative desulfurization with magnetic MOF supported W-MoO3 catalyst under oxygen as oxidant. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 277, 119224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.Y.; Huang, Z.X.; Wang, H.X.; Li, L.; Ye, C.S.; Qiu, T. In situ bridging encapsulation of a carboxyl-functionalized phosphotungstic acid ionic liquid in UiO-66: A remarkable catalyst for oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 225, 115818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Chamack, M.; Omidkhah, M. Reverse microemulsion synthesis of polyoxometalate-based heterogeneous hybrid catalysts for oxidative desulfurization. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 6513–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Samples | First Determination (%) | Second Determination (%) | Average Value (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [C2(MIM)2]PW12O40 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.45 |
| [C4(MIM)2]PW12O40 | 0.83 | 1.32 | 1.08 |
| [C6(MIM)2]PW12O40 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 |
| Elements | Atomic (%) |
|---|---|
| C | 27.29 |
| N | 10.03 |
| O | 47.93 |
| P | 3.12 |
| W | 11.63 |
| Catalyst | Solvent | Solubility (g/100 g) | Solvent | Solubility (g/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [C2(MIM)2]PW12O40 | n-octane | 0.0276 | Acetonitrile | 0.0325 |
| [C4(MIM)2]PW12O40 | n-octane | 0.0193 | Acetonitrile | 0.0275 |
| [C6(MIM)2]PW12O40 | n-octane | 0.0166 | Acetonitrile | 0.0250 |
| Entry | Extractants | Sulfur Removal (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [C2(MIM)2]Cl2 | 68.67 |
| 2 | [C4(MIM)2]Cl2 | 60.66 |
| 3 | [C6(MIM)2]Cl2 | 57.21 |
| 4 | Acetonitrile | 48.37 |
| 5 | Methanol | 31.68 |
| 6 | BMIMBF4 | 55.17 |
| 7 | BMIMPF6 | 56.86 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Tan, J.; Hu, B. Polyoxometalate Dicationic Ionic Liquids as Catalyst for Extractive Coupled Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization. Catalysts 2021, 11, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030356
Li J, Guo Y, Tan J, Hu B. Polyoxometalate Dicationic Ionic Liquids as Catalyst for Extractive Coupled Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization. Catalysts. 2021; 11(3):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030356
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingwen, Yanwen Guo, Junjun Tan, and Bing Hu. 2021. "Polyoxometalate Dicationic Ionic Liquids as Catalyst for Extractive Coupled Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization" Catalysts 11, no. 3: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030356
APA StyleLi, J., Guo, Y., Tan, J., & Hu, B. (2021). Polyoxometalate Dicationic Ionic Liquids as Catalyst for Extractive Coupled Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization. Catalysts, 11(3), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030356